NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements
Multiple Choice Questions
Single Correct Answer Type
Question 1. On addition of cone. H
2
SO
4
to a chloride salt, colourless fumes are evolved but in case of iodide salt, violet fumes come out. This is because

Solution:
(c) HI formed during reaction is oxidized to I
2
which is violet in colour.
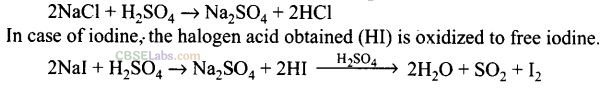
Question 2. In qualitative analysis when H
2
S is passed through an aqueous solution of
salt acidified with dil. HCl, a black precipitate is obtained. On boiling the precipitate with dil. HNO
3, it forms a solution of blue colour. Addition of excess of aqueous solution of ammonia to this solution gives
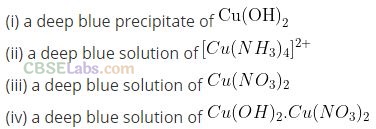
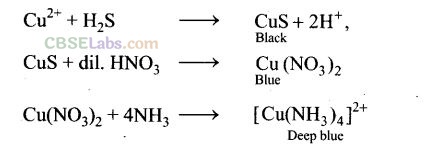
Solution:
(b) Black precipitate of copper sulphide is formed which gives blue colour of copper nitrate on boiling with dilute HNO
3
. When aqueous solution of ammonia is added to it, deep blue colour of
Question 3. In a cyclotrimeta phosphoric acid molecule, how many single and double bonds are present? .
(a) 3 double bonds; 9 single bonds
(b) 6 double bonds; 6 single bonds
(c) 3 double bonds; 12 single bonds
(d) Zero double bonds; 12 single bonds
Solution:
(c) Cyclotrimetaphosphoric acid contains three double bonds and 9 single bonds as shown below
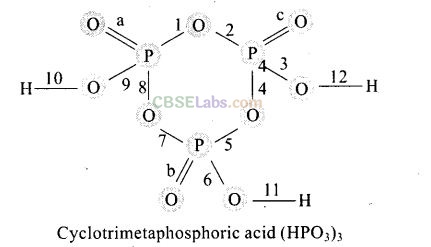
a, b, and c are three pi-bonds and numerics 1 to 12 are sigma bonds.
Question 4. Which of the following element can be involved in pπ-dπ bonding ?
(a) Carbon (b) Nitrogen (c) Phosphorus (d) Boron
Solution:
(c) Phosphorus can be involved in pπ-dπ bonding due to presence of vacant d orbitals C, N, and B do not have o’ orbitals.
Question 5. Which of the following pairs of ions are isoelectronic and isostructural?
![]()
Solution:
(a) CO
2-
and NO
3
are isoelectronic with 32 electrons and sp2 hybridisation
hence trigonal planar structure.
Question 6. Affinity for hydrogen decreases in the group from fluorine to iodine. Which of the halogen acids should have highest bond dissociation enthalpy?
(a) HF (b) HCl (c) HBr (d) HI
Solution:
(a)
HF On moving top to bottom HCl Size of halogen atom increases HBr H-X bond length increases HI Bond dissociation enthalpy decreases
Question 7. Bond dissociation enthalpy of E – H (E = element) bonds is given below. Which of the compounds will act as strongest reducing agent?
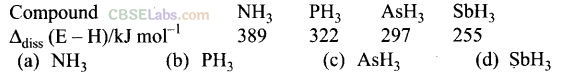
Solution:
(d) SbH
3
will act as strongest reducing agent due to minimum bond enthalpy.
Question 8. On heating with concentrated NaOH solution in an inert atmosphere of CO
2, white phosphorus gives a gas. Which of the following statement is incorrect about the gas?
(a) It is highly poisonous and has smell like rotten fish.
(b) Its solution in water decomposes in the presence of light.
(c) It is more basic than NH
3
(d) It is less basic than NH
3
Solution:
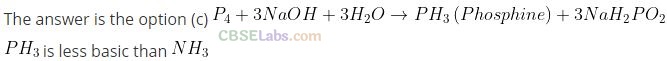
Question 9. Which of the following acid forms three series of salts?
(a) H
2
PO
2
(b) H
3
BO
3
(C)H
3PO
4
(d)H
3
PO
3
Solution:
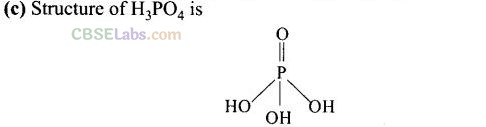
H
3PO
4
has 3 -OH groups i.e., has three ionisable H-atoms and hence forms three series of salts. These three possible series of salts of H
3PO
4
are as follows: .
NaH
2PO
4
, NaHPO
4
and Na
3
PO
4
Question 10. Strong reducing behaviour of H
3
PO
2
is due to
(a) low oxidation state of phosphorus
(b) presence of two -OH groups and one P – H bond
(c) presence of one -OH group and two P – H bonds
(d) high electron gain enthalpy of phosphorus
Solution:
(c) H
3
PO
2
is a monobasic acid. It acts as a reducing agent as it has two P – H bonds.
