A Journey through States of Water NCERT Class 6th Science Chapter 8 Question Answer
A Journey through States of Water Class 6 Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Reflect on what you did really well in this activity. (Page 154)
Answer:
We increased the exposed area in the case of water in the plate. Water in the bottle had lesser exposed area. It was found that water evaporates faster as the exposed area increases.
Question 2.
What did I do well? Was I able to label all the parts of the water cycle? Which parts of the water cycle were unclear to me? (Page 159)
Answer:
We could label some parts of water cycle. It was difficult to distinguish between lake and river water. Also labelling ground water is difficult.
Let Us Enhance Our Learning (Pages 161-162)
Question 1.
Which of the following best describes condensation?
(i) The conversion of water into its vapour state.
(ii) The process of water changing from a liquid into gaseous state.
(iii) The formation of clouds from tiny water droplets.
(iv) The conversion of water vapour into its liquid state.
Answer:
(iv) The conversion of water vapour into its liquid state describes condensation.
Question 2.
Identify in which of the given processes, evaporation is very important
(i) Colouring with
(a) crayons
(b) water colours
(c) acrylic colours
(d) pencil colours
(ii) Writing on paper with
(a) pencil
(b) ink pen
(c) ball point pen
Answer:
(i) (b) water colours
(ii) (b) ink pen
![]()
Question 3.
We see green coloured plastic grass at many places these days. Space around natural grass feels cooler than space around the plastic grass. Can you find out why?
Answer:
Space around natural grass feels cooler because it absorbs moisture from air.
Question 4.
Give examples of liquids other than water, which evaporate.
Answer:
Milk, oil, whisky, eye drops, sanitizer.
Question 5.
Fans move air around, creating a cooling sensation. It might seem strange to use a fan to dry wet clothes since fans usually make things cooler, not warmer. Normally, when water evaporates, it requires heat, not cold air. What do you think about this?
Answer:
Fans move the air faster around clothes and help these to dry faster because water evaporates faster.
Question 6.
Usually, when sludge is removed from drains, it is left in heaps next to the drain for 3-4 days. Afterward, it is transported to a garden or a field where it can be used as manure. This approach reduces transportation cost of the sludge and enhances the safety of individuals handling it. Reflect upon it and explain how.
Answer:
Water (moisture) from the sludge evaporates with time making it handling and transportation easier.
Question 7.
Observe the activities in your house for a day. Identify the activities that involve evaporation. How does understanding the process of evaporation help us in our daily activities? ,
Answer:
We perform various activities where process of evaporation help us.
(i) We dry our clothes on a sunny and windy environment.
(ii) We can smell the food being cooked even without entering the kitchen.
(iii) Washed utensils dry up after some time.
Question 8.
How is water present in the solid state’in nature?
Answer:
Ice, snow and frost are the solid state of water present in nature.
Question 9.
Reflect on the statement “Water is our responsibility before it is our right.” Share your thoughts.
Answer:
Only a small portion of water available on earth is fit for use by plants, animals and humAnswer:Most of the water is available in the oceans which we cannot use directly. We need water for drinking and many other activities. With increasing population the availability of safe water is decreasing. Though it is our right to get water’for our existence but at the same time it is our responsibility to keep water bodies free from pollution.
Question 10.
The seat of a two-wheeler parked on a sunny day has become very hot. How can you cool it down?
Answer:
To cool down the hot seat of a two-wheeler parked on a sunny day, we can:
- Cover it with a wet cloth: Place a damp cloth or towel over the seat. The water will absorb heat as it evaporates, cooling the seat.
- Sprinkle water on it: Lightly sprinkle water directly on the seat. The evaporating water will help to lower the temperature.
- Use a sunshade or cover: If available, use a sunshade or seat cover to protect the seat from direct sunlight, which will help keep it cooler.
- Park in the shade: If possible, move the two-wheeler to a shaded area to reduce the seat’s exposure to direct sunlight.
![]()
Activities
Activity 8.6 (Page 152)
Fill up the blank boxes in Fig. 8.5,(below) marked as A, B, C and 1, 2, 3, 4 for conversion of different states of water using the words—liquid, freezes, evaporates, gas, condenses. Two words have been filled for you.

