RD Sharma class 10 solutions Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.7
RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions Quadratic Equations Exercise 8.7
Question 1.
Find two consecutive numbers whose squares have the sum 85. (C.B.S.E. 2000)
Solution:
Let first number = x
Then second number = x + 1
According to the condition
x² + (x + 1)
2
= 85
⇒ x² + x² + 2x + 1 = 85
⇒ 2x² + 2x + 1 – 85 = 0
⇒ 2x² + 2x – 84 = 0
⇒ x² + x – 42 = 0
⇒ x² + 7x – 6x – 42 = 0
⇒ x (x + 7) – 6 (x + 7) = 0
⇒ (x + 7) (x – 6) = 0
Either x + 7 = 0, then x = -7 or x – 6 = 0, then x = 6
(i) If x = -7, then the first number = -7 and second number = -7 + 1 = -6
(ii) If x = 6, then the first number = 6 and second number = 6 + 1 = 7
Hence numbers are -7, -6 or 6, 7
Question 2.
Divide 29 into two parts so that the sum of the squares of the parts is 425.
Solution:
Total = 29
Let first part = x
Then second part = 29 – x
According to the condition
x² + (29 – x)
2
= 425
⇒ x² + 841 + x² – 58x = 425
⇒ 2x² – 58x + 841 – 425 = 0
⇒ 2x² – 58x + 416 = 0
⇒ x² – 29x + 208 = 0 (Dividing by 2)
⇒ x² – 13x – 16x + 208 = 0
⇒ x(x – 13) – 16 (x – 13) = 0
⇒ (x – 13) (x – 16) = 0
Either x – 13 = 0, then x = 13 or x – 16 = 0, then x = 16
(i) If x = 13, then First part =13 and second part = 29 – 13 = 16
(ii) If x = 16, then First part =16 and second part = 29 – 16 = 13
Parts are 13, 16
Question 3.
Two squares have sides x cm and (x + 4) cm. The sum of their areas is 656 cm
2
. Find the sides of the squares. (C.B.S.E. 1997)
Solution:
Side of the first square = x cm
Its area = (side)
2
= x² cm
2
Side of the second square = (x + 4) cm
Its area = (x + 4)
2
cm
2
According to the condition,
x² + (x + 4)
2
= 656
⇒ x² + x² + 8x + 16 = 656
⇒ 2x² + 8x + 16 – 656 = 0
⇒ 2x² + 8x – 640 = 0
⇒ x² + 4x – 320 = 0 (Dividing by 2)
⇒ x² + 20x – 16x – 320 = 0
⇒ x (x + 20) – 16 (x + 20) = 0
⇒ (x + 20) (x – 16) = 0
Either x + 20 = 0, then x = -20 Which is not possible being negative
or x – 16 = 0, then x = 16
Side of the first square = 16 cm
and side of the second square = 16 + 4 = 20 cm
Question 4.
The sum of two numbers is 48 and their product is 432. Find the numbers.
Solution:
Sum of two numbers = 48
Let first number = x
The second number = 48 – x
According to the condition,
x (48 – x) = 432
⇒ 48x – x² = 432
⇒ – x² + 48x – 432 = 0
⇒ x² – 48x + 432 = 0
⇒ x² – 12x – 36x + 432 = 0