Question 11. On heating lead nitrate forms oxides of nitrogen and lead. The oxides formed
are
(a)NO
2
, PbO (b) NO
2
, PbO (c) NO, PbO (d) NO, PbO
2
Solution:
(b) 2Pb(NO
3
)
2
—> 2PbO + 4NO
2
+
O
2
Question 12. Which of the following element does not show allotropy?
(a) Nitrogen (b) Bismuth (c) Antimony (d) Arsenic
Solution:
(a) Nitrogen does not show allotropy due to its weak N – N single bond.
Therefore, ability of nitrogen to form polymeric structure or more than one structure become less. Hence, nitrogen does not show allotropy.
Question 13. Maximum covalency of nitrogen is
(a) 3 (b) 5 (c) 4 (d) 6
Solution:
(c) Maximum covalency of nitrogen is four as it cannot extend its valency beyond four [ NH
4
, R
4
N] due to absence of vacant d orbitals.
Question 14. Which of the following statement is wrong?
(a) Single N – N bond is stronger than the single P – P bond.
(b) PH
3
can act as a ligand in the formation of coordination compound with transition elements.
(c) NO
2
is paramagnetic in nature.
(d) Covalency of nitrogen in N
2
O
2
is four.
Solution:
(a) Nitrogen forms pπ-pπ multiple bond and the bond strength is very high. Single N – N bond is weaker than single P – P bond.
Question 15. A brown ring is formed in the ring test for NO
3
ion. It is due to the formation of

Solution:
(a) When freshly prepared solution of FeSO
4
is added in a solution containing NO
3
ion, it leads to formation of a brown coloured complex. This is known as brown ring test of nitrate.
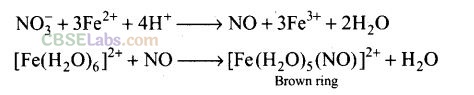
Hence, 2 moles of ammonia will produce 2 moles of NO.
Question 16. Elements of group 15 form compounds in +5 oxidation state. However, bismuth forms only one well characterized compound in +5 oxidation state. The compound is
(a) Bi
2
O
5
(b) BiF
5
(c) BiCl
5
(d)Bi
2
S
5
Solution:
(b) Bismuth commonly shows +3 oxidation state instead of +5 oxidation state due to inert pair effect. But Bi forms BiF
5
compound due to high electronegativity and small size of fluorine atom.
Question 17.On heating ammonium dichromate and barium azide separately we get
(a) N
2
in both cases
(b) N
2
with ammonium dichromate and NO with barium azide
(c) N
2
O with ammonium dichromate and N
2
with barium azide
(d) N
2
O with ammonium dichromate and N
2
O with barium azide
Solution:
(a)
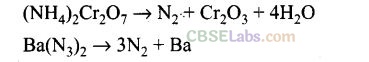
Question 18. In the preparation of HNO
3
, we get NO gas by catalytic oxidation of ammonia. The moles of NO produced by the oxidation of two moles of NH
3
will be (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 6
Solution:
(a) Two moles of NH
3
will produce 2 moles of NO on catalytic oxidation of ammonia in preparation of nitric acid

Question 19. The oxidation state of central atom in the anion of compound NaH
2
PO
2
will be
(a) +3 (b) +5 (c) +1 (d) -3
Solution:
![]()
Question 20. Which of the following is not tetrahedral in shape?
(a) NH
4
(b) SiCl
4
(c) SF
4
(d) S0
2
Solution:
(c) SF
4
trigonal bipyramidal structure.
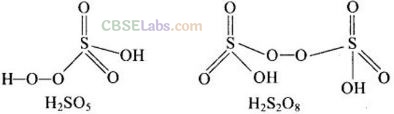
Question 21. Which of the following pairs are’peroxoacids of sulphur?
(a) H
2
S0
4
and H
2
S
2
O
8
(b) H
2
SO
5
and H
2
S
2
O
7
(c) H
2
S
2
O
7
and H
2
S
2
O
8
(d) H
2
S
2
O
6
and H
2
S
2
O
7
Solution:
(a) Peroxoacids of sulphur must contain one -O – O – bond as shown below
Question 22. Hot cone. H
2
SO
4
acts as moderately strong oxidizing agent. It oxidises both metals and non-metals. Which of the following element is oxidised by cone. H
2
SO
4
into two gaseous products?
(a) Cu (b) S (c) C (d) Zn
Solution:
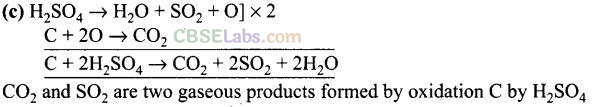
Question 23. A black compound of manganese reacts with a halogen acid to give greenish
yellow gas. When excess of this gas reacts with NH
3
an unstable trihalide is formed. In this process, the oxidation state of nitrogen changes from
(a) -3 to +3 (b) -3 to 0 (c) -3 to +5 (d) 0 to -3
Solution:
(a) Mn0
2
+ 4HCl -» MnCl
2
+ 2H
2
O + Cl
(greenish yellow gas)
When excess of Cl2 reacts with NH
3
the products are NCl
3
and HCl.
