Get Free NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Ex 8.1 Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions are extremely helpful while doing homework. Exercise 8.1 Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions were prepared by Experienced LearnCBSE.online Teachers. Detailed answers of all the questions in Chapter 8 Maths Class 10 Introduction to Trigonometry Exercise 8.1 Provided in NCERT Textbook.
Topics and Sub Topics in Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry:
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 8 | Introduction to Trigonometry |
| 8.1 | Introduction |
| 8.2 | Trigonometric Ratios |
| 8.3 | Trigonometric Ratios Of Some Specific Angles |
| 8.4 | Trigonometric Ratios Of Complementary Angles |
| 8.5 | Trigonometric Identities |
| 8.6 | Summary |
- Class 10 Maths Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.1
- प्रश्नावली 8.1 का हल हिंदी में
- Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Ex 8.2
- प्रश्नावली 8.2 का हल हिंदी में
- Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Ex 8.3
- प्रश्नावली 8.3 का हल हिंदी में
- Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Ex 8.4
- प्रश्नावली 8.4 का हल हिंदी में
- Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Extra Questions
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.1
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.1 are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths . Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Ex 8.1.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Maths |
| Chapter | Chapter 8 |
| Chapter Name | Introduction to Trigonometry |
| Exercise | Ex 8.1 |
| Number of Questions Solved | 11 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
Ex 8.1 Class 10
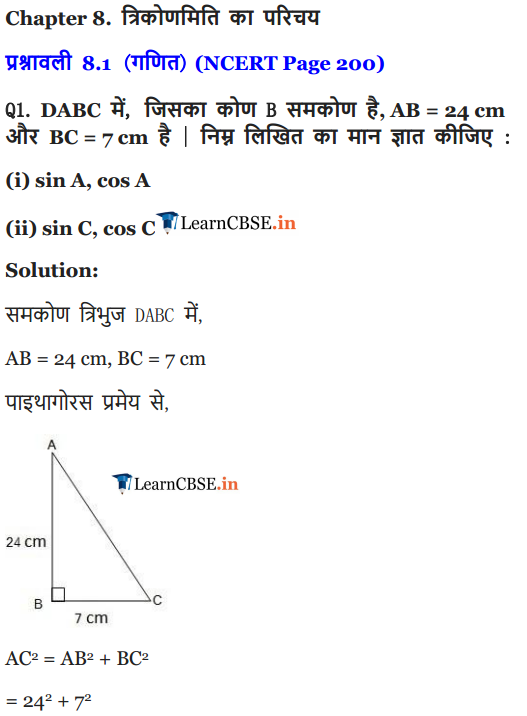
Maths Question 1.
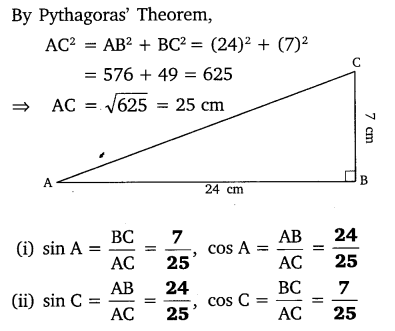
In ∆ABC right angled at B, AB = 24 cm, BC = 7 cm. Determine:
(i) sin A, cos A
(ii) sin C, cos C
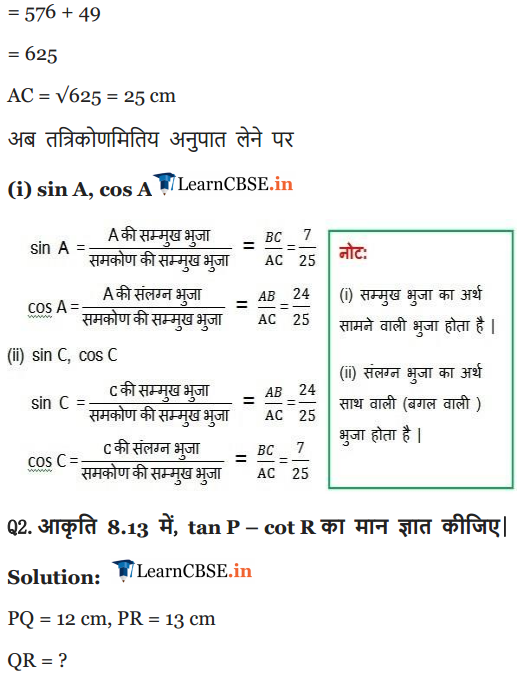
Solution:
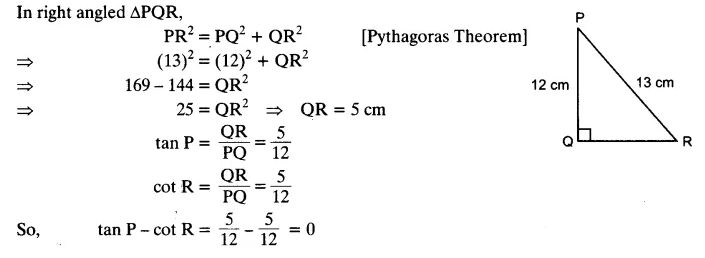
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 2.
