Diversity in the Living World NCERT Class 6th Science Chapter 2 Question Answer
Diversity in the Living World Class 6 Questions and Answers
Let us enhance our learning (pages 31-33)
Question 1.
Here are two types of seeds. What differences do you find among the roots and leaf venation of their plants?

Answer:
Differences between wheat and kidney beans:
| Features | Wheat (Monocot) | Kidney Beans (Dicots) |
| (i) Root system | Fibrous root system | Taproot system |
| (ii) Root characteristics | Dense network of thin roots | Central thick taproot with lateral branches |
| (iii) Leaf venation | Parallel venation | Reticulate venation , |
| (iv) Leaf venation characteristics. | Veins run parallel along the length of the leaf. | Network of branching veins with a permanent midrib. |
Question 2.
Names of some animals are given below. Group them based on their habitats. Write the names of aquatic animals in the area marked ‘A’ and terrestrial animals in the area marked ‘B’. Enter the names of animals living in both habitats in part ‘C’.
Horse, Dolphin, Frog, Sheep, Crocodile, Squirrel, Whale, Earthworm, Pigeon, Tortoise

Answer:
(A) Aquatic animals:
(i) Dolphin
(ii) Whale
(B) Terrestrial animals:
(i) Horse
(ii) Sheep
(iii) Squirrel
(iv) Earthworm
(v) Pigeon
(C) Both A and B (Amphibians)
(i) Frog
(ii) Crocodile
(iii) Tortoise
![]()
Question 3.
Manu’s mother maintains a kitchen garden. One day, she was digging out radish from the soil. She told Manu that radish is a kind of root. Examine a radish and write what type of root it is. What type of venation would you observe in the leaves of radish plant?
Answer:
Radish is a type of root known as a taproot. Taproot are thick, primary roots that grow deep into the soil other than with a conical shape.
Leaf Venation: The leaves of radish plant exhibit‘reticulate venation, which is typical of dicotyledonous plants. This venation pattern consists of a prominent central vein with smaller veins branching out, forming a network.
Question 4.
Look at the image of a mountain goat and a goat found in the plains. Point out the similarities and differences between them. What are the reasons for these differences?

Answer:
Similarities:
- Both are goats and belong to the same family.
- Herbivore diet: Both are herbivores. That is they eat plants including roots, stems, leaves etc.
Differences:
| Mountain Goat | Plains Goat |
| 1. Has thick, long fur to protect against cold mountain temperatures. | Has shorter fur suited for warmer climates. |
| 2. Generally stockier and more muscular, adapted for climbing rocky terrains. | Leaner build suitable for flat, open areas. |
| 3. Specialised hooves with a rough texture for better grip on rocky surfaces. | Hooves more suited for walking on flat, grassy lands. |
Question 5.
Group the following animals into two groups based on any feature other than those discussed in the chapter— cow, cockroach, pigeon, bat, tortoise, whale, fish; grasshopper, lizard.
Answer:
(i) Flying Animals:
(a) Pigeon
(b) Bat
(c) Cockroach
(d) Grasshopper
(ii) Non-flying Animals:
(a) Cow
(b) Tortoise
(c) Whale
(d) Fish
(e) Lizard
Question 6.
As the population grows and people want more comfortable lives, forests are being cut down to meet various needs. How can this affect our surroundings? How do you think we can address this challenge?
Answer:
Impact of Deforestation:
- Loss of Biodiversity
- Changes in Climate
- Soil Erosion
- Water Cycle Disruption
- Decreased Air Quality.
Addressing the Challenge
- Protected Areas: Establishing more national parks and wildlife sanctuaries to protect existing forests.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local communities in forest conservation efforts. We should plant more trees near our surroundings.
- Legislation: Implementing and enforcing laws that prevent illegal logging and deforestation.
Question 7.
Analyse the flowchart. What can be examples of *A’ and ‘B’?

Answer:
Examples of ‘A’: These are plants that have reticulate venation in their leaves. Examples: Mango, Hibiscus, Rose, Chickpea (Chana), Mustard. Examples of ‘B’: These are plants that do not have reticulate venation (i.e., they have parallel venation). Examples: Wheat, Maize, Grass.
![]()
Question 8.
