NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 6 Science Chapter 15 Air Around Us:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 15 | Air Around us |
| 15.1 | Is air present everywhere around us? |
| 15.2 | What is air made up of? |
| 15.3 | How does oxygen become available to animals and plants living in water and sons? |
| 15.4 | How is the oxygen in the atmosphere replaced? |
| 15.5 | Summary |
1. What is the composition of air?
Ans:
Air is mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and a few other gases. Some dust particles may also be present in it.
2. Which gas in the atmosphere is essential for respiration?
Ans:
Oxygen.
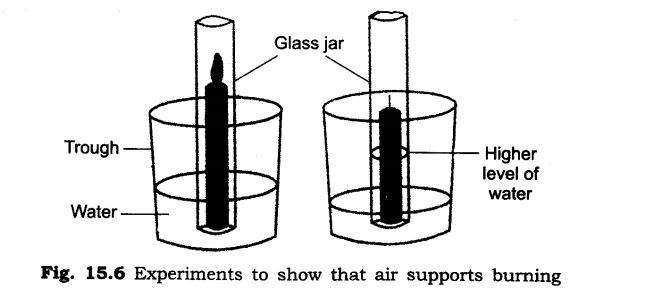
3. How will you show that air supports burning?
Ans:
Take a small burning candle. Cover the burning candle with a glass jar. After few minutes the candle is extinguished. As the supply of air is stopped due to glass jar the burning of candle is also stopped. This experiment proves that air supports burning
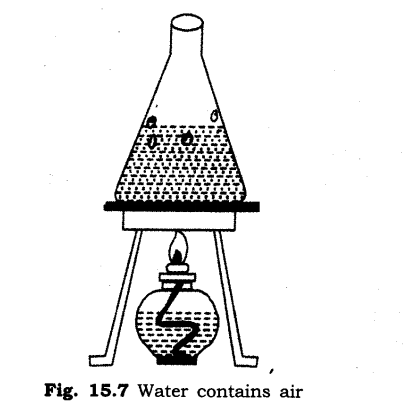
4. How will you show that air is dissolved in water?
Ans:
Take some water in a glass vessel or beaker. Heat it slowly on a tripod stand. Before the water begins to boil, look carefully at the inner surface of the vessel. You will see tiny bubbles on the inside. On heating, air dissolved in water escapes in the form of these bubbles.
5. Why does a lump of cotton wool shrink in water?
Ans:
Lump of cotton wool has air among gaps of cotton fibres. When water replaces the air from these gaps, the cotton lump becomes heavy and also shrinks due to removal of air gaps.
6. The layer of air around the earth is known as………………….
Ans:
Atmosphere
7. The component of air used by green plants to make their food, is………………….
Ans:
Carbon dioxide.
8. List five activities that are possible due to presence of air.
Ans:
The activities that are possible due to the presence of air, are:
(a) To make a simple firki
(b) To make a weather cock
(c) To breathe for survival
(d) For burning of substance
(e) For photosynthesis
9. How do plants and animals help each other in exchange of gases in the atmosphere?
Ans:
Animals and plants use oxygen from air during respiration and release carbon dioxide gas in air. But green plants also release oxygen gas by using carbon dioxide during photosynthesis. Thus, we can say that animals and plants help each other in exchange of gases.
Class 6 Science Chapter 15 VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Name the main component of air.
Ans:
Nitrogen gas
2. What is the source of oxygen gas in air?
Ans:
Photosynthesis by green plants is source of oxygen gas in air.
3. What is the percentage of nitrogen in air?
Ans:
78.1%
4. What is the percentage of oxygen in air?
Ans:
20.9%
5. What is the source of carbon dioxide in air?
Ans:
Respiration by animals and plants and burning of fuel.
6. Mention one necessary condition for the combustion to take place.
Ans:
Presence of air.
Class 6 Science Chapter 15 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Why is air considered as a mixture?
Ans:
Air contains oxygen and nitrogen as its major constituents of air. These gases retain their properties in air. So the air is called a mixture.
