NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions

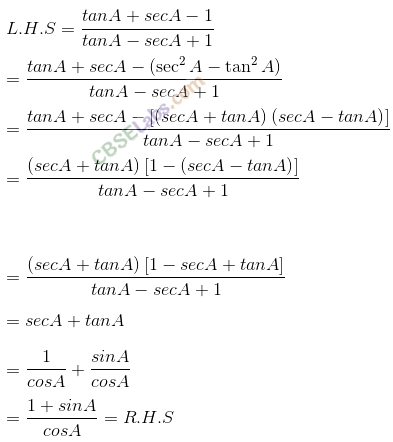
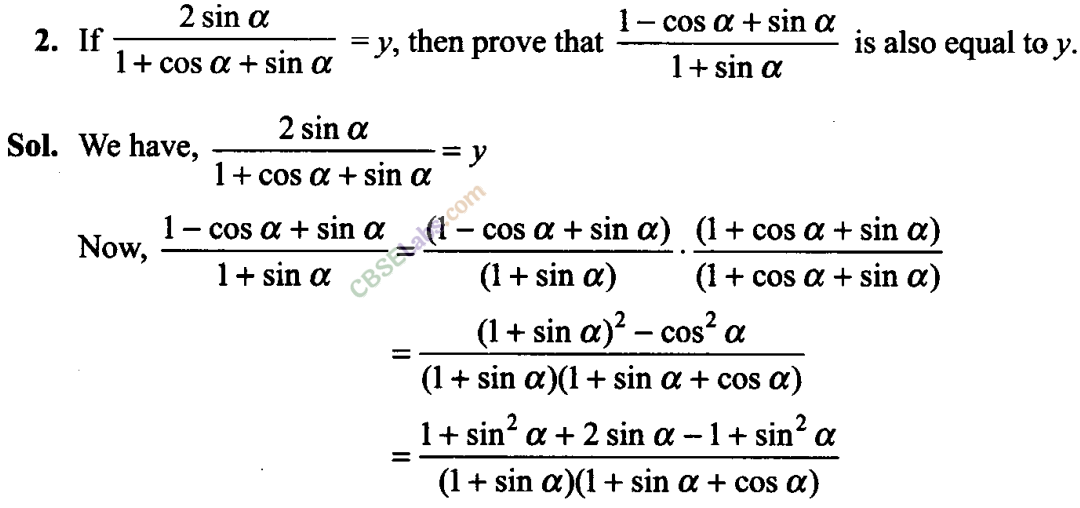
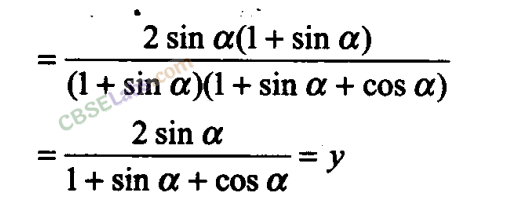
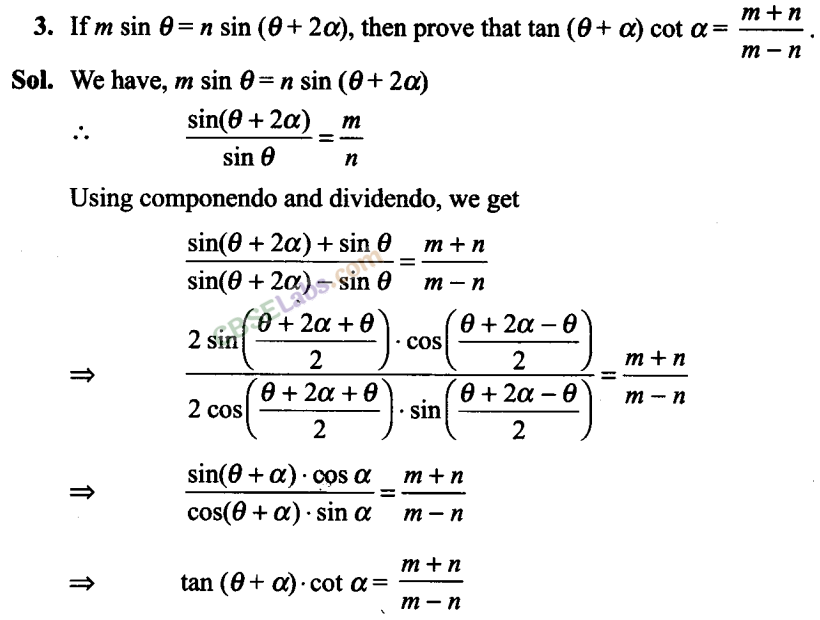
Q4. If cos (α + ) =4/5 and sin (α- )=5/13 , where α lie between 0 and π/4, then find the value of tan 2α.
![]()
Sol:
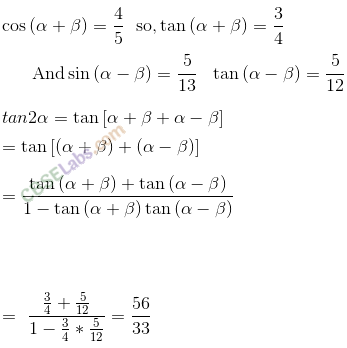
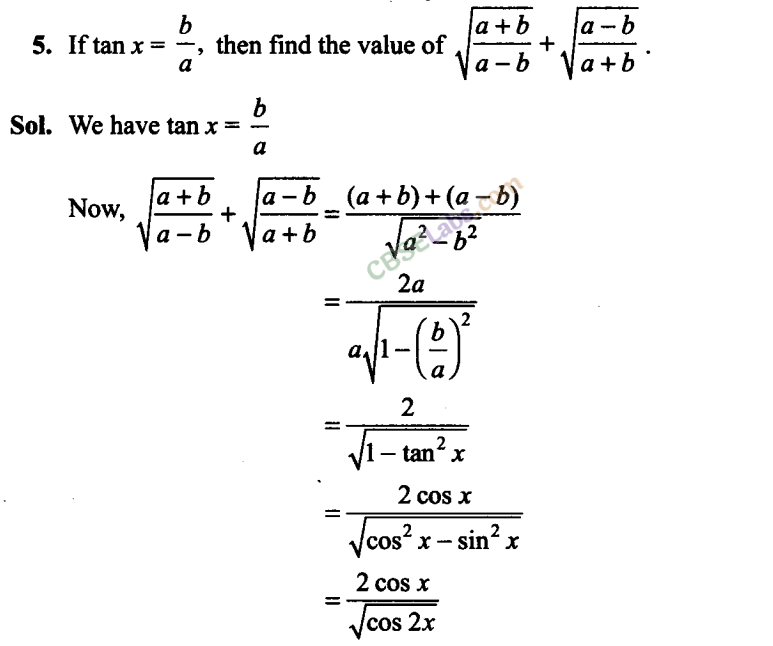
Q6. Prove that cos cos /2- cos 3 cos 9/2 = sin 7/2 sin 4 .
