NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
Multiple Choice Questions
Single Correct Answer Type
Question 1. In the extraction of chlorine by electrolysis of brine,

Solution:
(a) Extraction of chlorine from brine is based on the oxidation reaction of

Question 2. When copper ore is mixed with silica in a reverberatory furnace, copper matte is produced. The copper matte contains
(a) sulphides of copper (II) and iron (II)
(b) sulphides of copper (II) and iron (III)
(c) sulphides of copper (I) and iron (II)
(d) sulphides of copper (I) and iron (III)
Solution:
(c) When copper ore is mixed with silica, iron oxide slags off as iron silicate and copper is produced in the form of copper matte which contains Cu
2
S (I) and FeS (II).
Question 3. Which of the following reaction is an example of autoreduction?
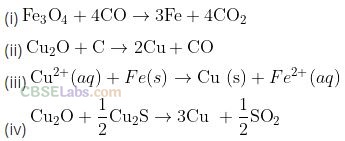
Solution:

This reaction includes reduction of copper (I) oxide by copper (I) sulphide. In this process, copper is reduced by itself hence this process is known as autoreduction and the solidified copper so, obtained is known as blister copper.
Question 4. A number of elements are available in the earth’s crust but most abundant
elements are
(a) Al and Fe (b) Al and Cu (c) Fe and Cu (d) Cu and Ag
Solution:
(a) Al and Fe are most abundant elements in the earth’s crust.
Question 5. Zone refining is based on the principle that .
(a) impurities of low boiling metals can be separated by distillation
(b) impurities are more soluble in molten metal than in solid metal
(c) different components of a mixture are differently adsorbed on an adsorbent
(d) vapour of volatile compound can be decomposed in pure metal
Solution:
(b) Zone refining method is based on the principle that impurities are more soluble in molten metal than in the solid state of the metal.
Question 6. In the extraction of copper from its sulphide ore, the metal is formed by the reduction of Cu
2
O with
(a) FeS (b) CO (c) Cu
2
S (d) SO
2
Solution:
(c) In the extraction of copper from its sulphide ore, the metal is formed by the reduction of Cu
2
O with Cu
2
S. This reaction completes with the process of autoreduction.
Chemical reaction occurring in this reaction is as follows
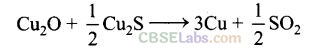
In this process, copper appears as blister copper.
Question 7. Brine is electrolysed by using inert electrodes. The reaction at anode is
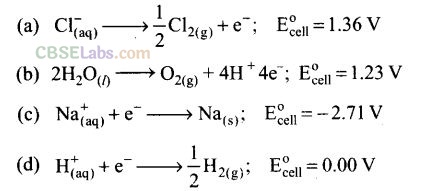
Solution:
(a) For oxidation at anode, two possible reactions are oxidation of chlorine and of oxygen. Out of these two, oxidation of chlorine ion is preferred because oxidation of oxygen requires overvoltage.
Chlorine is obtained by electrolysis giving out hydrogen and aqueous NaOH as byproducts.
Question 8. In the metallurgy of aluminium
(a) Al
3+ is oxidized to Al(s)
(b) graphite anode is oxidized to carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide
(c) oxidation state of oxygen changes in the reaction at anode
(d) oxidation state of oxygen changes in the overall reaction involved in the process.
Solution:
(b) In metallurgy of aluminium, graphite anode is oxidized to carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide hence it is to be replaced after it is used up.
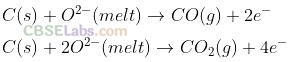
Question 9. Electrolytic refining is used to purify which of the following metals?
(a) Cu and Zn (b) Ge and Si (c) Zr and Ti (d) Zn and Hg
Solution:
(a) Copper and zinc are two metals which are generally purified by using electrolyte refining. In this process, impure metal is used as anode and pure metal is used as a cathode. Impurities from the blister copper or impure zinc deposit as anode mud. .
Question 10. Extraction of gold and silver involves leaching the metal with CN
+
ion. The metal is recovered by
(a) displacement of metal by some other metal from the complex ion
(b) roasting of metal complex
(c) calcinations followed by roasting
(d) thermal decomposition of metal complex
Solution:
(a) The metal in cyanide process is recovered by displacement of metal by some more reactive metal from the complex.
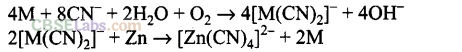
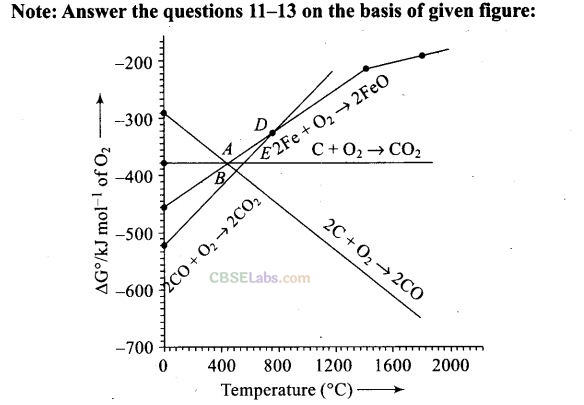
Question 11. Choose the correct option of temperature at which carbon reduces FeO to iron and produces CO.
(a) Below temperature at point A
(b) Approximately at the temperature corresponding to point A
(c) Above temperature at point A but below temperature at point D
(d) Above temperature at point A
Solution:

Question 12. Below point ‘A’ FeO can
(a) be reduced by carbon monoxide only
(b) be reduced by both carbon monoxide and carbon
(c) be reduced by carbon only
(d) Cannot be reduced by both carbon and carbon monoxide
Solution:
(a) Below point A Gibbs free energy change for the formation of CO
2 from CO has lower value (more negative value) than Gibbs free energy change for the formation of FeO . Hence, FeO will be reduced by CO only below point A.
Question 13. For the reduction of FeO at the temperature corresponding to point D, which of the following statement is correct?

Solution:
(a) At point D both the curves of oxidation of iron and oxidation of CO meet each other.
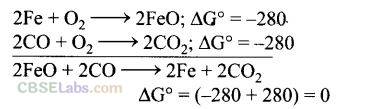
Question 14. At the temperature corresponding to which of the points in figure of Q. 11-13, FeO will be reduced to Fe by coupling the reaction 2FeO —> 2Fe + 02 with all of the following reactions?

Solution:
(b, d) The reduction reaction ranges depend upon the points of corresponding intersections in AG° versus T plots.
At point B and E, FeO will be reduced to Fe because at these points AG° value of all three oxidation reactions is lesser than that of reduction reaction.
Question 15. Which of the following options are correct?
(a) Cast iron is obtained by remelting pig iron with scrap iron and coke using hot air blast.
(b) In extraction of silver, silver is extracted as cationic complex.
(c) Nickel is purified by zone refining.
(d) Zr and Ti are purified by van Arkel method.
Solution:
(a, d) Iron obtained from blast is called pig iron. It contains about 4% carbon and many impurities such as Mn, P, Si, etc. The pig iron is remelted with scrap iron. This is known as cast iron. It has slightly less carbon content (3%) and is extremely hard and brittle.
Question 16. In the extraction of aluminium by Hall-Heroult process, purified A1203 is mixed with CaF2 to
(a) lower the melting point of A1203.
(b) increase the conductivity of molten mixture.
(c) reduce Al
+3
into Al(s).
(d) acts as catalyst.
Solution:
(a, b) CaF
2
mixed with purified Al
2
O
3
helps in lowering the melting point of Al
2
O
3
and increases the conductivity of the molten mixture.
Question 17. Which of the following statements are correct about the role of substances added in the froth floatation process?
(a) Collectors enhance the non-wettability of the mineral particles.
(b) Collectors enhance the wettability of gangue particles.
(c) By using depressants in the process two sulphide ores can be separated.
(d) Froth stabilizers decrease wettability of gangue.
Solution:
(a, c) Collectors like sodium ethyl xanthate are added to enhance the non-wettability of sulphide ore particles.
In the concentration of galena ore, sodium cyanide is used as a depressant for zinc sulphide. NaCN forms a complex with NaCN and deposits on the surface of ZnS which prevents it for the formation of Froth while PbS forms a froth.
Thus, by using depressant, two sulphides ores can be separated.
Question 18. In the froth floatation process, zinc sulphide and lead sulphide can be separated by
(a) using collectors
