CBSE Notes CBSE Notes Science NCERT Solutions Science
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 15 Our Environment Pdf free download is part of Class 10 Science Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given NCERT Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 15 Our Environment. According to new CBSE Exam Pattern, MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science pdf Carries 20 Marks.
CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 15 Our Environment
Biodegradable and Non-biodegradable Wastes, Ecosystem, Components of Ecosystem. The environment includes our physical surroundings like air (or atmosphere), water bodies, soil (land and all the organisms such as plants, animals, human beings and micro-organisms like bacteria and fungi (called decomposers). The waste materials produced by the various activities of man £nd animals are poisonous to some extent and can be divided into two main groups
1. Biodegradable Wastes:
Substances that are broken down by the biological processes are said to be biodegradable. These substances are decomposed through the actions of fungi, bacteria, and other living organisms. Temperature and sunlight also play an important role in the decomposition of biodegradable substances.
For Examples: Food waste, trees leaves, urine and fecal matter, sewage agricultural residue, paper, wood, cloth, cow-dung etc.
2. Non-Biodegradable Wastes:
Substances that are not broken down by biological
processes. These substances may be in solid, liquid or gaseous form. These substances are inert and simply persist in the environment for a long time or may harm the various members of the ecosystem.
For Examples: These includes DDT (Di-chloro-di phenyl trichloro ethane-in-pheneyle the cheoro ethane), insecticides, pesticides, mercury, lead, arsenic aluminum, plastics, polythene bags, glass, radioactive wastes. These non-biodegradable wastes are major pollutants of the environment.
Harmful effects of biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable Substance
- The waste destroys the natural beauty and our surroundings become dirty.
- Decomposition of these wastes results in the production of foul smell, which spreads to the surrounding areas.
- These wastes may also block the drains creating pools of waste, which becomes the breeding sites of mosquitoes. The latter is carriers of diseases like malaria and dengue.
Difference between Biodegradable and Non-Biodegradable wastes
| Biodegradable wastes | Non-Biodegradable wastes |
| 1. The wastes that are broken down naturally by microbial action. | 1. The wastes that are not broken down by the microbes. |
| 2. Biodegradation forms harmless and non- poisonous products. | 2. No such action is possible. |
| 3. They release raw materials back to nature. | 3. They do not release raw materials. |
| 4. They pollute the environment only when they are produced in quantity beyond the capacity of the environment to degrade them. | 4. Non-biodegradable wastes pollute the environment even in small quantity. |
| 5. Bioconcentration does not occur. | 5. Bioconcentration or biomagnifications occurs when wastes enter food chains. |
| 6. Recycling is possible both naturally or through human efforts. | 6. Recycling is possible only through human efforts. |
Ecosystem:
An ecosystem is a self-contained unit of living things (plants, animals and decomposers), and their non-living environment (soil, air and water). For example; a forest, a pond, a lake, a green land etc.
In an ecosystem, energy and matter are continuously exchanged between living and non¬living components.
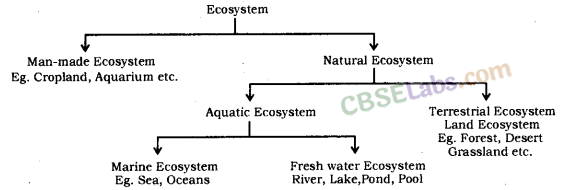
An ecosystem can be both natural or man-made. Some examples of natural ecosystems are grass land, forest, sea, river, desert, mountain, pond, lake etc.
The desert, grass land and mountains represent the terrestrial ecosystem (land-based ecosystem).
The ponds, rivers, lakes and sea represent the aquatic ecosystem (water-based ecosystem). Man-made artificial ecosystems are garden, crop fields, park, aquarium, etc.
Components of Ecosystem:
There are two components of an ecosystem : (i) biotic component and (ii) abiotic component.
1. Biotic component:
It includes three types of organisms :
(a) Producers:
All green plants, blue green algae can produce their food (Sugar and starch) from inorganic substance using light energy (Photosynthesis). Therefore, all green plants are called producers. They are also called autotrophs.