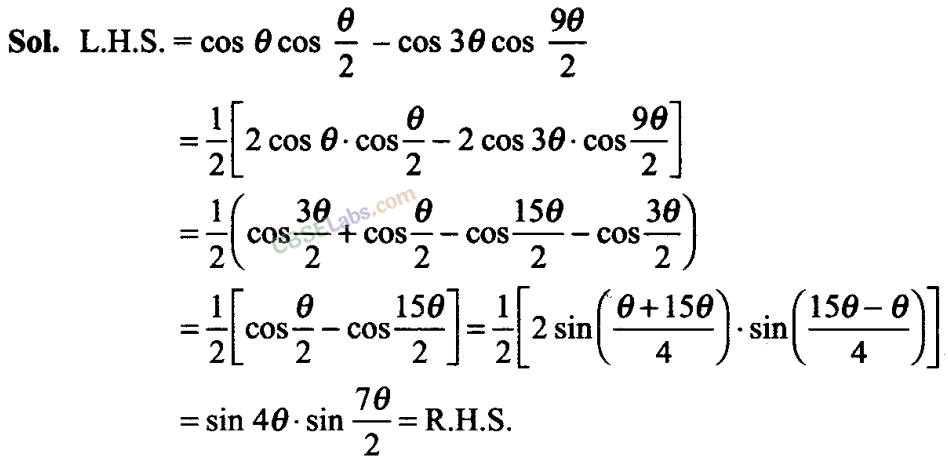
Q7. If a cos θ + b sin θ =m and a sin θ -b cosθ = n, then show that a
2
+ b
2
-m
2
+ n
2
Sol:
We have, a cos θ + b sin θ = m (i)
and a sin θ -bcos θ = n (ii)
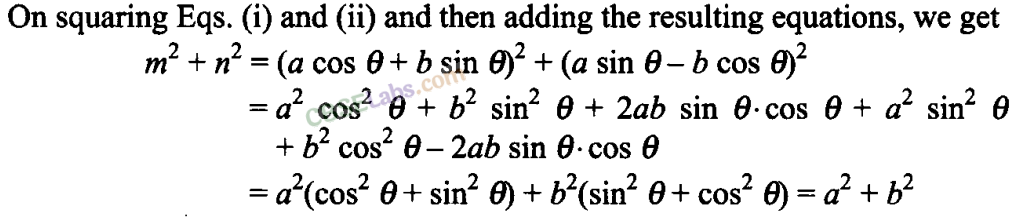
Q8. Find the value of tan 22°30′
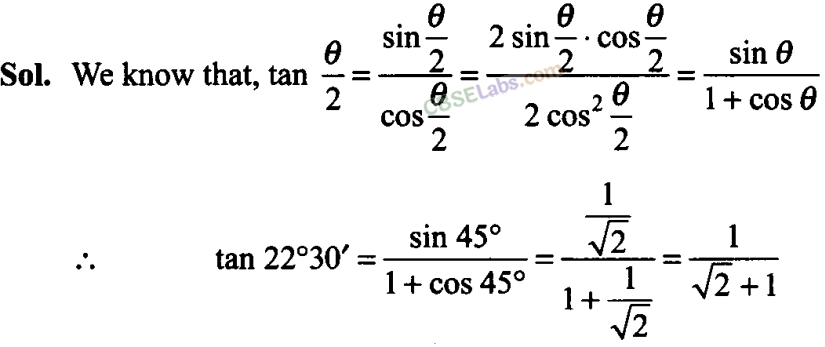
Q9. Prove that sin 4A = 4 sin A cos
3
A – 4 cos A sin
3
A.
Sol:
L.H.S. = sin 4A
= 2 sin 2A- cos 2A = 2(2 sin A cosA)(cos
2
A – sin
2
A)
= 4 sin A • cos
3
A – 4 cos A sin
3
A = R.H.S.
Q10. If tan + sin = m and tan – sin = n, then prove that m
2
-n
2
= 4 sin tan
Sol:
We have, tan + sin = m (i)
And tan -sin =n (ii)
Now, m + n = 2 tan
And m – n = 2 sin.
(m + n)(m -n) = 4 sin 6
tan
m
2
-n
2
= 4
sin
-tan
Q11. If tan (A + B) =p and tan (A – B) = q, then show that tan 2A = p+q / 1 – pq
Sol:
We have tan (A + B) =p and tan (A – B) = q
tan2A = tan [(A + B) + (A-B)]
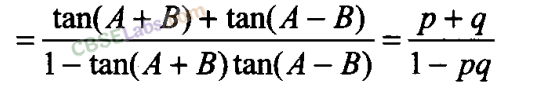
Q12. If cos + cos = 0 = sin + sin β, then prove that cos 2 + cos 2β = -2 cos (α + ).
