Metals and nonmetals class 10 : The NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science is designed to provide a strong foundation for further studies in science. Candidates who are searching for NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals And Non Metals questions and answers can refer to the class 10 science chapter 3 notes below. We have included all the important questions from Metals and Non Metals similar to that of your chapter 3 science Class 10 notes to help you secure a good score in Class 10 science exam

Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals , is derived from the NCERT textbook of Class 10 Science as prescribed in CBSE Schools of India. These CBSE NCERT Solutions will not only help in your Class 10 exam preparation but also in clearing other competitive exams. Read further to find out everything about NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals And Non Metals.
Metals and nonmetals Class 10
Before going through NCERT Solutions for class 10 science chapter 3 answers, let’s have a look at the list of topics and subtopics under NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 3 Notes for Metals and Non-Metals :
- Physical Properties of Metals And Non-Metals
- Chemical Properties Of Metals
- What happens when metals are burnt in air?
- What happens when metals react with water?
- What happens when metals react with acids?
- How do metals react with solutions of other Metal Salts
- The Reactivity Series
- How do Metals and Non-Metals react?
- Properties of Ionic Compounds
-
Occurrence of metals
- Extraction of metals
- Enrichment of Ores
- Extracting Metals Low in the Activity Series
- Extracting Metals in the Middle of the activities Series
- Extracting Metals towards the top of the Activity Series
- Refining of Metals
-
Corrosion
- Prevention of Corrosion
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-Metals PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
- Metals and Non-metals
- धातु और अधातु कक्षा 10 विज्ञान हिंदी में
- Class 10 Metals and Non-metals Important Questions
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Notes
- Metals and Non-metals NCERT Exemplar Solutions
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Extra Questions
- Class 10 Metals and Non Metals Mind Map
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Intext Questions
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 40
Question 1
Give an example of a metal which :
(i) is a liquid at room temperature.
(ii) can be easily cut with a knife.
(iii) is the best conductor of heat.
(iv) is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer:
(i) Mercury
(ii) Sodium
(iii) Silver
(iv) Lead
Question 2
Explain the meanings of malleable and ductile.
Answer:
Malleable : A metal that can be beaten into thin sheets on hammering is called malleable.
Ductile : A metal which can be drawn into thin wires is called ductile.
Malleable Meaning in Hindi
कुछ धातुओ को पीटकर पतली चादर बनाया जा सकता है | इस गुणधर्म को आघातवर्ध्य कहते है | कुछ धातुओ के पतले तार के रूप में खीचने कि क्षमता को तन्यता कहते है |
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 46
Question 1
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil ?
Answer:
Sodium is highly reactive. So it is kept immersed in kerosene oil to prevent its reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air to prevent accidental fires.
Question 2
Write equations for the reactions of
(i) iron with steam.
(ii) calcium and potassium with water.
Answer:
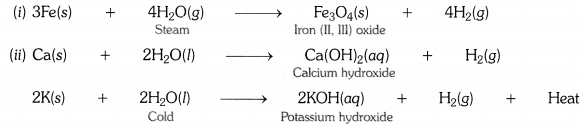
Question 3
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one.
The results obtained have been tabulated as follows :
| Metal | Iron (II) sulphate | Copper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | ||
| B | Displacement | No reaction | ||
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the Table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
(i) Which is the most reactive metal ?
(ii) What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
(iii) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Answer:
(i) B is the most reactive metal because it gives displacement reaction with iron (II) sulphate.
(ii) When metal B is added to copper (II) sulphate solution, a displacement reaction will take place due to which the blue colour of copper (II) sulphate solution will fade and a red-brown deposit of copper will be formed on metal B.
(iii) Metal B is the most reactive because it displaces iron from its salt solution. Metal A is less reactive because it displaces copper from its salt solution. Metal C is still less reactive because it can displace only silver from its salt solution and metal D is the least reactive because it cannot displace any metal from its salt solution. Hence, the decreasing order of reactivity of the metals is B > A > C > D.
Question 4
Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal ? Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H
2
SO
4
.
Answer:
Hydrogen gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal.
Chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4 :
Fe(s) + H
2
SO
4
(aq) → FeSO
4
(aq) + H
2
(g)
Question 5
What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate ? Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Answer:
Zinc is more reactive than iron. Therefore, when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate, then the greenish colour of iron (II) sulphate solution fades gradually due to the formation of colourless zinc sulphate solution and iron metal is deposited on zinc.

Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 49
Question 1
(i) Write the electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
(ii) Show the formation of Na
2
O and MgO by the transfer of electrons.
(iii) What are ions present in these compounds?
Answer:
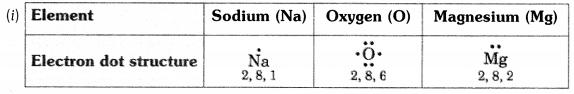
(ii) Formation of Na
2
O and MgO
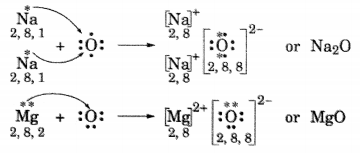
(iii) In Na
2
O, ions present are Na
+
and O
2-
.
In MgO, ions present are Mg
2+
and O
2-
.
Question 2
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points ?
(iii) What are ions present in these compounds?
Answer:
The ionic compounds are made up of positive and negative ions. There is a strong force of attraction between the oppositely charged ions, so a lot of heat energy is required to break this force of attraction and melt the ionic compound. Due to this, ionic compounds have high melting points.
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 53
Question 1
Define the following terms : (i) Mineral, (ii) Ore and (iii) Gangue.
Answer:
(i) Mineral : The natural materials in which the metals or their compounds are found in earth are called minerals.
(ii) Ore : Those minerals from which the metals can be extracted conveniently and profitably are called ores.
(iii) Gangue : The unwanted impurities like sand, rocky material, earth particles, lime stone, mica, etc in an ore are called gangue.
Question 2
Name two metals which are found in nature in the free state.
Answer:
Gold and platinum
Question 3
What chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide.
Answer:
Reduction process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide.
For example, zinc oxide is reduced to metallic zinc by heating with carbon.
ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
Besides carbon, highly reactive metals like sodium, calcium, aluminium etc. are used as reducing agents. These displace metals of low reactivity from their oxides.
For example,
Fe
2
O
3
(s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l) + Al
2
O
3
(s) + Heat
Gold is Metal or Nonmetal ?
Gold is a metal found in nature in the free state
Class 10 Metals and Non Metals NCERT Book Page Number: 55
Question 1
Metallic oxides of zinc, magnesium and copper were heated with the following metals :
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper | |
| 1. | Zinc oxide | |||
| 2. | Magnesium oxide | |||
| 3. | Copper oxide |
In which cases will you find displacement reactions taking place ?
Answer:
A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its oxide. But out of zinc, magnesium, and copper metals, magnesium is the most reactive, zinc is less reactive whereas copper is the least reactive metal.
The displacement will take place in the following cases :
| Metal | Zinc | Magnesium | Copper | |
| 1. | Zinc oxide | – | Displacement | – |
| 2. | Magnesium oxide | – | – | – |
| 3. | Copper oxide | Displacement | Displacement | – |
Question 2
Which metals do not corrode easily ?
Answer:
Gold and Platinum.
Question 3
What are alloys ?
Answer:
An alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal. For example, bronze is an alloy of copper and tin.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Textbook Chapter End Questions
Metals and Nonmetals Class 10
Question 1.
Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions ?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal.
(b) MgCl
2
solution and aluminium metal.
(c) FeSO
4
solution and silver metal.
(d) AgNO
3
solution and copper metal.
Answer:
(d) AgNO
3
solution and copper metal.
Question 2.
Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting ?
(a) Applying grease
(b) Applying paint.
(c) Applying a coating of zinc
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(c) Applying a coating of zinc.
Question 3.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be
(a) calcium
(b) carbon
(c) silicon
(d) iron
Answer:
(a) Calcium.
Question 4.
Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because
(a) zinc is costlier than tin
(b) zinc has a higher melting point than tin
(c) zinc is less reactive than tin
(d) zinc is more reactive than tin.
Answer:
(d) Zinc is more reactive than tin.
Metals and Non metals Class 10
Question 5.
You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(a) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non-metals.
Answer:
(a) Metals can be beaten into thin sheets with a hammer without breaking. Non-metals cannot be beaten with a hammer to form thin sheets. Non-metals break into pieces when hammered. Metals are malleable, while non-metals are non-melleable. When metals are connected into circuit using a battery, bulb, wires and switch, current passes through the circuit and the bulb glows. When non-metals (like sulphur) are connected, the bulb does not light up at all. Metals are good conductors of electricity.
(b) Because of malleability, metals can be casted into sheets. Metals are good conductors of electricity so these can be used for electrical cables.
Question 6.
What are amphoteric oxides ? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides ?
