NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory
Q1. A cubic vessel (with face horizontal + vertical) contains an ideal gas at NTP. The vessel is being carried by a rocket which is moving at a speed of500 ms’
1
in
vertical
direction. The pressure of the gas inside the vessel as observed by us on the ground
(a) remains the same because 500 ms’
1
is very much smaller than
v
rms
of the gas.
(b) remains the same because
motion
of the vessel as a whole does not affect the relative motion of the gas molecules and the walls.
(c) will increase by a factor equal to (v
2
rms
+ (500)
2
)/v
2
rms
where
v
rms
was the original mean square velocity of the gas.
(d) will be different on the top wall and bottom wall of the vessel.
Sol: (b) According to the ideal gas law,
P=nRT/V, here temperature of the vessel remain unchanged hence, the
pressure remains same from that point of view.
Now, let us discuss the phenomenon inside the vessel. The gas molecules keep on colliding among themselves as well as with the walls of containing vessel. These collisions are perfectly elastic.
The number of collisions per unit volume in a gas remains constant. So, the pressure of the gas inside the vessel remains the same because motion of the vessel as a whole does not affect the relative motion of the gas molecules with respect to the walls.
Q2. 1 mole of an ideal gas is contained in a cubical volume V, ABCDEFGH at 300 K (figure). One face of the cube (EFGH) is made up of a material which totally absorbs any gas molecule incident on it. At any given time,
(a) the pressure on EFGH would be zero
(b) the pressure on all the faces will be equal
(c) the pressure of EFGH would be double the pressure on ABCD
(d) the pressure on EFGH would be half that on ABCD
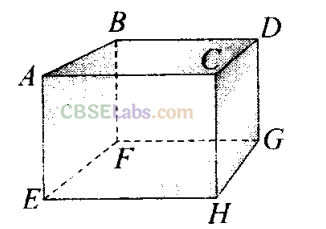
Sol:
(d) In an ideal gas, the gas molecules keep on colliding among themselves as well as with the walls of containing vessel. These collisions are perfectly elastic. So, their kinetic energy and momentum remains conserved.
So, the momentum transferred to the face ABCD = 2mv And the gas molecule is absorbed by the face EFGH. Hence it does not rebound. So, momentum transferred to the face EFGH = mv.
And the pressure on the faces is due to the total momentum to the faces. So, pressure on EFGH would be half that on ABCD.
Q3. Boyle’s law is applicable for an
(a) adiabatic process
(b) isothermal process
(c) isobaric process
(d) isochoric process
Sol: (b)
Key concept:
Boyle’s law: For a given mass of an ideal gas at constant temperature, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure.
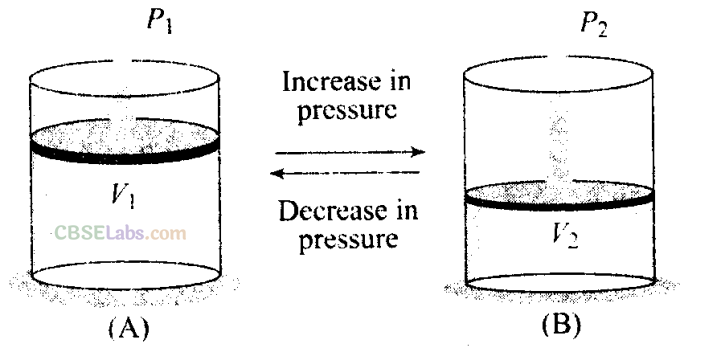
So we can say that when temperature is constant, Boyle’s law is applicable.
i.e., PV= nRT= constant
=>PV = constant (at constant temperature)
i.e.. p ∝ 1/V— [where, P = pressure. V= volume]
So, this law is applicable for an isothermal process, in which temperature remain constant.
Q4. A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction ( figure). If the temperature is increased
(a) both P and V of the gas will change
(b) only P will increase according to Charles’ law
(c) V will change but not P
(d) P will change but not V
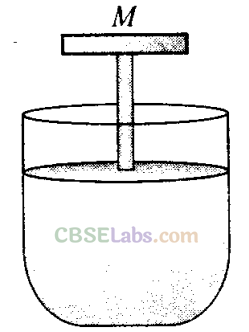

Q5. Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure. At two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P
l
and
P
2
?
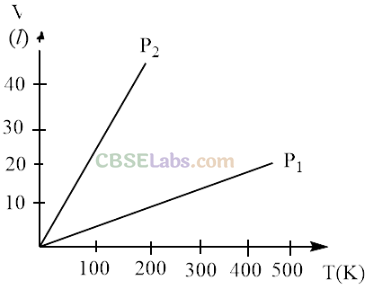
(a)P
1
> P
2
(b) P
1 =
P
2
(c) P
1
< P
2
(d) Data is insufficient