2. Name the major gas present in the (a) inhaled air (b) exhaled air.
Ans:
(a) Oxygen (b) Carbon dioxide.
3. Write the necessary conditions for rusting of iron to take place.
Ans:
Rusting of iron takes place in the presence of moisture and air. So the presence of air and water vapour in air are two necessary conditions for rusting of iron.
4. Name a device which uses wind energy to generate electricity.
Ans:
Windmills use the wind energy to convert wind energy into electrical energy
5. What is wind energy? Mention its two advantages.
Ans:
Blowing air is called wind. Wind possesses kinetic energy. The kinetic energy possessed by wind is called wind energy.
Uses of Wind Energy are:
(i) Wind energy is used to pump the ground water.
(ii) Wind energy is used to generate electricity with the help of windmills.
6. Mention two uses of air.
Ans:
The two uses of air are as below:
(a) For respiration all organisms need air.
(b) For burning of any substance air is needed.
7. Describe balance of oxygen in the air.
Ans:
The oxygen in air is used by the organisms present in air, water or soil or on earth for their respiration. During respiration carbon dioxide gas is released to air. But green plants during photosynthesis use carbon dioxide of air for preparing food and they release oxygen gas in the air. Thus the balance of oxygen in air is maintained.
8. What happens if the percentage of oxygen in the air reaches to 70%?
Ans:
If any substance catches fire it will become difficult to extinguish the fire, as oxygen supports combustion.
9. What happens if the percentage of carbon-dioxide increases in the air?
Ans:
The increased percentage of carbon-dioxide will cause green house effect, i.e. it will not allow the hot rays of sun to escape from the atmosphere after reflection once they enter the earth’s atmosphere, thereby increasing the temperature of earth, ice on mountains will melt and water level will rise.
10. You must have seen during rainy season, when it rains the animals like earthworm, snakes, snails etc. are commonly seen. Explain why?
Ans:
All these animals live in underground burrows or remain buried in the soil. They get oxygen from air that enters into the burrow through entrance of burrow or through pores in the soil. But when it rains, the water gets filled in their dwelling places and pores of the soil. So, they come out in search of air.
11. Why is carbon-dioxide gas used to extinguish fire?
Ans:
It is because carbon-dioxide does not support combustion. When sprayed on burning object it stops the supply of oxygen and extinguishes fire.
12. How will you prove that soil contains air in it?
Ans:
Take a glass tumbler add some soil in it, then pour some water on the soil slowly, the air-bubbles comes out of the soil. This proves that soil holds air in it.
13. Why do we see the sky and air clear and clean after rainfall?
Ans:
The dust particles which remain suspended in air get loaded and come down on the ground due to rainfall, this is the reason that the sky and the air look clean and clear after rainfall.
14. Explain why mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them?
Ans:
As you go up, above the sea-level the atmospheric pressure goes on decreasing and the amount of oxygen also decreases at higher altitude.
15. Explain why during an incident of fire, one is advised to wrap a woollen blanket over a burning object.
Ans:
Blanket cuts the supply of oxygen to the object that is burning, thereby prevents it from further burning.
Class 6 Science Chapter 15 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is air? Name the major constituents of air. Also give their volume proportions in air.
Ans:
Air is a mixture of gases. The major constituents of air are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and argon. The percentage composition of constituents of air are as given below:
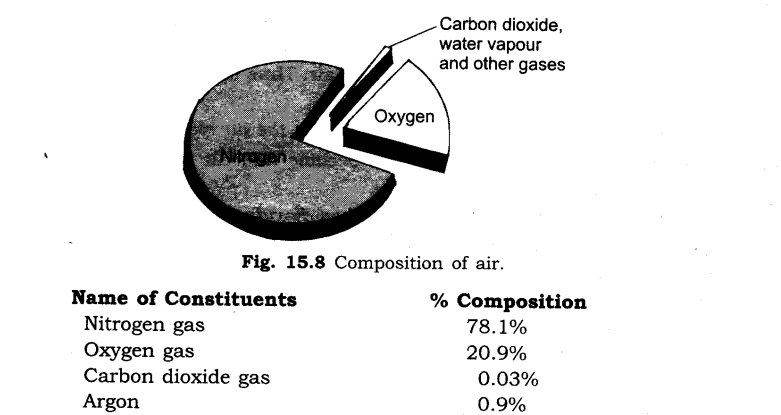
Other components of air are water vapour and dust particles.
