NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life
Multiple Choice Questions
Single Correct Answer Type
Question 1. Which of the following statement is not correct?
(a) Some antiseptics can be added to soaps.
(b) Dilute solutions of some disinfectants can be used as antiseptic.
(c) Disinfectants are antimicrobial drugs.
(d) Antiseptic medicines can be ingested.
Solution:
(d) Antiseptics are applied to the living tissues such as wounds, cuts and diseased skin surfaces. Antiseptic medicines such as antibiotics cannot be ingested.
Question 2. Which is the correct statement about birth control pills?
(a) Contain estrogen only
(b) Contain progesterone only
(c) Contain a mixture of estrogen and progesterone derivatives
(d) Progesterone enhances ovulation
Solution:
(c) Birth control pills contain a mixture of estrogen and progesterone derivatives. Both of these are sex hormones. Progesterone suppresses ovulation and estrogen control the menstrual cycle.
Question 3. Which statement about aspirin is not true?
(a) Aspirin belongs to narcotic analgesics.
(b) It is effective in relieving pain.
(c) It has antiblood clotting action.
(d) It is a neurologically active drug.
Solution:
(a) Aspirin inhibits the synthesis of compounds known as prostaglandins which stimulate inflammation in the tissues and cause pain. So, it is effective in relieving pain.
Aspirin has many other effects such as reducing fever (antipyretic) and preventing blood platelet coagulation. Because of this anti-blood clotting
action, it is widely used to prevent heart.attacks. It does not make a person addictive as it is non-narcotic drug.
Question 4. The most useful classification of drugs for medicinal chemists is
(a) on the basis of chemical structure
(b) on the basis of drug action
(c) on the basis of molecular targets
(d) on the basis of pharmacological effect
Solution:
(c) The most useful classification of drugs for medicinal chemists. It is on the basis of molecular targets. Target molecules are usually biomolecules like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic
acids
. These drugs possess some common structural features, may have the same mechanism of action on a specific drug target.
Question 5. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Some tranquilizers function by inhibiting the enzymes which catalyse the degradation of noradrenaline.
(b) Tranquilizers are narcotic drugs.
(c) Tranquilizers are chemical compounds that do not affect the message transfer from nerve to receptor.
(d) Tranquilizers are chemical compounds that can relieve pain and fever.
Solution:
(a) Tranquilizers are neurologically active drugs. Some tranquilizers are
antidepressants and the functions by inhibiting the enzymes which catalyse the degradation of noradrenaline.
If the enzyme is inhibited, the neurotransmitter noradrenaline is slowly metabolized and can thus activate the receptor for longer periods there by counteracting the effect of depression. Tranquilizers form an essential component of sleeping pills.
Question 6. Salvarsan is arsenic containing drug which was first used for the treatment of
(a) syphilis (b) typhoid (c) meningitis (d) dysentery
Solution:
(a) Salvarsan is arsenic containing drug which was first used for treatment of syphilis. Syphilis is an acute and chronic infections disease caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is a sexually transmitted infection. The primary route of transmission is through sexual contact but it may also be transmitted from mother to foetus during pregnancy or at birth.
Question 7. A narrow spectrum antibiotic is active against
(a) gram positive or gram negative bacteria
(b) gram negative bacteria only
(c) single organism or one disease
(d) both gram positive and gram negative bacteria
Solution:
(a) A narrow spectrum antibiotic is active against gram positive or gram negative bacteria.
Question 8. The compound that causes general antidepressant action on the central
nervous system belongs to the class of
(a) analgesics (b) tranquilizers
(c) narcotic analgesics (d) antihistamines
Solution:
(b) The compound that causes general antidepressant action on the central nervous system belongs to the class of tranquilizers.
Question 9. Compound which is added to soap to impart antiseptic properties is
(a) sodium laurylsulphate
(b) sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate
(c) rosin
(d) bithional
Solution:
(d) All soaps are made by boiling fats or oils with suitable hydroxide. Variations are made by adding different raw materials. Sodium laurylsulphate and sodium dodecylbenzenesulphonate are anionic detergents.
Question 10. A gum rosin added to soap to make it lather well. Bithional is added to soaps to impart antiseptic properties to soap.
Equanil is
(a) artificial sweetener (b) tranquilizer
(c) antihistamine (d) antifertility drug
Solution:
(b) Equanil is a tranquilizer used in controlling depression and hypertension.
Question 11. Which of the following enhances lathering property of soap?
(a) Sodium carbonate (b) Sodium rosinate
(c) Sodium stearate (d) Trisodium phosphate
Solution:
(b) Shaving soaps contain glycerol to prevent rapid drying. A gum called rosin is added in these soaps which forms sodium rosinate which enhances lathering property of soap.
Question 12. Glycerol is added to soap. It functions
(a) as a filler (b) to increase leathering
(c) to prevent rapid drying (d) to make soap granules
Solution:
(c) Glycerol is added to shaving soap to prevent rapid drying while to enhance the leathering property of soap, a gum called rosin is added to them. It forms sodium rosinate which lathers well.