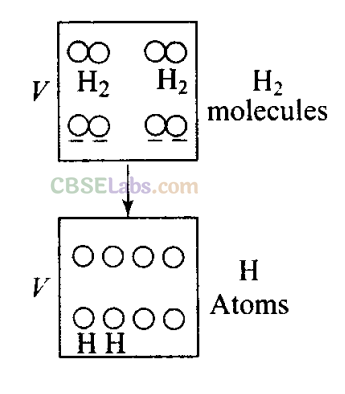
Q6. 1 mole of H 2 gas is contained in a box of volume V = 1.00 m 3 at T = 300 K. The gas is heated to a temperature of T= 3000 K and the gas gets converted to a gas of hydrogen atoms. The final pressure would be (considering all gases to be ideal)
(a) same as the pressure initially
(b) 2 times the pressure initially
(c) 10 times the pressure initially
(d) 20 times the pressure initially
Sol:
(d) The situation is shown in the diagram, H
2
gas is contained in a box is heated and gets converted to a gas of hydrogen atoms. Then the number of moles would become twice.
According to gas equation,
PV= nRT
P = Pressure of gas, n = Number of moles
R = Gas constant, T = Temperature PV=nRT
As volume (V) of the container is constant. Hence, when temperature (T) becomes 10 times, (from 300 K to 3000 K) pressure (P) also becomes 10 times, asP∝ T.
Pressure is due to the bombardment of particles and as gases break, the number of moles becomes twice of initial, so n
2
= 2n
1

Q7. A vessel of volume V contains a mixture of 1 mole of hydrogen and 1 mole of oxygen (both considered as ideal). Let f
1
(v)
dv
denotes the fraction of molecules with speed between v and (v +
dv
) with f
2
(v)
dv
, similarly for oxygen. Then,
(a) f
1
(v) + f
2
(v) = f (v) obeys the Maxwell’s distribution law
(b) f
1
(v), f
2
(v) will obey
the Maxwell’s
distribution law separately
(c) neither f
1
(v)nor f
2
(v)will obey the Maxwell’s distribution law
(d) f
2
(v) and f
1
(v)will be the same


The masses of hydrogen and oxygen molecules are different.
For a function f(v), the number of molecules dn = f[v), which are having speeds between v and v + dv. The Maxwell-Boltzmann speed distributionfunction ( N
v
= dn/dv depends on the mass of the gas molecules.
For each function f
1
(v) and f
2
(v), n will be different, hence each function f
1
(v) and f
2
(v) will obey the Maxwell’s distribution law separately.
Q8. An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure P. volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be
(a) 1.1 P
(b) P
(c) less than P
(d) between P and 1.1
Sol:
(d) According to the equation of ideal gas, PV= nRT
P = pressure
V = volume
n = number of moles of gases
R = gas constant
T = temperature
Thus we have to rewrite this equation in such a way that no. of moles is given by,