Planktons are very minute or microscopic organisms freely floating on the surface of water in a pond, lake, river or ocean. Planktons are of two types : Phytoplanktons and Zooplanktons.
The microscopic aquatic plants freely floating on the surface of water are called phytoplanktons.
The microscopic aquatic animals freely floating on water are called zooplanktons. The freely floating protozoa are an example of zooplankton.
(b) Consumers:
They are organisms which consume other organisms or their products as their food. All animals belong to this category. The consumers depend upon producers for their food directly or indirectly. They get their food by eating other organisms or their products. For example, man, goat, deer, fish, lion, cow, buffalo, etc., are common consumers.
The consumers can be classified into the following types :
- Herbivores.
- Carnivores.
- Parasite.
- Omnivores.
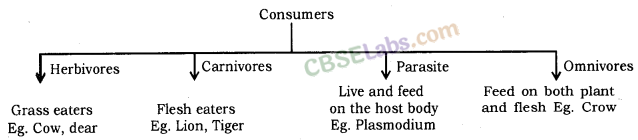
(i) Herbivores: These are organisms (animals) which get their food by eating the producers (or plant) directly. Herbivores are also called first order consumers. Some common examples of herbivores are : deer, rabbit, rat, squirrel, goat, cattle, etc.
(ii) Carnivores:
These are organisms (animals) which consume other animals. Therefore, carnivores feed on the flesh of herbivores. These are also called primary carnivores or second order consumers. Some common examples are snake, wild cat, jackal, frog, some birds, fishes, etc.
There are animals which prey upon primary carnivores. They are called second order consumers or third order consumers. For example, owl, peacock, tiger, lion, etc., are some second order carnivores and may be eaten by third order carnivores. The carnivores which are not preyed upon further are called top carnivores. For example, lion is a top carnivore.
(iii) Omnivores: The organisms which feed on both plants and animals are called omnivores. Human beings are common example of omnivores because they eat both plants (For example; pulses, grams, oilseeds, fruit, etc.) and animal products (milk, meat, egg, etc.).
(c) Decomposers: Fungi and bacteria which break down (decompose) the dead plants, animals complex compounds into the simpler one. The decomposers help in the replenishment of natural resources. These are also known as microorganism or saprotrophs. These are also called reducers.
Importance of Decomposers
- Decomposers help in disposing of the wastes and dead bodies of plants and animals. Therefore, they clean the environment and create space for a living of newer generations of organisms.
- The decomposers release minerals and other raw materials trapped in organic matter. These are picked up by plants. This also helps to maintain the fertility of soil.
- The decomposers produce some acids which are useful in solubilization of some minerals.
- Decomposers help in recycling the materials in the biosphere so that, the process of life may go on and on like an unending chain.
2. Abiotic Components: These are non-living components of an ecosystem. These include the physical environment.
- Edaphic factors like soil texture, topography, water, and air.
- Inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, nitrogen, oxygen, water, phosphorus, sodium, potassium, and calcium. These are involved in the cyclic of materials in the ecosystem.
- Organic compounds like proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. These largely form the living body and link the abiotic and biotic components.
Climatic factors: These are sunlight temperature, pressure humidity, moisture, rainfall, etc. these factors affect the distribution of the organisms.
Functions of an Ecosystem
- Ecosystem indicates available solar energy and the efficiency of an ecosystem to trap the same.
- It gives information about the available essential minerals and their recycling periods.
- It provides knowledge about the web of interactions and inter-relationship among the various population as well as between the population and the abiotic environment.
- It helps human beings to know about conservation of resources, protection from pollution and inputs required for maximizing productivity.
- In the ecosystem, two processes of energy flow and biogeochemical cycles (nutrients movement) proceed side by side. The energy flow is unidirectional while the movement of nutrients is cyclic.
Food chain, Food web, Trophic levels. Flow of energy ten percent law, Depletion of the ozone layer, Biological magnification. Mode of waste disposal.