NH
3
+ 3Cl
2
—> NCl
3
+3HCl
O.S. (-3) O.S.(+3)
Question 24. In the preparation of compounds of Xe, Bartlett had taken O
2
+
Pt F
6
–
as a base compound. This is because
(a) both O
2
and Xe have same size
(b) both O
2
and Xe have same electron gain enthalpy
(c) both O
2
and Xe have almost same ionization enthalpy
(d) both Xe and O
2
are gases.
Solution:
(c) Bartlett had taken 02 Pt as a base compound because 02 and Xe both have almost same ionization enthalpy. The ionization enthalpies of noble gases are the highest in their respective periods due to their stable electronic configurations.
Question 25. In solid state PCl
5
is a
(a) covalent solid
(b) octahedral structure
(c) ionic solid with [PCl
6
]
+
octahedral and [PCl
4
]
–
tetrahedral
(d) ionic solid with [PCl
4
]
+
tetrahedral and [PCl
6
]
–
octahedral
Solution:
(d) Structure of PCl
5
in solid state
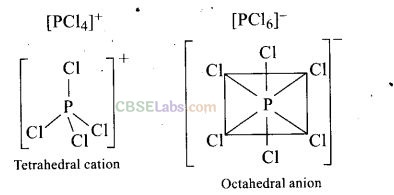
Question 26. Reduction potentials of some ions are given below. Arrange them in decreasing order of oxidizing power.
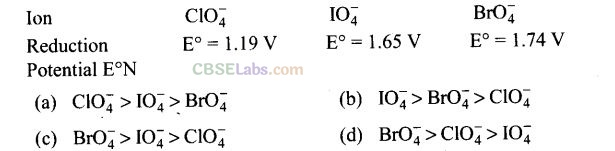
Solution:
(c) The higher the reduction potential, the higher is its tendency to get reduced. Hence, the order of oxidizing power is
BrO
4
–
> IO
4
–
> CIO
4
–
Question 27. Which of the following is isoelectronic pair?
(a) ICl
2
, ClO
2
(b) BrO
2
–
,BrF
2
+
(c) ClO
2
, BrF (d) CN
–
, O
3
Solution:
(b) Isoelectronic pair have same number of electrons

More than One Correct Answer Type
Question 28. If chlorine gas is passed through hot NaOH solution, two changes are observed in the oxidation number of chlorine during the reaction. These are
—— and ——-
Solution:
(a) 0 to +5
Question 29. Which of the following options are not in accordance with the properly mentioned against them?

Solution:
(b, c) Bond dissociation enthalpy order is Cl
2
> Br
2
> F
2
> I
2
Ionic character of metal halides increases as electronegativity of halogen increases
MI < MBr < MCI < MF
Question 30. Which of the following is correct for P
4
molecule of white phosphorus?
(a) It has 6 lone pairs of electrons (b) It has six P – P single bonds
(c) It has three P – P single bonds (d) It has four lone pairs of electrons,
Solution:
(b, d) Structure of P
4
molecule can be represented as
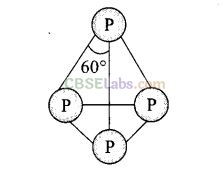
It has total four lone pairs of electrons situated at each P-atom.
It has six P – P single bond.
Question 31. Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Among halogens, radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum.
(b) Leaving F – F bond, all halogens have weaker X – X bond than X – X’ bond in interhalogens.
(c) Among interhalogen compounds maximum number of atoms ate present in iodine fluoride.
(d) Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds.
Solution:
(a, c, d) Among halogens radius ratio between iodine and fluorine is maximum
because iodine has maximum radius while fluorine has minimum radius. Also, due to highest radius ratio maximum number of atoms are present in iodine fluoride.
Interhalogen compounds are more reactive than halogen compounds because A – B bond of dissimilar halogen is weaker than A – A or B – B bond of halogens.
Question 32. Which of the following statements are correct for SO
2
gas?
(a) It acts as a bleaching agent in moist conditions.
(b) Its molecule has a linear geometry.
(c) Its dilute solution is used as disinfectant.
(d) It can be prepared by the reaction of dilute H
2
SO
4
with metal sulphide.
Solution:
(a, c) SO
2
acts as a bleaching agent in presence of moisture. This is due to reducing nature of SO
2
SO
2
+ 2H
2
O ->• H
2
SO
4
+ 2H
Coloured matter + H –> colourless matter. Its dilute solution is used as disinfectant.
Question 33. Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) All three N – O bond lengths in HNO
3
are equal.
(b) All P – Cl bond lengths in PCl
5
molecule in gaseous state are equal.
(c) P
4
molecule in white phosphorus have angular strain therefore white phosphorus is very reactive.
(d) PCl
5
is ionic in solid state in which cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral.
Solution:
(c, d)
(a) All the three N – O bond lengths in HNO
3
are not equal.
(b) All P – Cl bond lengths in PCl
5
molecule in gaseous state are not equal. Axial bond is longer than equatorial bond.
(c) P
4
molecule in white phosphorus have angular strain therefore white phosphorus is very reactive.