(b) adjusting the proportion of oil to water
(c) using depressant
(d) using froth stabilisers
Solution:
(b, c) Froth floatation method is used to extract metal from sulphide ore. ZnS and PbS can be separated by using depressant and adjusting the proportion of oil to water. Depressant used for this purposes is NaCN. It selectively prevents ZnS from coming to the froth.
Hence, (b) and (c) are correct choices.
Question 19. Common impurities present in bauxite are .
(a) CuO (b) ZnO (c) Fe
2
O
3
(d) SiO
2
Solution:
(c, d) Fe
2
O
3
and SiO2 are the common impurities present in bauxite.
Question 20. Which of the following ores are concentrated by froth floatation?
(a) Haematite (b) Galena
(c) Copper pyrites (d) Magnetite
Solution:
(b, c) Sulphide ores like galena (PbS) and copper pyrites (CuFe
S
2) are concentrated by froth floatation.
Question 21. Which of the following reactions occur during calcination?
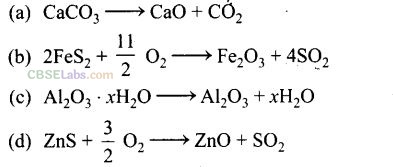
Solution:
(a, c) Calcination involves heating of the ore below is melting point in the absence of air or in limited supply of air. Oxygen containing ores like oxide, hydroxides and carbonates are calcined. Thus, the following reactions occur during calcination.
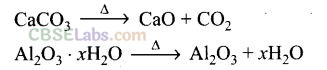
Question 22. For the metallurgical process of which of the ores, calcined ore can be reduced by carbon?
(a) Haematite (b) Calamine (c) Iron pyrites (d) Sphalerite
Solution:
(a, b) Oxides can be reduced by using carbon. Haematite (Fe
2
O
3
) and calamine (ZnCO
3
—> ZnO + CO
2) can be reduced by carbon.
Question 23. The main reactions occurring in blast furnace during extraction of iron from
haematite are
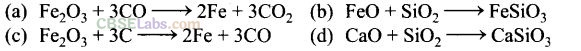
Solution:
(a, d) In blast furnace during extraction of iron, the following two are main reactions.

Question 24. In which of the following method of purification, metal is converted to its volatile compound which is decomposed to give pure metal?
(a) Heating with stream of carbon monoxide
(b) Heating with iodine
(c) Liquation
(d) Distillation
Solution:
(a, b) Vapour phase refining method includes

Question 25. Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) A depressant prevents certain type of particle to come to the froth.
(b) Copper matte contains Cu
2
S and ZnS.
(c) The solidified copper obtained from reverberatory furnace has blistered appearance due to evolution of SO
2
during the extraction.
(d) Zinc can be extracted by self-reduction.
Solution:
(a, c) Depressants can prevent frothing of a particular sulphide. The solidified copper obtained in reverberatory furnace has blistered appearance hence it is called blister copper.
Question 26. In the extraction of chlorine from brine .

Solution:
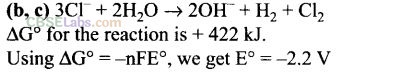
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 27.Why is an external emf of the more than 2.2 V required for the extraction of Cl
2
from brine?
Solution:
For the reaction of extraction of Cl
2
from brine solution:

Question 28. At temperatures above 1073 K coke can be used to reduce FeO to Fe. How can you justify this reduction with Ellingham diagram?
Solution:

Question 29. Wrought iron is the purest form of iron. Write a reaction used for the preparation of wrought iron from cast iron. How can the impurities of sulphur, silicon and phosphorus be removed from cast iron?
Solution:
The reaction is:
![]()
Limestone is added as flux and the impurities of sulphur, silicon and phosphorus change to their oxides and pass into slag.
Question 30. How is copper extracted from low grade copper ores?
Solution:
Copper is extracted by hydrometallurgy from low grade ores. It is leached out using acid or bacteria. The solution containing copper ions (Cu
+2
) is treated with scrap iron, zinc or H
2
as:
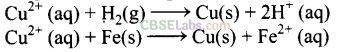
In this way, copper, is obtained.
Question 31. Write two basic requirements for refining of a metal by Mond’s process and by van Arkel method.Why?
Solution:
The basic requirements for refining a metal by Mond’s process and by van Arkel method are:
(i) The metal should form a volatile compound with an available reagent.
(ii) The volatile compound should be easily decomposable, so that metal can be easily recovered.
Question 32. Although carbon and hydrogen are better reducing agents but they are not used to reduce metallic oxides at high temperatures. Why?
Solution:
This is because carbon and hydrogen react with metals to form carbides and hydrides respectively at high temperature.
Question 33.How do we separate two sulphide ores by froth floatation method? Explain with an example.
Solution: The separation of two sulphide ores can be achieved by adjusting proportion of oil to water or by using depressants. In the case of an ore containing ZnS and PbS, the depressant used is NaCN. It forms complex with ZnS and prevents it from coming with froth but PbS remains with froth.
![]()
Question 34. The purest form of iron is prepared by oxidizing impurities from cast iron in a reverberatory furnace. Which iron ore is used to line the furnace? Explain by giving reaction.
Solution:
Haematite (Fe203) is used. It supplies the oxygen and oxidises carbon, silicon, manganese and phosphorus present in the cast iron to CO, Si02, MnO and P205 respectively.

Question 35. The mixture of compounds A and B is passed through a column of Al
2
O
3
by using alcohol as eluent. Compound A is eluted in preference to compound B. Which of the compounds A or B is more readily adsorbed on the column?
Solution:
Since compound A is eluted in preference to compound B. Compound B is more readily adsorbed on the column.
Question 36. Why is sulphide ore of copper heated in a furnace after mixing with silica? Iron oxide present as impurity in sulphide ore of copper forms a slag of iron silicate and copper is produced in the form of copper matte.
Solution:
FeO + SiO
2
> FeSiO
3
.
Question 37.Why are sulphide ores converted to oxide before reduction?
Solution:
Sulphides are not easily reduced while oxides are easily reduced. Due to this, sulphides are first oxidised and then subjected to reduction.
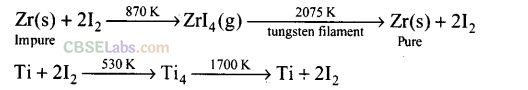
Question 38.Which method is used for refining Zr and Ti? Explain with equation?
Solution:
van Arkel method is used for refining Zr and Ti. In this method crude metal is heated with iodine to form volatile unstable compound. The compound is then decomposed to get pure metal.
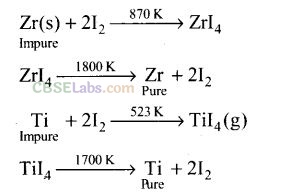
Question 39. What should be the considerations during the extraction of metals by electrochemical method?
Solution:
The following factors should be kept in mind to ensure proper precautions:
(i) Reactivity of the metal.
(ii) Suitability of the electrode.
Question 40. What is the role of flux in metallurgical processes?
Solution:
The ores, even after concentration, contain some gangue. To remove gangue, certain substances are mixed with concentrated ore which combine with the gangue to form a fusible material which is not soluble in molten metal. The substances used are called fluxes.
Fluxes are classified as (i) acidic flux and (ii) basic flux. Acidic flux removes basic impurities while basic flux removes acidic impurities.
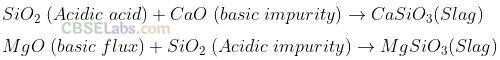
Question 41. How are metals used as semiconductors refined? What is the principle of the method used?
Solution:
Semiconductor is produced by zone refining method which is based on the principle that the impurities are more soluble in melt than in the solid state of metals.
Question 42. Write down the reactions taking place in blast furnace related to the metallurgy of iron at the temperature range 500-800 K.
Solution:
The following reactions take place in blast furnace during the metallurgy of iron at the temperature range 500-800 K.

