Measurement of Length and Motion NCERT Class 6th Science Chapter 5 Question Answer
Measurement of Length and Motion Class 6 Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Would it be convenient to use the unit metre to measure larger lengths, such as the length of a railway track between two cities, or to measure smaller lengths, such as the thickness of a page of a book? (Page 83)
Answer:
Length and distance measurements are given in units and the number of units. For long distances if small units like meters are used the number of units will be very large. This becomes inconvenient. Therefore long distances like distances among two cities are measured in kilometres.
Small thicknesses or lengths like the thickness of a page of book are measured in very small units like mm. If this is measured in metres or km then number of units become very small fractions inconvenient to handle.
Lengths like those of a room are measured in metres for convenience.
Question 2.
What do such kilometre stones indicate? How could Padma conclude that she was getting closer to her destination? (See fig. NCERT Textbook, Page 89) (Page 89)
Answer:
Kilometre stones on the roads between cities and places indicate the distance left to reach a place or city (the reference point). Padma saw that earlier kilometre stone showed the distance to Delhi as 70 km and the next kilometre stone showed the distance to Delhi as 60 km. She concluded that she was in motion and moving towards Delhi (the reference point with respect to which she was changing her position with time).
![]()
Question 3.
Does this mean that the position of Padma, with respect to the reference point, is changing with time? When does the position of an object change with respect to a reference point? Does it change when an object is moving? (Page 89)
Answer:
- Padma saw from the kilometre stones that the distance to Delhi is decreasing with time. This means that with respect to Delhi (reference point here), she was changing position with time.
- When the position of an object changes with time with respect to a reference point the object is said to be in a state of motion or is moving.
- Padma was changing her position with time with respect to Delhi, means that she was moving closer and closer to Delhi with time.
Let us enhance our learning (pages 97-99)
Question 1.
Some lengths are given in Column I of the following Table. Some units are given in Column II. Match the lengths with the units suitable for measuring those lengths.

Answer:
| Column I | Column II |
| Distance between Delhi and Lucknow | kilometre |
| Thickness of a coin | millimetre |
| Length of an eraser | centimetre |
| Length of school ground | metre |
Question 2.
Read the following statements and mark True (T) or False (F) against each.
(i) The motion of a car moving on a straight road is an example of linear motion.
Answer:
True
(ii) Any object which is changing its position with respect to a reference point with time is said to be in motion.
Answer:
True
(iii) 1 km = 100 cm
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Which of the following is not a standard unit of measuring length?
(i) millimetre
(ii) centimetre
(iii) kilometre
(iv) handspan
Answer:
(iv) handspan
Question 4.
Search for the different scales or measuring tapes at your home and school. Find out the smallest value that can be measured using each of these scales. Record your observations in a tabular form.
Answer:
| Type of Scale, Tape, Device | Smallest Value of Measurement |
| 15 cm Scale | 1 mm |
| Flexible Tape | 1 mm, 1 inch |
| Long Tape Roll | 1 cm, 1 inch |
| Vernier Calliper (from School Lab) | 0.1 mm |
| Screw Gauge (from School Lab) | 0.01 mm |
![]()
Question 5.
Suppose the distance between your school and home is 1.5 km. Express it in metres.
Ans.
∵ 1 km = 1000 metres
∴ 1.5 km = 1.5 × 1000
= 1500 metres
Question 6.
Take a tumbler or a bottle. Measure the length of the curved part of the base of glass or bottle and record it.
Answer:
Hint: Use a flexible measuring tape or a piece of string to measure the length of the curved part of the base of the tumbler, then measure the string against a ruler.
Question 7.
Measure the height of your friend and express it in
(i) metres
(ii) centimetres and
(iii) millimetres.
Answer:
Hint: Measure the height using a metre scale and express it in:
- Metres (e.g., 1.4 m)
- Centimetres (e.g., 140 cm)
- Millimetres (e.g., 1400 mm)
Question 8.
You are given a coin. Estimate how many coins are required to be placed one after the other lengthwise, without leaving any gap between them, to cover the whole length of the chosen side of a notebook. Verify your estimate by measuring the same side of the notebook and the size of the coin using a 15-cm scale.

