Work, Energy and Power Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 6
• Work is said to be done when a force applied on the body displaces the body through a certain distance in the direction of applied force.
It is measured by the product of the force and the distance moved in the direction of the force, i.e., W = F-S
• If an object undergoes a displacement ‘S’ along a straight line while acted on a force F that makes an angle 0 with S as shown.
The work done W by the agent is the product of the component of force in the direction of displacement and the magnitude of displacement.
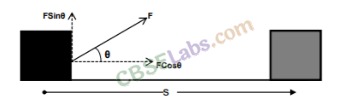
• If we plot a graph between force applied and the displacement, then work done can be obtained by finding the area under the F-s graph.
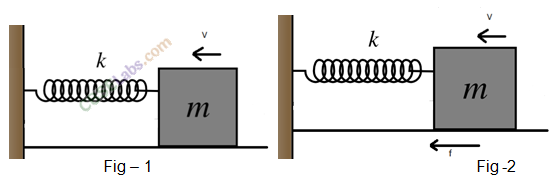
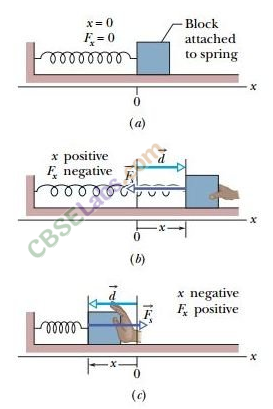
• If a spring is stretched or compressed by a small distance from its unstretched configuration, the spring will exert a force on the block given by
F = -kx, where x is compression or elongation in spring, k is a constant called spring constant whose value depends inversely on unstretched length and the nature of material of spring.
The negative sign indicates that the direction of the spring force is opposite to x, the displacement of the free-end.
• Energy
The energy of a body is its capacity to do work. Anything which is able to do work is said to possess energy. Energy is measured in the same unit as that of work, namely, Joule.
Mechanical energy is of two types: Kinetic energy and Potential energy.
• Kinetic Energy
The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its motion is known as its kinetic energy.
For an object of mass m and having a velocity v, the kinetic energy is given by:
K.E. or K = 1/2 mv
2
• Potential Energy
The energy possessed by a body by virtue of its position or condition is known as its potential energy.
There are two common forms of potential energy: gravitational and elastic.
—> Gravitational potential energy of a body is the energy possessed by the body by virtue of its position above the surface of the earth.
It is given by
(U)P.E. = mgh
where m —> mass of a body
g —> acceleration due to gravity on the surface of earth. h —> height through which the body is raised.
—> When an elastic body is displaced from its equilibrium position, work is needed to be done against the restoring elastic force. The work done is stored up in the body in the form of its elastic potential energy.
If an elastic spring is stretched (or compressed) by a distance Y from its equilibrium position, then its elastic potential energy is given by
U= 1/2 kx
2
where, k —> force constant of given spring
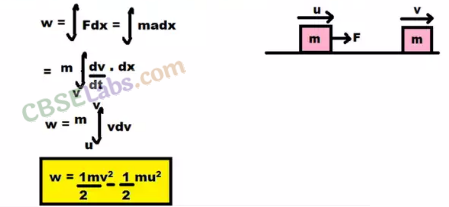
• Work-Energy Theorem
According to work-energy theorem, the work done by a force on a body is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the body.
• The Law of Conservation of Energy
According to the law of conservation of energy, the total energy of an isolated system does not change. Energy may be transformed from one form to another but the total energy of an isolated system remains constant.
• Energy can neither be created, nor destroyed.
• Besides mechanical energy, the energy may manifest itself in many other forms. Some of these forms are: thermal energy, electrical energy, chemical energy, visual light energy, nuclear energy etc.
• Equivalence of Mass and Energy
According to Einstein, mass and energy are inter-convertible. That is, mass can be converted into energy and energy can be converted into mass.

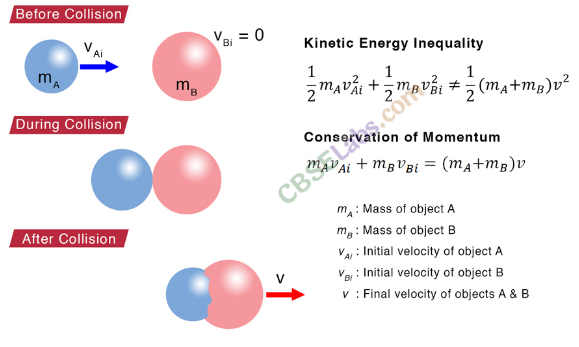
• Collision
Collision is defined as an isolated event in which two or more colliding bodies exert relatively strong forces on each other for a relatively short time.
Collision between particles have been divided broadly into two types.
(i) Elastic collisions (ii) Inelastic collisions
• Elastic Collision
A collision between two particles or bodies is said to be elastic if both the linear momentum and the kinetic energy of the system remain conserved.
Example: Collisions between atomic particles, atoms, marble balls and billiard balls.
• Inelastic Collision
A collision is said to be inelastic if the linear momentum of the system remains conserved but its kinetic energy is not conserved.