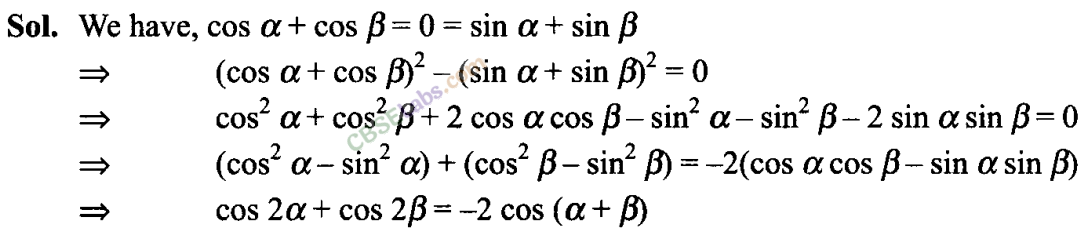
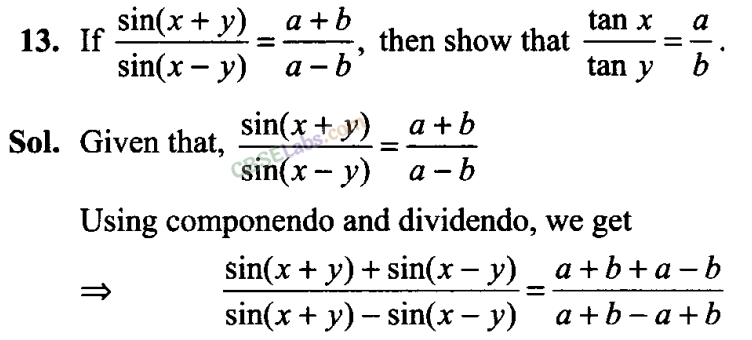
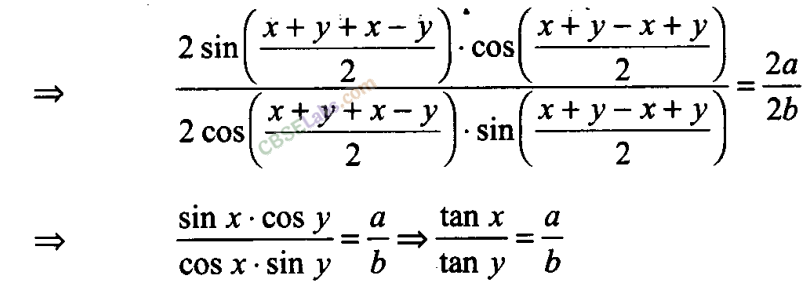
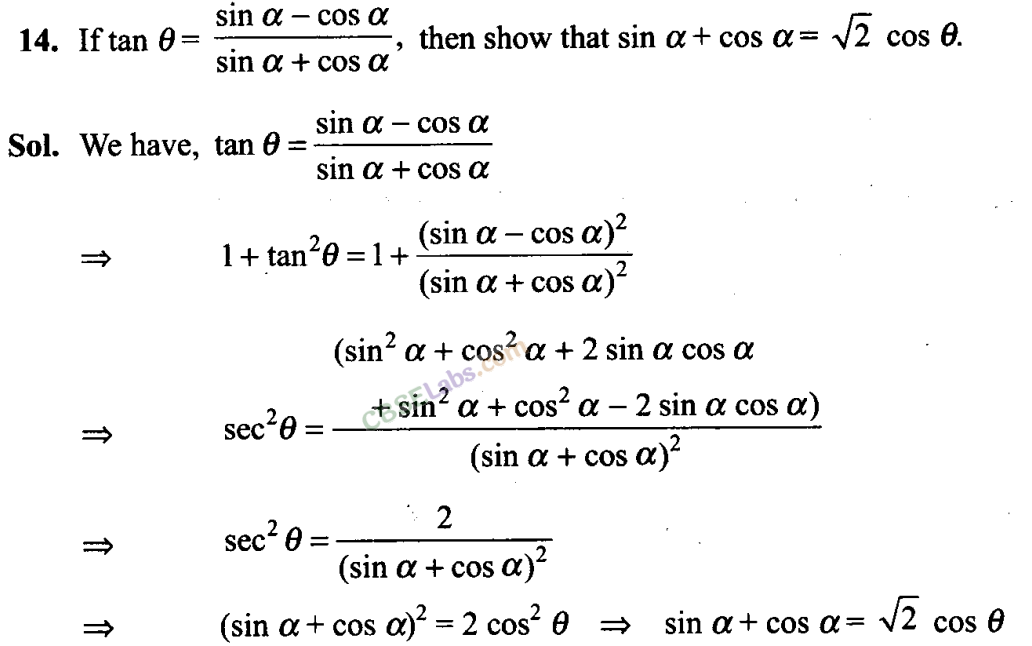
Q15. If sin θ+ cos θ =1, then find the general value of θ
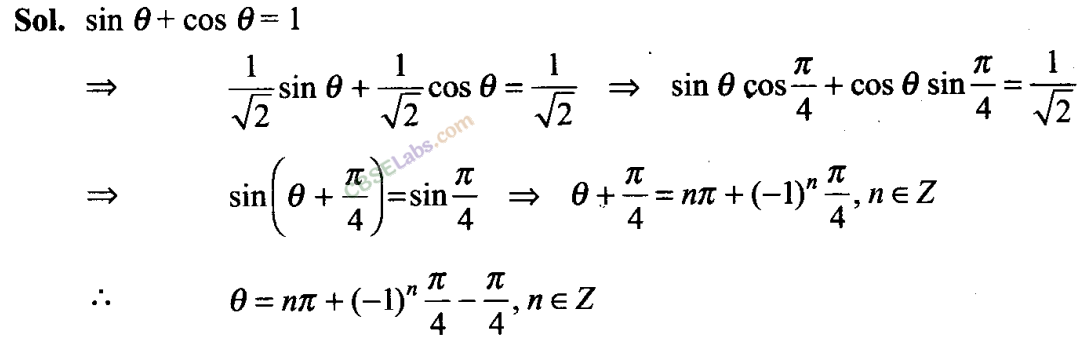
Q16. Find the most general value of θ satisfying the equation tan θ = -1 and cos θ = 1/√2 .
Sol:
We have tan θ = -1 and cos θ =1/√2 .
So, θ lies in IV quadrant.