More Than One Correct Answer Type
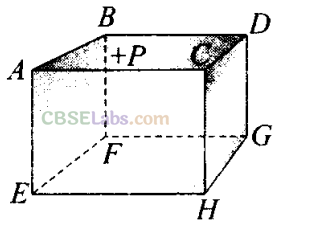
Q9. ABCDEFGH is a hollow cube made of an insulator (figure) face A BCD has positive charge on it. Inside the cube, we have ionised hydrogen.
The usual kinetic theory expression for pressure
(a) will be valid
(b) will not be valid, since the ions would experience forces other than due to collisions with the walls
(c) will not be valid, since collisions with walls would not be elastic
(d) will not be valid because isotropy is lost
Sol:
(b, d) According to the problem, ionized hydrogen is present inside the cube, they are having charge. Now, due to the presence of positive charge on the surface A BCD hydrogen ions would experience forces other than the forces due to collision with the walls of container. So, these forces must be of electrostatic nature. Hence, Isotropy of system is lost at only one face ABCD because of the presence of external positive charge. The usual expression for pressure on the basis of kinetic theory will be valid.
Q10. Diatomic molecules like hydrogen have energies due to both translational as well as rotational motion. From the equation in kinetic theory PV = 2/3 E,E is
(a) the total energy per unit volume
(b) only the translational part of energy because rotational energy is very small compared to the translational energy
(c) only the translational part of the energy because during collisions with the wall pressure relates to change in linear momentum
(d) the translational part of the energy because rotational energies of molecules can be of either sign and its average over all the molecules is zero
Sol:
(c) According to kinetic theory equation, PV = 2/3 E [where P= Pressure V = volume]
E is representing only translational part of energy. Internal energy contains all types of energies like translational, rotational, vibrational etc. But the molecules of an ideal gas is treated as point masses in kinetic theory, so its kinetic energy is only due to translational motion. Point mass does not have rotational or vibrational motion. Here, we assumed that the walls only exert perpendicular forces on molecules. They do not exert any parallel force, hence there will not be any type of rotation present. The wall produces only change in translational motion.
Q11. In a diatomic molecule, the rotational energy at a given temperature
(a) obeys Maxwell’s distribution
(b) have the same value for all molecules
(c) equals the translational kinetic energy for each molecule
(d) is (2/3)rd the translational kinetic energy for each molecule
Sol:
(a, d)
Key concept: Kinetic Energy of Ideal Gas:
Molecules of ideal gases possess only translational motion. So they possess only translational kinetic energy.
According to the problem we have to find the rotational energy of a diatomic molecule in the terms of translation kinetic energy.
First let us check the options by picking them one by one.
(a) Translational kinetic energy and rotational kinetic energy both obey Maxwell’s distribution independent of each other.
(b) Rotational kinetic energy is different for different molecule.
(c) Molecules of ideal gases possess only translational motion. So they possess only translational kinetic energy. But in case of non-ideal gas there is a smaller rotational energy.
(d) Here, 2 rotational and 3 translational energies are associated with each molecule. Translation kinetic energy of each molecule,
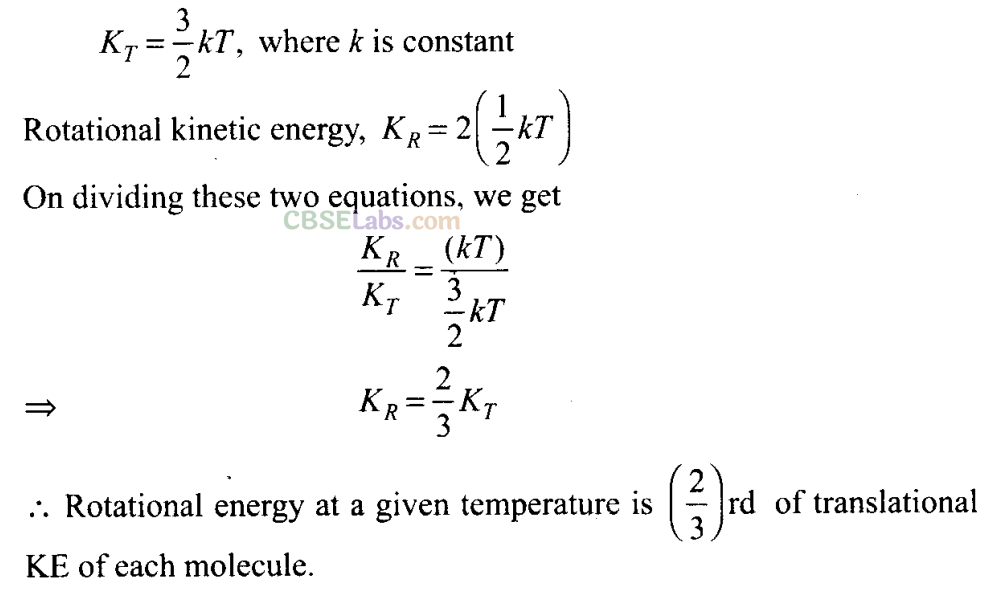
Important points: Kinetic energy per molecule of a gas does not depend upon the mass of the molecule but only depends upon the temperature of the gas.

Kinetic energy per mole of gas depends only upon the temperature of gas.
Kinetic energy per gram of gas depend upon the temperature as well molecular weight (or mass of one molecule) of the gas.
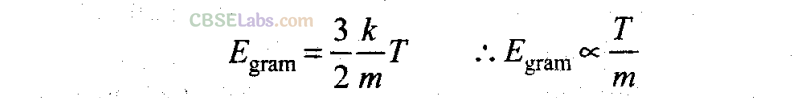
From the above expressions it is clear that higher the temperature of the gas, more will be the average kinetic energy possessed by the gas molecules at T= 0, E = 0, i.e. at absolute zero the molecular motion stops.
Q12. Which of the following diagrams (figure) depicts ideal gas behaviour ?
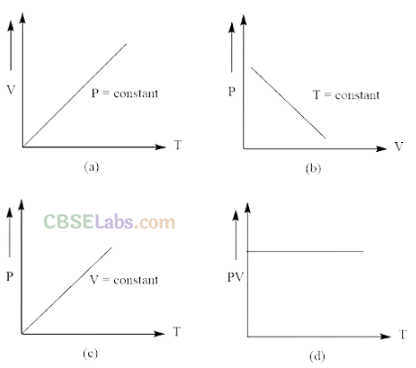