Food Chain:
The sequence of living organisms in a community in which one organism consumes another organism to transfer food energy, is called a food chain.
A food chain is unidirection where transfer of energy takes place in only one direction.
OR
Food chain is sequential process which represents “who eats whom”.
OR
Food chain refers to an arrangement of different biotic groups in a sequence of energy transfer. These biotic groups are producer herbivores, carnivores.
For example, T1(Grass) → T2(Deer) → T3(Lion)
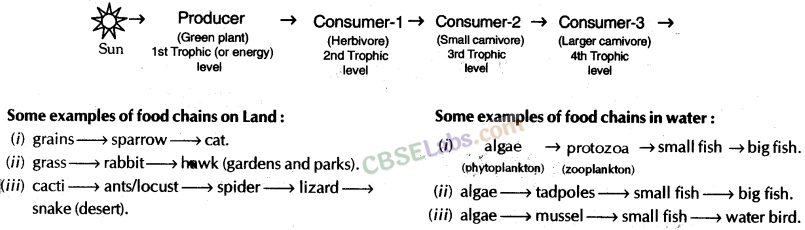
Examples of Food Chains: Simple food chain operating in a grass land or forest
Grass(Producer) → Deer(Herbivore) → Lion(Carnivore)
In this food chain, grass represent the producers (first tropic level). Grass synthesize their own food by the process of photosynthesis. Grass is eaten up by deer, which represents the herbivores or the primary consumers. Deer in turn is consumed by lion, the carnivores or the secondary consumers.
A food chain in grassland which has four steps is :
Grass(Producers) → Insect(Herbivores) → Frog(Carnivores) → Eagle(Secondary Carnivore)
Significance of Food Chains
- The study of food chains helps in understanding food relationships and interactions among the various organisms in an ecosystem. The food chains, transfer energy and materials between various living components of an ecosystem.
- The food chains transfer energy and materials between various living components in an ecosystem or biosphere.
- The food chains give dynamicity to an ecosystem or biosphere.
- The movement of toxic substances like pesticides, weedicides, etc., through food chains, can prove very harmful.
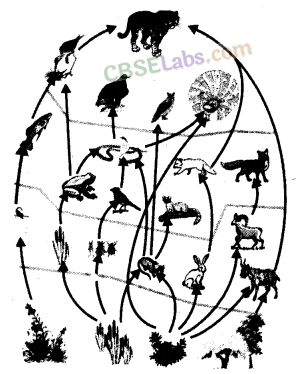
Food Web:
The inter-connected food chains operating in an ecosystem which establish a network of relationship between various species, are called a food web.
In a food web, one organism may occupy a position in more than one food chain. An organism can obtain its food from different sources and in turn, may be eaten up by different types of organisms.
Trophic Levels:
The various steps in the food chain at which the transfer of food (or energy) takes place is called trophic levels.
There is a gradual decrease in the amount of energy transfer from one trophic level to the next trophic level in a food chain.
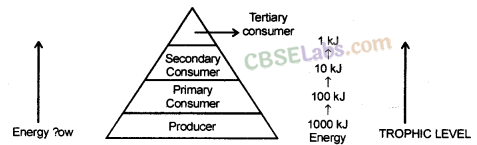
So only 10% of energy is transferred to next trophic level while 90% of energy is used by present trophic level in its life processes.
The various trophic levels are given below :
- The plant or the producers constitute the first trophic level.
- The herbivores or primary consumers form the second trophic level.
- Carnivores or secondary consumers make up the third trophic level.
- Large carnivores or the tertiary consumers which feed upon the small carnivores constitute the fourth trophic level.