Answer:

Conversion of different states of water
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Body Movements
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 6 Science Chapter 8 Body Movements:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 8 | Body Movements |
| 8.1 | Human Body and Its Movements |
| 8.2 | Gait of Animals |
1. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Joints of the bones help in the_____________ of the body.
(b) A combination of bones and cartilages forms the_______________ of the body.
(c) The bones at the elbow are joined by a______________
(d) The contraction of the____________ pulls the bones during
Ans:
(a) movement
(b) skeleton
(c) hinge
(d) muscle
2. Indicate ‘true’ and false’ among the following sentences:
(a) The movement and locomotion of all animals is exactly the same.
(b) The cartilages are harder than bones.
(c) The finger bones do not have joints.
(d) The fore arm has two bones.
(e) Cockroaches have an outer skeleton.
Ans:
(a) False
(b) False
(c) False
(d) True
(e) True
3. Match the items in column I with one or more items of column II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Upper jaw | (a) have fins on the body |
| (ii) Fish | (b) has an outer skeleton |
| (iii) Ribs | (c) can fly in the air |
| (iv) Snail | (d) is an immovable joint |
| (v) Cockroach | (e) protect the heart |
| (f) shows very slow movement | |
| (g) have a streamlined body |
Ans:

4. Answer the following questions:
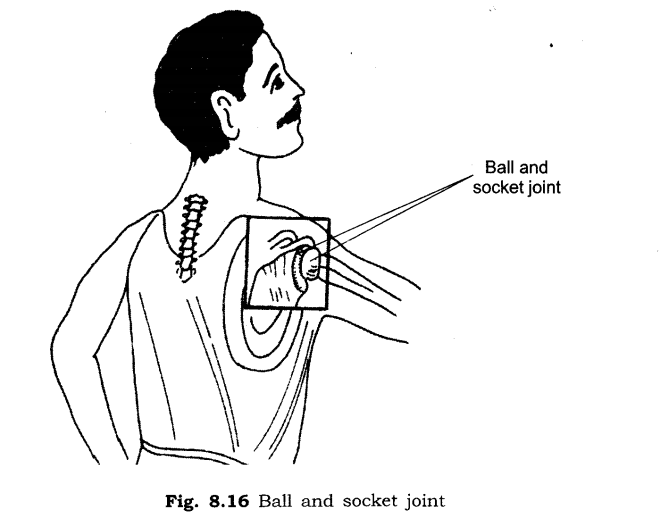
(a) What is a ball and socket joint?
(b) Which of the skull bones are movable?
(c) Why can our elbow not move backwards?
Ans:
(a) The rounded end of one bone fits into the hollow space of other bone. This is called ball and socket joint. Ball and socket joints allow movements in all the directions, e.g. shoulder and hip can be moved in all directions.
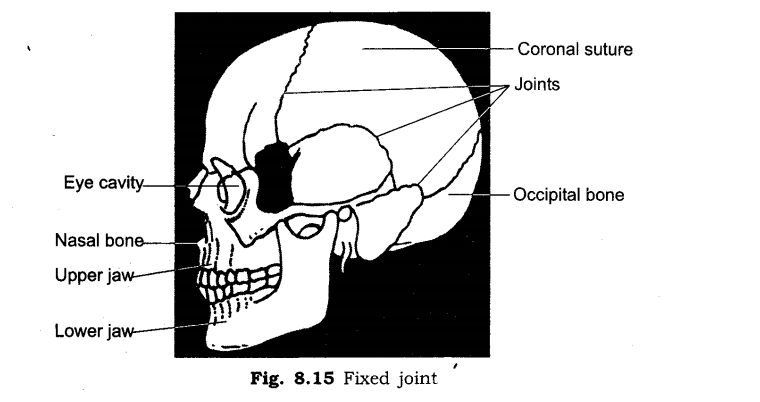
(b) In skull, only lower jaw is movable.
(c) Our elbow cannot move backwards because the elbow has a hinge joint that allows movement in only one direction.
Class 6 Science Chapter 8 VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What do you mean by movement?
Ans: The changing position of the body or any part of the body is called movement.