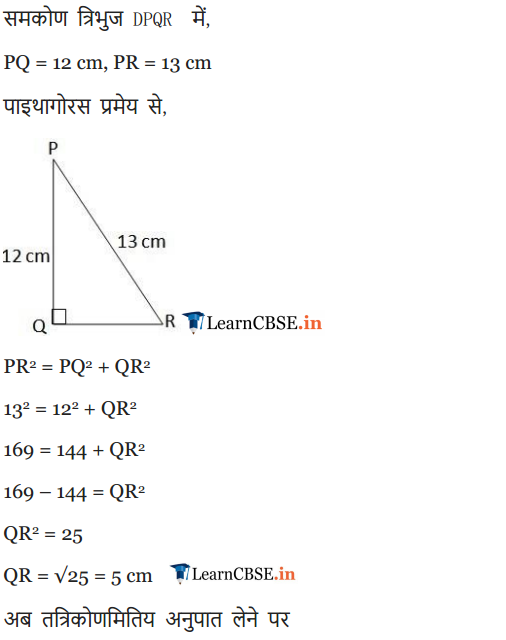
In given figure, find tan P – cot R.
Solution:
You can also download the free PDF of Chapter 8 Ex 8.1 Introduction to Trigonometry NCERT Solutions or save the solution images and take the print out to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
Download NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry PDF
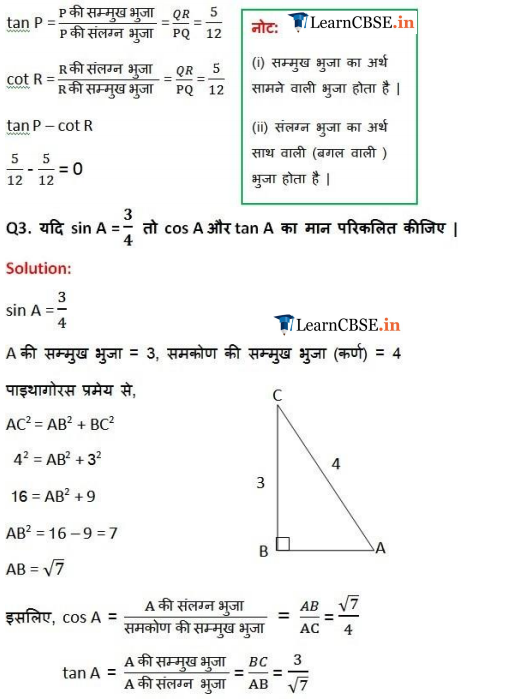
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 3.
If sin A = \(\frac { 3 }{ 4 }\) , calculate cos A and tan A.
