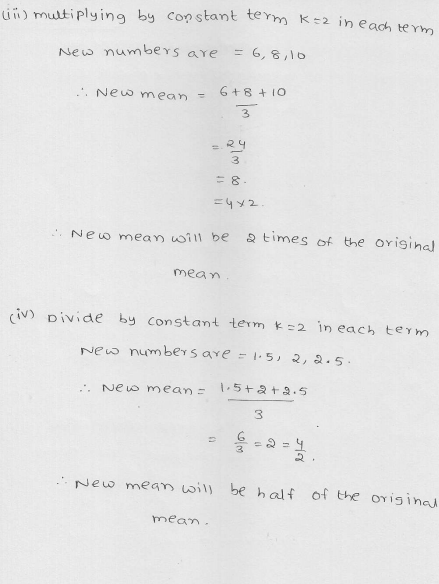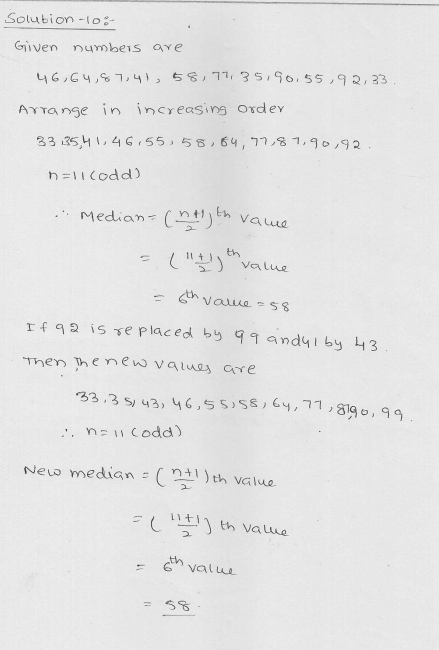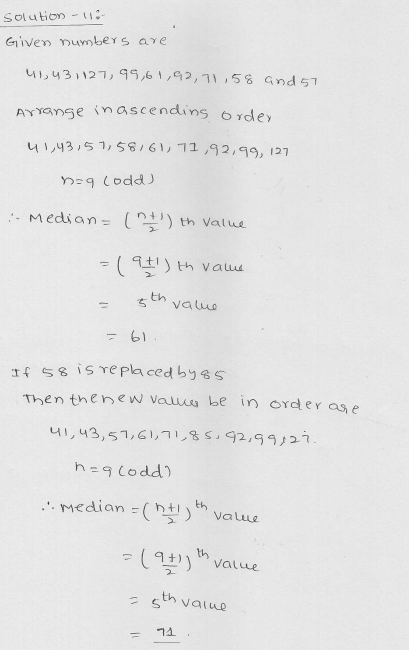RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 24 Measures of Central Tendency
Measures of Central Tendency Class 9 RD Sharma Solutions Ex 24.1
Question 1.
If the heights of 5 persons are 140 cm, 150 cm, 152 cm, 158 cm and 161 cm respectively. Find the mean height.
Solution:
Heights of 5 persons are 140 cm, 150 cm, 152 cm, 158 cm and 161 cm

Question 2.
Find the mean of 994, 996, 998, 1002 and 1000.
Solution:
Mean of 994, 996, 998, 1002 and 1000