So, graph of PV versus T will be a straight line parallel to the temperature axis (x-axis).
i.e., slope of this graph will be zero.
So, (d) is not correct.
Q13. When an ideal gas is compressed adiabatically, its temperature rises the molecules on the average have more kinetic energy than before. The kinetic energy increases,
(a) because of collisions with moving parts of the wall only
(b) because of collisions with the entire wall
(c) because the molecules gets accelerated in their motion inside the volume
(d) because of redistribution of energy amongst the molecules
Sol:
(a) Since the gas is ideal and the collisions of the molecules are elastic. When the molecules collides with the moving parts of the wall, its kinetic energy increases. But the total kinetic energy of the system will remain conserved. When the gas is compressed adiabatically, the total work done on the gas increases, its internal energy which in turn increases the KE of gas molecules and hence, the collisions between molecules also increases.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q14. Calculate the number of atoms in 39.4 g gold. Molar mass of gold is 197 g mole
-1

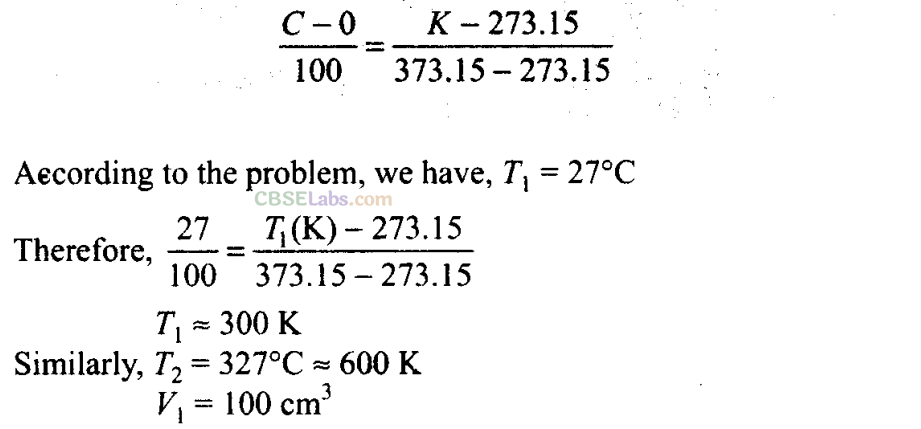
Q15. The volume of a given mass of a gas at 27°C, 1 atm is 100 cc. What will be its volume at 327°C?
Sol:
Key concept: Here the temperatures are given in Celsius. To apply ideal gas equation, we must convert the given temperature in kelvin. So, to convert them in kelvin we use the relation

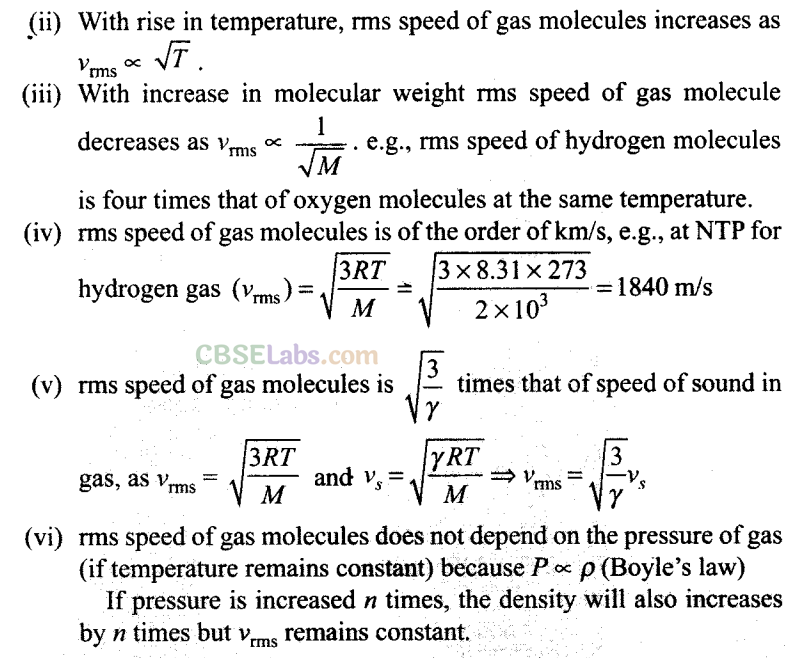
Q16. The molecules of a given mass a gas have
root
mean square speeds of 100 ms
-1
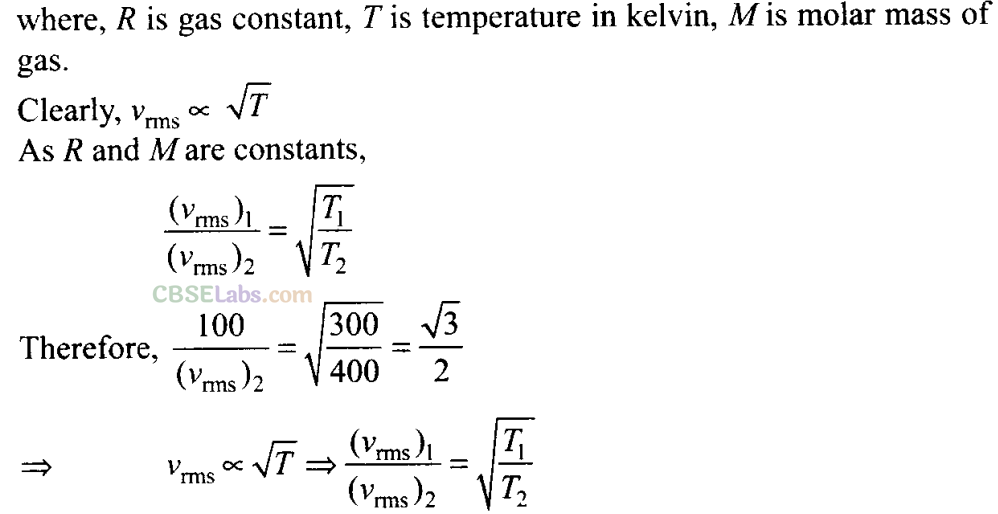
at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
Sol: Key concept:
Root Mean Square Speed: It is defined as the square root of mean of squares of the speed of different molecules