Flow Open Energy
Energy is used and conveyed from one trophic level to another in a food chain. This is called flow of energy. Green plants capture about 1% of the solar energy incident on the Earth through the biochemical process of photosynthesis. A part of this trapped energy is used by plants in performing their metabolic activities and some energy is released as heat into the atmosphere. The remaining energy is chemical energy stored in the plants as ‘carbohydrates’. When plants are eaten up by herbivores, the chemical energy stored in the plants is transferred to these animals. These animals (herbivores) utilize some of this energy for metabolic activities, some energy is “released as heat and the remaining energy is stored. The process of energy transferred is similarly repeated with carnivores and so on.
Ten percent law:
Ten percent law states that only 10 percent of the energy entering a particular trophic level of organisms is available for transfer to the next higher trophic level.
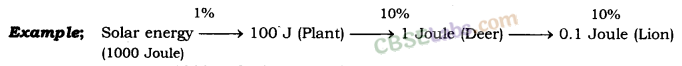
For example, Suppose 1000 J of solar energy is received by green plants, then only 1% of solar energy available on earth is utilized by plants. So only 10 J (1% of 1000 J) is trapped by plants and the rest 990 J of energy is lost to the environment. So, plants utilizes only 10 J of energy. Next, only 10% of the 10 J energy of plant, that is, 1 J, is available to the herbivore animal while 9 J is lost to the environment. Again, just 10% of the 1 J of energy of herbivore animals is utilized by carnivore animals. Thus, carnivore animals have only 0.1 J of energy while 0.9 J is lost to the environment.
Environmental Problems: Changes in the environment affect us and our activities change the environment around us. This led to the slow degradation of the environment that arose many environmental problems. For Example; depletion of the Ozone Layer and waste disposal.
Depletion of Ozone Layer:
Ozone (O3) layer is largely found in the stratosphere which is a part of our atmosphere from 12 km -50 km above sea level. This region is called ozonosphere. Ozone is deadly poisonous at the ground level.
Ozone is formed as a result of the following photochemical reaction.

Ozone layer is a protective blanket around earth which absorbs most of the harmful U.V. (Ultraviolet) radiation of the Sun, thus, protecting the living beings of the Earth from health hazards like skin cancer, cataract in eyes, weaken immune system, destruction of plants etc. The decline of Ozone layer thickness in Antarctica was first discovered in 1985 and was termed as OZONE HOLE.
Steps taken to limit damage of ozone layer: Excessive use of CFCs (Chloro Flouro Carbon) a synthetic, inert chemical. For example; Freon which are used as refrigerants and also in fire extinguishers caused Ozone depletion in the upper atmosphere. A single chlorine atom can destroys 1,00,000 Ozone molecules. U.N.E.P. (United Nation Environment Programme) did an excellent job in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels (KYOTO Protocol) by all countries.
Biological Magnification: The increase in concentration of harmful chemical substances like pesticides in the body of living organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification.
Example:

Maximum concentration of such chemicals gets accumulated in human bodies.
Garbage Disposal:
Industrialization and rise in demand of consumer goods have created a major problem in the form of wastes/garbage accumulation and its disposal especially in urban areas.
The disposal of waste should be done in a scientific way. There are different methods of waste disposal. The method to be used depends on the nature of the waste. Some of the important modes of waste disposal are :
- Incineration: Burning of waste on high temperature to form ash is called incineration. This process is carried out in an incinerator. Incineration is used to destroy household, chemical and biological wastes.
- Open dumping: A conventional method in which solid waste are dumped in selected areas of a town. It actually cause pollution
- Land fillings: Wastes are dumped in low living areas and are compacted by rolling with bulldozers
- Composting: Organic wastes are filled into a compost pit (2m × 1m × 1m). It is then covered with a thin layer of soil. After about three months the same garbage filled inside the pit changes into organic manure.
- Recycling: The solid wastes is broken down into its constituent simpler materials. These materials are then used to make new items. Even non-bio degradable solid wastes like plastic, metal can be recycled.
- Reuse: A very simple conventional technique of using an item again and again. For example; paper can be reused for making envelops, etc…
Environment: The combination of all the physical and biological conditions affecting the responses of living organisms is called environment.
Biodegradable wastes: The wastes which are broken down by the activity of micro¬organisms and enter into the biogeochemical cycle are known as biodegradable wastes.