Question 3.
Find the mean of first five natural numbers.
Solution:
First five natural numbers are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
∴ Mean = \(\overline { x } =\frac { 1+2+3+4+5 }{ 5 } =\frac { 15 }{ 5 } \) = 3
Question 4.
Find the mean all factors of 10.
Solution:
Factors of 10 = 1, 2, 5, 10
∴ Mean = \(\overline { x } =\frac { 1+2+5+10 }{ 4 } =\frac { 18 }{ 4 } \) = 4.5
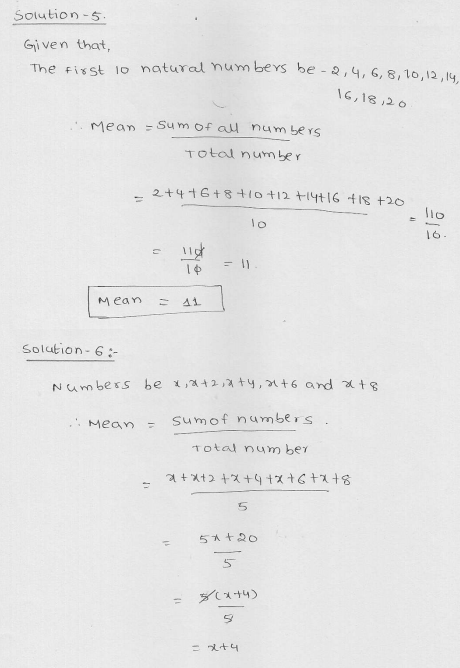
Question 5.
Find the mean of first 10 even natural numbers.
Solution:
First 10 even natural numbers are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20
∴ Mean = \(\overline { x } =\frac { 2+4+6+8+10+12+14+16+18+20 }{ 10 } =\frac { 110 }{ 10 } \) = 11
Question 6.
Find the mean of x, x + 2, x + 4, x + 6, x + 8.
Solution:
Sum = x + x + 2+ x + 4 + x + 6 + x + 8 = 5x + 20
∴ Mean = \(\overline { x } =\frac { \sum { { x }_{ i } } }{ n } \frac { 5x+20 }{ 5 } =x+4 \)
Question 7.
Find the mean of first five multiples of 3.
Solution:
First 5 multiples of 3 are = 3, 6, 9, 12, 15
∴ Mean = \(\overline { x } =\frac { 3+6+9+12+15 }{ 5 } =\frac { 45 }{ 5 } \) = 9
Question 8.
Following are the weights (in kg) or 10 new born babies in a hospital on a particular day:
3.4, 3.6, 4.2, 4.5, 3.9, 4.1, 3.8, 4.5, 4.4, 3.6. Find the mean \(\overline { X } \).
Solution:
Weights of 10 new bom babies are 3.4, 3.6, 4.2, 4.5, 3.9, 4.1, 3.8, 4.5, 4.4, 3.6
∴ Mean \(\overline { X } \) = \(\frac { 3.4+3.6+4.2+4.5+3.9+4.1+3.8+4.5+4.4+3.6 }{ 10 } \)
= \(\frac { 40.0 }{ 10 } \) = 4kg
Question 9.
The percentage of marks obtained by students of a class in mathematics are : 64, 36, 47, 23, 0, 19, 81, 93, 72, 35, 3, 1. Find their mean.
Solution:
Percentage of 12 students are 64, 36, 47, 23, 0, 19, 81, 93, 72, 35, 3, 1
∴ Mean \(\overline { X } \) = \(\frac { 64+36+47+23+0+19+81+93+72+35+3+1 }{ 12 } \)
= \(\frac { 474 }{ 12 } \) = 39.5
Question 10.
The numbers of children in 10 families of a locality are : 2, 4, 3, 4, 2, 0, 3, 5, 1, 1, 5. Find the mean number of children per family.
Solution:
Number of children in 10 families are 2, 4, 3, 4, 2, 0, 3, 5, 1, 1, 5
∴ Mean \(\overline { X } \) = \(\frac { 2+4+3+4+2+0+3+5+1+1+5 }{ 10 } \)
= \(\frac { 30 }{ 10 } \) = 3
Question 11.
Explain, by taking a suitable example, how the arithmetic mean alters by (i) adding a constant k to each term, (ii) subtracting a constant k from each them, (iii) multiplying each term by a constant k and (iv) dividing each term by a non-zero constant k.
Solution:
Let x1, x2, x3, x4, x5 are five numbers whose mean is \(\overline { x } \) i.e. = \(\frac { x1+x2+x3+x4+x5 }{ 5 } \) = \(\overline { x } \)

Hence we see that in each case, the mean is changed.
Question 12.
The mean of marks scored by 100 students was found to be 40. Later on its was discovered that a score of 53 was misread as 83. Find the correct mean.
Solution:
Mean score of 100 students = 40
∴Total = 100 x 40 = 4000
Difference in one score by mistake = 83 – 53 = 30
Actual total scores = 4000 – 300 = 3970
Actual mean = \(\frac { 3970 }{ 100 } \) = 39.70 = 39.7
Question 13.
The traffic police recorded the speed (in km/hr) of 10 motorists as 47, 53, 49, 60, 39, 42, 55, 57, 52, 48. Later on an error in recording instrument was found. Find the correct average speed of the motorists if the instrument recorded 5 km/hr less in each case.
Solution:
Speed of 10 motorist as recorded = 47, 53, 49, 60, 39, 42, 55, 57, 52, 48
Total of speed of 10 motorists = 47 + 53 + 49 + 60 + 39 + 42 + 55 +57 + 52 + 48 = 502

Question 14.
The mean of five numbers is 27. If one number is excluded, their mean is 25. Find the excluded number.
Solution:
Mean of 5 numbers = 27
Total = 27 x 5 = 135
By excluded one number, then mean of remaining 4 numbers = 25
Total = 4 x 25 = 100
Excluded number = 135 – 100 = 35
Question 15.
The mean weight per student in a group of 7 students is 55 kg. The individual weights of 6 of them (in kg) are 52, 54, 55, 53, 56 and 54. Find the weight of the seventh student.
Solution:
Mean weight of 7 students = 55 kg
Total weight of 7 students = 55 x 7 kg = 385 kg
Total weights of 6 students among them = 52 + 54 + 55 + 53 + 56 + 54 = 324 kg
Weight of 7th student = 385 – 324 = 61 kg
Question 16.
The mean weight of 8 numbers is 15. If each number is multiplied by 2, what will be the new mean?
Solution:
Weight of 8 numbers =15
By multiplying each number by 2, then the average will be = 15 x 2 = 30
New average = 30
Question 17.
The mean of 5 numbers is 18. If one number is excluded, their mean is 16. Find the excluded number.
Solution:
Mean of 5 numbers = 18
Total = 18 x 5 = 90
By excluding one number, the mean of remaining 5 – 1=4 numbers = 16
Total = 16 x 4 = 64
Excluded number = 90 – 64 = 26
Question 18.
The mean of 200 items was 50. Later on, it was discovered that the two items were misread as 92 and 8 instead of 192 and 88. Find the correct mean.
Solution:
Mean of 200 items = 50
Total = 50 x 200 = 10000
The number were misread as 92 instead of 192 and 8 instead of 88
Difference = 192 – 92 + 88 – 8 = 180
New total = 10000 + 180 = 10180
and new mean = \(\frac { 10180 }{ 200 } \) = 50.9
Question 19.
If M is the mean of x1, x2, xr3, x4, x5 and x6, prove that
(x1 – M) + (x2 – M) + (x3 – M) + (x4 – M) + (x5 – M) + (x6 – M) = 0.
Solution:
∵ M is the mean of x,, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6
Then M = \(\frac { x1+x2+x3+x4+x5+x6 }{ 6 } \)