2. At which part does the arm rotate?
Ans: The arm rotates on the round pit-like structure.
3. If you tie a scale with your arm, are you able to bend your elbow?
Ans: No, we cannot bend our elbow.
4. Name the places where two parts of the body are seen to be joined together.
Ans: These places are called joint.
5. If there are no joints then will it be possible to move?
Ans: No, it is not possible.
6. Can bones be bent?
Ans: No, bones cannot be bent.
7. Can we bend our body at every part?
Ans: No, we can bend our body only at joints.
8. How many types of joints are there?
Ans: There are five types of joints in our body.
9. Name the various types of joint.
Ans:
(i) Ball and socket joints
(ii) Pivotal joints
(iii) Hinge joints
(iv) Fixed joints
(v) Gliding joints
10. What is cavity in bone?
Ans: The hollow space in the bone is called cavity.
11. Give two examples of ball and socket joint.
Ans:
(i) Joint of upper arm and shoulder.
(ii) Joint of thigh and the hip.
12. Give an example of pivotal joint.
Ans. The joint of skull with backbone.
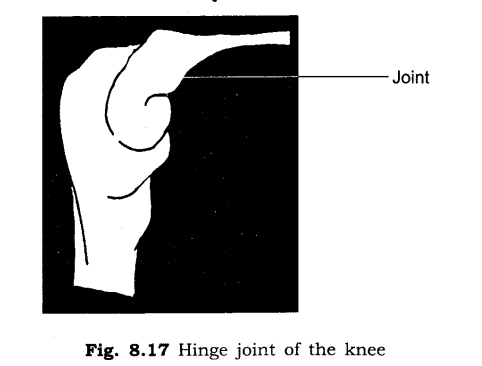
13. Give two examples of hinge joints.
Ans:
(i) Joints in fingers
(ii) Joints in knee
14. Give an example of fixed joint.
Ans: Joint of cranium skull.
15. Give an example of gliding joint.
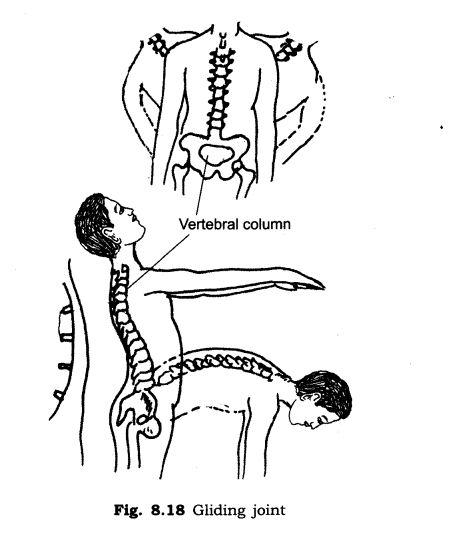
Ans: The joint in backbone.
16. What is skeleton?
Ans: The framework of bones in our body is called skeleton.
17. What are ribs?
Ans: The bones of the chest are called ribs.
18. What is rib cage?
Ans: Ribs are joined with backbone to form a box. This box is called rib cage.
19. What are shoulder bones?
Ans: The shoulder bones are formed by the collar bone and the shoulder blade. It connects the upper part of the chest and bones of the arm.
20. What are pelvic bones?
Ans: The bones which enclose the body part below the stomach are called pelvic bones.
21. What are cartilages?
Ans: Some additional parts of the skeleton which are not as hard as bones and are elastic in nature and can be bent are called cartilages, e.g. cartilage of ear.
22. Name the three components of skeleton.
Ans: Skeleton is made up of many bones, joints and cartilage.
23. Name the parts of the body which help in movement.
Ans: Contraction and relaxation of muscles and bones and joints help in movement.
24. Name two animals which move without bones.
Ans: (i) Earthworm (ii) Snail
25. Give an example of animal which can walk, climb and fly in the air.
Ans: Cockroaches.
26. Name the organ in cockroach which helps in walking.
Ans: The three pairs of legs in cockroach help in walking.
27. Which part of the cockroach help in flying?
Ans: There are two pairs of wings attached to the breast which help them in flying.
28. Name a bird which can swim in water.
Ans. Duck.