Answer:
Hint: Measure the diameter of the coin and the length of the notebook. Divide the length of the notebook by the diameter of the coin to estimate the number of coins required. Say the diameter of the coin is 2 cm and the length of the notebook is 18 cm. Then \(\frac{18}{2}\) = 9 coins can be placed side to side along the length of the notebook. Verify by placing the coins end-to-end and measuring again.
Question 9.
Give two examples each for linear, circular and oscillatory motion.
Answer:
- Linear motion: A car moving on a straight road, an eraser dropping straight down.
- Circular motion: A merry- go-round, the motion of a whirling stone tied to a thread.
- Oscillatory motion: A swinging pendulum, the motion of a metal strip pressed and released.
Question 10.
Observe different objects around you. It is easier to express the lengths of some objects in mm, some in cm and some in m. Make a list of three objects in each category and enter them in the following Table.
Sizes of objects around us

Answer:
Classify objects by the convenience of measuring in mm, cm, and m:
| Size | Objects |
| mm | Thickness of a coin, thickness of a cardboard and diameter of a small screw |
| cm | Length of a pencil, width of a book and height of a water bottle |
| m | Height of a room, Width of a playground and height of a lamppost |
Question 11.
A rollercoaster track is made in the shape shown in Fig. A ball starts from point A and escapes through point F. Identify the types of motion of the ball on the rollercoaster and corresponding portions of the track.

Rollercoaster track
Answer:
Portions of the track and corresponding types of motion:
- A to B: Linear motion
- B to C: Circular motion (loop)
- C to D to E: Circular motion
- E to F: Linear motion
![]()
Question 12.
Tasneem wants to make a metre scale by herself. She considers the following materials for it – plywood, paper, cloth, stretchable rubber and steel. Which of these should she not use and why?
Answer:
Tasneem should not use stretchable rubber because it can change length when stretched, leading to inaccurate measurements. Plywood, cloth, paper, and steel are more suitable as they maintain consistent lengths.
Question 13.
Think, design and develop a card game on conversion of units of length to play with your friends.
Answer:
Create cards with different lengths and corresponding units (mm, cm, m, km). Each card can have a length in one unit and players must match it to its equivalent in another unit. For example, a card with “100 cm” would match with “1 m”.
Activities
Activity 5.1: Let Us Measure (Page 86)
- Select some objects around you, such as a comb, a pen, a pencil, and an eraser to measure their lengths.
- Measure their lengths one by one using a metre scale and note down the measurements in Table 5.2.

Answer:
Measuring lengths
| Objectct | Length of the object |
| Comb | 15 cm |
| Pen | 14 cm |
| Pencil | 18 cm |
Activity 5.2: Let Us Explore (Page 90)
- Look around and prepare a list of five objects that are in motion and five objects that are at rest.
- Record your observations in Table 5.3.
- Think about how you decided whether an object was in motion or at rest.
Write your explanation (justification) in Table 5.3.

Observing things around you
Answer:
Table: Observing things around you
| Objects in motion | Justification | Objects at rest | Justification |
| Cow grazing in the field | Cow changes position with respect to grass in the field | Table in a classroom | Not moving |
| Switched on Fan | Blades of the fan rotate in a circular path | Chair with a teacher sitting | Stationary in the room |
| Car moving on the road | Car changes position with respect to objects on the road | Wall painting | Hanging at a fixed place on the wall |
| Hands of a wall clock | Showing circular motion to show time | A lamp on the lamp post | Standing still on the pole |
| Fruit falling from the tree | Fruit changes position from branch of the tree towards the ground below | A bird sleeping in its nest | Not changing its position with respect to the branches of the tree |
![]()
Activity 5.7: Let us Identify (Page 94)
- Look at the picture of a children’s park (Fig.) or visit a children’s park.
- Observe different kinds of motions. Classify them as linear, circular or oscillatory motion.
- List them in Table 5.4. Give your justification for why you put each in a certain category.

Types of Motion Observed in a children’s park

Answer:

NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances
Topics and Sub-Topics in Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Separation of Substances:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 5 | Separation of substances |
| 5.1 | Methods of separation |
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 5 Textbook Questions Solved
1. Why do we need to separate different components of a mixture? Give two examples.
Ans: Among different components of mixture there are many substances which are harmful or not useful for us. To remove these harmful or unuseful components we need to separate them. For example:
(a) Tea leaves are separated from the liquid with a strainer while preparing tea.
(b) Stone pieces from wheat, rice or pulses are picked out by hand.
2. What is winnowing? Where is it used?
Ans: Winnowing is used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture by wind or by blowing air. This process is used by farmers to separate lighter husk particles from heavier seeds of grain.

3. How will you separate husk or dirt particles from a given sample of pulses before cooking?
Ans: Husk or dirt particles can be separated by winnowing, being lighter they wall fly away from pulses.
4. What is Sieving? Where can it be used?
Ans. Sieving is a process by which fine particles are separated from bigger particles by using a sieve. It is used in flour mill or at construction sites. In flour mill, impurities like husks and stones are removed from wheat. Pebbles and stones are removed from sand by sieving.