Question 20.
Durations of sunshine (in hours) in Amritsar for first 10 days of August 1997 as reported by the Meteorological Department are given below:
9.6, 5.2, 3.5, 1.5, 1.6, 2.4, 2.6, 8.4, 10.3, 10.9
(i) Find the mean \(\overline { X }\)
(ii) Verify that \( \sum _{ i=1 }^{ 10 }{ \left( { x }_{ i }-\overline { X } \right) } \) = 0
Solution:
Duration of sun shine for 10 days (in hours)
= 9.6, 5.2, 3.5, 1.5, 1.6, 2.4, 2.6, 8.4, 10.3, 10.9


Question 21.
Find the values of n and X in each of the following cases:
(i) \(\sum _{ i=1 }^{ n }{ \left( { x }_{ i }-12 \right) } =-10\quad and\sum _{ i=1 }^{ n }{ \left( { x }_{ i }-3 \right) } =62\)
(ii) \(\sum _{ i=1 }^{ n }{ \left( { x }_{ i }-10 \right) } =30\quad and\sum _{ i=1 }^{ n }{ \left( { x }_{ i }-6 \right) } =150\)
Solution:
(i) \(\sum _{ i=1 }^{ n }{ \left( { x }_{ i }-12 \right) } =-10\)…(i)


Question 22.
The sums of the deviations of a set of n values x1, x2,… xn measured from 15 and -3 are -90 and 54 respectively. Find the value of n and mean.
Solution:
In first case,
(x1 – 15) + (x2 – 15) + (x3 – 15) + … + (xn – 15) = – 90
=> x1 + x2 + x3 + … + xn – 15 x n = – 90

Question 23.
Find the sum of the deviations of the variate values 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 14 from their mean.
Solution:
Mean of 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, 14 = \(\frac { 42 }{ 6 } \) = 7

Question 24.
If \(\overline { X } \) is the mean of the ten natural numbers x1, x2, x3, …, x10, show that (x1 – \(\overline { X } \)) + (x2 – \(\overline { X } \)) + … + (x10 – \(\overline { X } \)) = 0.
Solution:
\(\overline { X } \) is the mean of 10 natural numbers
x1, x2, x3, …, x10

RD Sharma Class 9 PDF Chapter 24 Measures of Central Tendency Ex 24.2
Question 1.
Calculate the mean for the following distribution
x 5 6 7 8 9
f 4 8 14 11 3
Solution:

Question 2.
Find the mean of the following data:
x 19 21 23 25 27 29 31
f 13 15 16 18 16 15 13
Solution:

Question 3.
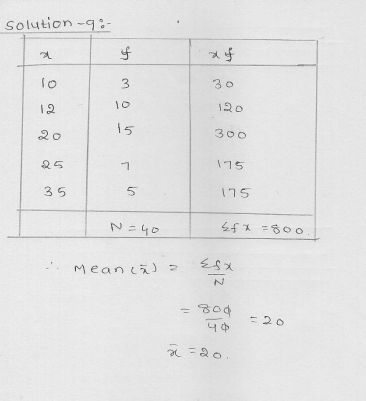
Find the mean of the following distribution:
x 10 12 20 25 35
f 3 10 15 7 5
Solution:

Question 4.
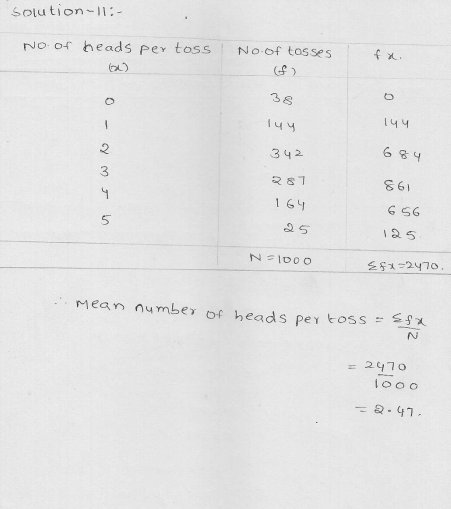
Five coins were simultaneously tossed 1000 times and at each toss the number of heads were observed. The number of tosses during which 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 heads were obtained are shown in the table below. Find the mean number of heads per toss.