29. What do you mean by streamlined?
Ans: If the body tapers at both the ends then such, shape of the body is said to be streamlined.
30.How does the snake move?
Ans: Snakes have a long backbone and many thin muscles which help in the movement. The snake’s body curves into many loops. Each loop of the snake gives it a forward push by pressing against the ground.
31. What do you mean by fractured bone?
Ans: Fractured bone means broken bone.
32. Why are fractured bones plastered?
Ans. Plaster keeps broken bones at their right place so that they grow and join properly.
33. Name organs that are protected by the rib cage?
Ans: Heart and Lungs.
34. Why do we need two muscles together to move a bone?
Ans: A muscle can only pull, it cannot push. Thus, two muscles are required to work together to move a bone. When one muscle contracts, the bone is pulled. When another muscle of the pair pulls, it brings the bone in its original position.
35. Name three animals that have streamlined body.
Ans: Fish, Birds, Snake.
36. Many people suffer from a problem called arthritis. Explain its connection with movement.
Ans: Arthritis is the pain in joints. With this problem people find difficulty in moving from one place to another.
37. How is a bird’s body adapted for flying?
Ans: The following adaptations are seen in the body of birds.
(i) Bones are hollow.
(ii) Forelimbs are modified into wings.
(iii) Body is streamlined.
Class 6 Science Chapter 8 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What are joints? Write the names of various types of joints.
Ans: The places where two parts of the body seem to be joined together are called joints. There are following types of joints:
- Ball and socket joints
- Pivotal joints
- Hinge joints
- Fixed joints
- Gliding joints
2. What is skeleton? Draw a diagram to show the human skeleton.
Ans: The bones in our body form a framework to give a shape to the body. The framework is called skeleton
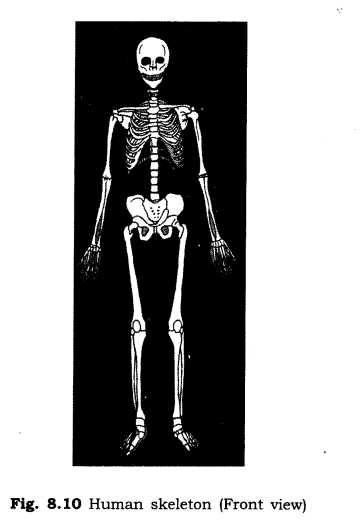
3. Write two ways by which we may know the shape of human skeleton.
Ans:
(i) We can know the shape of skeleton by feeling.
(ii) We could know the shape by X-ray images of human body
4:Write the differences between bones and cartilage.
Ans:
| Bone | Cartilage |
| (i) They are hard. | (i) They are soft. |
| (ii) They cannot bend. | (ii) They can bend. |
| (iii) They are used to make the framework of whole body. | (iii) They help to make some parts of the body. |
5. How do the muscles work?
Ans: The muscles work in pairs. When one of them contracts, the bone is pulled in that direction, the other muscle of the pair relaxes. To move the bone in the opposite direction, the relaxed muscle contracts to pull the bone towards its original position, while the first relaxes.A muscle can only pull. It cannot push.