Question 13. Which of the following is an example of liquid dishwashing detergent?
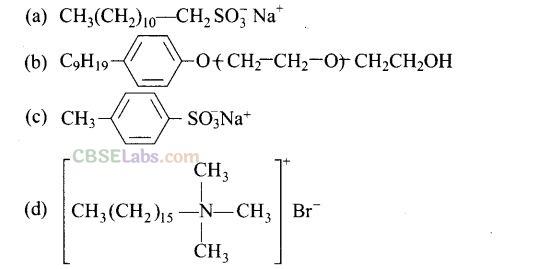
Solution:
(b) Liquid dishwashing detergents are non-ionic detergents.
Question 14. Polyethyleneglycols are used in the preparation of which type of detergents? (a) Cationic detergents . (b) Anionic detergents
(c) Non-ionic detergents (d) Soaps
Solution:
(c) Polyethyleneglycols are used in the preparation of non-ionic detergents.
Question 15. Which of the following is not a target molecule for drug function in body?
(a) Carbohydrates (b) Lipids
(c) Vitamins (d) Proteins
Solution:
(c) Drugs usually interact with biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids. These are called drug targets. Vitamins are not a target molecule for drug function in body.
Question 16. Which of the following statement is not true about enzyme inhibitors?
(a) Inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
(b) Prevent the binding of substrate.
(c) Generally, a strong covalent bond is formed between an inhibitor and an enzyme.
(d) Inhibitors can be competitive or non-competitive.
Solution:
(c) Inhibitors are chemical substances which tend to reduce the activity of a particular enzyme. Generally, a weak bond such as H-bonding, van der Waals interaction, etc. is formed between the enzyme and the inhibitor.
Question 17. Which of the following chemical can be added for sweetening of food items at cooking temperature and does not provide calories?
(a) Sucrose (b) Glucose (c) Aspartame (d) Sucralose
Solution:
(d) Sucralose is an artificial sweetening agent which is 600 times sweeter than sucrose and does not provide calories.
Question 18. Which of the following will not enhance nutritional value of food?
(a) Minerals (b) Artificial sweeteners
(c) Vitamins (d) Amino acids
Solution:
(b) Artificial sweeteners are non-caloric substitutes for sugar. They are often intensely more sweet than sugar but do not enhance nutritional value of food. Vitamins and minerals are essential nutrients because they perform hundreds of roles in the body.
Amino acids will also enhance the nutritional value of food.
More than One Correct Answer Type
Question 19. Which of the following statements are incorrect about receptor proteins?
(a) Majority of receptor proteins are embedded in the cell membranes.
(b) The active site of receptor proteins opens on the inside region of the cell.
(c) Chemical messengers are received at the binding sites of receptor proteins.
(d) Shape of receptor does not change during attachment of messenger.
Solution:
(b, d) Receptor proteins are embedded in the cell membrane and their active
sites project outside region of the cell membrane. Shape of the receptor changes during the attachment of messenger.
Question 20. Which of the following are not used as food preservatives?
(a) Table salt (b) Sodium hydrogen carbonate
(c) Cane sugar (d) Benzoic acid
Solution:
(b, d) Table salt and cane sugar are used, as food preservatives while sodium hydrogen carbonate and benzoic acid are not used as food preservatives.
Question 21. Compounds with antiseptic properties are
(a) CHCl, (b) CHI
3
(c) Boric acid (d) 0.3 ppm aqueous solution of Cl
2
Solution:
(b, c)
(a) CHCl
3
(chloroform) was used as an anaesthesia in surgery but now it is used in the production of the Freon refrigerant R-22.
(b) Iodoform (CFH
3
) produces iodine on coming in contact with skin, so it is used as an antiseptic for wounds.
(c) Boric acid (IT
3
BO
3
) in dilute aqueous solution is a weak antiseptic for eyes. Thus, chemical messenger gives message to the all without entering the cell.
(d) Chlorine in the concentration of 0.2 of 0.4 ppm in aqueous solution and sulphur dioxide in very low concentrations, are disinfectants.
Question 22. Which of the following statements are correct about barbiturates?
(a) Hypnotics or sleep producing agents.
(b) These are tranquilizers.
(c) Non-narcotic analgesics.
(d) Pain reducing without disturbing the nervous system.
Solution:
(a, b) Barbiturates are tranquilizers which are used as hypnotics or sleep inducing agents.
Question 23. Which of the following are sulpha drugs?
(a) Sulphapyridine (b) Prontosil
(c) Salvarsan (d) Nardil
Solution:
(a, b)
(a) Sulphapyridine is a sulphonamide antibacterial drug.
(b) Prontosil is also called sulphamidochrysoidine.
(c) Salvarsan is arsenic based antibacterial drug.
(d) Nardil is an antidepressant drug.
Question 24. Which of the following are antidepressants?
(a) Iproniazid (b) Phenelzine (c) Equanil (d) Salvarsan
Solution:
(a, b, c)
(a) Iproniazid is a hydrazine drug used as an antidepressant.
(b) Phenelzine is also known as Nardil. It is used in the treatment of major depressive disorder.