θ = 7/4
So, general solution is θ = 7π/4 + 2 n π, n∈ Z
Q17. If cot θ + tan θ = 2 cosec θ, then find the general value of θ
Sol:
Given that, cot θ + tan θ = 2 cosec θ
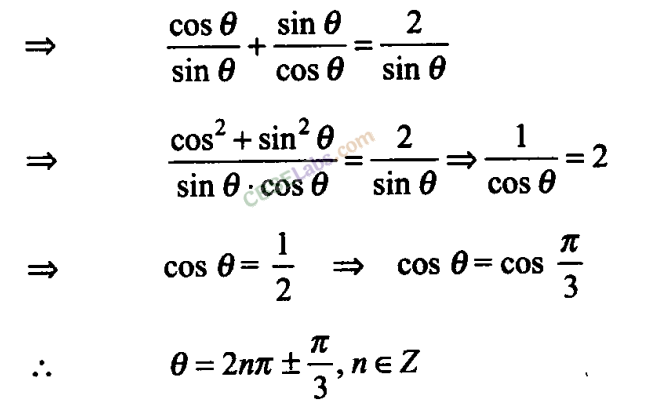
Q18. If 2 sin
2
θ =3 cos θ, where O≤θ≤2, then find the value of θ
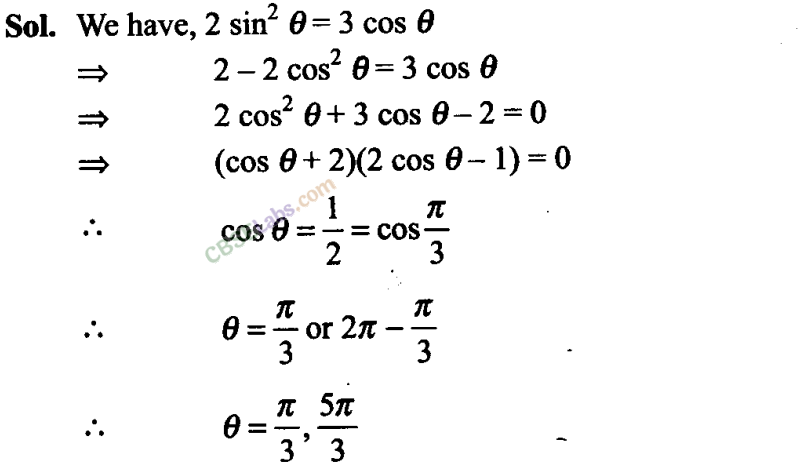
Q19. If sec x cos 5x + 1 = 0, where 0 < x <π/2 , then find the value of x.
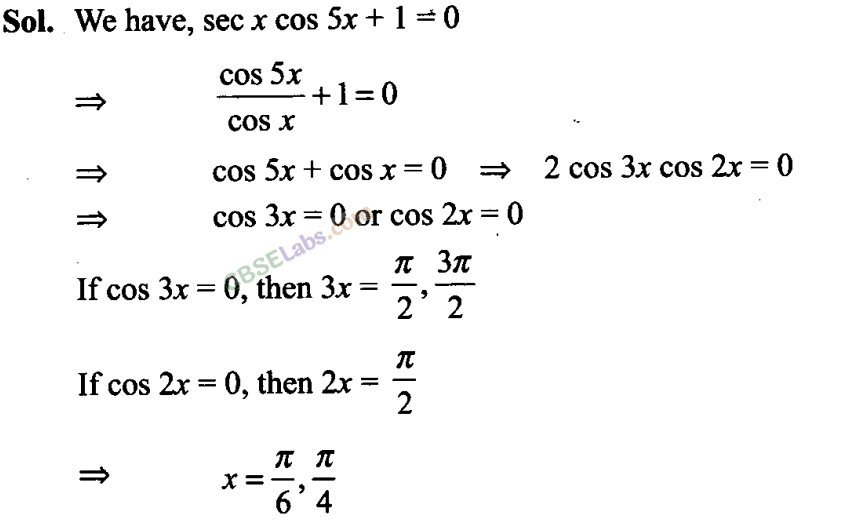
Long Answer Type Questions
Q20. If sin(θ + α) = a and sin(θ + β) = b , then prove that cos2(α – β) – 4abcos(α – β) = 1-2a
2
-2b
2
Sol:
We have sin(θ + α) = a —(i)
sin(θ + β) = b ——-(ii)
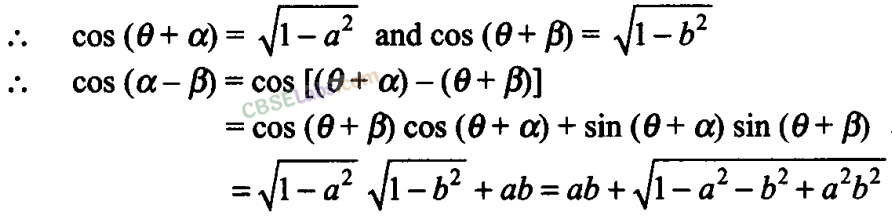
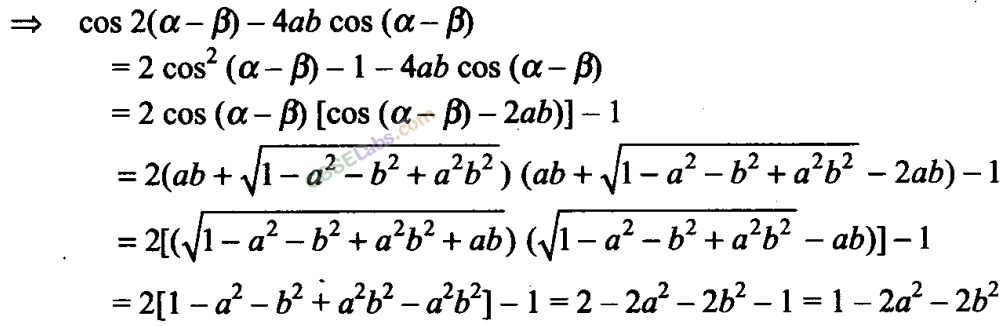