Solution:

Question 5.
The mean of the following data is 20.6. Find the value of p.
x 10 15 p 25 35
f 3 10 25 7 5
Solution:
Mean = 20.6

Question 6.
If the mean of the following data is 15, find p?.
x 5 10 15 20 25
f 6 p 6 10 5
Solution:
Mean = 15

Question 7.
Find the value of p for the following distribution whose mean is 16.6.
x 8 12 15 p 20 25 30
f 12 16 20 24 16 8 4
Solution:
Mean = 16.6

Question 8.
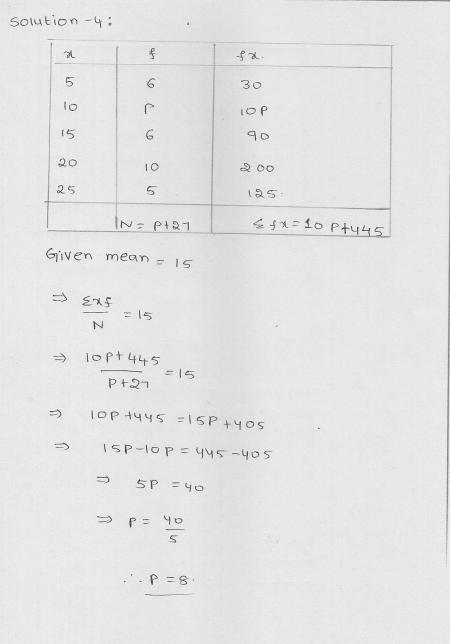
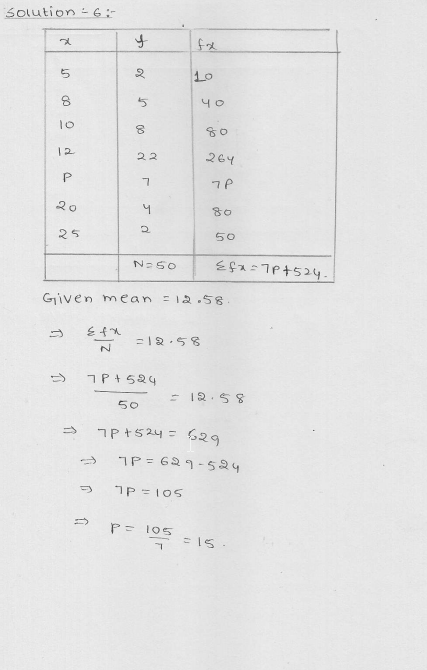
Find the missing value of p for the following distribution whose mean is 12.58.
x 5 8 10 12 p 20 25
f 2 5 8 22 7 4 2
Solution:
Mean = 12.58

Question 9.
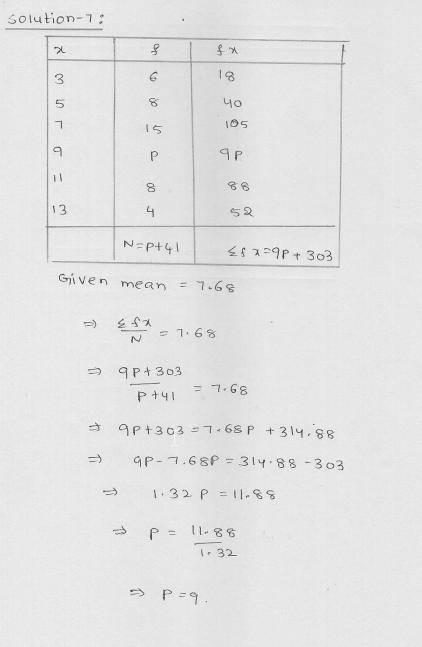
Find the missing frequency (p) for the following distribution whose mean is 7.68.
x 3 5 7 9 11 13
f 6 8 15 p 8 4
Solution:
Mean = 7.68


Question 10.
Find the value of p, if the mean of the following distribution is 20.
x 15 17 19 20 + p 23
f 2 3 4 5p 6
Solution:
Mean = 20

Question 11.
Candidates of four schools appear in a mathematics test. The data were as follows:

If the average score of the candidates of all the four schools is 66, find the number of candidates that appeared from school III.
Solution:
Let number of candidates in school III = p
Then total number of candidates in 4 schools = 60 + 48 + p + 40 = 148 + p
Average score of 4 schools = 66
∴Total score = (148 + p) x 66
Now mean score of 60 in school I = 75 .
∴Total = 60 x 75 = 4500
In school II, mean of 48 = 80
∴Total = 48 x 80 = 3840
In school III, mean of p = 55
∴Total = 55 x p = 55p
and in school IV, mean of 40 = 50
∴Total = 40 x 50 = 2000
Now total of candidates of 4 schools = 148 + p
and total score = 4500 + 3840 + 55p + 2000 = 10340 + 55p
∴10340 + 55p = (148 + p) x 66 = 9768 + 66p
=> 10340 – 9768 = 66p – 55p
=> 572 = 11p
∴ p = \(\frac { 572 }{ 11 } \)
Number of candidates in school III = 52
Question 12.
Find the missing frequencies in the following frequency distribution if it is known that the mean of the distribution is 50.
x 10 30 50 70 90
f 17 f1 32 f1 19
Total 120
Solution:
Mean = 50