(c) Equanil is used in controlling depression and hypertension.
(d) Salvarsan is an antibacterial drug. It is used in the treatment of Syphilis.
Question 25. Which of the following statements are incorrect about penicillin?
(a) An antibacterial fungus.
(b) Ampicillin is its synthetic modification.
(c) It has bacteriostatic effect.
(d) It is a broad spectrum antibiotic.
Solution:
(c, d) Penicillin destroys bacteria by destroying the cell wall of the microorganism or kill the bacteria so, it has bacteriocidal effect. Penicillin has a narrow or limited spectrum.
Question 26. Which of the following compounds are administered as ant-acids?
(a) Sodium carbonate (b)Sodium Hydrogen carbonate
(c)Aluminium carbonate (d)Magnism Hydroxide
Solution:
(b,d) Sodium Hydrogen carbonate and Magnism Hydroxide ,both are mild alkalies ,are used as ant-acids.
Question 27 .Amongst the following antihistamine ,which are ant-acids?
(a)Ranitidine (b) Brompheniramine
(c)Terfenadine (d)Cimetidine
Solution:
(a, d) Ranitidine and cimetidine are antihistamines which are used as ant-acids. These drug result in release of lesser amount of acid. Brompheniramine and terfenadine are antihistamines which act as antiallergic in drugs.
Question 28. Veronal and Luminal are derivatives of barbituric acid which are ………….
Solution:
(a, d) Tranquilizers are neurologically active drugs. Veronal and luminal are derivatives of barbituric acid used as tranquilizers.
Question 29. Which of the following are anionic detergents?
(a) Sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohol.
(b) Ester of stearic acid and polyethylene glycol.
(c) Quaternary ammonium salt of amine with acetate ion.
(d) Sodium salts of sulphonated long chain hydrocarbons.
Solution:
(a, d) Sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohol and sodium salts of sulphonated long chain hydrocarbons are anionic detergents e.g., Sodium laurylsulphate CH
3
(CH
2
)
10
CH
2
OSO
3
–
Na
+
and sodium dodecylbenzene sulphonate.
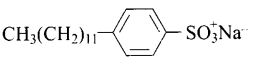
Question 30. Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Cationic detergents have germicidal properties.
(b) Bacteria can degrade the detergents containing highly branched chains.
(c) Some synthetic detergents can give foam even in ice cold water.
(d) Synthetic detergents are not soaps.
Solution:
(a, c, d)
(a) Cationic detergents are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides or bromides as anions. These detergents have germicidal properties.
(b) Bacteria cannot degrade the detergents containing highly branched chains, therefore, in most of the detergents used these days, the branching is kept to a minimum so that the detergents become easily biodegradable.
(c) Some synthetic detergents can give foam even in ice cold water.
(d) Synthetic detergents are cleansing agents which have all the properties of soaps, but which actually do not contain any soap.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 31. What is the average molecular mass of drugs?
Solution:
The average molecular mass of drugs is of the order of 100-500 u.
Question 32. Write the uses of medicines.
Solution:
Medicines are used in diagnosis, prevention and treatment of diseases.
Question 33. What are antiseptics?
Solution:
Antiseptics are chemicals which either kill or prevent the growth of micro-organisms and are applied to the living human tissues.
Question 34. Which type of drugs come under antimicrobial drugs?
Solution:
Antiseptics, antibiotics, disinfectants and sulpha drugs come under antimicrobial drugs.
Question 35. Where are receptors located?
Solution:
Receptors are embedded on the outer surface of the cell membrane.
Question 36. What is the harmful effect of hyperacidity?
Solution:
Hyperacidity in the intestine creates ulcer, gastric reflux and oesophagitis.
Question 37. Which site of an enzyme is called allosteric site?
Solution:
Sites different from active site of enzyme where a molecule can bind and affect the active site is called allosteric site. Some drugs may also bind at this site.
Question 38. What type of forces are involved in binding of substrate to the active site of enzyme?
Solution:
Ionic bonding, hydrogen bonding, van der Waals interaction, dipole-dipole interaction, etc., are involved in binding.
Question 39. What is the commonality between the antibiotic arsphenamine and azo dye?
Solution:
Antibiotic, arsphenamine possesses -As = As – linkage that resembles -N =N – linkages in azo dyes.
Question 40. Which class of drugs is used in sleeping pills?
Solution:
Tranquilizers are used in sleeping pills.
Question 41. Aspirin is pain relieving antipyretic drug but can be used to prevent heart attack. Explain.
Solution:
Aspirin prevents platelet coagulation and thus has antiblood clothing action, therefore, can prevent blood clotting in heart.
Question 42. Both antacids and antiallergic drugs are antihistamines but they cannot replace each other. Explain why?
Solution:
Antihistamines are the drugs which control the allergy effects produced by histamines. Antacids are the substances which neutralise gastric acidity. Antihistamine do not affect the secretion of acid in stomach and the reason is that both antiallergic and antacid drugs work on different receptors.
Question 43. What is a soft soap?
Solution:
Soft soaps are potassium salts of fatty acids (such as palmitic acid, stearic acid and oleic acid).