Solution:
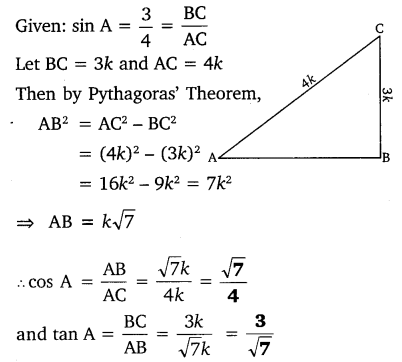
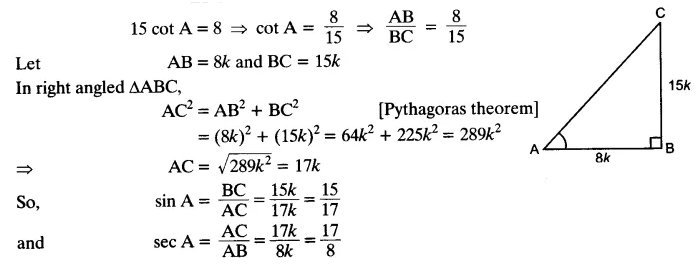
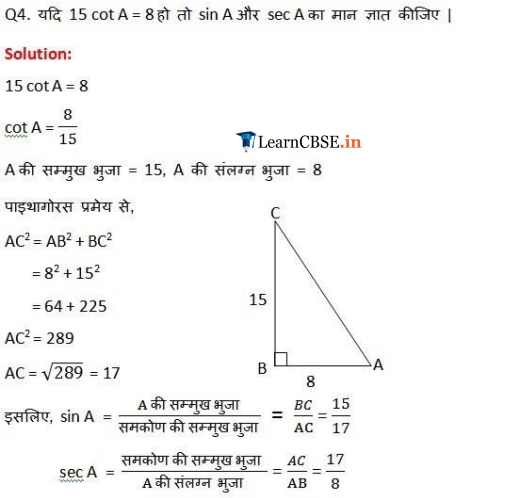
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 4.
Given 15 cot A = 8, find sin A and sec A.
Solution:
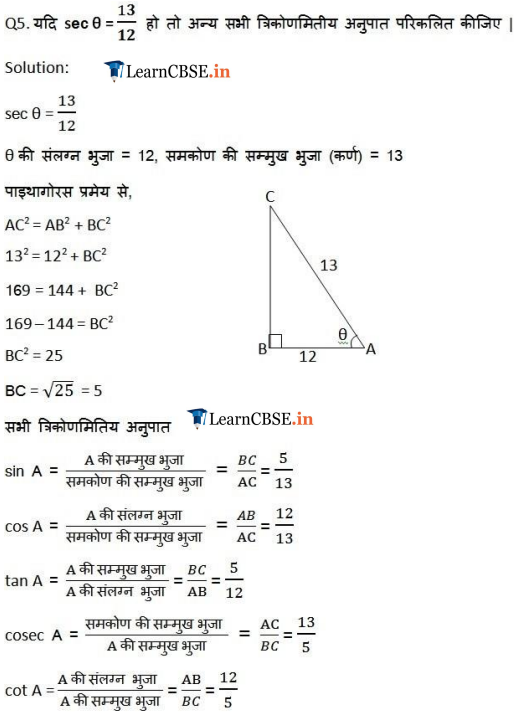
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 5.
Given sec θ = \(\frac { 13 }{ 12 }\) , calculate all other trigonometric ratios.
Solution:
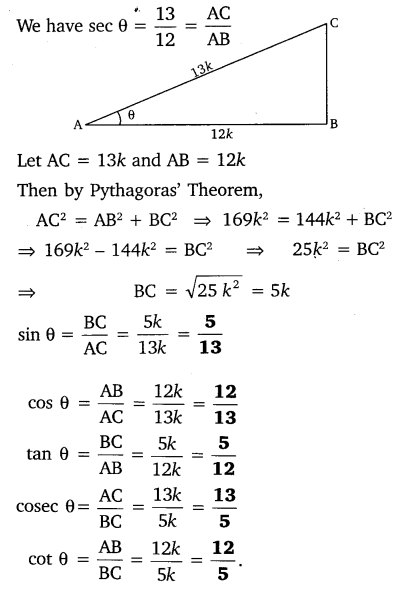
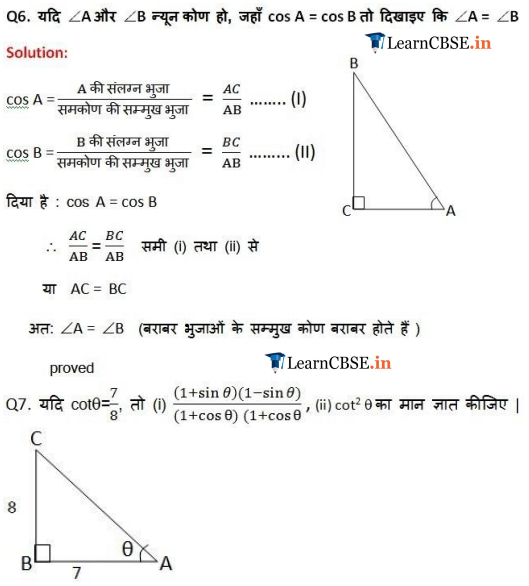
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 6.