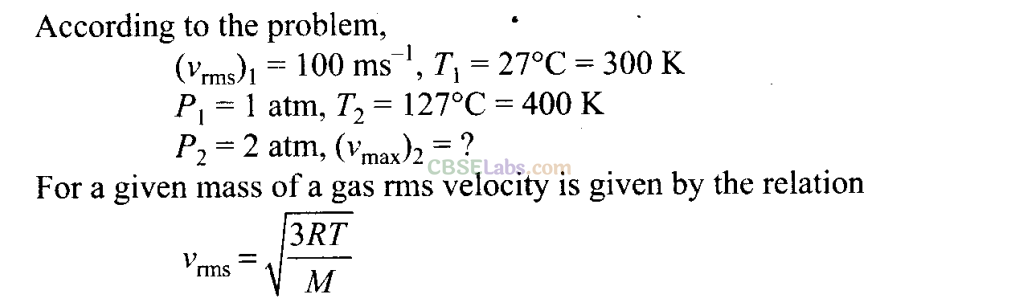
Q17. Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 x 10
16
ms
-1
and 1 x I0
6
ms
-1
respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
Sol:
rms speed for w-molecules is defined as:
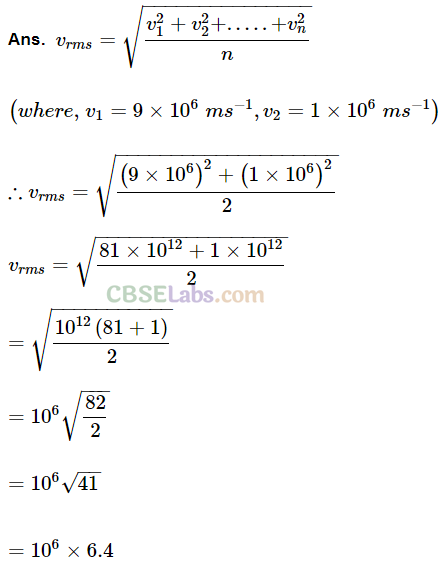
![]()
Q18. A gas mixture consists of 2.0 moIes of oxygen and 4.0 moles of neon at temperature T. Neglecting all vibrational modes, calculate the total internal energy of the system. (Oxygen has two rotational modes.)
Sol:
Key concept: Degree of Freedom:
The term degree of freedom of a system refers to the possible independent motions, systems can have or
The total number of independent modes (ways) in which a system can possess energy is called the degree of freedom (f).
The independent motions can be translational, rotational or vibrational or any combination of these.
So the degree of freedom are of three types:
(i) Translational degree of freedom
(ii) Rotational degree of freedom
(iii) Vibrational degree of freedom
General expression for degree of freedom
f=3A- B; where A = Number of independent particles.
B = Number of independent restriction