(d) PCl
5
is ionic in solid state in which cation is tetrahedral and anion is octahedral.
![]()
Question 34. Which of the following orders are correct as per the properties mentioned against each?

Solution:
(a, d) Acidic strength of oxides in a group decreases down the group and increases along a period from left to right.
Thermal stability of hydrides of group 16 decreases down the group.
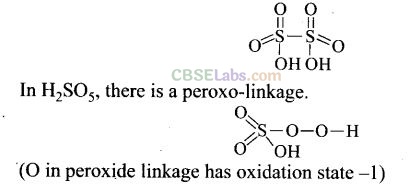
Question 35. Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) S – S bond is present in H
2
S
2
O
6
.
(b) In peroxosulphuric acid (H
2
SO
5
) sulphur is in +6 oxidation state.
(c) Iron powder along with Al
2
O
3
and K
2
O is used as a catalyst in the preparation of NH
3
by Haber’s process
(d) Change in enthalpy is positive for the preparation of SO
3
by catalytic
oxidation of SO
2
.
Solution:
(a, b)
Question 36. In which of the following reactions cone. H
2
S0
4
is used as an oxidizing reagent?
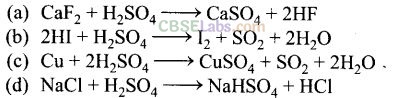
Solution:
(b, c) In the above given four reactions, (b) and (c) represent oxidizing behaviour of H
2
S0
4
. As we know that oxidizing agent reduces itself as oxidation state of central atom decreases.
Here,
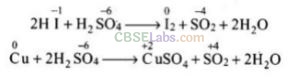
Question 37. Which of the following statements are true?
(a) Only type of interactions between particles of noble gases are due to weak dispersion forces.
(b) Ionisation enthalpy of.molecular oxygen is very close to that of xenon.
(c) Hydrolysis of XeF
6
is a redox reaction.
(d) Xenon fluorides are not reactive.
Solution:
(a, b) Weak dispersion forces are present between particles of noble gases. Ionization enthalpy of molecular oxygen is very close to that of xenon.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 38. In the preparation of H
2
S0
6
by contact process, why is S0
3
not absorbed directly in water to form H
2
S0
4
?
Solution:
The S0
3
is absorbed directly in H
2
S0
4
, acid fog is formed which is difficult to condense.
Question 39. Write a balanced chemical equation, for the reaction showing catalytic oxidation of NH
3
by atmospheric oxygen.
Solution:
![]()
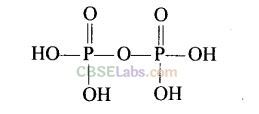
Question 40. Write the structure of pyrophosphoric acid.
Solution:
H
4
P
2
O
7
is pyrophosphoric acid. Its structure is
Question 41. PH
3
forms bubbles when passed slowly in water but NH
3
dissolves. Explain.
Solution:
NH
3
forms hydrogen bonds with water and therefore soluble in water but
PH
3
cannot form hydrogen bonds with water and, therefore, is not soluble in water. It escapes as gas.
Question 42. In PCl
5
, phosphorus is in sp
3
d hybridised state but all its five bonds are not equivalent. Justify your answer with reason.
Solution:
In PCl
5
, phosphorus undergoes sp
3
d hybridisation and a trigonal bipyramidal configuration comes into existence.
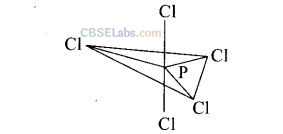
The equatorial P–Cl bonds are equivalent while two axial bonds are different and larger than equatorial bonds.
Question 43. Why is nitric oxide paramagnetic in gaseous state but the solid obtained on cooling is diamagnetic?
Solution:
Nitric oxide (NO) in the gaseous state is monomer having one unpaired electron as it is paramagnetic in nature.
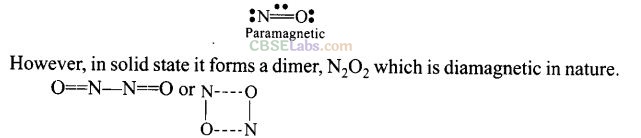
Question 44. Give reason to explain why ClF
3
exists but FCl
3
does not exist.
Solution:
ClF
3
is known because chlorine can exhibit +3 oxidation state due to promotion of
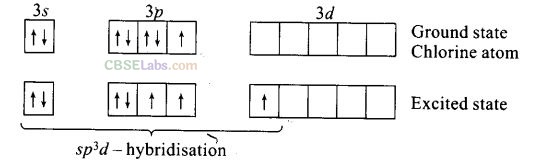
Each of the three singly occupied orbitals overlap with p-orbital of each of three fluorine atoms to form ClF
3
(trigonal bipyramidal geometry, T-shaped molecule).
No (i-orbitals are present in the valency shell of fluorine and thus excitation is not possible. Fluorine, therefore, does not exhibit positive oxidation state and so the formation of FCl
3
is not possible.
Question 45. Out of H
2
O and H
2
S, which one has higher bond angle and why?
Solution:
Oxygen is more electronegative than sulphur therefore bond pair of electrons of O – H bond will be closer to oxygen. As a result, there will be more bond pair-bond pair repulsion between bond pairs of two O – H bonds.