OR
Write chemical equations that show aluminium oxide reacts with acid as well as base. [CBSE2011]
Answer:
Those metal oxides which show basic as well as acidic behaviour are known as amphoteric oxides. In other words, metal oxides that react wtih both acids and bases to form salt and water are called amphoteric oxides. Aluminium oxide and zinc oxide are amphoteric in nature.
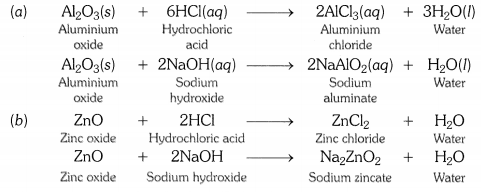
Question 7.
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals which will not.
Answer:
(i) Metals above hydrogen in the activity series like sodium and magnesium displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
(ii) Metals below hydrogen in the activity series like copper, silver do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
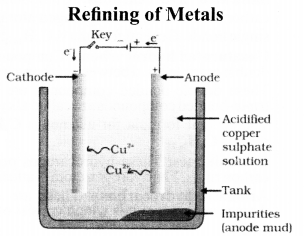
Question 8.
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte ?
Answer:
Cathode – Pure metal
Anode – Impure metal
Electrolyte – Metal salt solution
Question 9.
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it, as shown in the figure.
(a) What will be the action of gas on
(i) dry litmus paper ?
(ii) moist litmus paper ?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
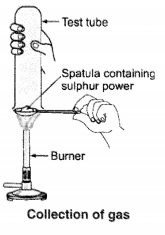
Answer:
(i) Dry litmus paper – no action.
(ii) Moist litmus paper – becomes red.
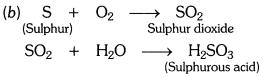
Question 10.
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Answer:
Ways to prevent rusting of iron are :
(a) By painting
(b) By galvanizing
Question 11.
What type of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen ?
Answer:
Non-metals combine with oxygen to form acidic oxides or neutral oxides.
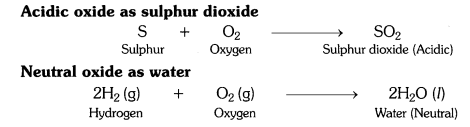
Question 12.
Give reasons :
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Answer:
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery because these are malleable and ductile. These are highly resistant to corrosion.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are very reactive and catch fire when exposed to air. This is due to their low ignition temperature and high reactivity.
(c) Aluminium forms a non-reactive layer of aluminium oxide on its surface. This layer prevents aluminium to react with other substances. That’s why aluminium is used to make cooking utensils.
(d) It is easier to reduce a metal oxide into free metal. Since it is easier to obtain metals from their oxides than from their carbonates or sulphides directly, therefore, the carbonate and sulphide ores are first converted to oxides for extracting the metals.
Question 13.
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Answer:
The sour substances such as lemon or tamarind juice contain acids. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxide or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and makes them shining red-brown again.
Question 14.
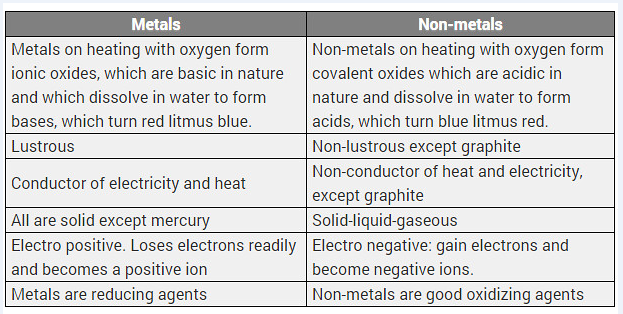
Differentiate between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties. [CBSE 2017 (Delhi)]
Answer:
Difference between metals and non-metals
| Metals | Non-metals |
| (i) Metals form basic oxides or amphoteric oxides. | (i) Non-metals form acidic or neutral oxides. |
| (ii) Metals replace hydrogen from acids and form salts. | (ii) Non-metals do not replace hydrogen from acids. |
| (iii) With chlorine, metals form chlorides which are electrovalent. | (iii) With chlorine, non-metals form chlorides which are covalent. |
| (iv) With hydrogen few metals form hydrides which are electrovalent. | (iv) With hydrogen, non-metals form many stable hydrides which are covalent. |
Question 15.
A man went door-to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty repeat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he has used ?