If ∠A and ∠B are acute angles such that cos A = cos B, then show that ∠A = ∠B.
Solution:

Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 7.
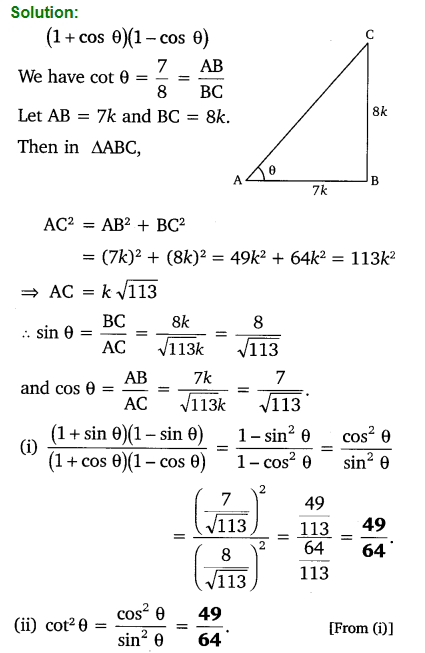
If cot θ = \(\frac { 7 }{ 8 }\), evaluate:
(i) \(\frac { \left( 1+sin\theta \right) \left( 1-sin\theta \right) }{ \left( 1+cos\theta \right) \left( 1-cos\theta \right)}\)
(ii) cot²θ
Solution:
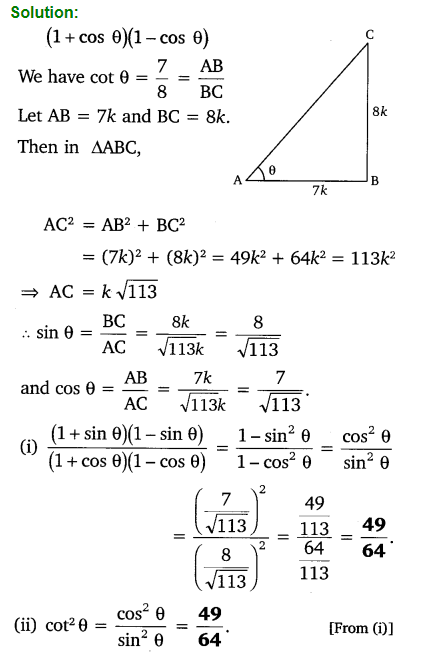
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 8.
If 3 cot A = 4, check whether \(\frac { 1-tan^{ 2 }A }{ 1+tan^{ 2 }A }\) = cos² A – sin² A or not.
Solution:
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 9.
In triangle ABC, right angled at B, if tan A = \(\frac { 1 }{ \surd 3 }\), find the value of:
(i) sin A cos C + cos A sin C
(ii) cos A cos C – sin A sin C
Solution:
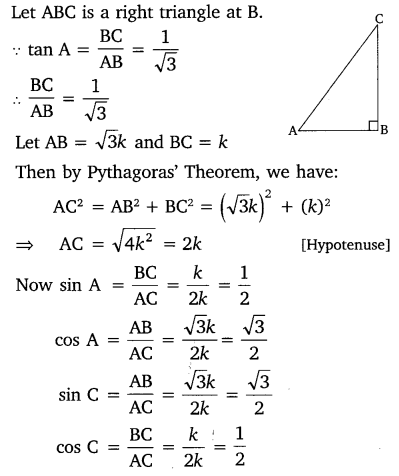
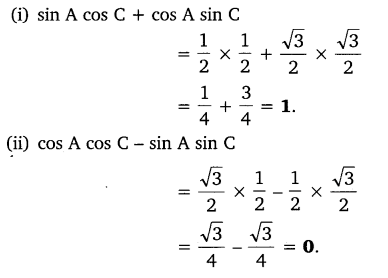
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 10.