RD Sharma Class 9 PDF Chapter 24 Measures of Central Tendency Ex 24.3
Question 1.
83, 37, 70, 29, 45, 63, 41, 70, 34, 54
Solution:
We know that median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \frac { n }{ 2 } th\quad term+\left( \frac { n }{ 2 } +1 \right) th\quad term \right] \)
(When n is even)
= \(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } th\quad term\)
83, 37, 70, 29, 45, 63, 41, 70, 34, 54
Arranging in ascending order, 29, 34, 37, 41, 45, 54, 63, 70, 70, 83
Here n = 10 which an even
Median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)[5th term + 6th term]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (45+54) = \(\frac { 99 }{ 2 } \) = 49.5
Question 2.
133, 73, 89, 108, 94, 104, 94, 85, 100, 120
Solution:
133, 73, 89, 108, 94, 104, 94, 85, 100, 120
Arranging in ascending order, 73, 85, 89, 94, 94, 100, 104, 108, 120, 133
Here n = 10 which is an even
Median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)[5th term + 6th term]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (94+100) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) x 194 = 97
Question 3.
31, 38, 27, 28, 36, 25, 35, 40
Solution:
31, 38, 27, 28, 36, 25, 35, 40
Arranging in ascending order, 25, 27, 28, 31, 35, 36, 38, 40
Here n = 8 which is even
Median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)[4th term + 5th term]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (31+35) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) x 66 = 33
Question 4.
15, 6, 16, 8, 22, 21, 9, 18, 25
Solution:
15, 6, 16, 8, 22, 21, 9, 18, 25
Arranging in ascending order = 6, 8, 9, 15, 16, 18, 21, 22, 25
Here n = 9 which is odd
Median \(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } th\quad term\) = \(\frac { 9+1 }{ 2 } th\quad term\) = \(\frac { 10 }{ 2 } th\quad \)
= 5th term = 16
Question 5.
41, 43, 127, 99, 71, 92, 71, 58, 57
Solution:
41, 43, 127, 99, 71, 92, 71, 58, 57
Arranging in ascending order = 41, 43, 57, 58, 71, 71, 92, 99, 127
Here n = 9 which is an odd
Median \(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } th\quad term\) = \(\frac { 9+1 }{ 2 } th\quad term\) = \(\frac { 10 }{ 2 } th\quad\)
= 5th term = 71
Question 6.
25, 34, 31, 23, 22, 26, 35, 29, 20, 32
Solution:
25, 34, 31, 23, 22, 26, 35, 29, 20, 32
Arranging in ascending order = 20, 22, 23, 25, 26, 29, 31, 32, 34, 35
Here n = 10 which is even
Median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \frac { n }{ 2 } th\quad term+\left( \frac { n }{ 2 } +1 \right) th\quad term \right] \)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) [5th term + 6th term]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (26 + 29) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) x 55 = \(\frac { 55 }{ 2 } \) = 27.5
Question 7.
12, 17, 3, 14, 5, 8, 7, 15
Solution:
12, 17, 3, 14, 5, 8, 7, 15
Arranging in ascending order = 3, 5, 7, 8, 12, 14, 15, 17
Here n = 8 which is odd
Median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \frac { n }{ 2 } th\quad term+\left( \frac { n }{ 2 } +1 \right) th\quad term \right] \)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) [4th term + 5th term]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (8+12) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) x 20 = 10
Question 8.
92, 35, 67, 85, 72, 81, 56, 51, 42, 69
Solution:
92, 35, 67, 85, 72, 81, 56, 51, 42. 69
Arranging in ascending order = 35, 42, 51, 56, 67, 69, 72, 81, 85, 92
Here n = 10 which is even
Median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \frac { n }{ 2 } th\quad term+\left( \frac { n }{ 2 } +1 \right) th\quad term \right] \)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) [5th term + 6th term]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) (67+69) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) x 136 = 68
Question 9.
Numbers 50, 42, 35, 2x + 10, 2x – 8, 12, 11, 8 are written in descending order and their median is 25, find x.
Solution:
50, 42, 35, 2x + 10, 2x – 8, 12, 11, 8 are in descending order
Here n = 8 which is even
Now Median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \frac { n }{ 2 } th\quad term+\left( \frac { n }{ 2 } +1 \right) th\quad term \right] \)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) [4th term + 5th term] = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)[2x + 10 + 2x – 8]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) [4x + 2] = 2x + 1
But median = 25
2x + 1 = 25
=> 2x = 25 – 1 = 24