Answer:
The dishonest goldsmith dipped the gold bangles in aqua-regia (which contains 1 part of concentrated nitric acid and 3 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid, by volume). Aqua-regia dissolved a considerable amount of gold from gold bangles and hence reduced their weight drastically. The dishonest goldsmith can recover the dissolved gold from aqua-regia by a suitable treatment.
Question 16.
Give reasons why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (analloy of iron).
Answer:
(i) Copper is a better conductor of heat than steel.
(ii) Copper does not corrode easily. But steel corrodes easily.
(iii) Copper does not react with water at any temperature, whereas iron reacts with water on heating.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 10 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 |
| Chapter Name | Metals and Non-metals |
| Number of Questions Solved | 31 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Metals and non metals: Properties of metals and non-metals, reactivity series, Formation and properties of ionic compounds, Basic metallurgical processes, corrosion and its prevention.
Question 1
What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Solution:
Amphoteric oxides are the oxides, which react with both acids and bases to form salt and water. E.g. ZnO and Al
2
O
3
.
Question 2
Name two metals, which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids, and two metals which will not.
Solution:
Very reactive metals like Zn and Mg displace hydrogen from dilute acids. On the other hand less reactive metals like Cu, Ag, etc. do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Question 3
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, what would you take as the anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Solution:
Anode is impure, thick block of metal M.
Cathode is a thin strip/wire of pure metal M.
Electrolyte is a suitable salt solution of metal M.
Metals and nonmetals Class 10 PDF
Question 4
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Solution:
By coating the surface of iron by rust proof paints.
By applying oil or grease to the surface of iron objects so that supply of air consisting of moisture is cut off form the surface.
Question 5
What types of oxides are formed when non-metals combine with oxygen?
Solution:
When non-metals combine with oxygen it forms either neutral or acidic oxides. CO is a neutral oxide; N
2
O
5
or N
2
O
3
is an acidic oxide.
extraction of metals from ores class 10
Question 6
Give reason
i. Metals replace hydrogen from dilute acids, where as non-metals do not.
ii. Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Solution:
i. Metals are electropositive in nature. They readily lose electrons. These electrons reduce the protons liberated from the acid to liberate hydrogen gas, where as non-metals possess a tendency to gain electrons and hence they do not furnish electrons to protons liberated from acids. Hence H
2
gas is not liberated.
ii. As it is easier to reduce metal oxides to metal, prior to reduction, metal sulphides and carbonates must be converted to oxides.
Question 7
Differentiate between metals and non-metals on the basis of their chemical properties.
Solution:
Question 8
Explain why the surface of some metals acquires a dull appearance when exposed to air for a long time.
Solution:
This is due to the surface oxidation of metals when exposed to moist air. For e.g. copper turns green on its surface due to the formation of basic copper carbonate Cu(OH)
2
. CuCO
3
. Similarly silver becomes black due to the formation of black Ag
2
S and Aluminium forms a white coating of Al2O3 on its surface.
Question 9
State which of the following metals would give hydrogen when added to dilute hydrochloric acid. i. Iron, ii. Copper iii. Magnesium
Copper does not react with dilute hydrochloric acid at all. This shows that copper is even less reactive than iron.

Question 10
Name a non-metallic element, which conducts electricity.
Solution:
Carbon in the form of graphite conducts electricity, as there is a free electron in each carbon atom, which moves freely in between the hexagonal layers.
Question 11
Which metals do not corrode easily?
Solution:
Gold and platinum and other noble metals do not corrode in air.
Question 12
What are alloys?
Solution:
Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal.E.g. steel, brass, bronze, etc.
Question 13
Define the following terms.
(i) Minerals
(ii) Ores
(iii) Gangue
Solution:
(i) Minerals
All compounds or elements, which occur naturally in the earth’s crust, are called minerals. Example: Alums, K
2
SO
4
.Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
. 24 H
2
O, Bauxite Al
2
O
3
.2H
2
O
(ii) Ores
Those minerals from which a metal can be profitably extracted are called ores. Bauxite (Al
2
O
3
.2H
2
O) is the ore of Al, copper pyrite CuFeS
2
. All minerals are not ores but all ores are minerals.
(iii) Gangue
When an ore is mined from the earth, it is always found to be contaminated with sand rocky materials. The impurity of sand and rock materials present in the ore is known as gangue.
Question 14
Name two metals that are found in nature in the free state.
Solution:
Gold and platinum are found in the free state in nature.
Question 15
What is chemical process used for obtaining a metal from its oxide?
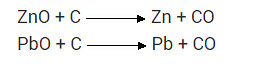
Question 16
Name two metals, which can form hydrides with metals.