⇒ x (x – 12) – 36 (x – 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 12) (x – 36) = 0
Either x – 12 = 0, then x = 12 or x – 36 = 0, then x = 36
(i) If x = 12, then First number = 12 and second number = 48 – 12 = 36
(ii) If x = 36, then First number = 36 and second number = 48 – 36 = 12
Numbers are 12, 36
Question 5.
If an integer is added to its square, the sum is 90. Find the integer with the help of quadratic equation.
Solution:
Let the given integer be = x
According to the condition
x² + x = 90
⇒ x² + x – 90 = 0
⇒ x² + 10x – 9x – 90 = 0
⇒ x (x + 10) – 9 (x + 10) = 0
⇒ (x + 10) (x – 9) = 0
Either x + 10 = 0, then x = -10 or x – 9 = 0, then x = 9.
The integer will be -10 or 9
Question 6.
Find the whole number which when decreased by 20 is equal to 69 times the reciprocal of the number.
Solution:
Let the given whole number = x
Then its reciprocal = \(\frac { 1 }{ x }\)
According to the condition,
x – 20 = 69 x \(\frac { 1 }{ x }\)
⇒ x – 20 = \(\frac { 69 }{ x }\)
⇒ x² – 20x = 69
⇒ x² – 20x – 69 = 0
⇒ x² – 23x + 3x – 69 = 0
⇒ x (x – 23) + 3 (x – 23) = 0
⇒ (x – 23) (x + 3) = 0
Either x – 23 = 0, then x = 23
or x + 3 = 0, then x = -3, but it is not a whole number
Required whole number = 23
Question 7.
Find two consecutive natural numbers whose product is 20.
Solution:
Let first natural number = x
Then second number = x + 1
According to the condition,
x (x + 1) = 20
⇒ x² + x – 20 = 0
⇒ x² + 5x – 4x – 20 = 0
⇒ x (x + 5) – 4 (x + 5) = 0
⇒ (x + 5) (x – 4) = 0
Either x + 5 = 0, then x = -5 which is not a natural number
or x – 4 = 0, then x = 4
First natural number = 4 and second number = 4 + 1=5
Question 8.
The sum of the squares of two consecutive odd positive integers is 394. Find them.
Solution:
Let first odd number = 2x + 1
Then second odd number = 2x + 3
According to the condition
(2x + 1)
2
+ (2x + 3)
2
= 394
⇒ 4x² + 4x + 1 + 4x² + 12x + 9 = 394
⇒ 8x² + 16x + 10 = 394
⇒ 8x² + 16x + 10 – 394 = 0
⇒ 8x² + 16x – 384 = 0
⇒ x² + 2x – 48 = 0 (Dividingby8)
⇒ x² + 8x – 6x – 48 = 0
⇒ x(x + 8) – 6(x + 8) = 0
⇒ (x + 8) (x – 6) = 0
Either x + 8 = 0, then x = 8 but it is not possible as it is negative
or x – 6 = 0, then x = 6
First odd number = 2x + 1 = 2 x 6 + 1 = 13
and second odd number = 13 + 2 = 15
Question 9.
The sum of two numbers is 8 and 15 times the sum of their reciprocals is also 8. Find the numbers.
Solution:
Sum of two numbers = 8
Let first number = x
Then second number = 8 – x
According to the condition,