Question 46. SF
6
is known but SCl
6
is not. Why?
Solution:
Due to small size, six fluorine atoms can be accommodated around sulphur atom while chlorine atoms being larger in size are difficult to accommodate.
The other reason is that the fluorine being highly electronegative and oxidising in nature is capable of unpairing the paired orbitals of the values shell of sulphur atom and thereby showing the highest, oxidation state of +6 while chlorine is not able to do this.
Question 47. On reaction with Cl
2
, phosphorus forms two types of halides ‘A’ and ‘B’. Halide A is yellowish-white powder but halide ‘B’ is colourless oily liquid. Identify A and B and write the formulas of their hydrolysis products.
Solution:
When dry chlorine is passed over white phosphorus heated gently in a retort, first phosphorus trichloride is formed. PCl
3
further reacts with Cl
2
and forms phosphorus pentachloride PCl
5
.

Question 48. In the ring test of NO
3
ion.Fe
2+
ion reduces nitrate ion to nitric oxide, which
combines with Fe
2+
(aq.) ion to form brown complex. Write the reactions involved in the formation of brown ring.
Solution:
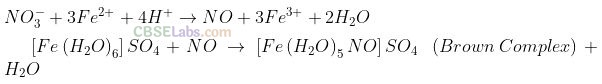
Question 49. Explain why does the stability of oxoacids of chlorine increase in the order given below:
HClO < HClO
2
< HClO
3
< HClO
4
Solution:
Oxygen is more electronegative than chlorine, therefore dispersal of negative charge present on chlorine increases from CIO to ClO
4
ion because number of oxygen atoms attached to chlorine increases. Therefore, stability of ions will increase in the order given below:
ClO<ClO
2
<ClO
3
<ClO
5
Thus due to increase in stability of conjugate base, acidic strength of corresponding acid increases in the following order HClO < HClO
2
< HClO
5
< HClO
4
Question 50. Explain why ozone is thermodynamically less stable than oxygen.
Solution:
Ozone is thermodynamically unstable with respect to oxygen because it

Question 51. P
4
O
6
reacts with water according to equation P
4
O
6
+ 6H
2
O
Calculate the volume of 0.1 M NaOH solution required to neutralize the acid formed by dissolving 1.1 g of P
4
O
6
in H
2
O.
Solution:

Question 52. White phosphorus reacts with chlorine and the product hydrolysis in the presence of water. Calculate the mass of HCl obtained by the hydrolysis of the product formed by the reaction of 62 g of white phosphorus with chlorine in the presence of water.
Solution:

Question 53. Name three oxoacids of nitrogen. Write the disproportionation reaction of that oxoacid of nitrogen in which nitrogen is in +3 oxidation state.
Solution:
The three oxyacids of nitrogen are:
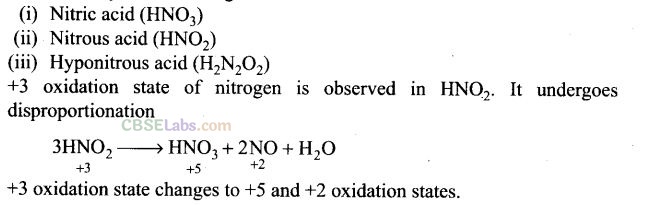
Question 54. Nitric acid forms an oxide of nitrogen on reaction with P
4
O
10
. Write the reaction involved. Also write the resonating structures of the oxide of nitrogen formed.
Solution:
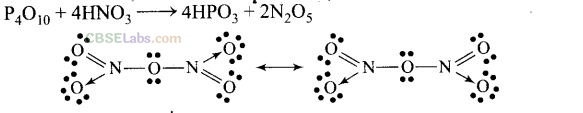
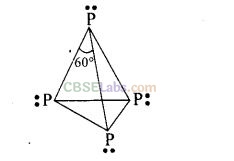
Reactivity: White phosphorus is very reactive in comparison to red phosphorus. This is due to angular strain in white phosphorus on account of bond angles (60°).
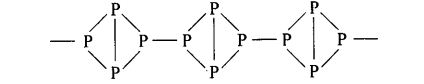
Question 55. Phosphorus has three allotropic fonns —(i) white phosphorus (ii) red phosphorus and (iii) black phosphorus. Write the difference between white and red phosphorus on the basis of their structure and reactivity.
Solution:
Yellow or white phosphorus: It is a discrete tetrahedral molecule. The molecular formula is P4. The four phosphorus atoms lie at the comers of a regular tetrahedron. Each P atom is linked to each of the three other atoms by single covalent bonds i.e., six P – P bonds are present and each P atom has a lone pair.
Question 56. Give an example to show the effect of concentration of nitric acid on the formation of oxidation product.
Solution:
Dilute and concentrated nitric acid give different oxidation products on reaction with metals. For example, zinc with very dilute HNO
3
(6%) forms NH
4
NO
3
, with dilute HNO
3
(20%) forms N
2
O and with cone. HNO
3
(70%) forms NO
2
.