Solution:
Sodium and calcium form stable hydrides on reacting with hydrogen.
Question 17
Does every mineral have a definite and a fixed composition? Explain.
Solution:
Yes, every mineral has a definite and a fixed composition. Minerals are widely distributed in the earth’s crust in the form of oxides, carbonates, sulphides, sulphates, nitrates, etc. These minerals are formed as a result of chemical changes taking place during the formation of earth.
Class 10 metals and nonmetals
Question 18
Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile.
Solution:
Malleable is being able to be beaten/hammered into thin sheets.
Ductile is being able to be drawn into thin wires.
Question 19
i. Write the electron dot structures for sodium, oxygen and magnesium.
ii. Show the formation of MgO and Na
2
O by the transfer of electrons.
iii. What are the ions present in these compounds?
Solution:
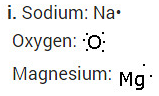
ii. Formation of Magnesium oxide
When magnesium reacts with oxygen, the magnesium atom transfers its two outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing 2 elections, the magnesium atoms form a magnesium ion (Mg
2+
) and by gaining 2 electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (O
2-
).
![]()
Formation of Sodium oxide
Two sodium atoms transfer their 2 outermost electrons to an oxygen atom. By losing two electrons, the two sodium atoms form two sodiumions (2Na
+
). And by gaining two electrons, the oxygen atom forms an oxide ion (O
2-
.)
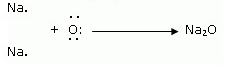
iii. The ions present in sodium oxide compound (Na
2
0) aie sodium ions (2Na
+
and oxide ions (O
2-
).
The ions present in Magnesium oxide compound (MgO) are magnesiumions Mg
2+
and oxide ions (O
2-
).
Question 20
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Solution:
The sour substances such as lemon (or tamarind juice) contain acids. These acids dissolve the coating of copper oxide or basic copper carbonate present on the surface of tarnished copper vessels and make them shining red-brown again.
Question 21
Give an example of a metal which
i. is a liquid at room temperature.
ii. can be easily cut with a knife.
iii. is the best conductor of heat.
iv. is a poor conductor of heat.
Solution:
i. Mercury is in liquid state at room temperature.
ii. Sodium and potassium are soft metals which can be easily cut with a knife.
iii. Silver is the best conductor of electricity.
iv. Mercury is a poor conductor of heat.
Question 22
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene?
Solution:
Sodium metal is kept immersed in kerosene to prevent their reaction with oxygen, moisture and carbon dioxide of air.
Question 23
Why do ionic compounds have high melting points?
Solution:
These compounds are made up of positive and negative ions. There is a strong force of attraction between the oppositively charged ions, so a lot of heat energy is required to break this force of attraction and melt the ionic compounds. This is why ionic compounds have high melting points.
Question 24
A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Solution:
Aqua regia (By volume, this contains 3 parts of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 1 part of concentrated nitric acid) is the solution, which is used to sparkle the bangles like new, but their weight will be reduced drastically.
Question 25
Write equations for the reactions of
(i) iron with water
(ii) calcium and potassium with water
Solution:

Question 26
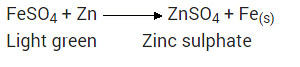
What would you observe when zinc is added to a sodium of iron(II) sulphate? Write the chemical reaction that takes place?
Solution:
Zinc is more reactive (more electro positive) than iron. Therefore it displaces iron from its salt solution. The colour of ferrous sulphate is pale green which becomes colourless.
Metals and nonmetals class 10
Question 27
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test-tube over the burning sulphur.
What will be the action of this gas on:
Dry litmus paper?
Moist litmus paper?
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
Solution:
a) When sulphur is brunt in air then sulphur dioxide gas is formed.
(i) Sulphur dioxide gas has no action on dry litmus paper.
(ii) Sulphur dioxide gas turns moist blue litmus paper to red.
(b) S
(s)
+ O
2(g)
—> SO
2(g)
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) [1 Mark each]
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 1.
What is the colour of aqueous solution of CuSO
4
and FeSO
4
as observed in the laboratory?
(a) CuSO
4
– blue; FeSO
4
– light green
(b) CuSO
4
– blue; FeSO
4
– dark green
(c) CuSO
4
– green; FeSO
4
– blue
(d) CuSO
4
– green; FeSO
4
– colourless
Answer:
(a) Colour of CuSO
4
solution is blue and FeSO
4
solution is light green.
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 2.