(ii) If x = 5, then First number = 5 and second number = 8 – 5 = 3
Numbers are 3, 5
Question 10.
The sum of a number and its positive square root is \(\frac { 6 }{ 25 }\). Find the number.
Solution:


Question 11.
The sum of a number and its square is \(\frac { 63 }{ 4 }\) , find the numbers.
Solution:

Question 12.
There are three consecutive integers such that the square of the first increased by the product of the other two gives 154. What are the integers ?
Solution:
Let first integer = x
Then second integer = x + 1
and third integer = x + 2
According to the condition,
x² + (x + 1) (x + 2) = 154
⇒ x² + x² + 3x + 2 = 154
⇒ 2x² + 3x + 2 – 154 = 0
⇒ 2x² – 16x + 19x – 152 = 0
⇒ 2x(x – 8) + 19 (x – 8) = 0
⇒ (x – 8) (2x + 19) = 0
Either x – 8 = 0, then x = 8
or 2x + 19 = 0, then 2x = -19 ⇒ x = \(\frac { -19 }{ 2 }\) But it is not an integer
First number = 8
Second number = 8 + 1=9
and third number = 8 + 2 = 10
Question 13.
The product of two successive integral multiple of 5 is 300. Determine the multiplies.
Solution:
Let first multiplie of 5 = 5x
Then second multiple = 5x + 5
According to the condition,
5x (5x + 5) = 300
⇒ 25 x² + 25x – 300 = 0
⇒ x² + x – 12 = 0 (Dividing by 25)
⇒ x² + 4x – 3x – 12 = 0
⇒ x (x + 4) – 3 (x + 4) = 0
⇒ (x – 4) (x – 3) = 0
Either x + 4 = 0, then x = -4
or x – 3 = 0, then x = 3
(i) When x = -4, then
Required multiples of 5 will be
5 (-4) = -20, -20 + 5 = -15
or when x = 3, then
Required multiples will be
5 x 3 = 15, 15 + 5 = 20
Required number are -20, -15 or 15, 20
Question 14.
The sum of the squares of two numbers is 233 and one of the numbers is 3 less than twice the other number. Find the nqmbers.
Solution:
Let first number = x
Then second number = 2x – 3
According to the condition,
x² + (2x – 3)
2
= 233
⇒ x² + 4x² – 12x + 9 = 233
⇒ 5x² – 12x + 9 – 233 = 0
⇒ 5x² – 12x – 224 = 0
⇒ 5x² – 40x + 28x – 224 = 0
⇒ 5x (x – 8) + 28 (x – 8) = 0
⇒ (x – 8) (5x + 28) = 0
Either x – 8 = 0, then x = 8
or 5x + 28 = 0, then 5x = -28 ⇒ x = \(\frac { -28 }{ 5 }\) But it is not possible
x = 8
First number = 8
Second number = 2x – 3 = 2 x 8 – 3 = 16 – 3 = 13
Number are 8, 13
Question 15.
Find two consecutive even integers whose squares have the sum 340.
Solution:
Let first even integer = x
The second even integer = x + 2
According to the condition,
x² + (x + 2)
2
= 340
x² + x² + 4x + 4 = 340
⇒ 2x² + 4x + 4 – 340 = 0
⇒ 2x² + 4x – 336 = 0
⇒ x² + 2x – 168 = 0
⇒ x² + 14x – 12x – 168 = 0
⇒ x (x + 14) – 12 (x + 14) = 0
⇒ (x + 14) (x – 12) = 0
Either x + 14 = 0, then x = -14
or x – 12 = 0, the x = 12
(i) If x = -14, then
First number = -14
and second number = -14 + 2 = -12
(ii) If x = 12, then
First number =12
and second number =12 + 2 = 14
Hence even numbers are 12, 14 or -14, -12
Question 16.
The difference of two numbers is 4. If the difference of their reciprocals is \(\frac { 4 }{ 21 }\), find the numbers. (C.B.S.E. 2008)
Solution:
Let first number = x
Then second number = x – 4
According to the condition,

Either x – 7 = 0, then x = 7
or x + 3 = 0, then x = -3
(i) If x = 7, then
First number = 7
and second number = 7 – 4 = 3
(ii) If x = -3, then
First number = -3
and second number = -3 – 4 = -7
Number are 7, 3 or -3, -7
Question 17.
Find two natural numbers which differ by 3 and whose squared have the sum 117.
Solution:
Let first number = x
Then second number = x – 3
According to the condition,
x² + (x – 3)
2
= 117
⇒ x² + x² – 6x + 9 = 117
⇒ 2x² – 6x + 9 – 117 = 0
⇒ 2x² – 6x – 108 = 0
⇒ x² – 3x – 54 = 0 (Dividing by 2)
⇒ x² – 9x + 6x – 54 = 0
⇒ x (x – 9) + 6 (x – 9) = 0
⇒ (x- 9) (x + 6) = 0
Either x – 9 = 0, then x = 9
or x + 6 = 0, then x = -6 which is not a natural number
First natural number = 9
and second number = 9 – 3 = 6
Question 18.
The sum of squares of three consecutive natural numbers is 149. Find the numbers.
Solution:
Let first number = x
Then second number = x + 1
and third number = x + 2
According to the condition,
x² + (x + 1)
2
+ (x + 2)
2
= 149
⇒ x² + x² + 2x + 1 + x2 + 4x + 4 = 149
⇒ 3x² + 6x + 5 – 149 = 0
⇒ 3x² + 6x – 144 = 0
⇒ x² + 2x – 48 = 0 (Dividing by 3)
⇒ x² + 8x – 6x – 48 = 0
⇒ x (x + 8) – 6 (x + 8) = 0
⇒ (x + 8) (x – 6) = 0 .
Either x + 8 = 0, then x = -8, But it is not a natural number
or x – 6 = 0, then x = 6
Numbers are 6, 6 + 1 = 7, 6 + 2 = 8 or 6, 7, 8
Question 19.
The sum of two numbers is 16. The sum of their reciprocals is \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\). Find the numbers. (C.B.S.E. 2005)
Solution:
Sum of two numbers = 16
Let first number = x
Then second number = 16 – x
According to the condition,