Non-biodegradable wastes: The wastes which cannot be broken down by the enzymes produced by microorganisms into simpler and harmless products in nature are called non- biodegradable wastes.
Garbage: Domestic wastes including the kitchen waste are termed as garbage.
Incineration: Destruction of waste materials by burning at high temperature is called incineration.
Biotic Community: A group of various populations of organisms living in a region is called the biotic community.
Ecosystems: The self-contained and distinct functional unit capable of independent existence made by the interaction of living and non-living components is called an ecosystem.
Ecosystem component consists of two components- Abiotic and biotic
- Abiotic: Components consist of inorganic and organic substances and climatic factors.
- Biotic: Components consist of a living organism.
Autotrophs: Those organisms which can produce their own food are called autotrophs or producers. All green plants are producers.
Consumers: Those organisms which are unable to synthesise their food themselves and consume the food produced by producers or eat other organisms as food, are known as consumers.
Decomposers: Bacteria and fungi which break down the complex organic compounds present in the dead plants and animals and their products into simpler substances are known as decomposers.
Food Chain:
A series of organisms in a community in which one organism consumes another organism to transfer food energy is called a food chain.
Characteristics:
- A food chain helps in understanding the food relationship and interactions among various organisms in an ecosystem.
- There is a progressive decline in the amount of energy available as we move from one trophic level to another in a food chain.
Trophic levels: Each step of the food chain is known as a trophic level. 10% of food taken by one trophic level is available for the next trophic level.
Food Web: The web formed by the interconnection of food-chains of the various trophic levels is called a food web.
Biomagnification:
The increase in the concentration of the harmful chemicals in the body of an
organism per unit its mass at each successive trophic level in a food chain is known as biomagnification.
Ozone Depletion: The thinning of the ozone layer is called ozone depletion.
Ozone-depleting substances: Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), oxides of nitrogen, methane, carbon tetrachloride and chlorine are the ozone-depleting substances.
Four practices which can help in the protection of our environment:
- Disposal of wastes after separating them into biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste material.
- Use of unleaded petrol and alternate sources of energy, and keeping the engine properly tuned and serviced and the tyres inflated to the right pressure so that the vehicle runs efficiently.
- The use of gunny bags and paper bags in place of polythene/plastic bags.
- Activities such as gardening, rain-water harvesting and use of compost in place of fertilizers will help protect our environment from further damage.
Harmful effects of agricultural practices on the environment.
- Excessive use of fertilisers changes the chemistry of soil and kills useful microbes.
- Excessive use of non-biodegradable chemical pesticides leads to biological magnification.
- Extensive cropping causes loss of soil fertility.
- Excess use of groundwater for agriculture lowers the water table.
- Agricultural practices lead to some amount of damage to the natural ecosystem/habitat.
1. Environment:
The physical, chemical and ‘ biological conditions of the region in which an organism lives is called its Environment. It includes air, light, soil, temperature, water and the presence or absence of other organisms, i.e., the conditions for development or growth.
The environment has three main components, viz :
- Physical surroundings [soil, air and water bodies]
- Living organisms [plants, animals, decomposers (bacteria and fungi)]
- Meteorological factors (or climatic factors) . [sunlight, temperature, rainfall, humidity, pressure and wind speed].
2. Physical environment: It is also called a abiotic or non-living environment. It includes :
- Soil, water bodies and air on the surface of the earth.
- Meteorological factors.
The physical environment is essential for :
- Supply of nutrient elements to the living beings.
- Providing space to the organisms for living.
- Controlling weather of a place.
3. Biotic (or biological) environment: It includes :
- Plants.
- Animals (including human beings).
- Decomposers (bacteria and.fungi).
Other important constituents of the biotic environment includes Kites and vultures as they feed on dead organisms and act as scavengers (cleansing agents) of the environment.