2. Demonstrate through a simple experiment that the air mainly contains nitrogen and oxygen in the volume ratio of 4: 1.
Ans: Aim of experiment:
To show that air contains nitrogen and oxygen in the ratio 4 : 1 by volume:
Procedure:
Take a glass container and fix a candle at its centre. Put some quantity of water in the container. Place an empty, dry gas jar over it. Mark five marks above water surface on the jar at equal distances shown in the figure given below.
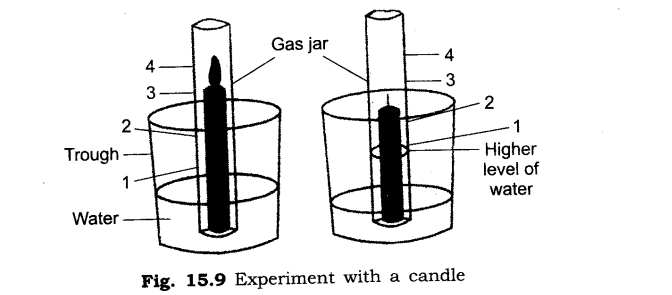
The candle is lightened and is covered with the gas jar. After some time the candle is extinguished and the water level is raised in gas jar. The raised level in water is 1 / 5 of the volume of air in the gas jar.
This proves that one part of the air of the jar is a gas which supports combustion, i.e., oxygen. Hence, 1/5 by volume is oxygen in air.
3. Air is a mixture. Prove this statement.
Ans:
The components of mixture can be easily separated and they retain their properties.
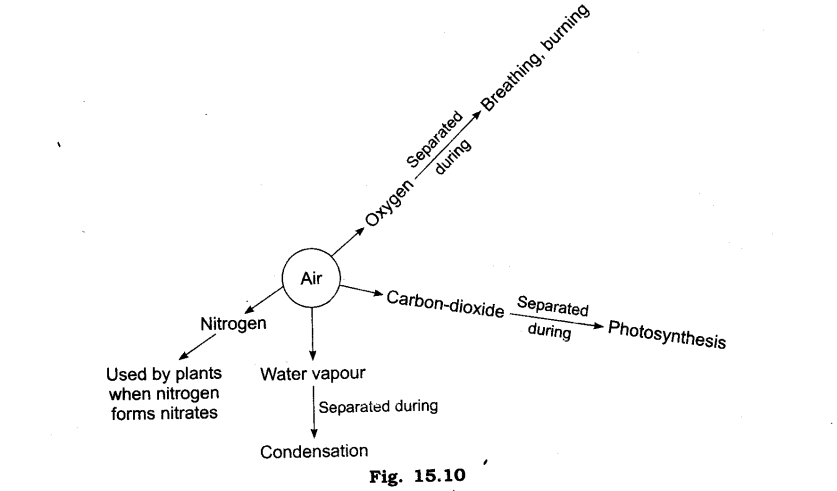
The components of air are: oxygen, nitrogen, water vapour and carbon-dioxide, all these gases can be easily separated and they retain their properties.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science – All Chapters
- Chapter 1 Food Where Does It Come From
- Chapter 2 Components of Food
- Chapter 3 Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4 Sorting Materials Into Groups
- Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
- Chapter 6 Changes Around Us
- Chapter 7 Getting to Know Plants
- Chapter 8 Body Movements
- Chapter 9 The Living Organisms and Their Surroundings
- Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
- Chapter 11 Light Shadows and Reflection
- Chapter 12 Electricity and Circuits
- Chapter 13 Fun with Magnets
- Chapter 14 Water
- Chapter 15 Air Around Us
- Chapter 16 Garbage In Garbage Out