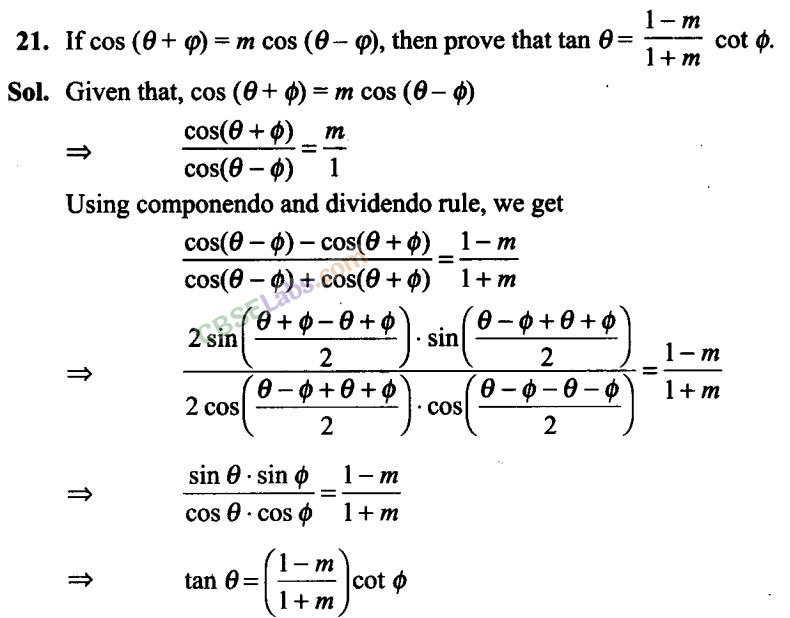
Q22. Find the value of the expression
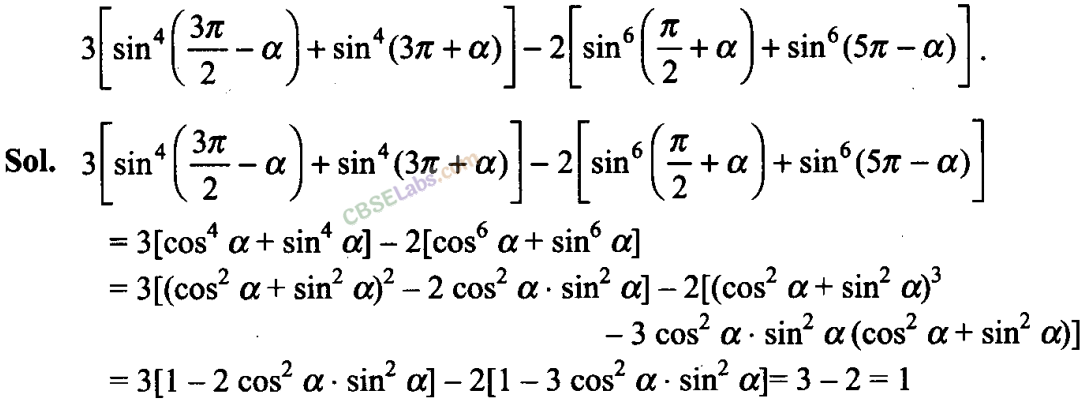
Q23. If a cos 2+b sin 2 = c has α and β as its roots, then prove that tan α +tan β = 2b/a+c
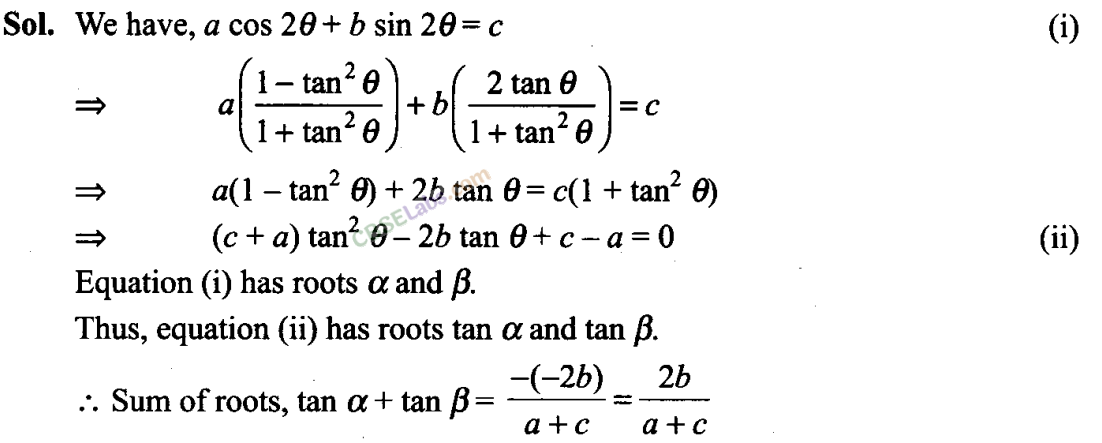
Q24. If x = sec ϕ-tanϕandy = cosec ϕ + cot ϕ then show that xy + x -y +1=0.
Q25. If lies in the first quadrant and cos =8/17 , then find the value of cos (30° + ) + cos (45° – ) + cos (120° – ).
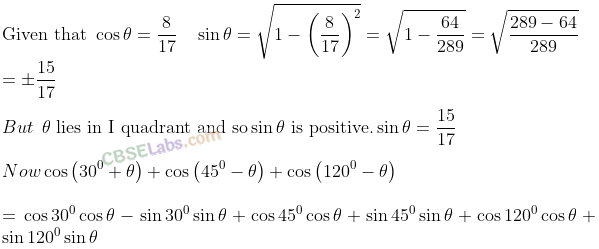
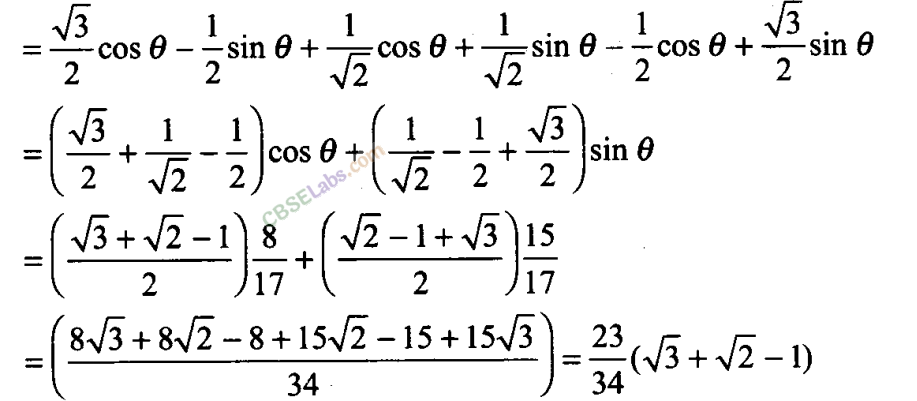
Q26. Find the value of the expression cos
4
π/8 + cos
4
3π/8 + cos
4
5π/8 + cos
4
7π/8
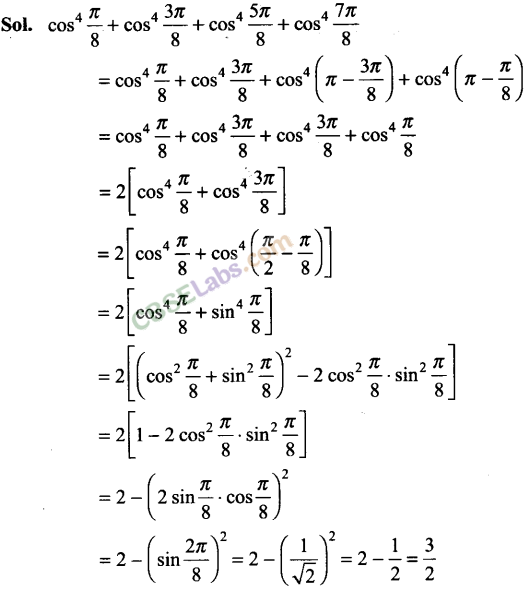
Q27. Find the general solution of the equation 5 cos
2
+7 sin
2
-6 = 0.