Question 44. If soap has high alkali content it’irritates skin. How can the amount of excess alkali be determined? What can be the source of excess alkali?
Solution:
Acid-base titration can be used to determine the excess amount of alkali in soap. The excess alkali left after hydrolysis of oils or fats can be the source of alkalinity in soap.
Question 45. Explain why sometimes foaming is seen in river water near the place where sewage water is poured after treatment?
Solution:
Detergents (which are not biodegradable) persist in water even after sewage treatment and that causes foaming in river water.
Question 46. Which category of the synthetic detergents is used in toothpaste?
Solution:
Anionic detergents such as cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide are used in hair shampoos and hair conditioners.
Question 47. Hair shampoos belong to which class of synthetic detergent?
Solution:
Cationic detergents such as cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide are used in hair shampoos and hair conditioners.
Question 48. Dishwashing soaps are synthetic detergents. What is their chemical nature?
Solution:
Non-ionic detergents such as polyethylene glycol stearate are used as
dishwashing soaps.
Question 49. Draw the diagram showing micelle formation by the following detergent. CH
3
(CH
2
)
10
CH
2
O SO
3
–
Na
+
.
Solution:
Micelle formation of the detergent can be shown as:
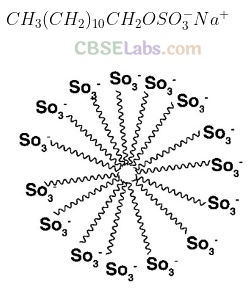
Question 50. How does the branching of hydrocarbon chain of synthetic detergents affect their biodegradability?
Solution:
Straight chain hydrocarbons in synthetic detergent leads to easy biodegrad-ability because the branched chain hydrocarbon tail is a source of pollution. Therefore, lesser the branching more is the biodegradability.
Question 51. Why is it safer to use soap from the environmental point of view?
Solution:
Soaps are biodegradable. The detergents are quite stable and are non- biodegradable because of branching in hydrocarbon chain hence cause water pollution. Therefore, it is safer to use soap from the environmental point of view.
Question 52. What are analgesics?
Solution:
Analgesics are neurologically active pain killing drugs that reduce pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, co¬ordination or paralysis or some other disturbances of nervous system. For example, aspirin, ibuprofen, paracetamol, diclofenac sodium, etc.
Question 53. What is the scientific explanation for the feeling of depression?
Solution:
A person suffers from depression when he has low levels of noradrenaline. Noradrenaline is a neurotransmitter which plays a role in mood changes. Low level of noradrenaline lowers the signal-sending activity and make the person suffer from depression.
Question 54. What is the basic difference between antiseptics and disinfectants?
Solution:
Antiseptics are applied to living tissues whereas disinfectants are applied to non-living objects such as drains, toilets, floors and utensils.
Question 55. Between sodium hydrogen carbonate and magnesium hydroxide which is a better antacid and why?
Solution:
Magnesium hydroxide is a better antacid because being insoluble, it does not allow the pH to increase above neutral. However, sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO
3
) being soluble, its excess can make the stomach alkaline and trigger the production of even more acid.
Question 56. Which analgesics are called opiates?
Solution:
Narcotic analgesics which are obtained from opium poppy are called opiates. Examples are morphine and its derivatives like codeine and heroin (morphine diacetate).
Question 57. What is the medicinal use of narcotic drugs?
Solution:
The narcotic drugs relieve pain and produce sleep. Therefore, these are commonly used for the relief of postoperative pain, cardiac pain and pain of terminal cancer and in child birth.
Question 58. What are antagonistic drugs?
Solution:
Drugs that bind to the receptor site and inhibit its natural function are called antagonistic drugs. For example, cimetidine antacid drug.
Question 59. What is the mode of action of antimicrobial drugs?
Solution:
Antimicrobial drugs can kill the microorganism such as bacteria, fungi, viruses or other parasites. They can, alternatively inhibit the pathogenic action of microbes.
Question 60. What is the side product of soap industry? Give reactions showing soap formation.
Solution:
Glycerol is obtained as a side product during the formation of soaps.
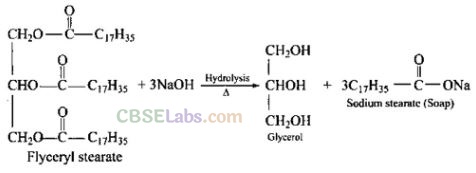
Question 61. What is the difference between bathing soap and washing soaps?
Solution:
Bathing soaps are potassium salts of long chain fatty acids. They are usually soft and also free from unused alkali. While washing soaps are sodium salts of long chain fatty acids. They are usually hard and also contain some residual alkali.
Question 62. How are transparent soaps manufactured?
Solution:
Transparent soaps are prepared by dissolving the soap in ethanol and then evaporating the excess solvent.
Question 63. What is the advantage of using antihistamines over antacids in the treatment of acidity?