Diatomic gas: Molecules of diatomic gas are made up of two atoms joined rigidly to one another through a bond. This cannot only move bodily, but also rotate about one of the three co-ordinate axes. However its moment of inertia about the axis joining the two atoms is negligible compared to that about the other two axes.
Hence it can have only two rotational motion. Thus a diatomic molecule has 5 degree of freedom: 3 translational and 2 rotational.
Monoatomic gas: Molecules of
monoatomic gas can move in any direction in space so it can have three independent motions and hence 3 degrees of freedom (all translational).
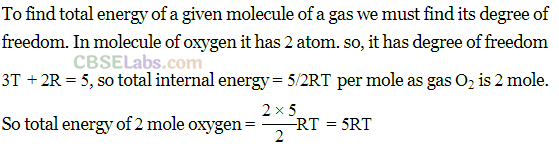
Neon (Ne) is a monoatomic gas having 3 degrees of freedom.
Energy per mole = 3/2RT
Hence, Energy = 4 x3/2 RT = 6RT ….(ii)
[Using Eqs. (i) and (ii)]
Total energy = 5RT = 6RT= 11RT
Q19. Calculate the ratio of the mean free paths of the molecules of two gases having molecular diameters 1 A and 2 A. The gases may be considered under identical conditions of temperature, pressure and volume.

Short Answer Type Questions


When the partition is removed, the gases get mixed without any loss of energy. The mixture now attains a common equilibrium pressure and the total volume of the system is sum of the volume of individual chambers V1 and V2. Let P be the pressure after the partition is removed.
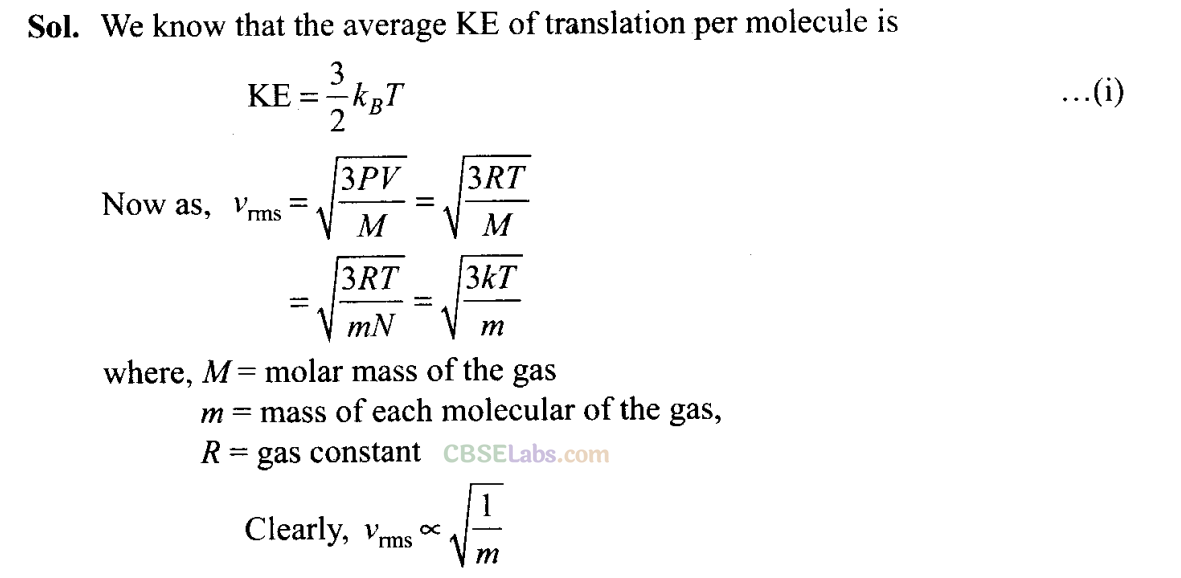
Q21. A gas mixture consists of molecules of A, B and C with masses m A > m B > m c . Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of (a) average KE, (b) rms speeds.
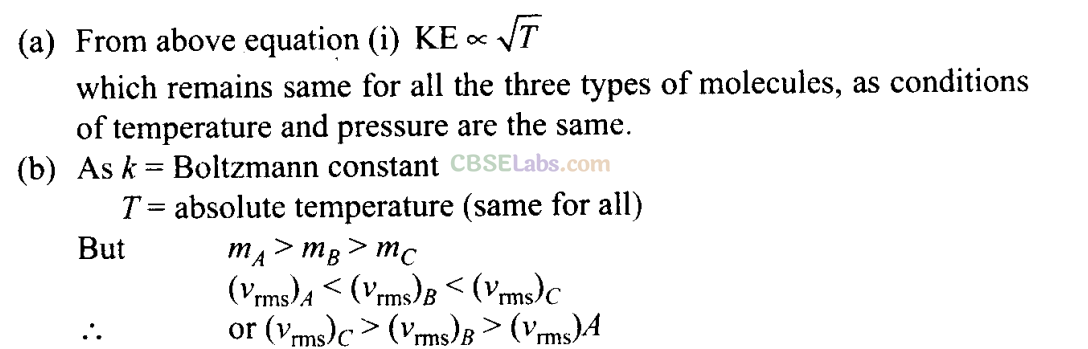
Q22. We have 0.5 g of hydrogen gas in a cubic chamber of size 3 cm kept at NTP. The gas in the chamber is compressed keeping the temperature constant till a final pressure of 100 atm. Is one justified in assuming the ideal gas law, in the final state? (Hydrogen molecules can be consider as spheres of radius 1 A).