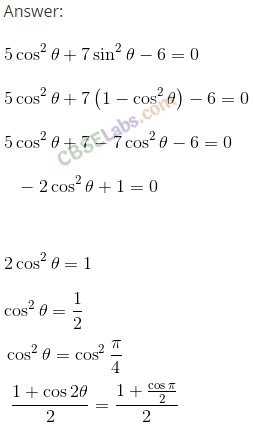
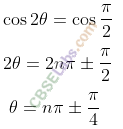
Q28. Find the general solution of‘the equation sin x – 3 sin 2x + sin 3x = cos x – 3 cos 2x + cos 3x.
Sol:
We have, (sin x + sin 3x) – 3 sin 2x = (cos x + cos 3x) – 3 cos 2x
=> 2 sin 2x cos x – 3 sin 2x = 2 cos 2x.cos x – 3 cos 2x
=> sin 2x(2 cos x – 3) = cos 2x(2 cos x – 3)
=> sin 2x = cos 2x (As cos x ≠ 3/2)
=> tan 2x = 1 => tan 2x = tan π/4
=> 2x = nπ + π/4 , n∈Z
x = nπ/2 +π/8 , n∈Z
Q29. Find the general solution of the equation (√3- l)cos + (√3+ 1)sin = 2.
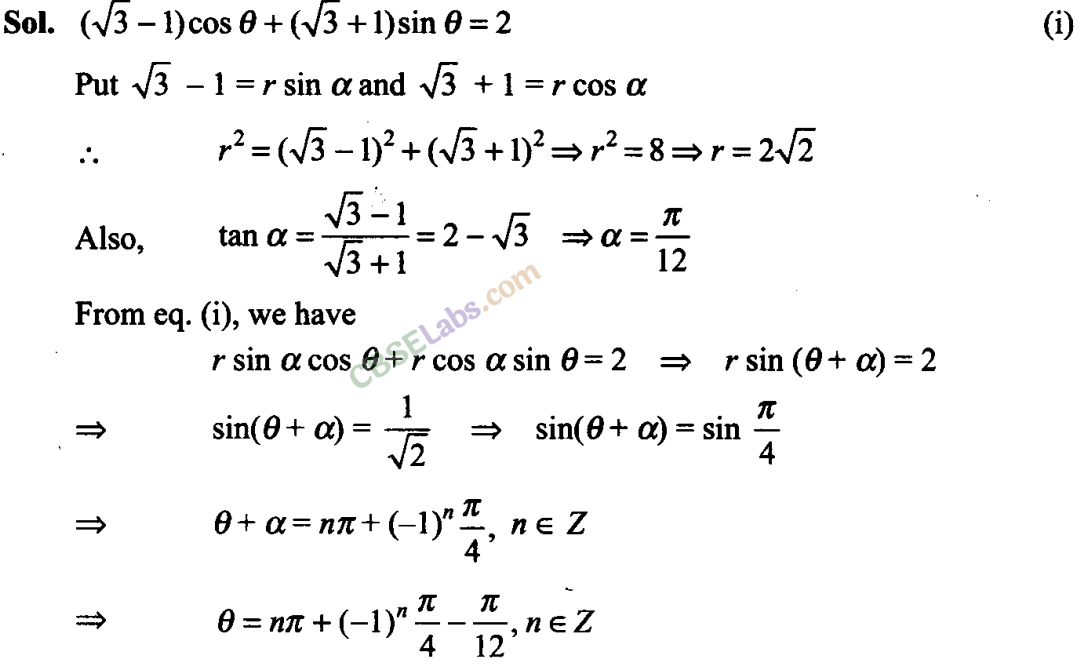
Objective Type Questions
Q30. If sin + cosec =2, then sin
2
+ cosec
2
is equal to
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) None of these
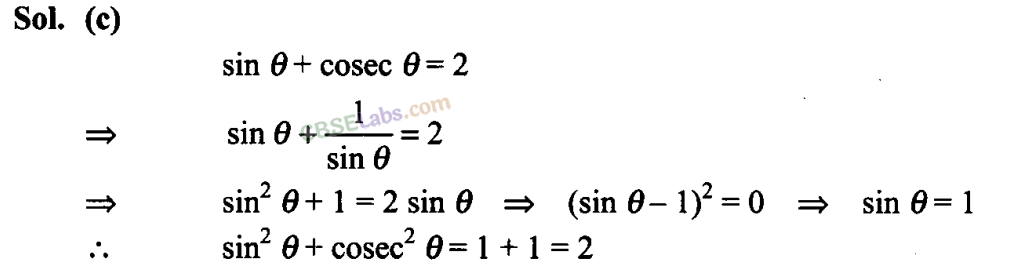
Q31. If f(x) = cos
2
x + sec
2
x, then ‘
(a) f(x) <1
(b) f(x) = 1
(c) 2 <f(x) < 1
(d) fx) ≥ 2
Q32. If tan θ = 1/2 and tan ϕ = 1/3, then the value of θ + ϕ is
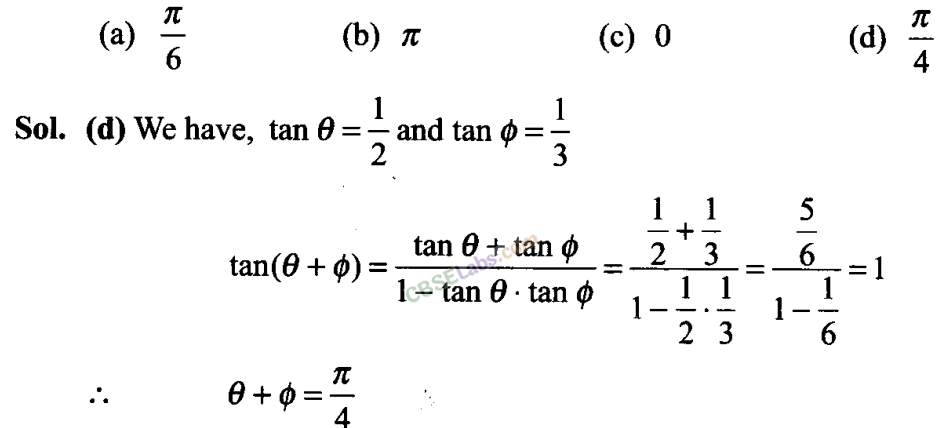
Q33. Which of the following is not correct?