Solution:
Antacids neutralise the acid produced in the stomach. They do not control the cause of production of excess acid. Therefore, antacids control only the symptoms but not the cause. On the other hand, antihistamines are the drugs which suppress the action of histamine which is the chemical responsible for stimulation of secretion of pepsin and HCl in the stomach. These influence and prevent the binding of histamine with the receptors present in the stomach wall resulting in lower acid production and therefore, better treatment. This is the advantage of antihistamines over antacids.
Question 64. What are the functions performed by histamine in the body?
Solution:
Histamine is a potent vasodilator. It contracts muscles in the gut and bronchi. It relaxes some other muscles e.g., in the’walls of fine blood vessels. Histamine is also responsible for congestion in the nose associated with common cold and allergies. Histamine stimulates the release of pepsin and hydrochloric acid in the stomach.
Question 65. With the help of an example explain how do tranquilizers control the feeling of depression?
Solution:
Noradrenaline plays an important role in mood change. If the level of noradrenaline is low, the person suffers from depression.
Question 66. Why are certain drugs called enzyme inhibitors?
Solution:
Enzymes have active sites that bind the substrate for effective and quick chemical reaction. The functional groups present at the active site of enzyme react with functional groups of substrate via .ionic bonding, van der Waals’ interaction, etc. Some drugs interfere with this interaction by blocking the binding site of enzyme and also prevent the binding of actual substrate with enzyme. This inhibits the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Therefore, these are called inhibitors.
Question 67. What are fillers and what role these fillers play in soap?
Solution:
Some substances are added to soap to affect the properties in order to make it useful for a particular application, are called fillers. For example, glycerol is added in shaving soaps, to prevent it from rapid drying. Laundry soaps contain fillers like sodium rosinate, sodium silicate, borax and sodium carbonate to increase their leather forming ability. In medicated soaps, substances of medicinal value are added. In some soaps deodorants are also added.
Question 68. Sugar is the main source of energy as it produces energy on metabolic decomposition. But these days low chloride drinks are more popular, why?
Solution:
In low calorie drinks, some artificial sweetening agents (like aspartame, alitame, sucralose, saccharin etc.) are present which are often many hundred times sweeter than sugar but do not metabolise and hence, do not produce any energy.
Question 69. Pickles have a long shelf life and do not get spoiled for months, why?
Solution:
Table salt, sugar vegetable oils and sodium benzoate, etc. are used as preservatives. These do not allow moisture and air to enter the material and hence, bacteria cannot thrive on them. Therefore, pickles do not get spoiled for months.
Question 70. What is the difference between saccharin and saccharic acid?
Solution:
Saccharin (o-sulpho benzoicimide) is an artificial sweetener, whereas saccharic acid (dicarboxylic acid) is obtained by the oxidation of glucose with cone. HNO
3
or by bacterial oxidation.

Question 71. Name an artificial sweetener which is derivative of sucrose.
Solution:
Sucralose is trichloro derivative of sucrose. It is about 600 times sweeter than sucrose. However, it neither provides calories nor causes tooth decay.
Question 72. Name two ct-amino acids which form a dipeptide which is 100 times more sweet than cane sugar?
Solution:
Aspartic acid and phenylalanine are two a-amino acids which form the methyl ester of dipeptide and named as aspartame (an artificial sweetener) which is 100 times more sweet than cane sugar.
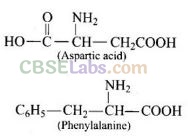
Question 73. Aspartame is unstable at cooking temperature, where would you suggest aspartame to be used for sweetening?
Solution:
Since aspartame is unstable and decomposes at cooking temperature, therefore, it is used as a sweetening agent in cold foods and soft drinks.
Question 74. Sodium salts of some acids are Very useful as food preservatives. Suggest a few such acids.
Solution:
Sodium salts of benzoic acid, sorbic acid and propanoic acid, etc., are used as food preservatives.
Question 75. Explain the role of allosteric site in enzyme inhibition?
Solution:
Some drugs do not bind to the enzyme’s active site. These bind to a different site of enzyme which is called allosteric site. This bonding of inhibitor at allosteric site changes the shape of the active site in such a way that substrate cannot recognise it. As a result, the affinity of the substrate for the active site is reduced.
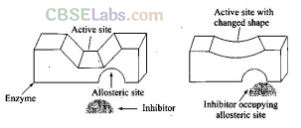
It may be noted that if the bond formed between enzyme and inhibitor is strong covalent bond and therefore cannot be broken easily, then the enzyme gets blocked permanently. The body then degrades the enzyme inhibitor complex and synthesizes new enzyme.
Question 76. How are receptor proteins located in the cell membrane?
Solution:
Receptor proteins are embedded in cell membranes in such a way that their small part possessing active sites projects out of the surface of the membrane and opens on the outside region of the cell membrane.
Question 77. What happens when the bond formed between an enzyme and an inhibitor is a strong covalent bond?
Solution:
If the bond formed between an enzyme and an inhibitor is a strong covalent bond and cannot be broken easily, then the enzyme is blocked permanently, The body then degrades the enzyme-inhibitor complex and synthesises the new enzyme.
Matching Column Type Questions
Question 78. Match the medicines given in Column I with their use given in Column II.