5. How will you separate sand and water from their mixture?
Ans. We will separate sand and water by sedimentation and decantation method. First we leave this mixture for some time. After some time, the sand which is; heavier is settled down at the bottom. After that we wall pour water into another container and the mixture will be separated.
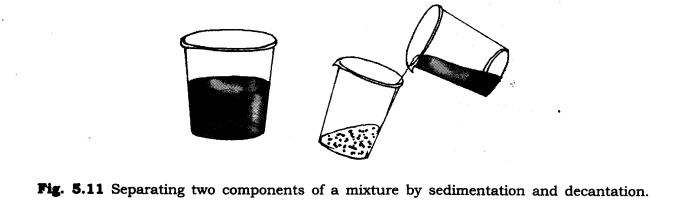
6. Is it possible to separate sugar mixed with wheat flour? If yes, how will you do it?
Ans. Sugar can be separated from wheat flour by sieving. Due to difference in the size of particles, sugar will stay on sieve and wheat flour will pass through it.
7. How would you obtain clear water from a sample of muddy water?
Ans. We will obtain clear water from a sample of muddy water by the process of filtration.
A filter paper is one such filter that has very fine pores in it. Figure 5.12(a, b) shows the steps involved in using a filter paper. A filter paper folded in the form of a cone is fixed in a funnel. The mixture is then poured on the filter paper. Solid particles in the mixture do not pass through it and remain on the filter.
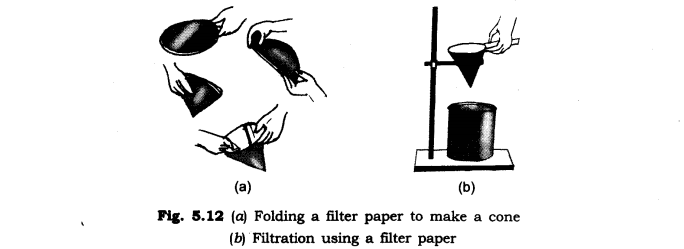
8. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The method of separating seeds of paddy from its stalks is called .
(b) When milk, cooled after boiling, is poured onto a piece of cloth the cream (malai) is left behind on it. This process of separating cream from milk is an example of ______.
(a) Salt is obtained from sea water by the process of ____________ .
(b) Impurities settled at the bottom when muddy water was kept overnight in a bucket. The clear water was then poured off from the top. The process of separation used in this example is called ____________.
Ans.
(a) threshing
(b)filtration
(b) evaporation
(d) sedimentation and decantation
9. True or false?
(a) A mixture of milk and water can be separated by filtration.
(b) A mixture of powdered salt and sugar can be separated by the process of winnowing.
(c) Separation of sugar from tea can be done with filtration.
(d) Grain and husk can be separated with the process of decantation.
Ans.
(a) False
(b) False
(c) False
(d) False
10. Lemonade is prepared by mixing lemon juice and sugar in water. You wish to add ice to cool it. Should you add ice to the lemonade before or after dissolving sugar ? In which case would it be possible to dissolve more sugar ?
Ans. We should add ice after dissolving sugar. When the temperature is high then more sugar can be dissolved. After mixing ice it gets cool and less sugar will dissolve in it.
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is strainer?
Ans. Strainer is a kind of sieve which is used to separate a liquid from solid.
2. Name the method used to separate cream from curd.
Ans. Centrifugation.
3. How will you separate mango from a mixture of mango and apple?
Ans. By picking.
4. You are given a mixture of salt and sand. Can you separate them by picking?
Ans. No, we cannot separate them by picking.
5. Name the method used to separate the pieces of stone from grain.
Ans. Handpicking.
6. How can you separate grains from stalk?
Ans. We separate grains from stalk by threshing.
7. What types of material can we separate by using handpicking?
Ans. The materials having different size and colour can be separated by handpicking.
8. Name the other methods used to separate solid materials of different size.
Ans. Sieving.
9. Name the process used to separate heavier and lighter components of a mixture.
Ans. Winnowing.
10. Can the above stated method be used if both the components have same weight?
Ans. No, this method cannot be used.
11. What is evaporation?
Ans. The process of conversion of water into vapour is called evaporation.
12. Name the method by which we get salt from ocean water.
Ans. Evaporation.
13. Define condensation.
Ans. The process of conversion of water vapour into liquid form is called condensation.
14. Write opposite process of evaporation.
Ans. Condensation.
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
l. What is mixture?
Ans. When two or more than two substances are mixed together in any ratio then it is called a mixture.
2. Write various methods of separation of components from their mixture.
Ans.
- Handpicking
- Threshing
- Winnowing
- Sedimentation
- Decantation
- Filtration
- Evaporation
- Condensation
3. Define the term handpicking.
Ans. The process used to separate slightly larger particles from a mixture by hand is called handpicking. For example: Stone pieces can be separated from wheat or rice by handpicking.
4. What do you mean by threshing? Where is it used?
Ans. Threshing is a process in which we separate grain from stalks. This process is used by farmer to separate gram, wheat, rice, mustard seeds in his field.
5. Write three methods of separation.
Ans. Handpicking, threshing and winnowing.
6. How will you separate oil and water from their mixture?
Ans. Oil, being lighter than water, will float on it. Two distinct layers are formed and slowly oil is allowed to flow into another container and is separated from water. Separating funnel can also be used to separate the two.
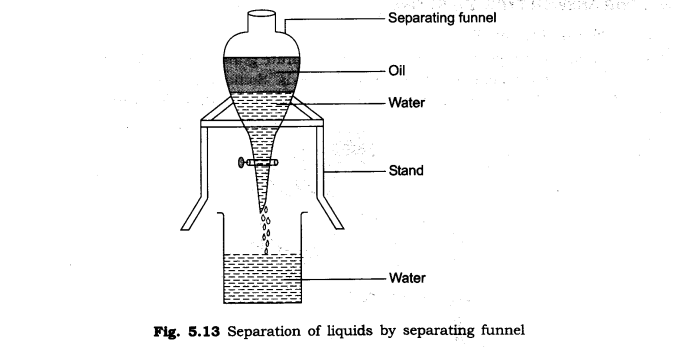
7. What is evaporation?
Ans. The process of conversion of water into vapour is called evaporation. This process takes place continuously where water is present. Common salt from sea water is obtained using this method.
8. Define winnowing.
Ans. The process is used to separate components from a mixture in which one component is heavier or lighter than other is called winnowing. Winnowing is done with the help of wind or by blowing air.
9. What do you mean by sieving? Give an example.
Ans. Sieving allows the fine flour particles to pass through the holes of the sieve while the bigger particles or impurities remain on the sieve. For example, in a flour mill, impurities like husk and stones are removed from wheat before grinding it.
10. Match the column:
Class 6 Science Chapter 5 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What is threshing?
Ans. Threshing is a process that is used to separate grain from stalks. In this process the stalks are beaten to free the grain seeds. Sometimes threshing is done with the help of bullocks. Machines are also used to thresh large quantities of grain.