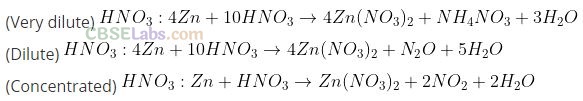
Question 57. PCl
5
reacts with finely divided silver on heating and a white silver salt is obtained, which dissolves on adding excess aqueous NH
3
solution. Write the reactions involved to explain what happens.
Solution:
PCl
5
reacts with silver to form white silver salt (AgCl). This dissolves in aqueous ammonia to form soluble complex.
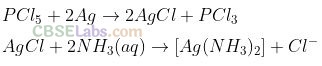
Question 58. Phosphorus forms a number of oxoacids. Out of these oxoacids phosphinic acid has strong reducing property. Write its structure and also write a reaction showing its reducing behaviour.
Solution:
Phosphinic acid is hypophosphorus acid (H
3
PO
2
) which acts as a reducing agent due to possession of P – H bonds.
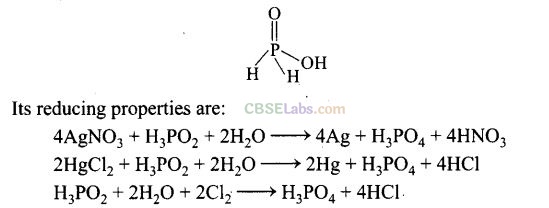
Matching Column Type Questions
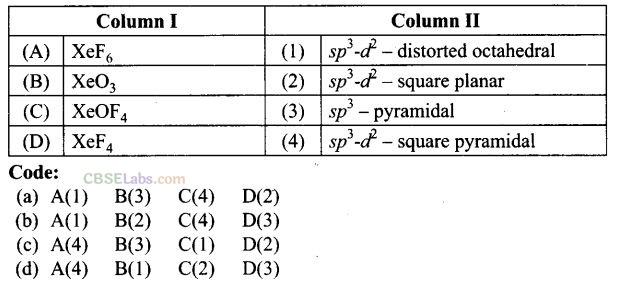
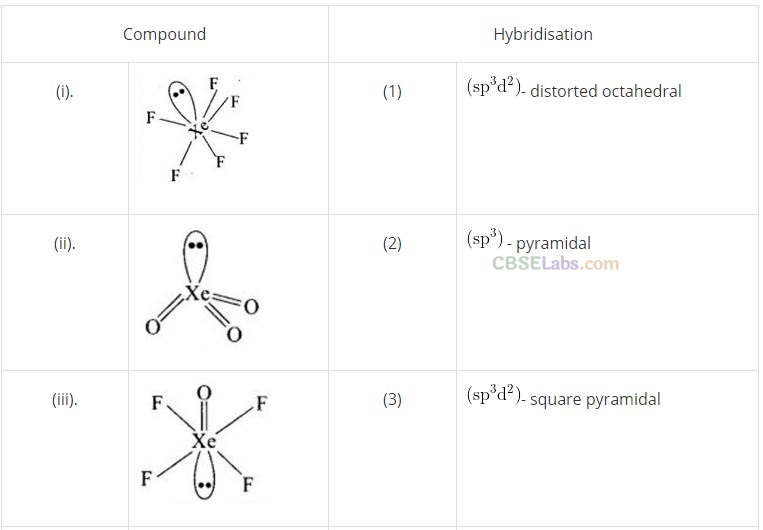
Question 59. Match the compounds given in Column I with the hybridization and shape given in Column II and mark the correct option.
Solution:
(a) (A -> 1), (B -> 3), (C -> 4), (D -» 2)

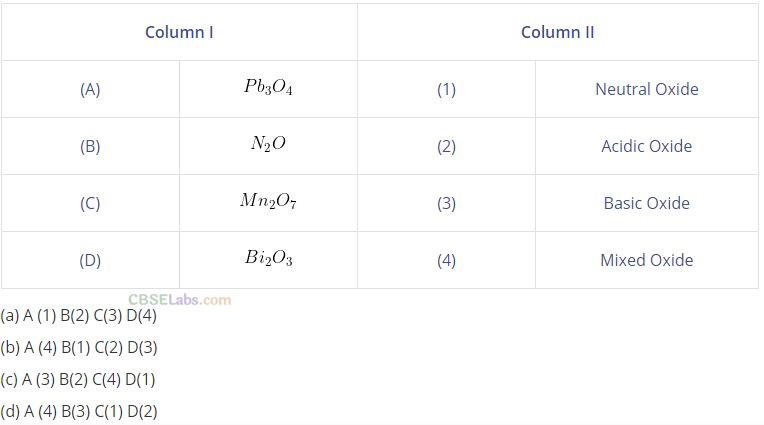
Question 60. Match the formulas of oxides given in Column I with the type of oxide given in Column II and mark the correct option.
Solution:
(b) (A —> 4), (B->1), (C-> 2), (D ->3)

Question 61. Match the items of Column I and Column II and mark the correct option.
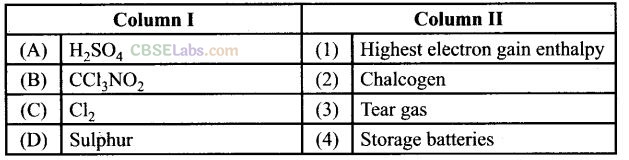

Solution:
(a) (A -> 4), (B -» 3), (C -> 1), (D -» 2)
(a) H
2
SO
4
is used in storage batteries
(b) CCl
3
NO
2
is known as tear gas.