Question 43. Give two requirements for vapour phase refining.
Solution:
(i) The metal should form a volatile compound with available reagent.
(ii) The volatile compound should be unstable and easily decomposable so that the recovery is easy.
Question 44. Write the chemical reactions involved in the extraction of gold by cyanide process. Also give the role of zinc in the extraction.
Solution:
Gold particles present in the ore are treated with a dilute solution of NaCN and air is circulated. Gold particles dissolve by forming soluble complex.
![]()
Au is recovered from solution by the addition of electropositive metal like zinc.
![]()
Extraction of gold by cyanide process involves both oxidation and reduction. Formation of cyanide complex involves oxidation of gold while its recovery involves reduction. Zn acts as a reducing agent.
Matching Column Type Questions
Question 45. Match the items of Column I with items of Column II and assign the correct code:

Solution:
(b) (A ->2), (B —>4), (C —> 5), (D —> 3)
(a) Pendulum is made up of nickel steel.
(b) Molecular formula of malachite is Cu CO
3
.Cu (OH)
2
(c) Molecular formula of calamine is ZnCO
3
.
(d) Molecular formula of cryolite is Na
3
AlF
6.
Question 46. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code:
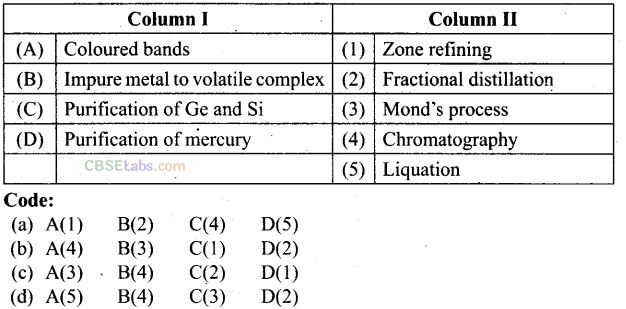
Solution:
(b) (A -> 4), (B —> 3), (C -> 1), (D -> 2)
(a) Coloured bands are observed in chromatography.
(b) Impure metal is converted to volatile complex by using Mond’s process.
(c) Ge and Si are purified by zone refining method.
(d) Purification of mercury is done by fractional distillation.
Question 47. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code:

Solution:
(a) (A –> 4), (B –>2), (C–> 3), (D —> 1)
(a) Cyanide process is used for extraction of Au through formation of anionic complex [Au(N)
2
]
–
.
(b) Froth floatation process is used for dressing of ZnS.
(c) Electrolytic reduction method is used for extraction of aluminium. Graphite electrode is used for this purpose.
(d) Zone refining is used for purification of Ge.
Question 48. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II and assign the correct code:
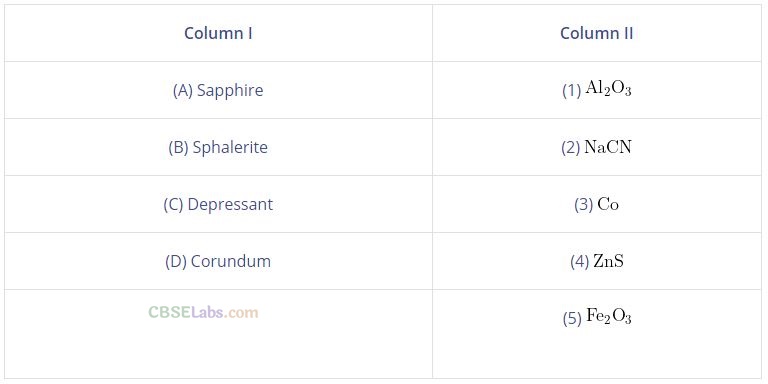
Solution:
(a) (A -> 3), (B -»4), (C -> 2), (D ->1)
(a) Sapphire is a gemstone which contains Co.
(b) Molecular formula of sphalerite is ZnS.
(c) NaCN is used as a depressant in froth floatation method.
(d) Molecular formula of corundum is Al
2
O
3
.
Question 49. Match the items of Column I with items of Column II and assign the correct code:
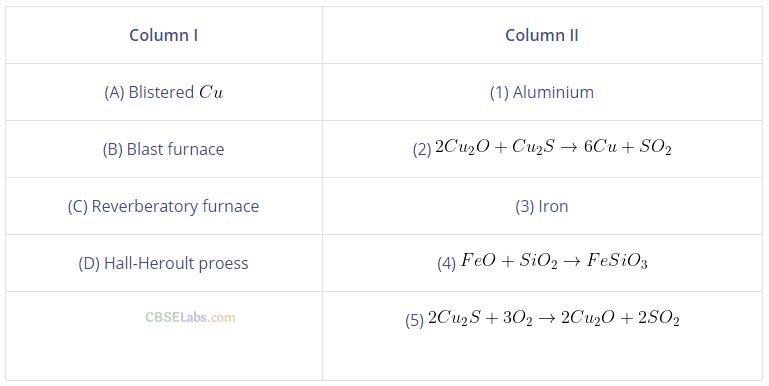
Solution:
(a) (A -> 2), (B ->3), (C -> 4), (D —> 1)
(a) Blistered Cu can be prepared by means of the following chemical reaction:
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the following choices.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true and the Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but the Reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but Reason is true.
(e) Assertion and Reason both are wrong.
Question 50. Assertion (A): Nickel can be purified by Mond’s process.
Reason (R): Ni(CO)
4
is a volatile compound which decomposes at 460 K to give pure Ni.
Solution:
(a) Nickel treated with carbon monoxide forms nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)
4
while impurities are left behind. When the vapour of Ni(CO)
4
is heated at 460 K, it is decomposed to give pure nickel while carbon monoxide is removed as gas.
Question 51. Assertion (A): Zirconium can be purified by van Arkel method.
Reason (R): ZrI
4
is volatile and decomposes at 1800 K.
Solution:
(a) Zirconium is also purified by vapour phase refining in which it is treated with iodine to form ZrI
4
which on heating decomposes to give pure zirconium.
Question 52. Assertion (A): Sulphide ores are concentrated by froth floatation method. Reason (R): Cresols stabilize the froth in froth floatation method.
Solution:
(b) Sulphide ores are wetted by oil and becomes lighter and rises to the surface along with froths while impurities wetted by water become heavier and settle down.
Question 53. Assertion (A): Zone refining method is very useful for producing semiconductors.
Reason (R): Semiconductors are of high purity.
Solution:
(b) In zone refining method, the impurities of semiconductors are more soluble in molten zone and the ultrapure semiconductor crystallizes.
Question 54. Assertion (A): Hydrometallurgy involves dissolving the ore in a suitable reagent followed by precipitation by a more electropositive metal.
Reason (R): Copper is extracted by hydrometallurgy.
Solution:
(b) Copper is extracted by hydrometallurgical process. In this process, salts of metal are dissolved in suitable solvent like water and then reduced by more electropositive element.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 55. Explain the following:
(a)CO
2
is a better reducing agent below 710 K whereas CO is a better reducing agent above 710 K.
(b) Generally sulphide ores are converted into oxides before reduction.
(c) Silica is added to the sulphide ore of copper in the reverberatory furnac
(d) Carbon and hydrogen are not used as reducing agents at high temperatures.
(e) Vapour phase refining method is used for the purification of Ti.
Solution:
(a) According to Ellingham diagram, at temperature below 710 K,


NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Solutions
- Chapter 1 Solid State
- Chapter 2 Solution
- Chapter 3 Electrochemistry
- Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics
- Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry
- Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements
- Chapter 8 The d- and f-Block Elements
- Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds
- Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Chapter 13 Amines
- Chapter 14 Biomolecules
- Chapter 15 Polymers
- Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life