Either x – 12 = 0, then x = 12
or x – 4 = 0, then x = 4
(i) If x = 12, then
First number = 12
and second number = 16 – 12 = 4
(ii) If x = 4, then First number = 4
and second number = 16 – 4 = 12
Hence numbers are 4, 12
Question 20.
Determine two consecutive multiples of 3 whose product is 270.
Solution:
Let first multiple of 3 = 3x
Then second multiple of 3 = 3x + 3
According to the condition,
3x (3x + 3) = 270
⇒ 9x² + 9x – 270 = 0
⇒ x² + x – 30 = 0 (Dividing by 9)
⇒ x² + 6x – 5x – 30 = 0
⇒ x (x + 6) – 5 (x + 6) = 0
⇒ (x + 6) (x – 5) = 0
Either x + 6 = 0, then x = -6
or x – 5 = 0, then x = 5
(i) When x = -6, then
First number = 3x = 3 x (-6) = -18 and second number = -18 + 3 = -15
(ii) If x = 5, then
First number = 3x = 3 x 5 = 15 and second number =15 + 3 = 18
Hence numbers are 15, 18 or -18, -15
Question 21.
The sum of a number and its reciprocal is \(\frac { 17 }{ 4 }\) , Find the number.
Solution:

Question 22.
A two-digit number is such that the product of its digits is 8. When 18 is subtracted from the number, the digits interchange their places. Find the number.
Solution:
Product of two digits = 8
Let units digit = x
Then tens digit = \(\frac { 8 }{ x }\)
Number = x + 10 x \(\frac { 8 }{ x }\) = x + \(\frac { 80 }{ x }\)

Question 23.
A two-digit number is such that the product of the digits is 12. When 36 is added to the number the digits interchange their places. Determine the number.
Solution:


Question 24.
A two-digit number is such that the product of the digits is 16. When 54 is subtracted from the number, the digits are interchanged. Find the number.
Solution:


Question 25.
Two numbers differ by 3 and their product is 504. Find the numbers. (C.B.S.E. 2002C)
Solution:
Difference of two numbers = 3
Let first number = x
Then second number = x – 3
According to the condition,
x (x – 3) = 504
⇒ x² – 3x – 504 = 0
⇒ x² – 24x + 21x – 504 = 0
⇒ x (x – 24) + 21 (x – 24) = 0
⇒ (x – 24) (x + 21) = 0
Either x – 24 = 0, then x = 24
or x + 21 = 0, then x =-21
(i) If x = 24, then
First number = 24
and second number = 24 – 3 = 21
(ii) If x =-21, then
First number = -21
and second number = -21 – 3 = -24
Hence numbers are 24, 21 or -21, -24
Question 26.
Two numbers differ by 4 and their product is 192. Find the numbers. (C.B.S.E. 2000C)
Solution:
Let first number = x
Then second number = x – 4
According to the condition,
x (x – 4) = 192
⇒ x² – 4x – 192 = 0
⇒ x² – 16x + 12x – 192 = 0
⇒ x (x – 16) + 12 (x – 16) = 0
⇒ (x – 16) (x + 12) = 0
Either x – 16 = 0, then x = 16
or x + 12 = 0, then x = -12
(i) If x = 16, then
First number = 16
and second number = 16 – 4 = 12
(ii) If x = -12, then
First number = -12
and second number = -12 – 4 = -16
Hence numbers are 16, 12 or -12, -16
Question 27.
A two digit number is 4 times the sum of its digits and twice the product of its digits. Find the number. (C.B.S.E. 1999C)
Solution:
Let units digit of the number = x
and tens digit = y
Number = x + 10y
According to the given conditions,
x + 10y = 4 (x + y)
⇒ x + 10y = 4x + 4y
⇒ 10y – 4y = 4x – x
⇒ 3x = 6y
⇒x = 2y …(i)
and x + 10y = 2xy ….(ii)
Substituting the value of x in (i)
2y + 10y = 2 x 2y x y
⇒ 12y = 4y2
⇒ 4y2 – 12y = 0
⇒ y2 – 3y = 0
⇒ y (y – 3) = o
Either y = 0, but it is not possible because y is tens digit number
or y – 3 = 0, then y = 3
x = 2y = 2 x 3 = 6
and number = x + 10y = 6 + 10 x 3 = 6 + 30 = 36
Question 28.
The difference of the squares of two positive integers is 180. The square of the smaller number is 8 times the larger, find the numbers. [CBSE 2014]
Solution:
Let first large number = x
and smaller number = y
According to the condition,
x
2
– y
2
= 180 …(i)
and y
2
= 8x
From (i) and (ii),
x
2
– 8x – 180 = 0
⇒ x
2
– 18x + 10x – 180 = 0
⇒ x (x – 18)+ 10 (x – 18) = 0
⇒ (x – 18) (x + 10) = 0
Either x – 18 = 0, then x = 18
or x + 10 = 0, then x = -10 But it is not possible being negative
x = 18
First number =18
Then second number y
2
= 8x
y
2
= 8 x 18 = 144 = (12)
2
⇒ y = 12
Numbers are 18, 12
Question 29.
The sum of two numbers is 18. The sum of their reciprocals is \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\). Find the numbers. (C.B.S.E. 2005)
Solution:
Sum of two numbers = 18
Let one number = x
Then second number = 18 – x
According to the condition,

⇒ x
2
– 12x – 6x + 72 = 0
⇒ x (x – 12) – 6 (x – 12) = 0
⇒ (x – 12) (x – 6) = 0
Either x – 12 = 0, then x = 12
or x – 6 = 0, then x = 6
(i) If x = 12, then
First number = 12
Second number =18 – 12 = 6
(ii) If x = 6, then
First number = 6
Then second number = 18 – 6 = 12
Numbers are 6, 12
Question 30.
The sum of two numbers a and b is 15, and the sum of their reciprocals \(\frac { 1 }{ a }\) and \(\frac { 1 }{ b }\) is \(\frac { 3 }{ 10 }\). Find the numbers a and b. (C.B.S.E. 2005)
Solution:

or b – 5 = 0, then b = 5
(i) a = 15 – 10 = 5
(ii) or a = 15 – 5 = 10
Numbers are 5, 10 or 10, 5
Question 31.
The sum of two numbers is 9. The sum of their reciprocals is \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\). Find the numbers. [CBSE 2012]
Solution:
Sum of two numbers = 9
Let first number = x
Then second number = 9 – x
According to the condition,