Raj argues with his friend Sanjay that “Gudhal (hibiscus) plant is a shrub”. What questions can Sanjay ask for clarification?
Answer:
1. What is the nature of its stem?
2. What is the height of the Gudhal (hibiscus) plant?
3. Is the stem of the Gudhal plant woody?
Question 9.
Based on the information in the table, find out examples of these plants for each group.

(a) What other similarity do plants of group A have?
(b) What other similarity do plants of group B have?
Answer:
Examples for group A and B.
1. Rose, mango, radish, carrot and hibiscus
2. Grass, wheat, onions, maize and rice etc.
(a) Similarity of Plants in Group
A: Plants in Group A (dicots) typically have leaves with reticulate venation.
(b) Similarity of Plants in Group
B: Plants in Group B (monocots) generally have leaves with parallel venation.
Question 10.
Observe the labelled part of a duck in the picture given below. What differences do you observe in the feet of the duck compared to the other birds? Which activity would the duck be able to perform using this part?

(a) Duck
(b) Pigeon
Answer:
Differences in the Feet
(a) Duck has webbed feet
(b) Pigeon does not have webbed feet: has regular bird feet with separate toes.
Activities the Duck Can Perform with Webbed Feet
- Swimming: The webbed feet help the duck to paddle through water efficiently.
- Walking on Muddy or Wet Surfaces: Webbed feet provide stability and prevent the duck from sinking.
- The webbed feet a of duck are specially adapted for swimming, allowing it to move smoothly in water.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Components of Food
The topics and Sub Topics in Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Components of Food:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 2 | Components of Food |
| 2.1 | What do Different Food Items Contain? |
| 2.2 | What do Various Nutrients do For Our Body? |
| 2.3 | Balanced Diet |
| 2.4 | Deficiency Diseases |
Class 6 Science Chapter 2 Textbook Questions Solved
1. Name the major nutrients in our food.
Ans: The major nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals.
The table below shows the nutrients present in some food items:
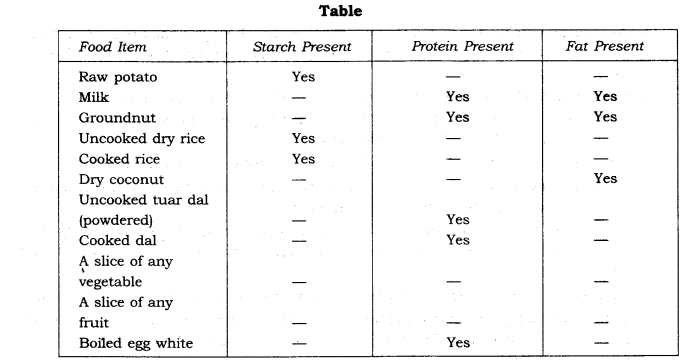
2. Name the following:
(a) The nutrients which mainly give energy to our body.
(b) The nutrients that are needed for the growth and maintenance of our body.
(c) A vitamin required for maintaining good eyesight.
(d) A mineral that is required for keeping our bones healthy.
Ans:
(a) Carbohydrates
(b) Proteins
(c) Vitamin A
(d) Calcium
3. Name two foods each rich in:
(a) Fats
(b) Starch
(c) Dietary fibre
(d) Protein
Ans:
(a) Ghee, butter,
(b) Raw potato, rice,
(c) Spinach, cabbage, carrot, ladies finger, (any two)
(d) Milk, egg, fish, meat, pulses (any two).
4. Tick (/) the statements that are correct, cross (X) those which dire incorrect.
(a) By eating rice alone, we can fulfill nutritional requirement of our body,
(b) Deficiency diseases can be prevented by eating a balanced diet.
(c) Balanced diet for the body should contain a variety of food items.
(d) Meat alone is sufficient to provide all nutrients to the body.
![]()
5. Fill in the blanks:
(a) ________ is caused by deficiency of Vitamin D. ,
(b) Deficiency of_________ causes a disease known as beri-beri.
(c) Deficiency of Vitamin C causes a disease known as________________ .
(d) Night blindness is caused due to deficiency of_______________ in our food.
Ans:
(a) Rickets
(b) Vitamin B1
(c) Scurvy
(d) Vitamin A
Class 6 Science Chapter 2 VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. Do all meals consist of the same food items?
