Get Free NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability Ex 16.2 PDF in Hindi and English Medium. Probability Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions are extremely helpful while doing your homework. Probability Ex 16.2 Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions were prepared by Experienced LearnCBSE.online Teachers. Detailed answers of all the questions in Chapter 16 Class 11 Probability Ex 16.2 provided in NCERT Textbook.
- Probability Class 11 Ex 16.1
- Probability Class 11 Ex 16.2
- Probability Class 11 Ex 16.3
- Probability Class 11 Miscellaneous Exercise
- प्रायिकता प्रश्नावली 16.1 का हल हिंदी में
- प्रायिकता प्रश्नावली 16.2 का हल हिंदी में
- प्रायिकता प्रश्नावली 16.3 का हल हिंदी में
- प्रायिकता विविध प्रश्नावली का हल हिंदी में
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability Ex 16.2 PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, BIE, Intermediate and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Ex 16.2

Question 1.
A die is rolled. Let E be the event “die shows 4” and F be the event “die shows even number”. Are E and F mutually exclusive?
Solution:
An experiment consists of rolling a die.
∴ S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
E: die shows 4 = {4}
F : die shows an even number = {2, 4, 6}
∴ E ∩F={4} ⇒ E∩F ≠ ⏀
⇒ E and F are not mutually exclusive.
Question 2.
A die is thrown. Describe the following events:
(i)
A: a number less than 7
(ii)
8: a number greater than 7
(iii)
C: a multiple of 3
(iv)
D: a number less than 4
(v)
E: an even number greater than 4
(vi)
F: a number not less than 3
Also find A ∪ B, A ∩ B, B ∪ C, E ∩ F, D ∩ E, A – C, D- E, E ∩ F’, F’.
Solution:
An experiment consists of rolling a die.
S = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
(i)
A: a number less than 7 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
(ii)
B: a number less than 7 = ⌽
(iii)
C: a multiple of 3 = {3, 6}
(iv)
D : a number less than 4 = {1, 2, 3}
(v)
E : an even number greater than 4 = {6}
(vi)
F : a number not less than 3 = {3, 4, 5, 6}
A ∪ B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) ∩ ⌽
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6!
A ∩ B = {1, 2,3,4, 5, 6) ∩ ⌽ = ⌽
B ∪C = ⌽∪{3,6} = {3,6}
E ∩ F = {6} ∩ {3, 4, 5, 6) = {6}
D ∩ E = {1,2, 3} ∩ (6} = ⌽
A – C = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) – {3, 6} = {1, 2, 4, 5}
D – E = {1, 2, 3} – {6} = {1, 2, 3}
F’ = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) – {3, 4, 5, 6) = {1, 2)
E ∩F’=(6)∩{l, 2}= ⌽
Question 3.
An experiment involves rolling a pair of dice and recording the numbers that come up. Describe the following events:
A: the sum is greater than 8.
B: 2 occurs on either die.
C: the sum is at least 7 and a multiple of 3.
Which pairs of these events are mutually exclusive?
Solution:
An experiment consists of rolling a pair of dice.
∴ Sample space consists 6 x 6 = 62 = 36 possible outcomes.
S = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2),
(3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6. 5), (6, 6)}
Now, A : the sum is greater than 8
= {(3, 6), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}
B : 2 occurs on either die = {(1, 2), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 2), (4, 2), (5, 2), (6, 2)}
C : The sum is at least 7 and a multiple of 3 = {(3, 6), (4, 5), (5, 4), (6, 3), (6, 6)}
A∩B =⌽, B∩C = ⌽
Thus above shows that A and B; B and C are mutually exclusive events.
Question 4.
Three coins are tossed once. Let A denote the event “three heads show, B denote the event “two heads and one tail show”, C denote the event “three tails show” and D denote the event “a head shows on the first coin”. Which events are
(i)
Mutually exclusive?
(ii)
Simple?
(iii)
Compound?
Solution:
An experiment consists of tossing threecoins:
∴ S = {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH, HTT, THT, TTH, TTT}
∴ A : Three heads show = {HHH}
B : Two heads and one tail show = {HHT, HTH, THH}
C : Three tail show = {TTT}
D : A head show on the first coin = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT}
(i)
Since A∩B = ⌽, A∩C = ⌽, B ∩ C = ⌽,
C ∩ D = ⌽.