A student took four test tubes I, II, III and IV containing aluminium sulphate, copper sulphate? ferrous sulphate and zinc sulphate solutions respectively. He placed an iron strip in each of them.
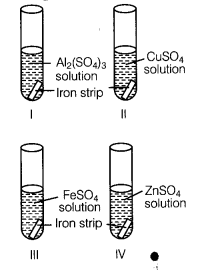
In which test tube, he found a brown deposit?
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer:
(b) In test tube II, because Fe is more reactive than copper but less reactive than Al arid Zn.
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 3.
Aluminium sulphate and copper sulphate solutions were taken in two test tubes I and II respectively. A few pieces of iron filings were then added to both the solutions. The four students A, B, C and D recorded their observations in the form of a table as given below:
| Student | Al 2 (SO 4 ) 3 solution (I) |
CuSO 4 solution (II) |
| A | Colourless solution -> Light green | Blue colour is retained |
| B | Colourless solution -> No change | Blue colour solution -> Green |
| C | Colourless solution -> Light blue | Blue colour solution -> Green |
| D | No change in colour | Blue colour of solution fades |
Which student has recorded the correct observation?
(a) D
(b) C
(c) B
(d) A
Answer:
(c) Student B
Iron does not react with Al
2
(SO
4
)
3
solution because iron is less reactive than aluminium. But Fe being more reactive than Cu displaces Cu from CuSO
4
solution.
![]()
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 4.
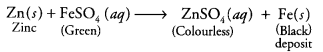
Aqueous solutions of zinc sulphate and iron sulphate were taken in test tubes I and II by four students A, B, C and D. Metal pieces of iron and zinc were dropped in the two solutions and observations made after several hours were recorded in the form of table as given below:
| Student Solution | Metal | Solution | Colour change Deposit/coating of solution | Deposit/coating obtained |
| A | Fe | ZnSO 4 | Turned green | Silvery grey deposit |
| Zn | FeSO 4 | No change | No change | |
| B | Fe | ZnSO 4 | No change | Black deposit |
| Zn | FeSO 4 | Colour faded | Grey coating | |
| C | Fe | ZnSO 4 | No change | No change |
| Zn | FeSO 4 | Turned colourless | Black deposit | |
| D | Fe | ZnSO 4 | No change | Grey deposit |
| Zn | FeSO 4 | No change. | Black deposit |
Which student has given the correct report?
(a) B
(b) D
(c) A
(d) C
Answer:
(d) Student C
(i) Fe is less reactive than zinc. So,
![]()
(ii) Zn is more reactive than Fe, so it displaces iron as follows:
Metals and nonmetals class 10
Question 5.
2 mL each of cone. HCl, cone. HNO
3
and a mixture of cone. HCl and cone. HNO
3
in the ratio of 3 : 1 were taken in test tubes labelled as A, B and C. A small piece of metal was put in each test tube. No change occurred in test tubes A’and Bbut the metal got dissolved in test tube C. The metal could be [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) Al
(b) Au
(c) Cu
(d) Pt
Answer:
(b, d) A mixture of cone. HCl and cone. HNO
3
in the ratio of 3 : 1 is known as aqua-regia. Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) dissolve only in aqua-regia as these metals are very less reactive.
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 6.
When an aluminium strip is kept (a) Green solution of FeSO
4
slowly turns brown
(b) Green solution of FeSO
4
rapidly turns brown
(c) No change in colour of FeSO
4
(d) Green solution of FeSO
4
slowly turns colourless
Answer:
(a) The green solution of ferrous sulphate slowly turns brown. As aluminium is more reactive than iron, it displaces iron from ferrous sulphate solution.
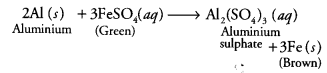
Metals and nonmetals class 10 Question 7.
Aluminium is used for making cooking utensils. Which of the following properties of aluminium are responsible for the same?
(i) Good thermal conductivity
(ii) Good electrical conductivity
(iii) Ductility
(iv) Fligh melting point [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(d) Good thermal conductivity, malleability, light weight and high melting point are the properties/of aluminium due to which it-is used for making cooking utensils.
Metals and nonmetals class 10
Question 8.