Ans: No, all meals do not have the same food items.
2. Why should a meal have different food items?
Ans: A meal should have different food items because our body needs different kinds of nutrients for proper functioning.
3. Do all foods contain all the required nutrients?
Ans: No, all foods do not contain sill the nutrients required by our body.
4. Name two main types of carbohydrates found in our food.
Ans:
(i) Starch (ii) Sugar
5. What are carbohydrates?
Ans: The compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen which provide energy for our body are called carbohydrates.
6. What happens when two or more drops of iodine solution fall on starch substance?
Ans: The colour of the substance becomes blue-black.
7. If any food item gives blue-black colour with iodine then which nutrient is present in the food?
Ans: Starch.
8. Name two substances which provide carbohydrates.
Ans:
(i) Potato
(ii) Rice/wheat/maize/sugar
9. Name the food nutrient indicated by an oily patch on paper.
Ans:An oily patch on paper shows the presence of fat.
10. Name two energy-providing nutrients.
Ans:
(i) Carbohydrates
(ii) Fats
11. Name a nutrient which helps in repairing the damaged body cells.
Ans: Proteins.
12. Name two nutrients which protect the body from diseases.
Ans:
(i) Vitamins
(ii) Minerals
13. Name two plant food items which provide proteins.
Ans:
(i) Dal (pulses)
(ii) Soyabean
14. Name two sources of proteins provided by animals.
Ans:
(i) Milk
(ii) Eggs
15. Which type of food is called body-building food?
Ans: The food containing proteins is called body-building food.
16. Name two food items which provide fats.
Ans:
(i) Oils
(ii) Ghee
17. Name various types of vitamins.
Ans: Various types of vitamins are:
- Vitamin A,
- Vitamin B-complex,
- Vitamin C,
- Vitamin D,
- Vitamin E,
- Vitamin K.
18. Name a vitamin which represents a group of vitamins.
Ans: Vitamin B-complex.
19. Name two sources of Vitamin A.
Ans:
(i) Fish-oil
(ii) Milk
20. Write two sources of Vitamin B.
Ans:
(i) Liver
(ii) Beans
21. Write two sources of Vitamin C.
Ans:
(i) Orange/lime
(ii) Amla
22. Write two sources of Vitamin D.
Ans:
(i) Fish
(ii) Butter
23. What is roughage?
Ans. The food containing plant fibres which sure also known as dietary fibres is called roughage.
24. What is the main Function of roughage?
Ans: The main function of roughage is to help our body get rid of undigested food.
25. Name some food items which provide roughage.
Ans: Whole grains, fresh fruits and vegetables are the main sources of roughage.
Class 6 Science Chapter 2 SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. What are nutrients? Name major nutrients.
Ans: The components of food which are needed by our body for growth and development are called nutrients. The major nutrients are:
(i) Carbohydrates
(ii) Fats
(iii) Proteins
(iv) Vitamins
(v) Minerals
2. What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Ans: They complete the energy requirements of the body so they are called energy providing food.
3. Write test for detecting the presence of starch.
Ans: Take a piece of the food item. Put 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution on it. If the colour of the food item becomes blue-black, then it indicates the presence of starch in the food item.
(i) Food + Iodine — Blue-black colour (starch present)
(ii) Food + Iodine — No blue-black colour (no starch present)
4. What are the functions of proteins?
Ans: Proteins are the most important nutrient. They are called body-building food. They help in the growth and repair of damaged cells and tissues of the body. They also help our body to fight against infections. Proteins make our nails, hair and muscles.
5. How can you test presence of proteins in a given food item?
Ans:Take a small quantity of the food item. If the sample is solid, grind it. Put some part of this in a clean test tube, add 10 drops of water to it and shake the test tube. Now, with the help of a dropper, add two drops of solution of copper sulphate and 10 drops of solution of caustic soda to the test tube. Shake well and place the test tube in test tube stand for a few minutes.
Observe colour of the contents of test tube. If colour of the contents turns violet, the food item contains protein.
Note: Copper sulphate and caustic soda solutions are harmful. Handle them with care.
Food + water + copper sulphate + caustic soda → violet colour → protein is present.
6. What are fats? Name some fat-containing substances.
Ans: The energy rich sources of food are called fats. They provide energy to the body. All types of nuts, mustard seeds, milk and butter are the major sources of fat. Like carbohydrates, fats also contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen but fats contain less oxygen than carbohydrates.
7. Write test for detecting, presence of fat.
Ans: Take small quantity of the food item. Rub it on a piece of white paper. Observe carefully, you will find that the piece of white paper shows an oily patch on it which indicates that the food item contains fat.
8. What are vitamins? Write various kinds of vitamins.
Ans: They are protective compounds with no energy value. They help in proper body functioning and are required by the body in very small quantities. Various kinds of vitamins are—Vitamin A, Vitamin B-complex, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E and Vitamin K.
9. People who eat sea-food do not suffer from Goitre. Explain.
Ans: It is so because sea-food is a rich source of Iodine and Goitre is a deficiency disease caused due to lack of Iodine.
10. Excess intake of fats is harmful for the body because it causes obesity. Would it be harmful for the body to take too much of proteins or vitamins in the diet?
Ans. Yes, excess intake of proteins and vitamins in the diet is harmful and may lead to other diseases.
11. Name the vitamin that our body prepares in the presence of sunlight.
Ans: Vitamin D.
12. Name a vitamin that is not present in milk.
Ans: Vitamin C.
13. A patient had stunted growth, swelling on face, discolouration of hair and skin disease. Doctor advised him to eat a lot of pulses, grams, egg white, milk etc. What is wrong with the patient? Explain.
Ans: The intake of protein is not enough in his diet and all these symptoms are caused due to deficiency of proteins.
14. A small child became very thin and lean and later he became so weak that he could not move. Which nutrients should he eat so as to improve his health?
Ans: Both carbohydrates and proteins.
15. What are the functions of minerals?
Ans: Minerals are protective part of foods occurring naturally and are needed by our body in small amount. Minerals are essential for proper growth of the body and to maintain good health. They do not provide energy. Milk, salt, eggs and green leafy vegetables are the main sources of minerals.
16. Write the functions of water in our body.
Ans: Water helps our body to absorb nutrients from the food. It also helps in removing the waste from the body in the form of urine and sweat. We get water from various types of liquids, fruits and vegetables.
17. What is obesity?
Ans: When a person eats too much fat-containing foods, then the fat gets deposited in his body and he may end up suffering from a condition called obesity.
18. What are deficiency diseases?
Ans: When a person eats such a food continuously for a long time which may not contain a particular nutrient, then this condition is called deficiency of that nutrient. Deficiency of one or more nutrients can cause diseases or disorders in our body. Such type of diseases are known as deficiency diseases.
Class 6 Science Chapter 2 LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
1. List various types of nutrients and write the functions of each.
Ans. The various types of nutrients are:
(i) Carbohydrates: They are mainly energy-providing nutrients.
(ii) Fats: They provide energy for the body. They give much more energy than carbohydrates if consumed in same amount.
(iii) Proteins: They are called body-building foods. Proteins help in the formation and repairing of body parts. Skin, hair, muscles, enzymes are made up of proteins.
(iv) Vitamins: Vitamins help in protecting our body against disease. They also protect eyes, bones, teeth and gums.
(v) Minerals: Minerals are essential for proper growth of body and to maintain good health.
2. What is a balanced diet? Write the components of balanced diet.
Ans: A diet which provides the right proportion of all the nutrients that our body needs along with roughage and water is called balanced diet. The various components of balanced diet are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, roughage and water.
3. Prepare a chart to show various vitamins and minerals and the disorders caused by their deficiency.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Science – All Chapters
- Chapter 1 The Wonderful World of Science
- Chapter 2 Diversity in the Living World
- Chapter 3 Mindful Eating: A Path to a Healthy Body
- Chapter 4 Exploring Magnets
- Chapter 5 Measurement of Length and Motion
- Chapter 6 Materials Around Us
- Chapter 7 Temperature and its Measurement
- Chapter 8 A Journey through States of Water
- Chapter 9 Methods of Separation in Everyday Life
- Chapter 10 Living Creatures: Exploring their Characteristics
- Chapter 11 Nature’s Treasures
- Chapter 12 Beyond Earth