⇒ A and B; A and C; B and C; C and D are mutually exclusive events.
(ii)
A and C are simple events.
(iii)
B and D are compound events.
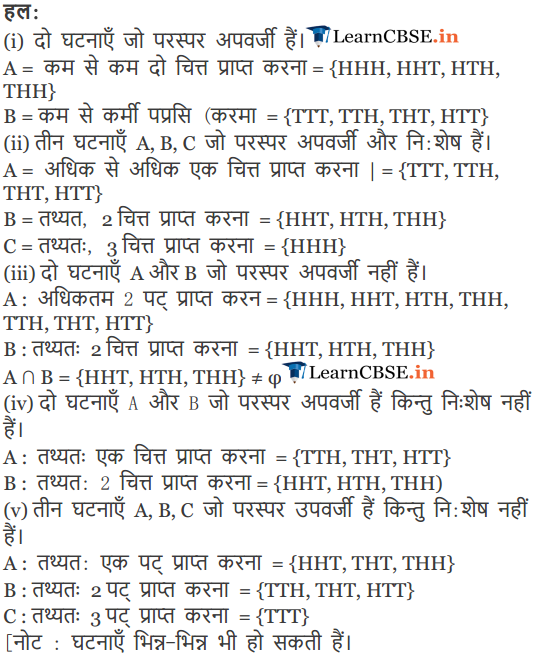
Question 5.
Three coins are tossed. Describe
(i)
Two events which are mutually exclusive.
(ii)
Three events which are mutually exclusive and exhaustive.
(iii)
Two events, which are not mutually exclusive.
(iv)
Two events which are mutually exclusive but not exhaustive.
(v)
Three events which are mutually exclusive but not exhaustive.
Solution:
An experiment consists of tossing three coins then the sample space S is S = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT}
(i)
Two events A and B which are mutually exclusive are
A : “getting atmost one head” and B: “getting atmost one tail”
(ii)
Three events A, B and C which are mutually exclusive and exhaustive are
A : “getting atleast two heads”
B : “getting exact two tails” and C: “getting exactly three tails”
(iii)
Two events A and B which are not mutually exclusive are
A : “getting exactly two tails” and B: “getting atmost two heads”
(iv)
Two events A and B which are mutually exclusive but not exhaustive are
A : “getting atleast two heads” and B: “getting atleast three tails”
(v)
Three events A, B and C which are mutually exclusive but not exhaustive are
A : “getting atleast three tails”
B : “getting atleast three heads”
C : “getting exactly two tails”
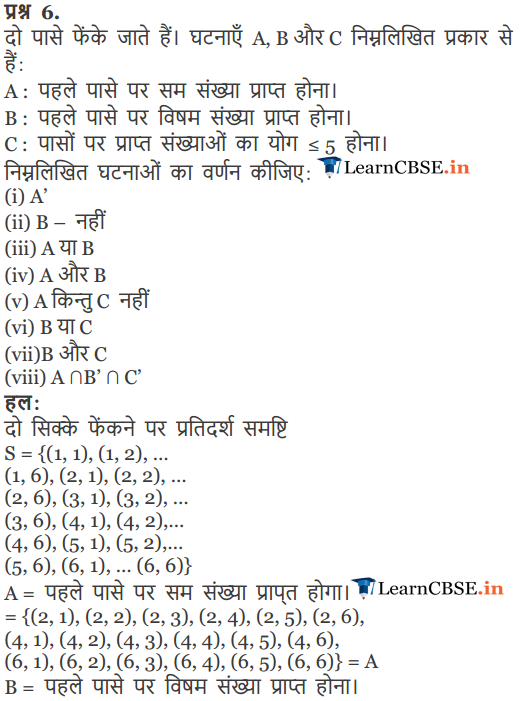
Question 6.
Two dice are thrown. The events A, B and C are as follows:
A: getting an even number on the first die.
B: getting an odd number on the first die.
C: getting the sum of the numbers on the dice ≤ 5.
Describe the events
(i)
A’
(ii)
not B
(iii)
A or B
(iv)
A and B
(v)
A but bot C
(vi)
B or C
(vii)
B and C
(viii)
A ∩ B’ ∩C’
Solution:
An experiment consists of rolling two dice Sample space consists 6 x 6 = 36 outcomes.
S = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6,1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}
A : getting an even number on the first die = {(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (6,1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}.
B : getting an odd number on the first die = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, b), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, b), (5,1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5,4), (5, 5), (5,6))
C: getting the sum of the numbers on the dice ≤5 = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3),
(3, 1), (3, 2), (4, 1)}
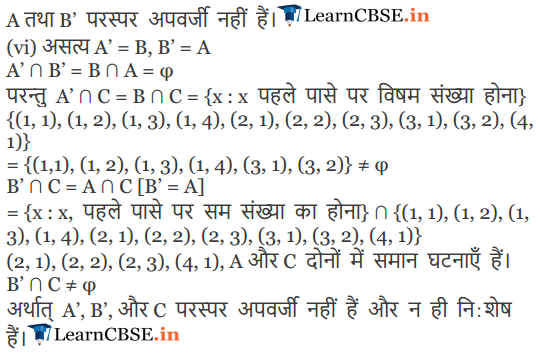
(i)
A’: getting an odd number on the first die=B
(ii)
not B : getting an even number on the first die = A
(iii)
A or B = A∪B = S
∴ A ∪B = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3), (3, 4 ), (3, 5), (3, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (6, 1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}}
(iv)
A and B = A ∩ B = ⌽
(v)
A but not C = A – C = {(2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (6, 1),(6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}
(vi)
B or C = BuC = {(1,1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1,5), (1,6), (2,1), (2,2), (2,3), (3,1), (3,2), (3,3), (3, 4), B or C = BuC = {(1,1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (1,5), (1,6), (2,1), (2,2), (2,3), (3,1), (3,2), (3,3), (3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4,1), (5,1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6)}
(vii)
B and C = B∩C = {(1,1), (1, 2), (1, 3), (1, 4), (3, 1), (3, 2)}
(viii)
A : getting an even number on the first die = B’
B’: getting an even number on the first die = {(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (6,1), (6, 2), (6,3), (6,4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}
C : getting the sum of numbers on two dice > 5. {(l, 5), (1, 6), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 3), (3, 4), (3, 6), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6,1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}
∴ A ∩ B’∩ C = {(2,4), (2,5), (2,6), (4,2), (4,3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (6,1), (6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4), (6, 5), (6, 6)}
Question 7.
Refer to question 6 above, state true or false : (give reason for your answer).
(i)
A and B are mutually exclusive
(ii)
A and 6 are mutually exclusive and exhaustive
(iii)
A = B’
(iv)
A and C are mutually exclusive
(v)
A and S’ are mutually exclusive.
(vi)
A’, B’, C are mutually exclusive and exhaustive.
Solution:
(i) True.
A = getting an even number on the first die.
B = getting an odd number on the first die. There is no common elements in A and B.
⇒ A ∩ B = ⌽
∴ A and B are mutually exclusive.
(ii) True.
From (i), A and B are mutually exclusive.
A ∪ B = {(1, 1), (1, 2) (1, 6), (2,1), (2, 2), (2, 6),…, (6,1), (6, 2), …, (6, 6) = S
∴ A∪B is mutually exhaustive.
(iii) True.
B = getting an odd number on the first die.
B’ = getting an even number on first die = A.
∴ A = B’
(iv) False.
Since A ∩ C={(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (4, 1)}
(v) False.
Since B’ = A [from (iii)]
∴ A∩B’=A∩A = A ≠ ⌽
(vi) False.
Since A’ = B and B’=A, A’ ∩ B’ = ⌽
B ∩ C = {(1,1), (1,2), (1, 3), (1,4), (3,1), (3, 2)} ≠ ⌽
A ∩ C = {(2, 1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (4,1)} ≠ ⌽
Thus A’, B’ and C are not mutually exclusive.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 16 Probability (प्रायिकता) Hindi Medium Ex 16.2







NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths All Chapters
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 7 Permutation and Combinations
- Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 9 Sequences and Series
- Chapter 10 Straight Lines
- Chapter 11 Conic Sections
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
- Chapter 14 Mathematical Reasoning
- Chapter 15 Statistics
- Chapter 16 Probability