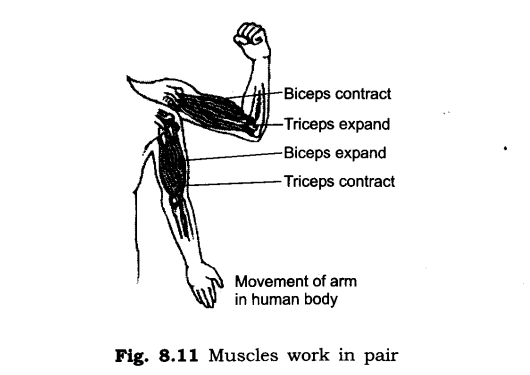
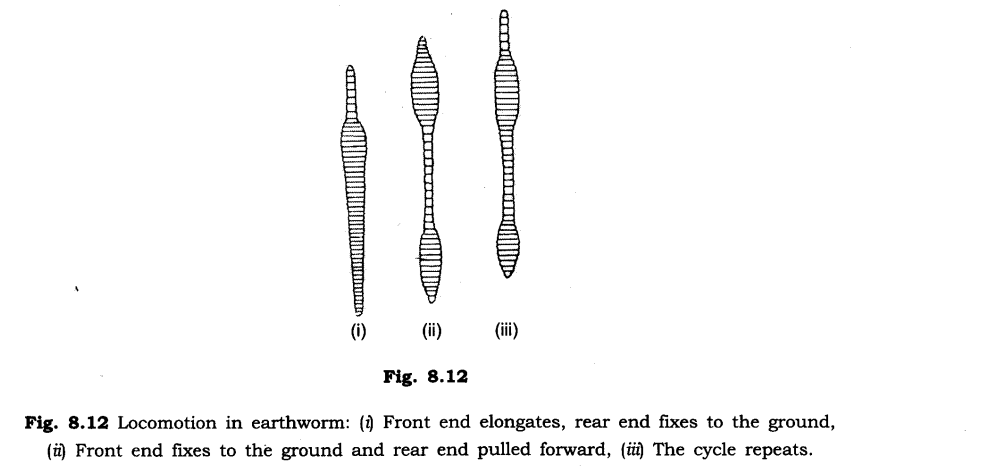
6. How does the earthworm move?
Ans: Earthworm does not have bones. It has muscles. During the movement, earthworm first extends front part of the body keeping the rear portion fixed to the ground. Then it fixes the front and releases the rear end. It then shortens the body and pulls the rear end forward. In this way by repeating such muscular expansions and contractions earthworm moves.
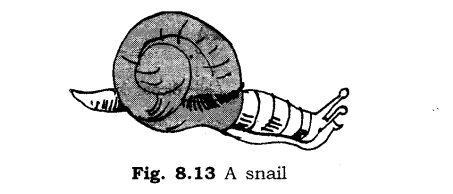
7. How does the snail move?
Ans: The rounded structure on the back of the snail is called shell. It is the outer skeleton (exoskeleton) of snail. When it starts moving a thick structure and the head of the snail may come out of an opening in the shell. The thick structure is called foot, which is made up of strong muscles. It helps snail in moving.
8. How does fish move in water?
Ans: The body of fish is streamlined. The streamlined shape helps the fish to move in water. The skeleton of fish is covered with muscles which make the front part of the body to curve to one side and the tail part swings towards the opposite side. This makes a jerk and pushes the body forward. In this way it moves in water.
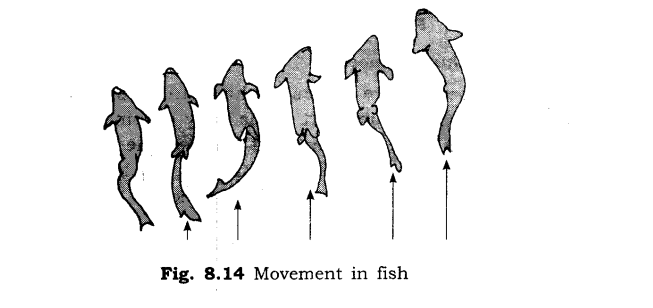
Class 6 Science Chapter 8 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Explain various kinds of joints found in our body and give example of each.
Ans: There are five types of joints in our body:
(i) Fixed joints: Those joints which do not allow movement are called fixed joint.
(ii) Ball and socket joint: This joint allows movement in all directions. The rounded end of one bone fits into the hollow space of other bone. For example, joint between upper arm and shoulder.
(iii) Pivotal joint: This type of joint allow movement in all planes, i.e. up and down, side and other planes. For example, head.
(iv) Hinge joint: The joint which allows movement only in one plane is called hinge joint. For example, fingers, knees.
(v) Gliding joint: These joints allow only a limited amount of movement of sliding nature of cartilage. For example, the joints of backbone.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science – All Chapters
- Chapter 1 The Wonderful World of Science
- Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
- Chapter 3 Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body
- Chapter 4 Exploring Magnets
- Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion
- Chapter 6 Materials Around Us
- Chapter 7 Temperature and its Measurement
- Chapter 8 A Journey through States of Water
- Chapter 9 Methods of Separation in Everyday Life
- Chapter 10 Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics
- Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
- Chapter 12 Beyond Earth