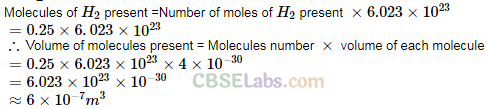
Q23. When air is pumped into a cycle tyre the volume and pressure of the air in the tyre both are increased. What about Boyle’s law in this case?
Sol:
Here, according to the question, when air is pumped, more molecules are pumped and Boyle’s law is stated for situation where, mass of molecules remains constant.
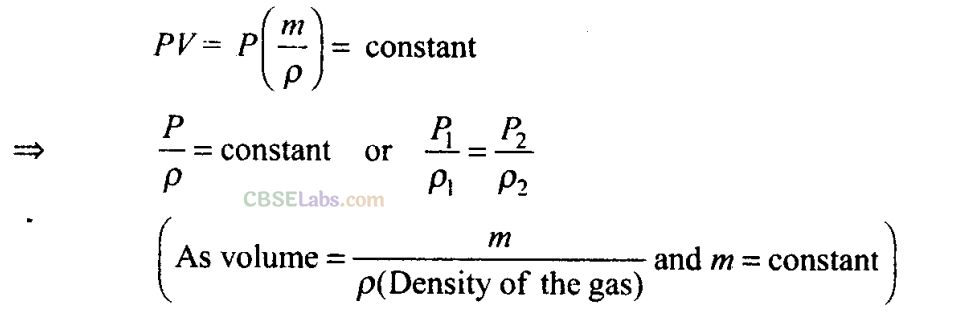
In this case, when air is pumped into a cycle tyre, mass of air in it increases as the number of air molecules keep increasing. Hence, this is a case of variable mass, Boyle’s law (and even Charle’s law) is only applicable in situations, where mass of gas molecules remains fixed. Hence, Boyle’s law is not applicable in this case.
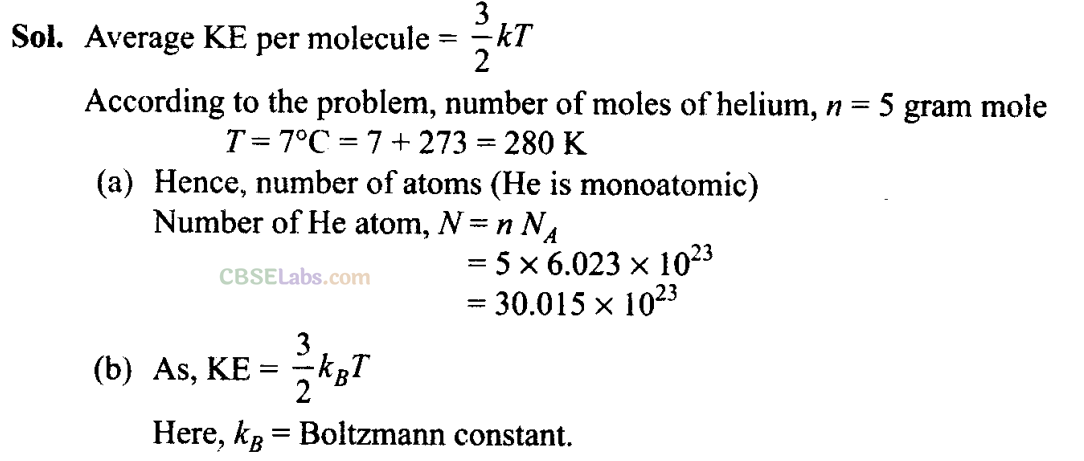
Q24. A balloon has 5.0 mole of helium at 7°C. Calculate
(a) the number of atoms of helium in the balloon.
(b) the total internal energy of the system.
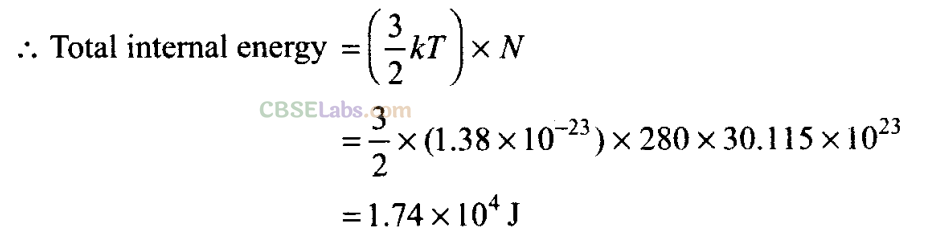
Important point:
The above degrees of freedom are shown at room temperature. Further at high temperature, in case of diatomic or polyatomic molecules, the atoms with in the molecule may also vibrate with respect to each other. In such cases, the molecule will have an additional degrees of freedom, due to vibrational motion.
An object which vibrates in one dimension has two additional degrees of freedom. One for the potential energy and one for the kinetic energy of vibration. Helium is a mono atomic gas and It has only 3 degrees of freedom. But after addition its degree of freedom will be 5.
Q25. Calculate the number of degrees of freedom of molecules of hydrogen in 1 cc of hydrogen gas at NTP.
Sol:
Key concept: Total number of degrees of freedom in a thermodynamical system = Number of degrees of freedom associated per molecule x number of molecules.