2. Describe the method to obtain salt from sea water.
Ans. Sea water contains many salts mixed in it. One of them is common salt, when sea water is allowed to stand in shallow pits, water gets evaporated by sunlight and slowly turns into water vapour. In a few days, the water evaporates completely leaving behind the solid salts. Common salt is then obtained from this mixture of salts by further purification.
3. What is decantation?
Ans. Decantation is a process, of separation of insoluble solids from liquid. The suspension of solid particles in liquid is allowed to stand for some time. The solid particles then settle down at the bottom of the container and clean water goes up. Without disturbing the settled particles the clean water is transferred into other container.
4. Where is decantation used? Give two examples.
Ans.
(i) Decantation is used to separate insoluble solids or liquid from liquid. Rain water is a mixture of mud and water. It is purified by decantation.
(ii) Oil and water also get separated by this method because oil floats up.
5. How will you prepare cheese (paneer)?
Ans. For making paneer, a few drops of lemon juice sire added to milk as it boils. This gives a mixture of particles of solid paneer and liquid. The paneer is then separated by filtering the mixture through a fine cloth or strainer.
6. Explain the method that can be used for separating the following mixture:
(i) Sand and husk
(ii) Wheat, sugar and stalk
(iii) Water and petrol
(iv) Rice and salt
(v) Sand and salt
Ans.
(i) Mixture of sand and husk: Sand and husk can be separated by the method of winnowing.
(ii) Mixture of wheat, sugar and stalk: For separating stalk from the mixture we should follow the winnowing method because milk is lighter than other two components and get separated. Wheat and sugar can be separated by sieving because they are in different sizes.
(iii) Mixture of water and petrol: Water does not dissolve in petrol. So, it can be separated by the use of separating funnel.
(iv) Mixture of rice and salt: Rice and salt can be separated by sieving.
(v) Mixture of sand and salt: Sand and salt is mixed with water, salt dissolves in water and sand can be separated solution by sedimentation and decantation followed by filtration. After that using evaporation common salt is separated.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science – All Chapters
- Chapter 1 The Wonderful World of Science
- Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
- Chapter 3 Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body
- Chapter 4 Exploring Magnets
- Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion
- Chapter 6 Materials Around Us
- Chapter 7 Temperature and its Measurement
- Chapter 8 A Journey through States of Water
- Chapter 9 Methods of Separation in Everyday Life
- Chapter 10 Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics
- Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
- Chapter 12 Beyond Earth