(c) Cl
2
has highest electron gain enthalpy.
(d) Sulphur is a member of chalcogen i.e., one producing elements.
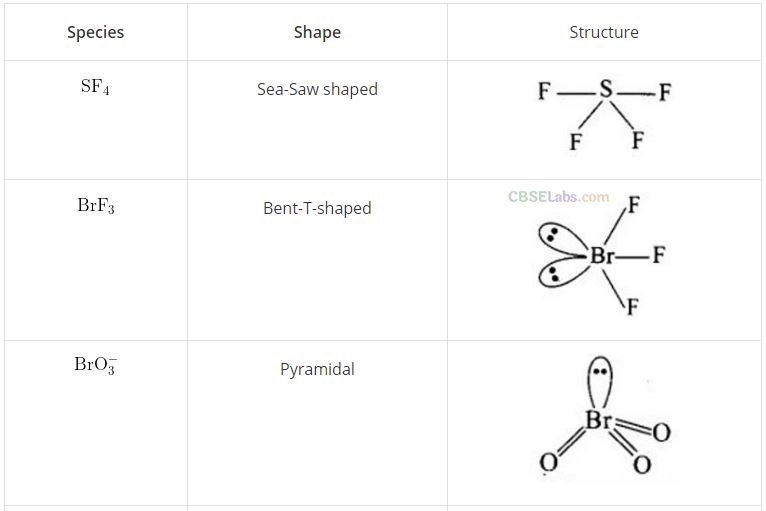
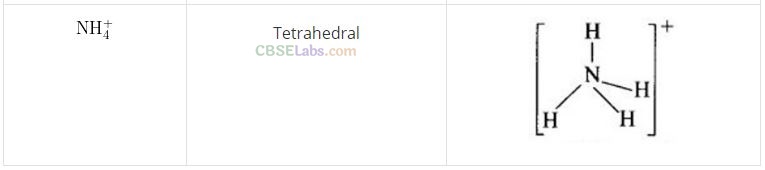
Question 62. Match the species given in Column I with the shape given in Column II and mark the correct option.
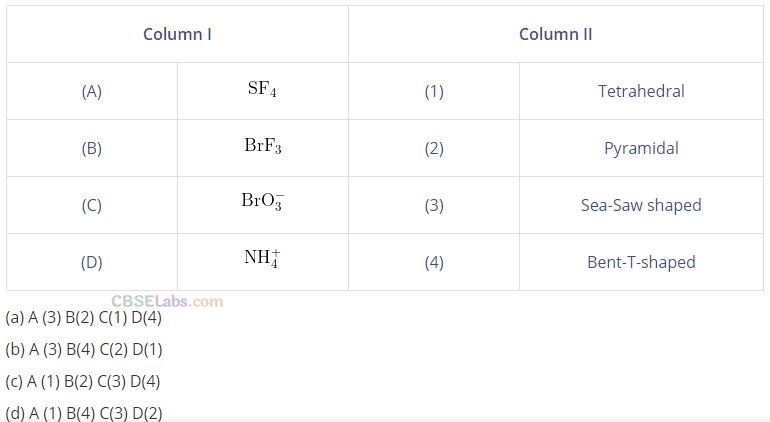
Solution:
(b) (A ->3), (B -> 4), (C —> 2), (D —> 1)
Question 63. Match the items of Column I and Column II and mark the correct option.
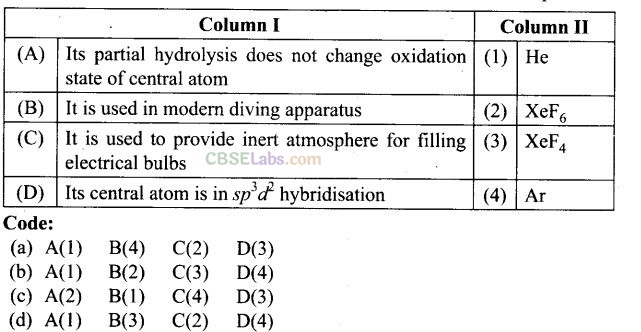
Solution:
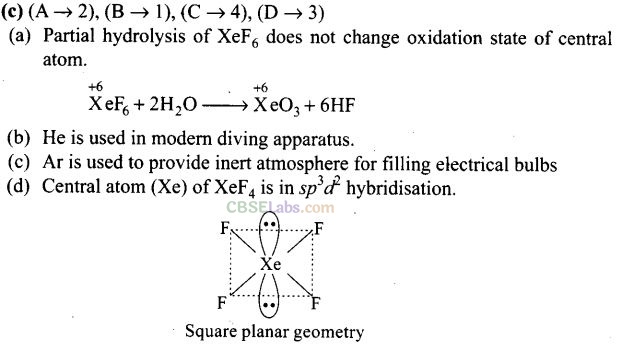
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the following choices:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are correct statements and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are correct statements but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is correct but Beason is wrong.