(a) sin θ = – 1/5 (b) cos θ = 1 (c) sec θ = -1/2 (d) tan θ = 20
Sol:
(c)
We know that, the range of sec θ is R – (-1, 1).
Hence, sec θ cannot be equal to -1/2
Q34. The value of tan 1° tan 2° tan 3° … tan 89° is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 1/2
(d) Not defined
Sol: (b)
tan 1° tan 2° tan 3° … tan 89°
= [tan 1° tan 2° … tan 44°] tan 45°[tan (90° – 44°) tan (90° – 43°)… tan (90° – 1°)]
= [tan 1° tan 2° … tan 44°] [cot 44° cot 43°……. cot 1°]
= 1-1… 1-1 = 1
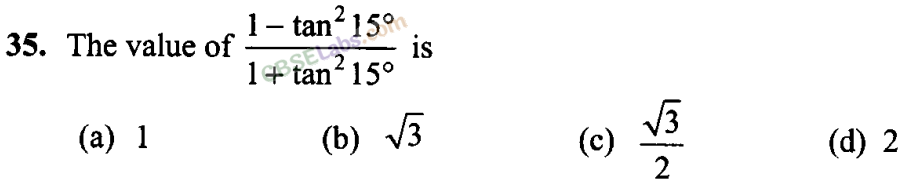
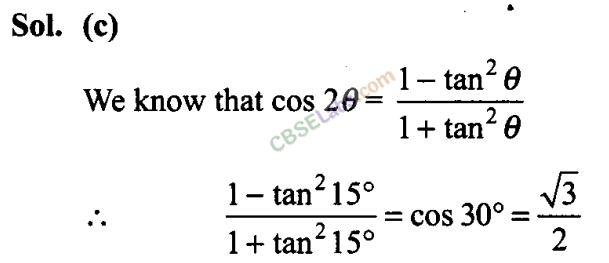
Q36. The value of cos 1° cos 2° cos 3° … cos 179° is
(a) 1/
√
2
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) -1
Sol: (b)
Since cos 90° = 0, we have
cos 1° cos 2° cos 3° …cos 90°… cos 179° = 0
Q37. If tan θ = 3 and θ lies in the third quadrant, then the value of sin θ is
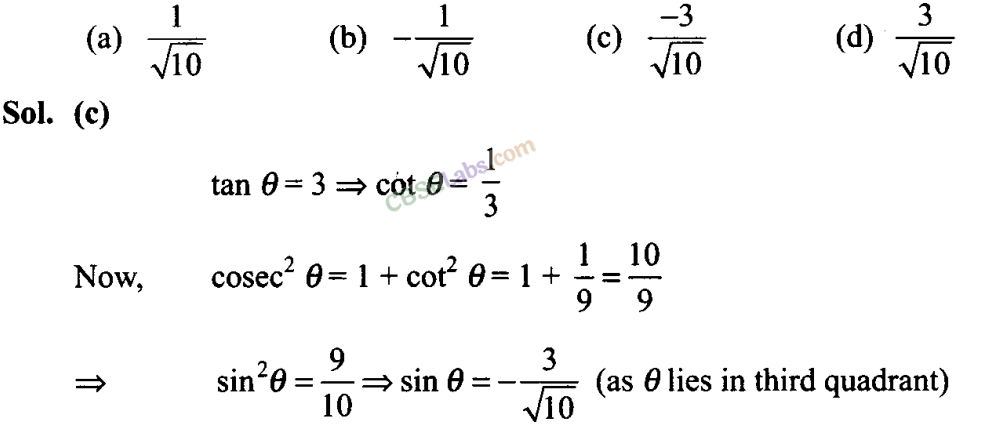
Q38. The value of tan 75° – cot 75° is equal to
Q39. Which of the following is correct?
(a) sin 1° > sin 1
(b) sin 1° < sin 1
(c) sin l° = sin l
(d) sin l° = π/18° sin 1
Sol:
We know that, in first quadrant if θ is increasing, then sin θ is also increasing.