Example: When we drop a ball of wet putty on to the floor then the collision between ball and floor is an inelastic collision.
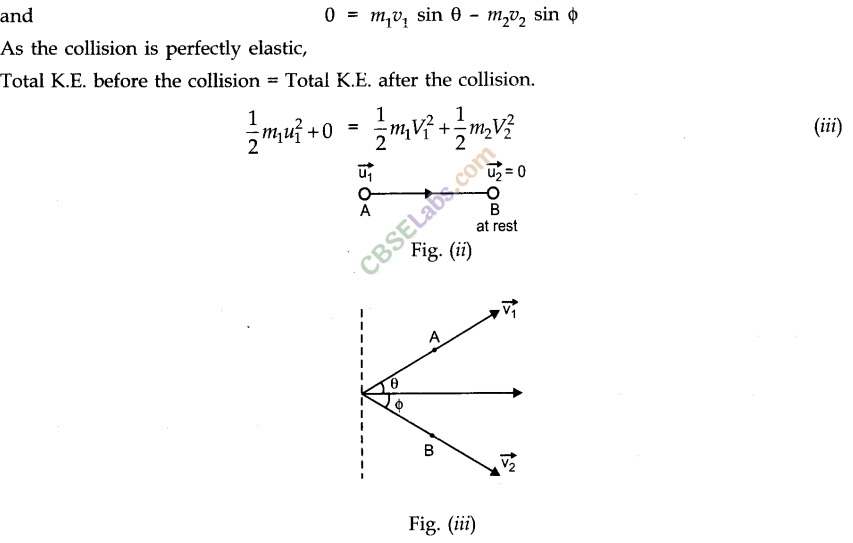
• Collision is said to be one dimensional, if the colliding particles, move along the same straight line path both before as well as after the collision.
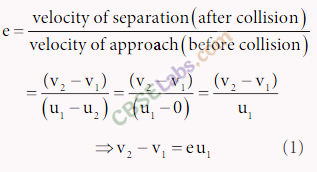
• In one dimensional elastic collision, the relative velocity of approach before collision is equal to. the relative velocity of separation after collision.
•
Coefficient of Restitution or Coefficient of Resilience
Coefficient of restitution is defined as the ratio of relative velocity of separation after collision to the relative velocity of approach before collision.
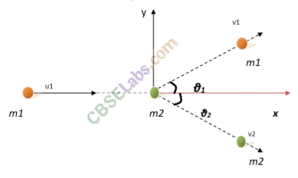
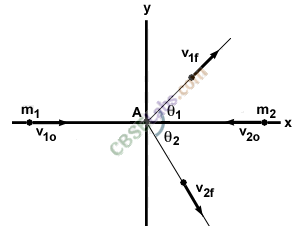
• Elastic and Inelastic Collisions in Two Dimensions
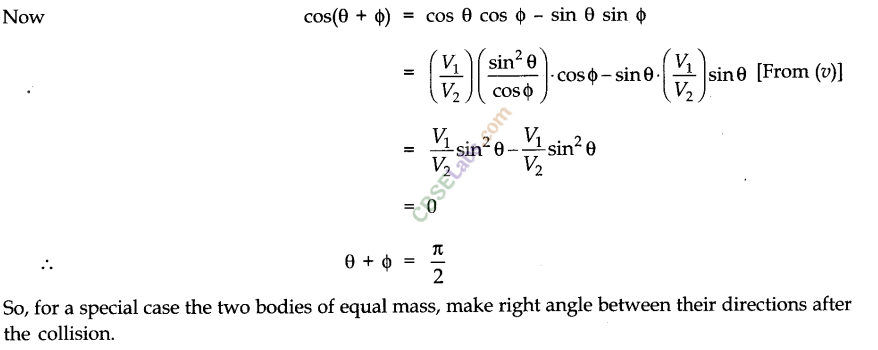
• Non-conservative Forces
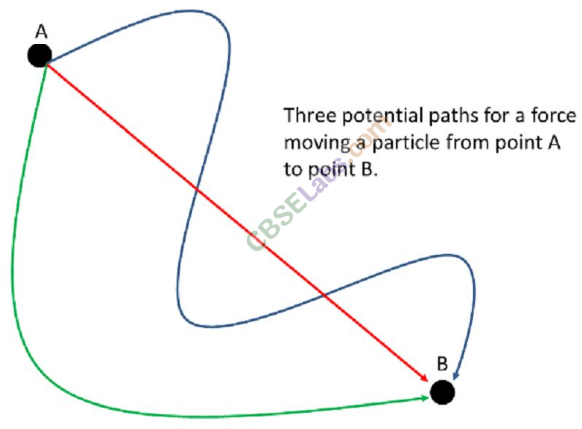
A force is said to be non-conservative if the work done in moving from one point to another depends upon the the path followed.
Let W, be the work done in moving from A to B following the path 1. W2 through the path 2 and W3 through the path 3. Fig. (i).
Examples of non-conservative forces are :
(i) Force of friction (ii) Viscus force
Low of conservation of energy holds goods for both conservative and non-conservative forces.