(d) Assertion is wrong but Reason is correct.
(e) Both Assertion and Reason are wrong.
Question 64. Assertion (A): N
2
is less reactive than P
4
.
Reason (R): Nitrogen has more electron gain enthalpy than phosphorus.
Solution:
(c) N
2
is less reactive due to high bond dissociation energy. Its electron gain enthalpy is less than phosphorus.
Question 65. Assertion (A): HNO
3
makes from passive.
Reason (R): HNO
3
forms a protective layer of ferric nitrate on the surface of iron.
Solution:
(c) Passivity is attained by formation of a thin film of oxide on iron.
Question 66. Assertion (A): HI cannot be prepared by the reaction of KI with concentrated
H
2
SO
4
.
Reason (R): HI has lowest H – X bond strength among halogen acids.
Solution:
(b) Both statements are correct but are independent of each other.
Question 67. Assertion (A): Both rhombic and monoclinic sulphur exist as S
8
but oxygen exists as Oπ.
Reason (R): Oxygen forms pπ-pπ multiple bond due to small size and small bond length but pπ-pπ bonding is not possible in sulphur.
Solution:
(a) S exists as S
8
but oxygen exists as O
2
because oxygen forms p
π
-p
π
multiple bonds which is not possible in S.
Question 68. Assertion (A): NaCl reacts with concentrated H
2
SO
4
to give colourless fumes with pungent smell. But on adding MnO
2
the fumes become greenish yellow.
Reason (R): MnO
2
oxidises HCl to chlorine gas which is greenish yellow.
Solution:
(a) Colourless fumes of HCl become greenish yellow because MnO
2
oxidises HCl to chlorine gas.
Question 69. Assertion (A): SF
6
cannot be hydrolysed but SF
4
can be.
Reason (R): Six F atoms in SF
6
prevent the attack of H
2
O on sulphur atom of SF
6
.
Solution:
(a) SF
6
is sterically protected due to presence of six F atoms around S which prevents the attack of H
2
O on SF
6
.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 70. An amorphous solid “A” bums in air to form a gas “B” which turns lime water milky. The gas is also produced as a by-product during roasting of sulphide ore. This gas decolourises acidified aqueous KMnO
4
solution and reduces Fe
3+
to Fe
+2
. Identify the solid “A” and the gas “B” and write the reactions involved.
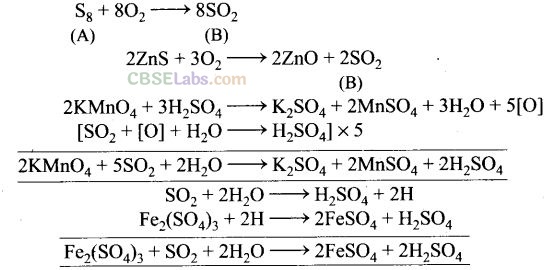
Solution:
A is sulphur (Sg) while B is sulphur dioxide (SO
2
).
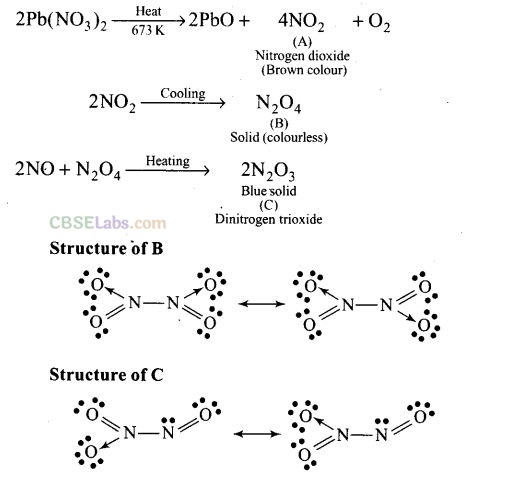
Question 71. On heating lead (II) nitrate gives a brown gas “A”. The gas “A” on cooling changes to colourless solid “B”. Solid “B” on heating with NO changes to a blue solid C. Identify A, B and C and also write reactions involved and draw the structures of B and C.
Solution:
The gas A is NO
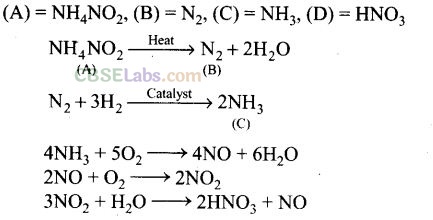
2
. The reactions are explained as under:
Question 72. On heating compound (A) gives a gas (B) which is a constituent of air. This gas when treated with 3 mol of hydrogen (H
2
) in the presence of a catalyst gives another gas (C) which is basic in nature. Gas C on further oxidation in moist condition gives a compound (D) which is a part of acid rain. Identify compounds (A) to (D) and also give necessary equations of all the steps involved. –
Solution:
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Solutions
- Chapter 1 Solid State
- Chapter 2 Solution
- Chapter 3 Electrochemistry
- Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics
- Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry
- Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements
- Chapter 8 The d- and f-Block Elements
- Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds
- Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Chapter 13 Amines
- Chapter 14 Biomolecules
- Chapter 15 Polymers
- Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life