Q26. An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity v
0
. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
Sol: Since, the container is suddenly stopped which is initially moving with velocity v
0
, there is no time for exchange of heat in the process. Then total KE of the container is transferred to gas molecules in the form of translational KE, thereby increasing the absolute temperature.
Let n be the no. of moles of the monoatomic gas in the container. Since molar mass of the gas is m.
Total mass of the container, M = mn
KE of molecules due to velocity v
0
,
KE = 1/2(mn) v
0
2
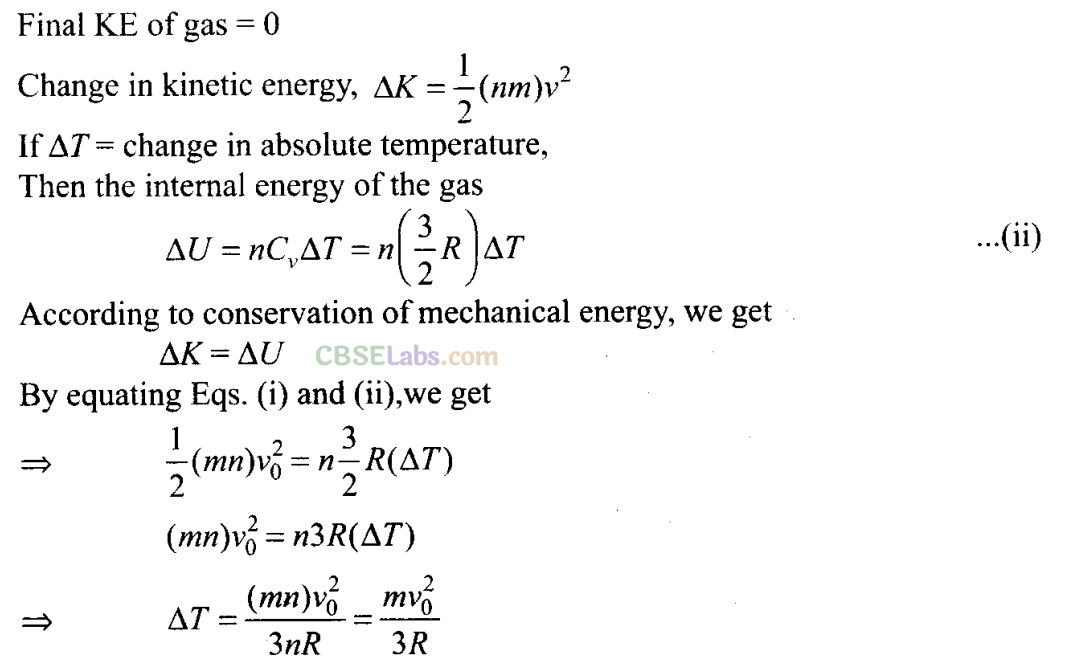
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Physics Solutions
- Chapter 1 Units and Measurements
- Chapter 2 Motion in a Straight Line
- Chapter 3 Motion in a Plane
- Chapter 4 Laws of Motion
- Chapter 5 Work, Energy and Power
- Chapter 6 System of Particles and Rotational Motion
- Chapter 7 Gravitation
- Chapter 8 Mechanical Properties of Solids
- Chapter 9 Mechanical Properties of Fluids
- Chapter 10 Thermal Properties of Matter
- Chapter 11 Thermodynamics
- Chapter 12 Kinetic Theory
- Chapter 13 Oscillations
- Chapter 14 Waves