=> \(\frac { 24 }{ 2 } \) = 12
Hence x = 12
Question 10.
Find the median of the following observations 46, 64, 87, 41, 58, 77, 35, 90, 55, 92, 33. If 92 is replaced by 99 and 41 by 43 in the above data, find the new median?
Solution:
46, 64, 87, 41, 58, 77, 35, 90, 55, 92, 33
Writing in ascending order = 33, 35, 41, 46, 55, 58, 64, 77, 87, 90, 92
Here n = 11 which is odd
Median = \(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } \) th term
= \(\frac { 11+1 }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { 12 }{ 2 } \)
= 6th term = 58
By replacing 92 by 93 and 41 by 43, then new order will be
33, 35, 43, 46, 55, 58, 64, 77, 87, 90, 99
Median = 6th term = 58
Question 11.
Find the median of the following data : 41, 43, 127, 99, 61, 92, 71, 58, 57. If 58 is replaced by 85, what will be the new median.
Solution:
41, 43, 127, 99, 61, 92, 71, 58, 57
Arranging in ascending order = 41, 43, 57, 58, 61, 71, 92, 99, 127
Here n = 9 which is odd
Median = \(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } \) th term = \(\frac { 9+1 }{ 2 } \) th term
= \(\frac { 10 }{ 2 } \) = 5th term = 61
By change 58 by 92, we get new order = 41, 43, 57, 61, 71, 92, 92, 99, 127
Median = 5th term = 71
Question 12.
The weights (in kg) of 15 students are : 31, 35, 27, 29, 32, 43, 37, 41, 34, 28, 36, 44, 45, 42, 30. Find the median. If the weight 44 kg is replaced by 46 kg and 27 kg by 25 kg, find the new median.
Solution:
Weights of 15 students are 31, 35, 27, 29, 32, 43, 37, 41, 34, 28, 36, 44, 45, 42, 30
Writing in ascending order = 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 34, 35, 36, 37, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45
here n = 15 which is odd
n+1 15+1
Median = \(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } \) th term = \(\frac { 15+1 }{ 2 } \)
= \(\frac { 16 }{ 2 } \)th term = 8th term = 35 kg
By replacing 44 kg by 46 kg and 27 kg by 25 kg we get new order,
25, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 34, 35, 36, 37, 41, 42, 43, 45, 46
Median = 8th term = 35 kg
Question 13.
The following observations have been arranged in ascending order. If the median of the data is 63, find the value of x: 29, 32, 48, 50, x, x + 2, 72, 78, 84, 95
Solution:
Median = 63
29, 32, 48, 50, x, x + 2, 72, 78, 84, 95
Here n = 10 which is even
median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \frac { n }{ 2 } th\quad term+\left( \frac { n }{ 2 } +1 \right) th\quad term \right] \)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \frac { 10 }{ 2 } th\quad term+\left( \frac { 10 }{ 2 } +1 \right) th\quad term \right] \)
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) [5th term + 6th term]
= \(\frac { 16 }{ 2 } \) [x+x+2] = \(\frac { 2x + 2 }{ 2 } \) = x + 1
x + 1 = 63 = x = 63 – 1 = 62
Hence x = 62
RD Sharma Class 9 PDF Chapter 24 Measures of Central Tendency 24.4
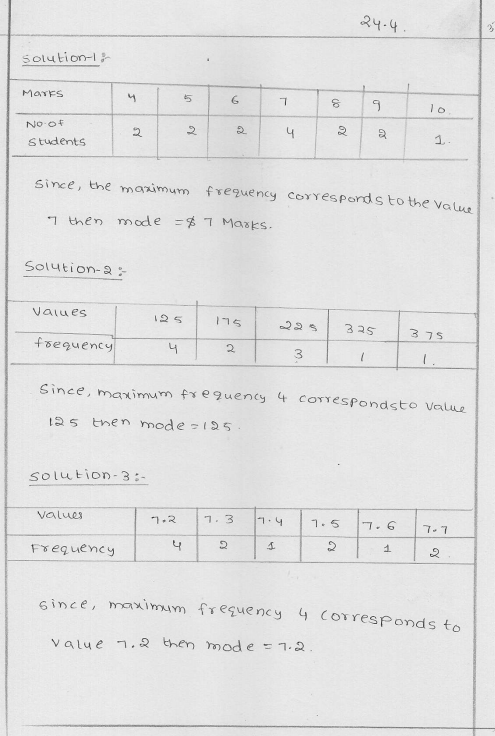
Question 1.
Find out the mode of the following marks obtained by 15 students in a class:
Marks : 4, 6, 5, 7, 9, 8, 10, 4, 7, 6, 5, 9, 8, 7, 7.
Solution:
Marks obtained are in ascending order,
4, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 9, 9, 10
Here we see that 7 is the number which is maximum times i.e. 4 times
Mode = 7
Question 2.
Find the mode for the following data:
125, 175, 225, 125, 225, 175, 325, 125, 375, 225, 125
Solution:
Arranging in ascending order,
125, 125, 125, 125, 175, 175, 225, 225, 225, 325, 375
We see that, 125 is the number which is in maximum times
Mode = 125
Question 3.
Find the mode for the following series:
7.5, 7.3, 7.2, 7.2, 7.4, 7.7, 7.7, 7.5, 7.3, 7.2, 7.6, 7.2
Solution:
Arranging in ascending order,
7.2, 7.2, 7.2, 7.2, 7.3, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.5, 7.6, 7.7, 7.7
We see that 7.2 comes in maximum times
Mode = 7.2
Question 4.
Find the mode of the following data in each case:
(i) 14, 25, 14, 28, 18, 17, 18, 14, 23, 22, 14, 18
(ii) 7, 9, 12, 13, 7, 12, 15, 7, 12, 7, 25, 18, 7
Solution:
(i) 14, 25, 14, 28, 18, 17, 18, 14, 23, 22, 14, 18
Arranging in ascending order,
14, 14, 14,. 14, 17, 18, 18, 18, 22, 23, 25, 28
Here we see that 14 comes in maximum times
Mode = 14
(ii) 7, 9, 12, 13, 7, 12, 15, 7, 12, 7, 25, 18, 7
Arranging in order,
7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 9, 12, 12, 12, 13, 15, 18, 25
Here we see that 7 comes in maximum times
Mode = 7
Question 5.
The demand of different shirt sizes, as obtained by a survey, is given below:

Find the modal shirt sizes, as observed from the survey.
Solution:
From the given data

From above, we see that
Modal size is 39 as it has maximum times persons
RD Sharma Solutions Class 9 Chapter 24 Measures of Central Tendency VSAQS
Question 1.
If the ratio of mode and median of a certain data is 6 : 5, then find the ratio of its mean and median.
Solution:
We know that
Mode = 3 median – 2 mean…(i)
and \(\frac { mode }{ median } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 5 } \)
Mode = \(\frac { 6 }{ 5 } \)median
∴From (i), \(\frac { 6 }{ 5 } \) median = 3 median – 2 mean
=> 2 mean = 3 median – \(\frac { 6 }{ 5 } \)median
2 mean = \(\frac { 15-6 }{ 5 } \)median = \(\frac { 9 }{ 5 } \)median
\(\frac { mean }{ median } \) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 5X2 } \) = \(\frac { 9 }{ 10 } \)
∴Ratio = 9:10
Question 2.
If the mean of x + 2, 2x + 3, 3x + 4, 4x + 5 is x + 2, find x.
Solution:
Mean of x + 2, 2x + 3, 3x + 4, 4x + 5 = x + 2
=> \(\frac { x + 2+2x + 3+3x + 4+4x + 5 }{ 4 } \) = x + 2
=> 10x + 14 = 4x + 8
=> 10x – 4x = 8 – 14
=> 6x= – 6
∴ x = – 1
Question 3.
If the median of scores ,\(\frac { x }{ 2 } \), \(\frac { x }{ 3 } \), \(\frac { x }{ 4 } \), \(\frac { x }{ 5} \) and \(\frac { x }{ 6 } \) (where x > 0) is 6, then find the value \(\frac { x }{ 6 } \)
Solution:
\(\frac { x }{ 2 } \), \(\frac { x }{ 3 } \), \(\frac { x }{ 4 } \), \(\frac { x }{ 5} \), \(\frac { x }{ 6 } \)
Here n = 5
Median = \(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } \) th term = \(\frac { 5+1 }{ 2 } \) th
\(\frac { 6 }{ 2 } \) = 3rd term = \(\frac { x }{ 4 } \)
\(\frac { x }{ 4 } \) = 6 => x = 24
\(\frac { x }{ 6 } \) = \(\frac { 24 }{ 6 } \) = 4
∴Hence = \(\frac { x }{ 6 } \) = 4
Question 4.
If the mean of 2, 4, 6, 8, x, y is 5, then find the value of x + y.
Solution:
Mean of 2, 4, 6, 8, x, y is 5
\(\frac { 2+4+6+8+x+y }{ 6 } \) = 5
\(\frac { 20+x+y }{ 6 } \) = 5
=> 20 + (x +y) = 30
=> x + y = 30 – 20 = 10
∴x + y = 10
Question 5.
If the mode of scores 3, 4, 3, 5, 4, 6, 6, x is 4, find the value of x.
Solution:
Mode of 3, 4, 3, 5, 4, 6, 6, x is 4
∴ 4 comes in maximum times
But here ,
3 2
4 2
5 1
6 2
3, 4 and 6 are equal in number
∴ x must be 4 so that it becomes in maximum times
Question 6.
If the median of 33, 28, 20. 25, 34, x is 29. find the maximum possible value of x.
Solution:
Median of 33, 28, 20, 25, 34, x is 29
Now arranging in ascending order 20, 25, 28, x, 33, 34
Here n = 6
Median = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ \frac { 6 }{ 2 } th\quad term+\left( \frac { 6 }{ 2 } +1 \right) th\quad term \right] \)
29 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) [3rd term + 4th term]
29 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) [28+x]
58 = 28 + x
=> x = 58 – 28 = 30
∴Possible value of x = 30
Question 7.
If the median of the scores 1, 2, x, 4, 5 (where 1 <2 <x <4 <5) is 3, then find the mean of the scores.
Solution:
Scores are 1, 2, x, 4, 5 and median 3
Here n = 5 which is odd
Median = \(\frac { n+1 }{ 2 } \) th term = \(\frac { 5+1 }{ 2 } \) = \(\frac { 6 }{ 2 } \) th
=> 3 = 3rd term = x
=> 3 = x
∴ x = 3
Mean of the score = \(\frac { 1+2+3+4+5 }{ 5 } \) = 3
Question 8.
If the ratio of mean and median of a certain data is 2 : 3, then find the ratio of its mode and mean.
Solution:
We know that mode = 3 median – 2 mean

\(\frac { mode }{ mean } \) = \(\frac { 5 }{ 2 } \)
Ratio in mode and mean = 5 : 2
Question 9.
The arithmetic mean and mode of a data are 24 and 12 respectively, then find the median of the data.
Solution:
Mean = 24
Mode = 12
We know that mode = 3 median – 2 mean
12 = 3 median – 2 x 24
12 = 3 median – 48
3 median 12 + 48 = 60
Median = \(\frac { 60 }{ 3 } \) = 20
Question 10.
If the difference of mode and median of a data is 24, then find the difference of median and mean.
Solution:
Mode – Median = 24
Mode = 24 + median
But mode = 3 median – 2 mean
3 median – 2 mean = 24 + median
3 median – median – 2 mean = 24
=> 2 median – 2 mean = 24
=> Median – Mean = 12 (Dividing by 2)
RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 24 Measures of Central Tendency MCQS
Mark the correct alternative in each of the following:
Question 1.
Which one of the following is not a measure of central value?
(a) Mean
(b) Range
(c) Median
(d) Mode
Solution:
Range (b)
Question 2.
The mean of n observations is \(\overline { X } \) . If k is added to each observation, then the new mean is
(a) \(\overline { X } \)
(b) \(\overline { X } \) + k
(c) \(\overline { X } \) – k
(d) k\(\overline { X } \)
Solution:
Mean of n observation = \(\overline { X } \)
By adding k to each observation the new mean will be \(\overline { X } \) + k (b)
Question 3.
The mean of n observations is \(\overline { X } \) . If each observation is multiplied by k, the mean of new observations is
(a) k\(\overline { X } \)
(b) \(\frac { \overline { X } }{ k } \)
(c) \(\overline { X } \) + k
(d) \(\overline { X } \) – k
Solution:
Mean of n observations = \(\overline { X } \)
By multiplying each observation by k,
the new mean = k\(\overline { X } \) (a)
Question 4.
The mean of a set of seven numbers is 81. If one of the numbers is discarded, the mean of the remaining numbers is 78. The value of discarded number is
(a) 98
(b) 99
(c) 100
(d) 101
Solution:
Mean of 7 numbers = 81
Total = 7 x 81 = 567
By discarding one number, the mean of the remaining 7 – 1 = 6 numbers = 78
Total = 6 x 78 = 468
Discarded number = 567 – 468 = 99 (b)
Question 5.
For which set of numbers do the mean, median and mode all have the same value?
(a) 2, 2, 2, 2, 4
(b) 1, 3, 3, 3, 5
(c) 1, 1, 2, 5, 6
(d) 1, 1, 1, 2, 5
Solution:
a) In set 2, 2, 2, 2, 4