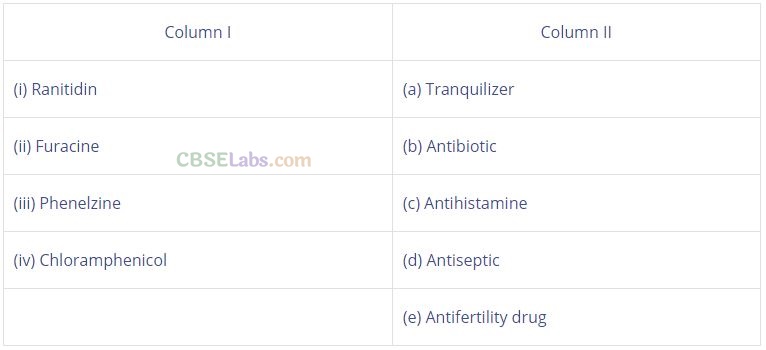
Solution:
(i —> c), (ii —» d), (iii —» a), (iv —» b)
(i) Ranitidine It prevents the interaction of histamine with the receptors present in the stomach wall. Thus, it controls the secretion of HCl and pepsin in stomach.
(ii) Furacine Furacine is an antiseptic. It can be applied to the living tissues to kill or to prevent the growth of microorganisms.
(iii) Phenelzine It is also known as Nardil. Its structure is
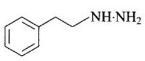
It is used to treat depression.
(iv) Chloramphenicol It is a broad spectrum antibiotic. It can be given orally in case of typhoid,- acute fever, dysentery, certain urinary infections, meningitis and pneumonia.
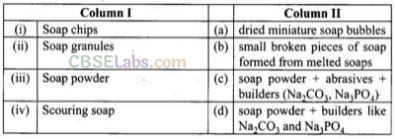
Question 79. Match the soaps given in Column I with items given in Column II.
Solution:
(i ->b), (ii —» a), (iii —» d), (iv -> c)
(i) Soap chips are made by running a thin sheet of melted soap into a cool cylinder and scraping off the soaps in small broken pieces.
(ii) Soap granules are dried miniature soap bubbles.
(iii) Soap powders contain soap powder and builders like sodium carbonate and trisodium phosphate. Builders make the soap act more rapidly.
(iv) Scouring soaps contain soap powder, a scouring agent (abrasive) such as powdered pumice or finely divided sand and builders.
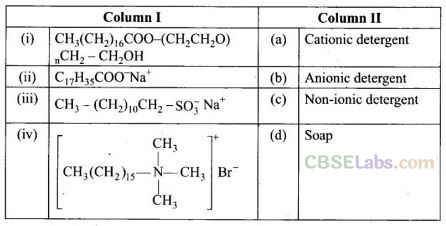
Question 80. Match structures given in Column I with the type of detergents given in Column II.
Solution:
(i —> c), (ii —> d), (iii —> b), (iv -> a)
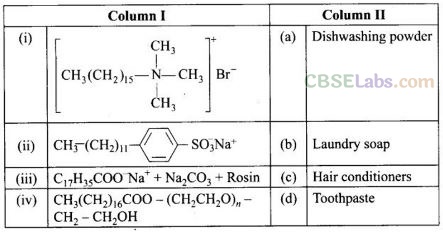
Question 81. Match the detergents given in Column I with their uses given in Column II.
Solution:
(i —> c), (ii —> d), (iii —> b), (iv —> a)
(i) Hair shampoos/conditioners are made up of cationic detergents. These are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with chlorides, bromides or acetates, e.g., cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide.
(ii) Anionic detergents are used in toothpaste e.g., sodium dodecyl benzene sulphonate. It can be prepared as follows
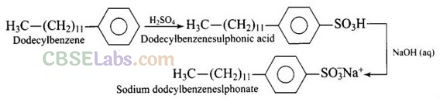
(iii) Laundry soaps contain fillers like sodium rosinate. Sodium silicate, borax and sodium carbonate. Sodium rosinate makes the soap to lather well.
(iv) Dishwashing powder are non-ionic detergents .
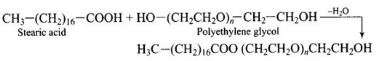
Question 82. Match the class of compounds given in Column I with their functions given in Column II.

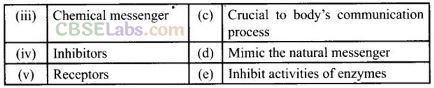
Solution:
(i -> b), (ii —> d), (iii —> a), (iv —> e), (v —> c)
(i) Antagonist drugs are used when blocking of message is required. For example, dopamine antagonist is a drug which blocks the dopamine receptors by receptor antagonism.
(ii) Agonist drugs are useful when there is lack of chemical messenger, e.g., heroin.
(iii) These chemical messengers are received at the binding sites of receptor. These communicate message between two neurons and that between neurons to muscles.
(iv) Inhibitors block the binding site of the enzyme and prevent the binding of the substrate, or inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme.
(v) Receptors are proteins that are crucial to body’s communication. They are embedded in the cell membrane in such a way that their small part possessing active site projects out of the surface of the membrane and opens on the outside region of the cell membrane.