By cross multiplication
18 = 9x – x
2
⇒ x
2
– 9x + 18 = 0
⇒ x
2
– 6x – 3x + 18 = 0
⇒ x (x – 6) – 3 (x – 6) = 0
⇒ (x – 6) (x – 3) = 0
Either x – 6 = 0, then x = 6
or x – 3 = 0, then x = 3
Numbers are 6 and (9 – 6) = 3, or 3 and (9 – 3) = 6
Numbers are 3, 6
Question 32.
Three consecutive positive integers are such that the sum of the square of the’ first and the product of other two is 46, find the integers. [CBSE 2010]
Solution:
Let first number = x
Then second number = x + 1
and third number = x + 2
According co the condition,
(x)
2
+ (x+ 1) (x + 2) = 46
x
2
+ x
2
+ 3x + 2 = 46
⇒ 2x
2
+ 3x + 2 – 46 = 0
⇒ 2x
2
+ 3x – 44 = 0
⇒ 2x
2
+ 11x – 8x – 44 = 0
⇒ x (2x + 11) – 4 (2x + 11) = 0
⇒ (2x + 11) (x – 4) = 0
Either 2x + 11 = 0, then x = \(\frac { -11 }{ 2 }\) which is not possible being fraction
or x – 4 = 0, then x = 4
Numbers are 4, 5, 6
Question 33.
The difference of squares of two numbers is 88. If the larger number is 5 less than twice the smaller number, then find the two numbers. [CBSE 2010]
Solution:
Let smaller number = x
Then larger number = 2x – 5
According to the condition,
(2x – 5)
2
– x
2
= 88
⇒ 4x
2
– 20x + 25 – x
2
– 88 = 0
⇒ 3x
2
– 20x – 63 = 0
⇒ 3x
2
– 27x + 7x – 63 = 0
⇒ 3x (x – 9) + 7 (x – 9) = 0
⇒ (x – 9) (3x + 7) = 0
Either x – 9 = 0, then x = 9
or 3x + 7 = 0, then x = \(\frac { -7 }{ 3 }\) which is not possible
Smaller number = 9
and greater number = 2x – 5 = 2 x 9 – 5 = 18 – 5 = 13
Hence numbers are 13, 9
Question 34.
The difference of squares of two numbers is 180. The square of the smaller number is 8 times the larger number. Find two numbers. [NCERT]
Solution:



Question 35.
Find two consecutive odd positive integers, sum of whose squares is 970.
Solution:
Let two consecutive positive integers be x and x + 2
A.T.Q.,
(x)
2
+ (x + 2)
2
= 970
⇒ x
2
+ x
2
+ 4x + 4 – 970 = 0
⇒ 2x
2
+ 4x – 966 = 0
⇒ x
2
+ 2x – 483 = 0 (Dividing by 2)
⇒ x
2
+ 23x – 21x – 483 = 0
⇒ x (x + 23) – 21 (x + 23) = 0
⇒ (x – 21) (x + 23) = 0
Either x – 21 = 0 or x + 23 = 0
x = 21 or x = – 23 (rejected being -ve)
As integers should be +Ve
x = 21 and x + 2 = 21 + 2 = 23
Hence integers are 21, 23
Question 36.
The difference of two natural numbers is 3 and the difference of their reciprocals is \(\frac { 3 }{ 28 }\). Find the numbers.
Solution:

y(y + 7) – 4(y + 7) = 0
(y – 4) (y + 7) = 0
y – 4 = 0 or y + 7 = 0
y = 4 or y = -7 (rejected being natural no.)
When y = 4, x = 3 + 4 = 7 [From (ii)]
Number are 7, 4
Question 37.
The sum of the squares of two consecutive odd numbers is 394. Find the numbers.
Solution:
Let two consecutive positive integers be x and x + 2
A.T.Q.,
(x)
2
+ (x + 2)
2
= 394
x
2
+ x
2
+ 4x + 4 – 394 = 0
2x
2
+ 4x – 390 = 0
x
2
+ 2x – 195 = 0 (Dividing by 2)
x
2
+ 15x – 13x – 195 = 0
x (x + 15) – 13 (x + 15) = 0
(x – 13) (x + 15) = 0
Either x – 13 = 0 or x + 15 = 0
x = 13 or x = -15 (rejected)
Number should be x = 13 and x = 13 + 2 = 15
or x = -15 and x = -15 + 2 = -13
Hence odd numbers are 13, 15 or -15, -13
Question 38.
The sum of the squares of two consecutive multiple of 7 is 637. Find the multiples. [ICSE 2014]
Solution:
Let first multiple of 7 = 7x
Then second = 7x + 7
(7x)
2
+ (7x + 7) = 637
49x
2
+ 49x
2
+ 98x + 49 = 637
98x
2
+ 98x + 49 – 637 = 0
98x
2
+ 98x – 588 = 0
x
2
+ x – 6 = 0 (dividing by 98)
x
2
+ 3x – 2x – 6 = 0
x (x + 3) – 2 (x + 3) = 0
(x + 3) (x – 2) = 0
Either x + 3 = 0, then x = -3, but not possible being negative
or x – 2 = 0, then x = 2
Numbers will be 14, 21
Question 39.
The sum of the squares of two consecutive even numbers is 340. Find the numbers. [CBSE 2014]
Solution:
Let first even number = 2x
Then second number = 2x + 2
(2x)
2
+ (2x + 2)
2
= 340
4x
2
+ 4x
2
+ 8x + 4 – 340 = 0
8x
2
+ 8x – 336 = 0
x
2
+ x – 42 = 0 (Dividing by 8)
x
2
+ 7x – 6x – 42 = 0
x (x + 7) – 6 (x + 7) = 0
⇒ (x + 7) (x – 6) = 0
Either x + 7 = 0, then x = -7 but not possible being negative
or x – 6 = 0, then x = 6
Numbers are 12, 14
Question 40.
The numerator of a fraction is 3 less than the denominator. If 2 is added to both the numerator and the denominator, then the sum of the new fraction and the original fraction is \(\frac { 29 }{ 20 }\). Find the original fraction.
Solution:


Question 41.
Find a natural number whose square diminished by 84 is equal to thrice of 8 more than the given number. [NCERT Exemplar]
Solution:
Let n be a required natural number.
Square of a natural number diminished by 84 = n
2
– 84
and thrice of 8 more than the natural number = 3 (n + 8)
Now, by given condition,
n
2
– 84 = 3 (n + 8)
⇒ n
2
– 84 = 3n + 24
⇒ n
2
– 3n – 108 = 0
⇒ n
2
– 12n + 9n – 108 = 0 [by splitting the middle term]
⇒ n (n – 12) + 9 (n – 12) = 0
⇒ (n – 12) (n + 9) = 0
⇒ n = 12 [n ≠ – 9 because n is a natural number]
Hence, the required natural number is 12.
Question 42.
A natural number when increased by 12 equals 160 times its reciprocal. Find the number. [NCERT Exemplar]
Solution:
Let the natural number be x.
According to the question,
x + 12 = \(\frac { 160 }{ x }\)
On multiplying by x on both sides, we get
⇒ x
2
+ 12x – 160 = 0
⇒ x
2
+ (20x – 8x) – 160 = 0
⇒ x
2
+ 20x – 8x – 160 = 0 [by factorisation method]
⇒ x (x + 20) – 8 (x + 20) = 0
⇒ (x + 20) (x – 8) = 0
Now, x + 20 = 0 ⇒ x = -20 which is not possible because natural number is always greater than zero
and x – 8 = 0 ⇒ x = 8.
Hence, the required natural number is 8.
Exercise 8.7








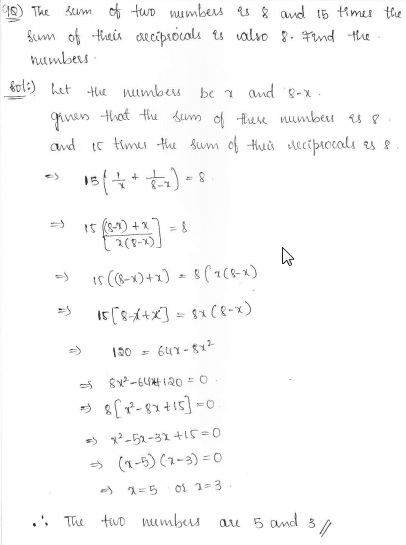

























RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.1
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.2
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.3
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.4
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.5
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.6
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.7
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.8
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.9
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.10
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.11
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.12
- Chapter 8 Quadratic Equations Ex 8.13