Mode = 3 as it come in maximum times
This set has mean, median and mode same (b)
Question 6.
For the set of numbers 2, 2, 4, 5 and 12, which of the following statements is true?
(a) Mean = Median
(b) Mean > Mode
(c) Mean < Mode
(d) Mode = Median
Solution:
The given set is 2, 2, 4, 5, 12

Question 7.
If the arithmetic mean of 7, 5, 13, x and 9 is 10, then the value of x is
(a) 10
(b) 12
(c) 14
(d) 16
Solution:
Arithmetic mean of 7, 5, 13, x, 9 is 10

Question 8.
If the mean of five observations x, x + 2, x + 4, x + 6, x + 8, is 11, then the mean of first three observations is
(a) 9
(b) 11
(c) 13
(d) none of these
Solution:
Mean = 11
But mean of x, x + 2, x + 4, x+ 6, x + 8


Question 9.
Mode is
(a) least frequent value
(b) middle most value
(c) most frequent value
(d) none of these
Solution:
Mode is most frequent value (c)
Question 10.
The following is the data of wages per day: 5, 4, 7, 5, 8, 8, 8, 5, 7, 9, 5, 7, 9, 10, 8 The mode of the data is
(a) 7
(b) 5
(c) 8
(d) 10
Solution:
Wages per day
5, 4, 7, 5, 8, 8, 8, 5, 7, 9, 5, 7, 9, 10, 8
=> 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 10
Here 8 comes in maximum times
Mode = 8 (c)
Question 11.
The median of the following data :
is ,
(a) 0
(b) -1.5
(c) 2
(d) 3.5
Solution:
Arranging in ascending order,
-3, -3, -1, 0, 2, 2, 2, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6, 6, 6


Question 12.
The algebraic sum of the deviations of a set of n values from their mean is
(a) 0
(b) n – 1
(c) n
(d) n + 1
Solution:
The algebraic sum of deviation of a set of n values from that mean
Question 13.
A, B, C are three sets of values of X:
A : 2, 3, 7, 1, 3, 2, 3
B: 7, 5, 9, 12, 5, 3, 8
C: 4, 4, 11, 7 ,2, 3, 4
Which one of the following statements is
correct?
(a) Mean of A = Mode of C
(b) Mean of C = Median of B
(c) Median of B = Mode of A
(d) Mean, Median and Mode of A are equal.
Solution:
Arranging the sets in ascending order
A{2, 3, 7, 1,3,2,3)
= {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 7)
B = {7, 5, 9, 12, 5, 3, 8)
= {3, 5, 5, 7, 8, 9, 12)
C = {4, 4, 11,7,2,3,4)
= {2, 3, 4, 4, 4, 7, 11)

Mode = 5 {as it comes max times}
(c) Mean of set C = \(\\ \frac { 2+3+4+4+4+7+11 }{ 7 } \)
= \(\\ \frac { 35 }{ 7 } \) = 5
Median = \(\\ \frac { 7+1 }{ 2 } \) th =\(\\ \frac { 8 }{ 2 } \) =4th term = 4
Mode =4 {as it comes max times}
In set A,mean = median = mode = 3 (d)
Question 14.
The empirical relation between mean, mode and median is
(a) Mode = 3 Median — 2 Mean
(b) Mode 2 Median — 3 Mean
(c) Median 3 Mode — 2 Mean
(d) Mean = 3 Median —2 Mode
Solution:
The empirical relations between mean, mode
and median is
Mode = 3 Median — 2 Mean (a)
Question 15.
The mean of a, b, c, d and e is 28. If the mean of a, c, and e is 24, what is the mean of b and d?
(a) 31
(b) 32
(c) 33
(d) 34
Solution:
Mean of a, b, c, d and e = 28
Total of a, b, c, d and e = 28 x 5 = 140
Mean of a, c and e is = 24
Total of a, c, e = 24 x 3 = 72
Total of b and d = 140 – 72 = 68
Mean = \(\\ \frac { 68 }{ 2 } \) = 34 (d)
RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions Chapter 24 Measures of Central Tendency Ex 24.1