Question 83. Match the classes of drugs given in Column I with their action given in Column II.
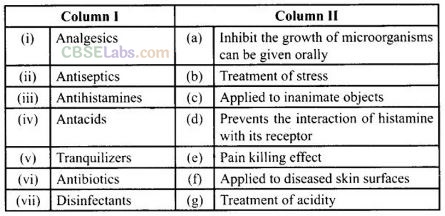
Solution:
(i —> e), (ii -> f), (iii —> d), (iv —> g), (v -> b), (vi —> a), (vii —» c)
(i) Analgesics reduce or abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusion, in coordination or paralysis or some other disturbances of nervous system, e.g., aspirin.
(ii) Antiseptics are the chemicals which either kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms. They are applied to living tissues such as wounds, cuts etc. e.g., tincture of iodine.
(iii) Antihistamines are anti-allergic drugs. These drugs interfere with the natural action of histamine by competing with histamine for binding sites of receptor where histamine exerts its effect, e.g., seldane.
(iv) Antacids are used to neutralize excess of acid released in stomach e.g., mixture of Mg(OFl)2 and Al(OH)3.
(v) Tranquilizers are used for the treatment of stress, and mid or even severe mental diseases e.g., equanil.
(vi) Antibiotics are antimicrobial drugs. Antibiotics are used as drugs to treat infections because of their low toxicity for humans and animals e.g., chloramphenicol.
(vii) Disinfectants are the chemicals which either kill or prevent the growth of microorganisms but they can be applied on non-living objects e.g., 1 per cent solution of phenol.
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices:
(a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain assertion.
(b) Assertion and reason-both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
(c) Both assertion and reason are wrong statement.
(d) Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statements.
(e) Assertion is wrong statements and reason is correct statement.
Question 84. Assertion (A): Penicillin (G) is an antihistamine.
Reason (R): Penicillin (G) is effective against gram positive as well as gram negative bacteria. .
Solution:
(c) Penicillin (G) is not a broad spectrum antibiotic so it is not effective against some gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
Question 85. Assertion (A): Sulpha drug contain sulphonamide group.
Reason (R): Salvarsan is a sulpha drug.
Solution:
(d) Salvarsan is an antibacterial drug containing arsenic and it does not contain sulphonamide group.
Question 86. Assertion (A): Receptors are crucial to body’s communication process. Reason (R): Receptors are proteins.
Solution:
(a) Neurotransmitters are small molecular which bind to the receptor for a very short time to transfer message to it and depart quickly unchanged after transferring the message, the receptor then forwards the message inside the cell. Receptors are proteins and they participate in the communication system of our body.
Question 87. Assertion (A): Enzymes have active sites that hold substrate molecule for a chemical reaction.
Reason (R): Drugs compete with natural substrate by attaching covalently to the active site of enzyme.
Solution:
(d) Drugs compete with natural substrate by attaching by weak bonds such as ionic bonding. H-bonding, van der Waals interaction, etc., to the active site of the enzyme.
Question 88. Assertion (A): Chemical messengers are chemicals that enable communi¬cation of message between two neutrons or between neurons and muscles. Reason (R): Chemicals enter the cell through receptor.
Solution:
(d) Chemicals bind to the receptors sites present on the surface of the membrane on the cell, but never enter the cell through receptor.
Question 89. Assertion (A): Transparent soaps are made by dissolving soaps in ethanol. Reason (R): Ethanol makes things invisible.
Solution:
(d) Ethanol removes air and moisture which scatter light.
Question 90. Assertion (A): Sodium chloride is added to precipitate soap after saponification.
Reason (R): Hydrolysis of esters of long chain fatty acids by alkali produces soap in colloidal form.
Solution:
(a) Hydrolysis of esters of long chain fatty acids by alkali gives soap a colloid. The process is called saponification.
Sodium chloride is added to precipitate soap which is in colloidal form.
Question 91. Assertion (A): Competitive inhibitors compete with natural substrate for their attachment on the active sites of enzymes.
Reason (R): In competitive inhibition, inhibitor binds to the allosteric site of the enzyme.
Solution:
(d) In competitive inhibition, inhibitor binds to the active site of the enzyme.
Question 92. Assertion (A): Non-competitive inhibitor inhibits the catalytic activity of enzyme by binding with its active site.
Reason (R): Non-competitive inhibitors changes the shape of the active site in such a way that substrate cannot recognize it.
Solution:
(e) Non-competitive inhibitors inhibit the catalytic activity of enzyme by binding with its allosteric site.
Question 93. Assertion (A): Chemical messenger gives message to the cell without entering the cell.
Reason (R): Chemical messenger is received at the binding site of receptor proteins.
Solution:
(b) Chemical messenger gives message to the cell without entering the cell because it is received at the binding site of the receptor.
Question 94. Assertion (A): Receptor proteins show selectivity for one chemical messenger over the other.
Reason (R): Chemical messenger binds to the receptor site and inhibits its natural function.