4. Ecosystem:
A community of organisms, interacting with each other, plus the environment in which they
live and with which they also interact. The examples of the ecosystem are a pond; a desert; a forest; a lake; a river; a mountain; the sea.
All the above ecosystems are made up of two main components.
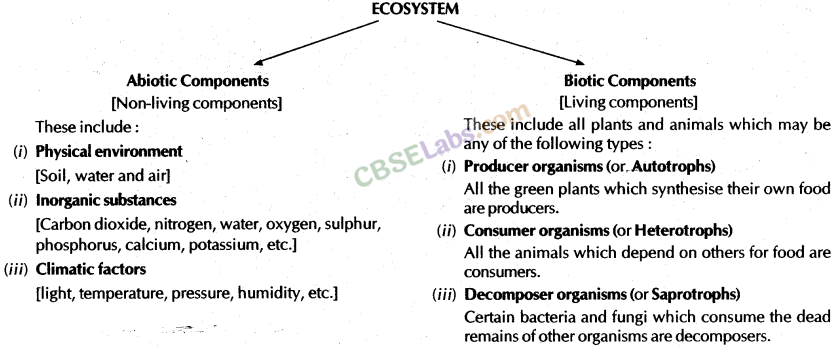
5. Autotrophs (Producers) and Heterotrophs (consumers):

6. Food chain:
The sequence of living organisms in a . community in which one organism.e^ts other and is
itself eaten by another organism to transfer energy is called a food chain. It is also defined as, “chain of organisms, existing in any natural community, through which energy is transferred”.
7. Ozone layer : Ozone (O 3 ) is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen unlike oxygen which is required for respiration by aerobic forms, ozone is a deadly poison. However, at the higher levels of the atmosphere,
ozone performs an essential function. It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun. This radiation is highly damaging to organisms, for example, it is known to cause skin cancer in human beings.
Ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere is a product of UV radiation, acting on oxygen (O2) molecule. The higher energy UV radiations split apart some molecular
oxygen (O2) into free oxygen (O) atoms. These atoms then combine with the molecular oxygen to form ozone as shown:
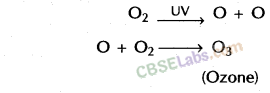
Depletion of ozone layer:
Ozone layer gets depleted – due to the use of chemicals called aerosol, spray propellants like chlorofluorocarbons. Depletion of ‘ ozone layer would cause skin cancer in men and animals and severe damage to the plants.
8. Biological magnification: It means accumulation of non-biodegradable chemicals (like pesticides) in the living organisms (like plants, animals, including man) in a food chain. “The increase in the concentration of harmful chemicals in the body of living organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification”.
9. Biodegradable wastes and Non-biodegradable wastes:

10. A generalised food chain:
11. Food web:
A food web is a network of food chains which establish a network of relationships between various species. Food web showing 8 interlinked food chains.
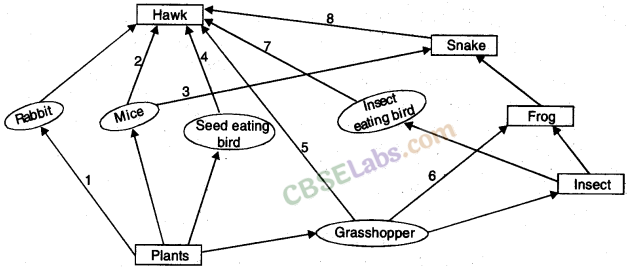

13. The flow of energy between various components of the environment:
- Green plants capture about 1 % of the energy and convert it into food energy.
- About f % of the food eaten is turned into the body of an organism and made available for the next level of consumers.
- About 10% of organic matter is present at each step and reaches the next level of consumers.
- Since so little energy is available for the next level of consumers, food chains generally consist of only three or four steps. The loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy remains after four trophic levels.
- There are generally a greater number of individuals at the lower trophic levels of an ecosystem, the greatest number is of the producers.
NCERT Notes for Class 10 Science
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 6 Life Processes Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 12 Electricity Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 15 Our Environment Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources Class 10 Notes