If copper is kept open in air, it slowly loses its shining brown surface and gains a green coating. It is due to the formation of [NCERT Exemplar]
(a) CuSO
4
(b) CuCO
3
(c) CU(NO
3
)
2
(d) CuO
Answer:
(b) Copper reacts with CO
2
present in air and forms a green coating on its surface due to the formation of basic copper carbonate [CuCO
3
.Cu(OH)
2
] as:
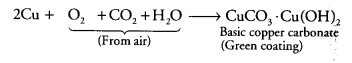
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals (Hindi Medium)

































Class 10 Science Metals and Non-metals Mind Maps
Metals and Non-Metals
There 92 well known naturally occurring minerals of which 70 are metals and rest 20 are the non-metals.
Physical Properties of Metals & Non-Metals
| Property | Metals | Non-Metals |
| Luster | They have shining surface. | They do not have shining surface except iodine. |
| Hardness | Generally hard except sodium, lithium & potassium .These are soft and can be cut with knife. | Generally soft except diamond (hardest natural substance) |
| State | Exist as solids except mercury. | Exist as solids or gases except bromine. |
| Malleability | Can be beaten into thin sheets. Gold & silver are the most malleable metals. | Non-malleable |
| Ductility | Can be drawn into thin wires. | Non-ductile |
| Conductor of heat & electricity | Good conductors of heat and electricity. Ag & Cu are best conductors of heat and Pb & Hg are poor conductor of heat. | Poor conductor of heat and electricity except graphite. |
| Density | High density & high melting point except Na & K. | Low density & melting point. |
| Sonorous | Produce sound on striking a hard surface. | Not sonorous |
| Oxides | Metallic oxides are basic in nature. | Non-metallic oxides are acidic in nature. |
Reaction between Metals and Non Metals
-
- Reactivity of an element can be explained as tendency to attain a completely filled outermost shell.
- Metals have 1, 2 or 3 e- in outermost shell and thus it is easier for them to loss e- rather than to gain. They loss e- & gains positive charge & are tenned as cation.
- In contrast, non-metals have 4-8 e- in outermost shell & thus they gain e- to achieve their octet. They gain e- as well as negative charge & tenned as anion.
- Cations & anions attract each other & are held by strong electrostatic force of attraction.
-
The compounds fonned by the transfer of electrons from metal to non-non-metal are known as ionic compounds or electrovalent compound.
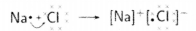
| Chemical Properties of Metals | ||
| Reaction with oxygen |
Metal + Oxygen → Metal Oxide (basic)
2Cu + O 2 → 2CuO 4Al + 3O 2 → 2Al 2 O 3 Zn & Al form amphoteric oxides i.e., they react with both acids & bases to produce salt & water Al 2 O 3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl 3 + 3H 2 O Al 2 O 3 + 2NaoH → 2NaAlO 2 + H 2 O Metal oxides are insoluble in water but some of them dissolve in water to form alkalis. Na 2 O(s) + H 2 O (l) → 2NaOH(aq) |
Na & K are vigorous elements & are kept immersed in kerosene oil.
Protective metal oxide layer prevents the metal from further oxidation such as found in Al, Zn, Pb etc. Cu doesn’t bum but hot metal coated with CuQ black colored layer. Ag & Au do not react with O 2
|
| Reaction with Water |
Metals + Water → Metal Oxides + H
2
Metal Oxides + H 2 O → Metal Hydroxide 2Na(s) + 2H 2 O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H 2 (g) + E2K(s) + 2H 2 O(l) → 2KOH(aq) + H 2 (g) + E |
Na & K: react violently with cold water.
Ca: reacts less violently. Mg: reacts with hot water. Al, Fe, Zn react with steam to from metal hydroxide & H 2 .
|
| Reaction with dilute Acids |
Metal + Dilute Acid → Salt + H
2
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g) Metal + HNO 3 → H 2 not evolved Reason- HNO 3 is strong oxidizing agent & oxidized H 2 to water. |
Mg & Mn react with very dil. HC1 to evolve H
2
gas.
The reactivity decreases in the order Mg > Al > Zn > Fe. Cu doesn’t react with dil. HCl. |
|
Reaction with Solutions of other Metal Salts
|
Reactive metals can displace less reactive metals from their compounds in solution or molten state.
Metals A+ Salt solution of B → salt of A+ Metal B CuS0 4 (aq) + Zn(s) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu(s) |
Reactivity Series: List of metals in order of their decreasing activities.
K > Na> Ca > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > H > Cu > Hg > Ag > Au. |
Occurrence of Metals
The elements or compounds, which occur naturally in the earth’s crust, are known as minerals.
At some places, minerals contain a very high percentage of a particular metal and the metal can be profitably extracted from it. These minerals arc called ores.