Solution:
(d) Chemical messenger binds the receptor site and gives the message to the cell without entering the cell.
Question 95. Assertion (A): All chemicals added to food items are called food preservatives.
Reason (R): All these chemicals increase the nutritive value of the food.
Solution:
(c) Chemicals which are added to food items to prevent them from spoiling against bacteria yeast and moulds are called food preservatives. They do not increase nutritive value of food.
Question 96. Assertion (A): Preservative are added to food items.
Reason (R): Preservatives inhibit the growth of microorganisms.
Solution:
(b) Preservatives are added to the food items because they inhibit the growth of microorganisms.
Question 97. Assertion (A): Artificial sweeteners are added to the food to control the intake of calories.
Reason (R): Most of the artificial sweeteners are inert and do not metabolise in the body.
Solution:
(b) Artificial sweeteners do not provide any calories because they are inert and do not metabolise in the body.
Long Answer Type Questions
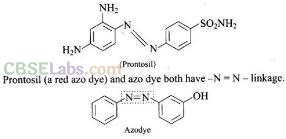
Question 98. In what respect do prontosil and Salvarsan resemble? Is there any resemblance between azo dye and prontosil? Explain.
Solution:
Both prontosil and Salvarsan and antibacterial drugs (antimicrobials) discovered by Paul Ehrlich. Salvarsan is also known as arsphenamine. It is an organoarsenic molecule and has -As = As- double bond.
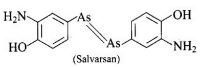
Salvarsan and prontosil show similarity in their structure. Both of these drugs are antimicrobials. Salvarsan contains -As = As- linkage whereas prontosil has -N = N- linkage.
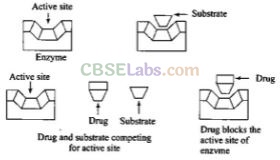
Question 99. How do enzymes catalyse a chemical reaction in the living system? Explain drug target interaction taking the example of enzyme as target.
Solution:
Enzymes catalyse many reactions by
(i) Holding the substrate for a chemical reaction. Active sites hold the substrate molecule in a suitable positions So that it can be attacked by the reagent effectively. Substrates bind to the active site of enzyme through ionic or hydrogen bonding or van der Waals or dipole-dipole, interactions.
(ii) Enzyme provides functional groups that will attack the substrate to carry out the chemical reaction. This function is carried out chemical
reaction: This function iscarried out by some other amino acid residues of protein present on the active site of the enzyme. These free amino group to attack the substrate and bring about chemical reaction. Drugs can inhibit these activities by blocking site of enzyme and prevent the binding of substrate. Such drugs are called enzyme inhibitors.
Question 100. Synthetic detergents have advantage over usual soaps as far as cleansing power is concerned. But use of synthetic detergents over a long time creates environmental pollution. How can the pollution caused by synthetic detergents be minimized? Classify the detergents according to their chemical nature.
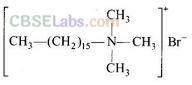
Solution:
Synthetic detergents are cleansing agents which have all the properties of soaps, but which actually do not contain any soap. These can be used both in soft and hard water as they given foam even in hard water. Detergents can be classified into three groups according their chemical nature.
(i) Anionic detergents – These are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons and sodium alkyl benzene sulphonates. e.g., CH
3
(CH
2
)
10
CH
2
OSO
3
–
Na
+
Anionic part of these detergents is involved in cleansing action.
(ii) Cationic detergents – These are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides or bromides as anions.
(iii) Non-ionic detergents – These do not contain any ion in their constitution, e.g., detergent formed by steric acid and polyethylene glycol. CH
3
(CH
2
)
16
C00(CH
2
CH
2
0)
n
CH
2
CH
2
OH.
Pollution by synthetic detergents can be minimized by reducing the branching of hydrocarbon chain or using unbranched hydrocarbons.
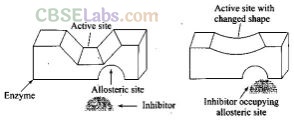
Question 101. What are enzyme inhibitors? Classify them on the basis of their mode of attachments on the active site of enzymes. With the help of diagrams explain how do inhibitors inhibit the enzymatic activity.
Ckemistnj in Evenjdai] Life 325
Solution:
Enzyme inhibitors block the binding site of enzyme and prevent the binding of substrate and then inhibit the catalytic activity of enzyme. They act in two different ways.
(i) Drugs which compete with substrate for their attachment on the active sites of enzymes are called competitive inhibitor.
(ii) Some drugs bind to a different site of enzyme called allosteric site. It changes the shape of the active site and substrate cannot recognize it. Such enzymes are called non-competitive inhibitor the bond formed between enzyme and an inhibitor is strong covalent bond then enzyme is blocked permanently.
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Solutions
- Chapter 1 Solid State
- Chapter 2 Solution
- Chapter 3 Electrochemistry
- Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics
- Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry
- Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements
- Chapter 8 The d- and f-Block Elements
- Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds
- Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Chapter 13 Amines
- Chapter 14 Biomolecules
- Chapter 15 Polymers
- Chapter 16 Chemistry in Everyday Life