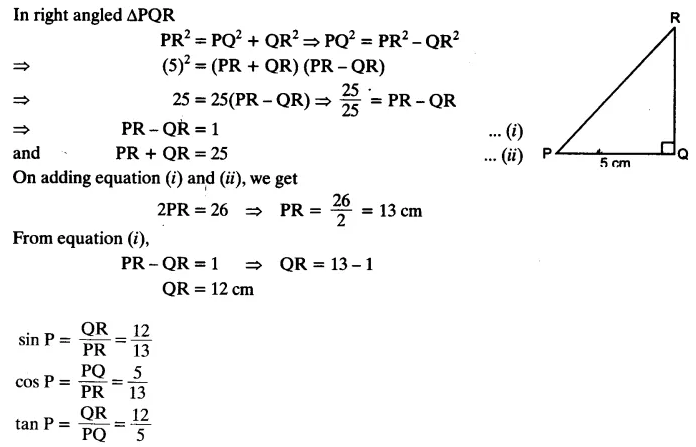
In ΔPQR, right-angled at Q, PR + QR = 25 cm and PQ = 5 cm. Determine the values of sin P, cos P and tan P.
Solution:
Ex 8.1 Class 10 Maths Question 11.
State whether the following statements are true or false. Justify your answer.
(i) The value of tan A is always less than 1.
(ii) sec A = \(\frac { 12 }{ 5 }\) for some value of angle A.
(iii) cos A is the abbreviation used for the cosecant of angle A.
(iv) cot A is the product of cot and A.
(v) sin θ = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) for some angle.
Solution:

NCERT
Solutions
for
Class
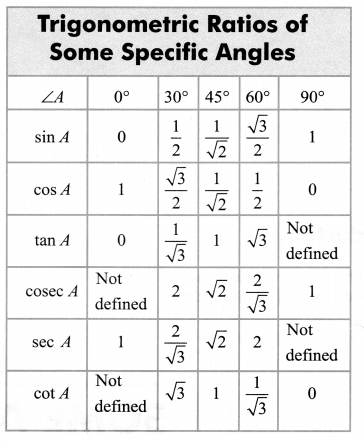
Trigonometric ratios of an acute angle in a right triangle express the relationship between the angle and the length of its sides.
Let ∆ABC be a triangle right angled at B. Then the trigonometric ratios of the angle A in right ∆ABC are defined as follows:
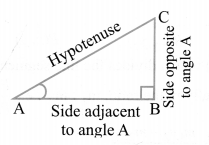
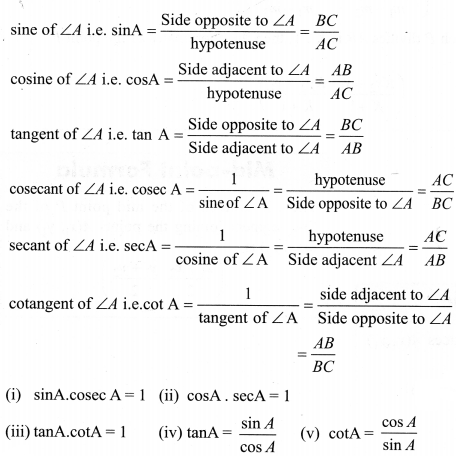
Note:
The values of the trigonometric ratios of an angle do not vary with the lengths of the sides of the triangle, if the angle remains same.
10
sin (90° – A) = cos A
cos (90° – A) = sin A
tan (90° – A) = cot A
cot (90° – A) = tan A
sec (90° – A) = cosec A
cosec (90° – A) = sec A
Note:
Here (90° – A) is the complementary angle of A.
Maths
An equation involving trigonometric ratios of an angle is called a trigonometric identity, if it is true for all values of the angle(s) involved.
(i) sin
2
θ + cos
2
θ = 1 [for 0° ≤ θ ≤ 90°]
(ii) sec
2
θ – tan
2
θ = 1 [for 0° ≤ θ ≤ 90°]
(iii) cosec
2
θ – cot
2
θ = 1 [for 0° < θ ≤ 90°]
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry (Hindi Medium) Ex 8.1

Chapter
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers
- Chapter 2 Polynomials
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions
- Chapter 6 Triangles
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry
- Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry
- Chapter 10 Circles
- Chapter 11 Constructions
- Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes
- Chapter 14 Statistics
- Chapter 15 Probability