∴sin 1° < sin 1 [∵ 1 radian = 57◦30′]
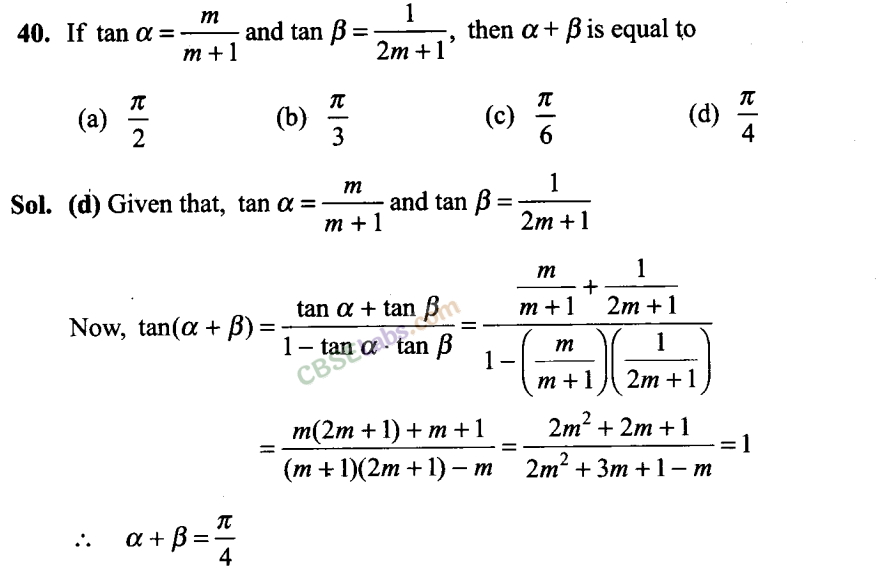
Q41. The minimum value of 3 cos x + 4 sin x + 8 is
(a) 5
(b) 9
(c) 7
(d) 3
Sol:
(d)
3 cos x + 4sin x + 8 = 5 (3/5 cos x + 4/5sin x) + 8
= 5(sin α cos x + cos α sin x) + 8
= 5 sin(α + x) + 8, where tan α = 3/4
Q42. The value of tan 3A – tan 2A – tan A is
(a) tan 3A . tan 2A . tan A
(b) -tan 3A .tan 2A . tan A
(c) tan A . tan 2A – tan 2A . tan 3A – tan 3A . tan A
(d) None of these
Sol:
(a)
3A= A+ 2A
=> tan 3A = tan (A + 2A)
=> tan 3 A = tanA + tan2A/ 1 – tan A . tan 2A
=> tan A + tan 2A = tan 3A – tan 3A• tan 2A . tan A
=> tan 3 A – tan 2A – tan A = tan 3A . tan 2A . tan A
Q43. The value of sin (45° + )- cos (45° – ) is
(a) 2 cos
(b) 2 sin
(c) 1
(d) 0
Sol:
(d)
sin (45° + ) – cos (45° – ) = sin (45° + ) – sin (90° – (45° – ))
= sin (45° + ) – sin (45°+ ) = 0
Q44. The value of (π/4+ ) cot (π/4- ) is
(a) -1
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) Not defined
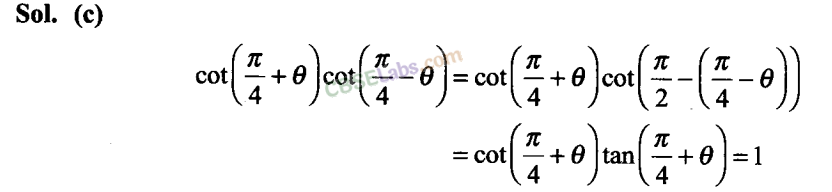
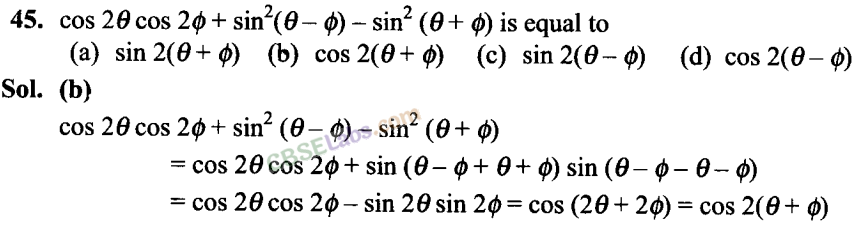
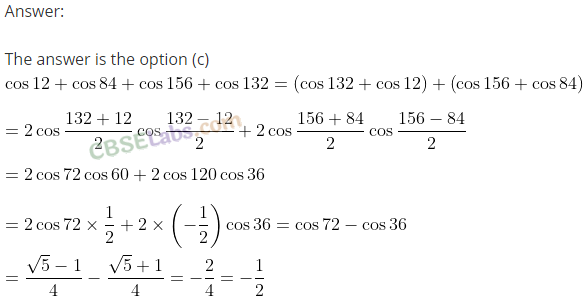
Q46. The value of cos 12° + cos 84° + cos 156° + cos 132° is
(a) 1/2
(b) 1
(c) -1/2
(d) 1/8
Q47. If tan A = 1/2 and tan B = 1/3 then tan (2A + B) is equal to
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
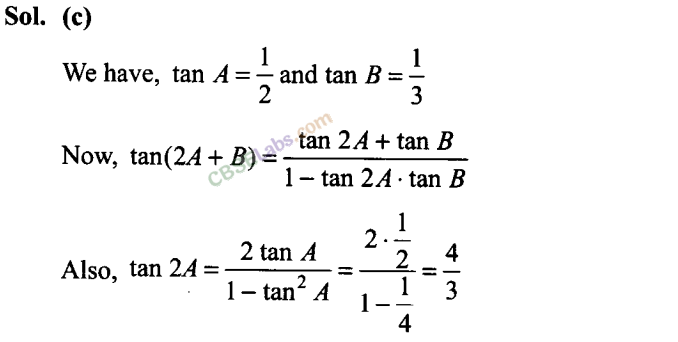
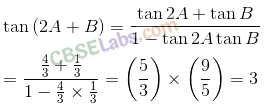
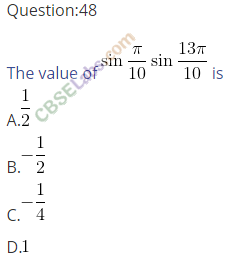
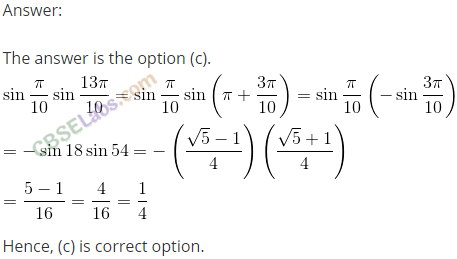
Q49. The value of sin 50° – sin 70° + sin 10° is equal to
(a) 1
(b) 0
(c) 1
(d) 2
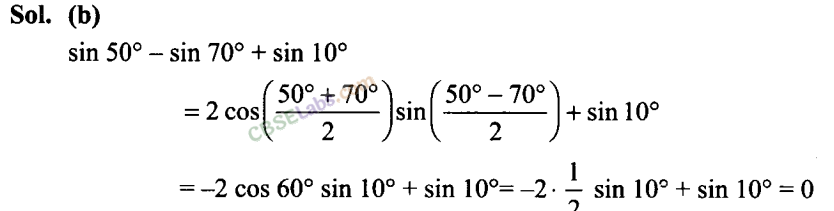
Q50. If sin + cos =1, then the value of sin 2 is
(a) 1
(b) 1
(c) 0
(d) -1

NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Solutions
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 7 Permutations and Combinations
- Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 9 Sequence and Series
- Chapter 10 Straight Lines
- Chapter 11 Conic Sections
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Three-Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
- Chapter 14 Mathematical Reasoning
- Chapter 15 Statistics
- Chapter 16 Probability