Corrosion
Corrosion is the deterioration of materials by chemical interaction with their environment for e.g. darkening of silver articles when exposed to air, gaining of green coat on copper, rusting of iron.
Prevention: The rusting of iron can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, galvanising, chrome plating, anodising or making alloys.
• Galvanisation is a method of protecting steel and iron from rusting by coating them with a thin layer of zinc.
• Alloy is a homogeneous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal & nonmetal. For e.g. stainless steel (alloy of Fe. Ni, & Cr), amalgam (alloy of Hg), brass (alloy of Cu & Zn) etc. The electrical conductivity & melting point of an alloy is less than that of pure metals.
Enrichment of Ores
Ores mined from the earth are usually contaminated with large amounts of impurities such as soil, sand, etc., called gangue. The impurities must be removed from the ore prior to the extraction of the metal.
The processes used for removing the gangue from the ore are based on the differences between physical or chemical properties of the gangue and the ore.
Extraction of Metals
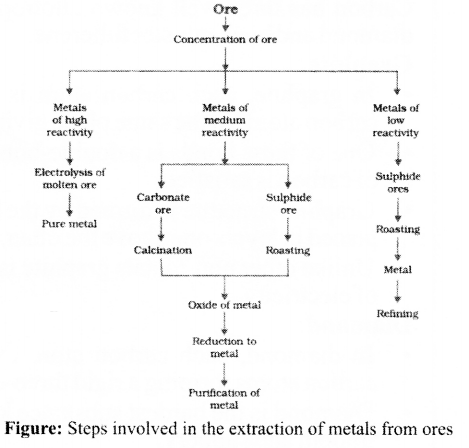
Extracting Metals towards the Top of the Activity Series
These metals are highly reactive & are obtained by electrolytic reduction. For e.g. Na, Mg, & Ca are obtained by the electrolysis of their molten chlorides.
The metals are deposited at the cathode whereas chlorine is liberated at anode.
At cathode
Na
+
+ e
–
→Na
At anode
2Cl
–
→ Cl
2
+ 2e
–
Similarly, aluminium is obtained by the electrolytic reduction of aluminium oxide.
Extracting Metals Low in the Activity Series
- These metals are the least reactive & are often found in a free state for e.g. An, Ag. Pt & Cu are found in the free state.
- However, Cu & Ag are also found in the combined state as their sulphide or oxide ores.
- The oxides of these metals can be reduced to metals by heating alone. For e.g. cinnabar (HgS), ore of mercury it is heated in air to converted it in mercuric oxide (HgO) which is then reduced to mercury by further heating.
- 2HgS(s) + 3O 2 (g) Heat 2HgO(s) + 2SO 2 (g)
- 2HgO(s) Heat 2Hg(l) + O(g)
- Another instance is reduction of Cu 2 S (ore of copper) to copper by heating.
- 2Cu 2 S + 3O 2 (g)Heat 2Cu 2 O(s) + 2SO 2 (g)
- 2CU 2 O + Cu 2 S Heat 6Cu(s) + SO 2
Extracting Metals Middle in the Activity Series
- These metals such as Fe, Zn, Pb, Cu, etc are moderately reactive & are usually present as sulphides or carbonates in nature.
- The sulphide ores are converted into oxides by heating strongly in the presence of excess air which is known as roasting.
- The carbonate ores are changed into oxides by heating strongly in limited air which is known as calcination.
- The metal oxides are then reduced to the corresponding metals by using suitable reducing agents such as carbon.
- For e.g. extraction of Zn
- Roasting: 2ZnS(s) + 3O 2 (g) Heat . 2ZnO(s) + 2SO 2 (g)
- Calcination: ZnCO 3 (s) Heat ZnO(s) + CO 2 (g)
- Reduction: ZnO(s) + C(s) → Zn(s) + CO(g)
- Sometimes displacement reactions can also be used in place of reduction & highly reactive metals such as Na, Ca, Al, etc., are used as reducing agents.
- For e.g. 3MnO 2 (s) + 4Al(s) → 3Mn(l) + 2Al 2 O 3 (s) + Heat
- Fe 2 O 3 (s) + 2Al(s) → 2Fe(l)+Al 2 O 3 (s) + Heat
- This reaction is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts and is known as the thermit reaction.
Now that you are provided all the necessary information regarding NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals and we hope this detailed article on metal and nonmetal class 10 notes is helpful. If you find any doubts regarding this article or NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals, leave your comments in the comment section below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources