NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 2 Relations and Functions are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 2 Relations and Functions.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. If A = {-1, 2, 3 } and B = {1, 3}, then determine
(i) AxB (ii) BxC (c) BxB (iv) AxA
Sol:
We have A = {-1,2,3} and B = {1,3}
(i) A x B = {(-1, 1), (-1, 3), (2, 1), (2, 3), (3,1), (3, 3)}
(ii) BxA = {( 1, -1), (1, 2), (1,3), (3,-1), (3,2), (3, 3)}
(iii) BxB= {(1,1), (1,3), (3,1), (3, 3)}
(iv) A xA = {(-1, -1), (-1, 2), (-1, 3), (2, -1), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, -1), (3, 2), (3,3)}
Q2. If P = {x : x < 3, x e N}, Q= {x : x≤2,x ∈ W}. Find (P∪ Q) x (P∩ Q), where W is the set of whole numbers.
Sol:
We have, P={x: x<3,x ∈ N} = {1,2}
And Q = {x :x≤ 2,x∈ W] = {0,1,2}
P∪Q= {0, 1,2} and P ∩ Q= {1,2}
(P ∪ Q) x (P ∩ Q) = {0,1, 2} x {1,2}
= {(0,1), (0, 2), (1,1), (1,2), (2,1), (2, 2)}
Q3. lfA={x:x∈ W,x < 2}, 5 = {x : x∈N, 1 <.x < 5}, C= {3, 5}. Find
(i) Ax(B∩Q) (ii) Ax(B∪C)
Sol:
We have, A = {x :x∈ W,x< 2} = {0, 1};
B = {x : x ∈ N, 1 <x< 5} = {2, 3,4}; and C= {3, 5}
(i)
B∩ C = {3}
A x (B ∩ C) = {0, 1} x {3} = {(0, 3), (1, 3)}
(ii)
(B ∪ C) ={2,3,4, 5}
A x (B ∪ C) = {0, 1} x {2, 3,4, 5}
= {(0,2), (0,3), (0,4), (0,5), (1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1, 5)}
Q4. In each of the following cases, find a and b. (2a + b, a – b) = (8, 3) (ii) {a/4, a – 2b) = (0, 6 + b)
Sol:
(i) We have, (2a + b,a-b) = (8,3)
=> 2a + b = 8 and a – b = 3
On solving, we get a = 11/3 and b = 2/3
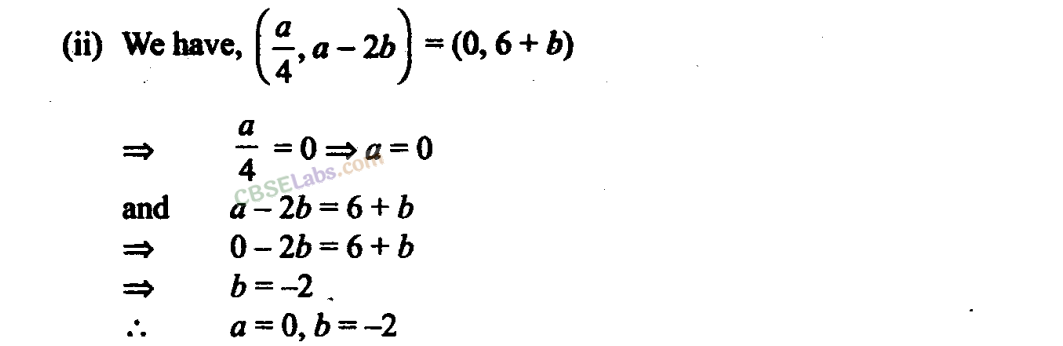
Q5. Given A = {1,2,3,4, 5}, S= {(x,y) :x∈ A,y∈ A}.Find the ordered pairs which satisfy the conditions given below
x+y = 5 (ii) x+y<5 (iii) x+y>8
Sol:
We have, A = {1,2, 3,4, 5}, S= {(x,y) : x ∈ A,y∈ A}
(i)
The set of ordered pairs satisfying x + y= 5 is {(1,4), (2,3), (3,2), (4,1)}
(ii)
The set of ordered pairs satisfying x+y < 5 is {(1,1), (1,2), (1,3), (2, 1), (2,2), (3,1)}
(iii)
The set of ordered pairs satisfying x +y > 8 is {(4, 5), (5,4), (5, 5)}.
Q6. Given R = {(x,y) : x,y ∈ W, x
2
+ y
2
= 25}. Find the domain and range of R
Sol:
We have, R = {(x,y):x,y∈ W, x
2
+ y
2
= 25}
= {(0,5), (3,4), (4, 3), (5,0)}
Domain of R = Set of first element of ordered pairs in R = {0,3,4, 5}
Range of R = Set of second element of ordered pairs in R = {5,4, 3, 0}
Q7. If R
1
= {(x, y)| y = 2x + 7, where x∈ R and -5 ≤ x ≤ 5} is a relation. Then find the domain and range of R
1
.
Sol:
We have, R
1
= {(x, y)|y = 2x + 7, where x∈ R and -5 ≤x ≤ 5}
Domain of R
1
= {-5 ≤ x ≤ 5, x ∈ R} = [-5, 5]
x ∈ [-5, 5]
=> 2x ∈ [-10,10]
=>2x + 7∈ [-3, 17]
Range is [-3, 17]
Q8. If R
2
= {(x, y) | x and y are integers and x
2
+y
2
= 64} is a relation. Then find R
2
Sol:
We have, R
2
= {(x, y) | x and y are integers and x
2
+ y
2
– 64}
Clearly, x
2
= 0 and y
2
= 64 or x
2
= 64 andy
2
= 0
x = 0 and y = ±8
or x = ±8 and y = 0
R
2
= {(0, 8), (0, -8), (8,0), (-8,0)}
Q9. If R
3
= {(x, |x|) | x is a real number} is a relation. Then find domain and range
Sol:
We have, R
3
= {(x, |x)) | x is real number}
Clearly, domain of R
3
= R
Now, x ∈ R and |x| ≥ 0 .
Range of R
3
is [0,∞)
Q10. Is the given relation a function? Give reasons for your answer.
(i) h={(4,6), (3,9), (-11,6), (3,11)}
(ii) f = {(x, x) | x is a real number}
(iii) g = {(n, 1 In)| nis a positive integer}
(iv) s= {(n, n
2
) | n is a positive integer}
(v) t= {(x, 3) | x is a real number}
Sol: (i)
We have, h = {(4,6),(3,9), (-11,6), (3,11)}.
Since pre-image 3 has two images 9 and 11, it is not a function.
(ii)
We have, f = {(x, x) | x is a real number}
Since every element in the domain has unique image, it is a function.
(iii) We have, g= {(n, 1/n) | nis a positive integer}
For n, it is a positive integer and 1/n is unique and distinct. Therefore,every element in the domain has unique image. So, it is a function.
(iii)
We have, s = {(n, n
2
) | n is a positive integer}
Since the square of any positive integer is unique, every element in the domain has unique image. Hence, ibis a function.
(iv)
We have, t = {(x, 3)| x is a real number}.
Since every element in the domain has the image 3, it is a constant function.
Q11. If f and g are real functions defined byf( x) = x
2
+ 7 and g(x) = 3x + 5, find each of the following
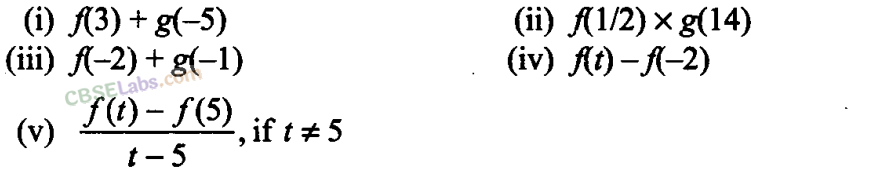

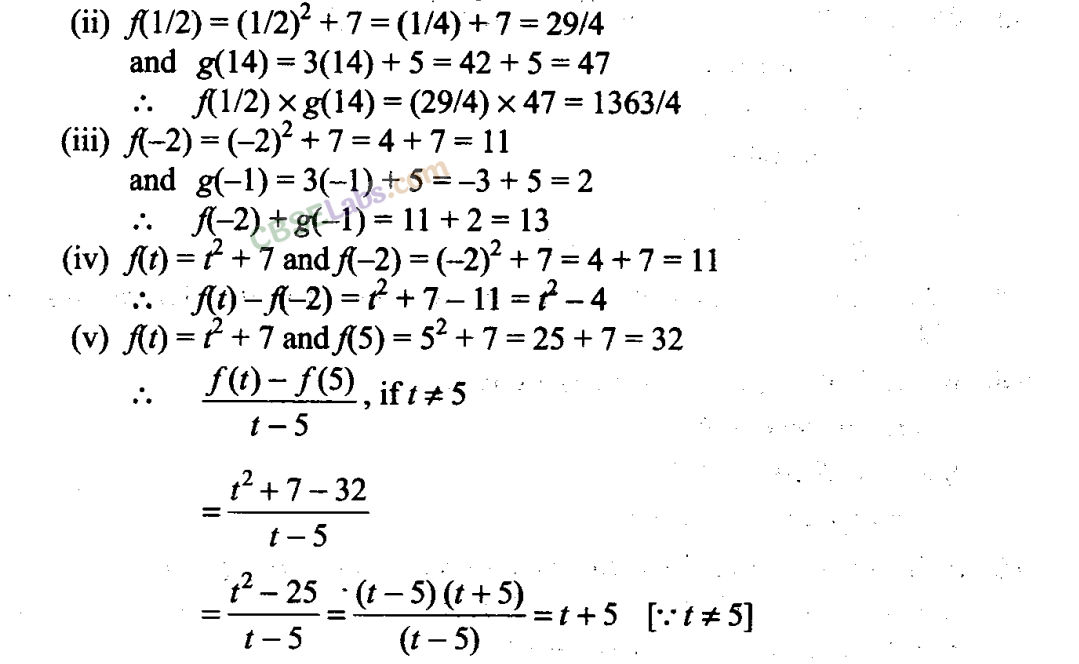
Q12. Let f and g be real functions defined by f(x) = 2x+ 1 and g(x) = 4x – 7.
(i) For what real numbers x,f(x)= g(x)?
(ii) For what real numbers x,f (x) < g(x)?
Sol:
We have,f(x) = 2x + 1 and g(x) = 4x-7
(i)
Now f (x) = g(x)
=> 2x+l=4x-7
=> 2x = 8 =>x = 4
(ii)
f (x) < g(x)
=> 2x + 1 < 4x – 7
=> 8 < 2x
=> x > 4
Q13. If f and g are two real valued ftmctions defined as f(x) = 2x + 1, g(x) = x
2
+ 1, then find.
![]()
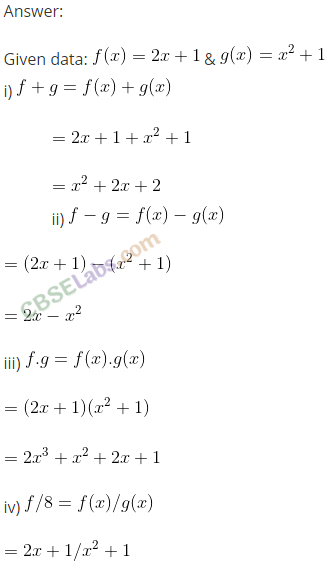
Q14. Express the following functions as set of ordered pairs and determine their range.
f:X->R,f{x) = x
3
+ 1, where X= {-1,0, 3, 9, 7}
Sol:
We have, f:X→ R,flx) = x
3
+ 1.
Where X = {-1, 0, 3, 9, 7}
Now f (-l) = (-l)
3
+1 =-l + 1 =0
f(0) = (0)
3
+l=0+l = l
f(3) = (3)
3
+ 1 = 27 + 1 = 28
f(9) = (9)
3
+ 1 = 729 + 1 = 730
f(7) = (7)
3
+ 1 = 343 + 1 = 344
f= {(-1, 0), (0, 1), (3, 28), (9, 730), (7, 344)}
Range of f= {0, 1, 28, 730, 344}
Q15. Find the values of x for which the functions f(x) = 3x
2
-1 and g(x) = 3+ x are equal.
Sol:
f(x) = g(x)
=> 3x
2
-l=3+x => 3x
2
-x-4 = 0 => (3x – 4)(x+ 1) – 0
x= -1,4/3
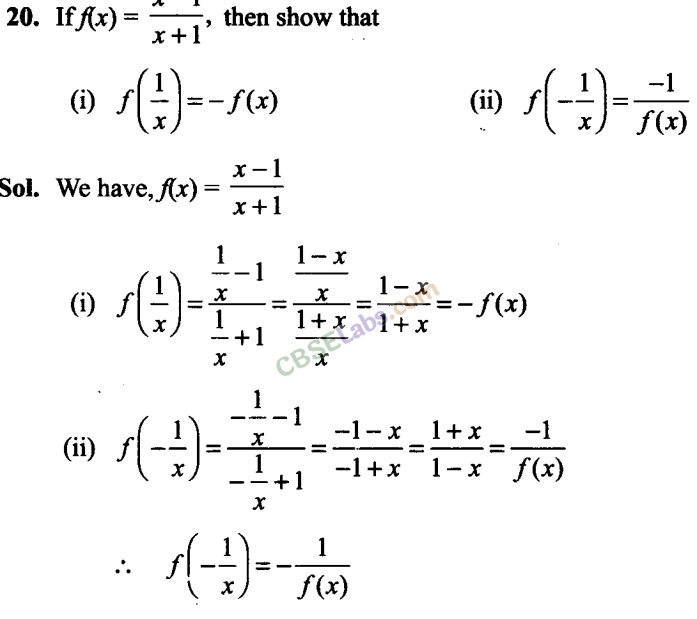
Q16. Is g = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4, 7)} a function? Justify. If this is described by the relation, g(x) = x +, then what values should be assigned to and ?
Sol:
We have, g = {(1, 1), (2, 3), (3, 5), (4,7)}
Since, every element has unique image under g. So, g is a function.
Now, g(x) = x + For (1,1), g(l) = a(l) + P
=> l = + (i)
For (2, 3), g(2) = (2) +
=> 3 = 2 + (ii)
On solving Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get = 2, = -l
f(x) = 2x-1
Also, (3, 5) and (4, 7) satisfy the above function.
Q17. Find the domain of each of the following functions given by
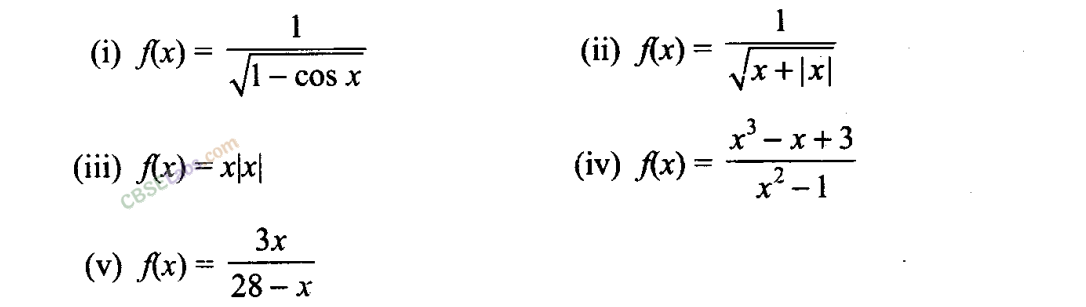
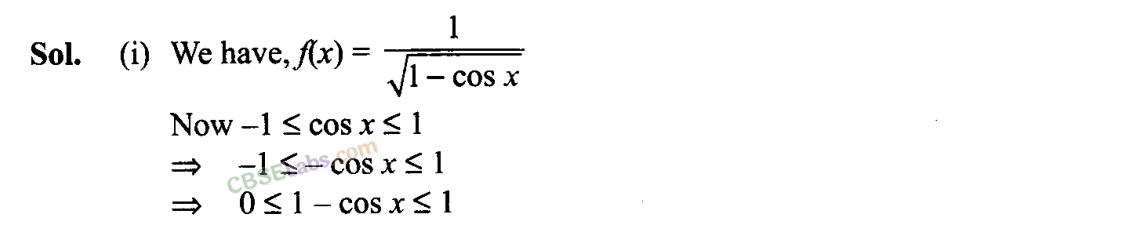

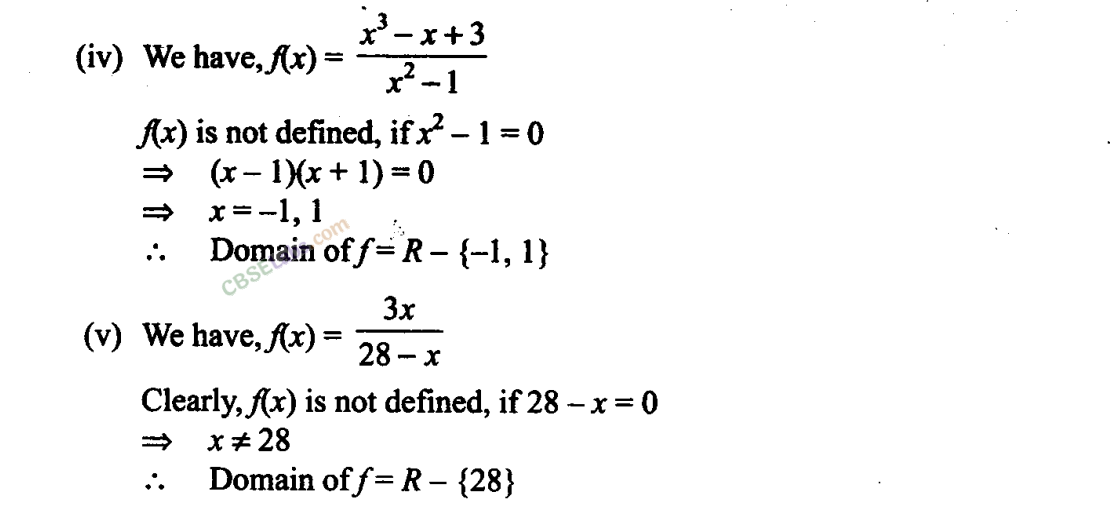
Q18. Find the range of the following functions given by

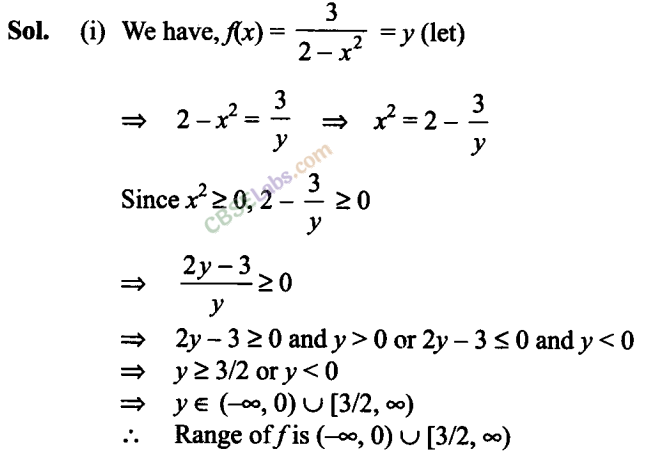
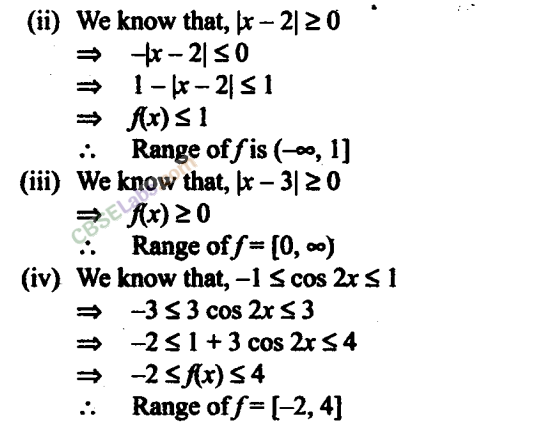
Q19. Redefine the function f(x) = |x-2| + |2+x| , -3 ≤x ≤3
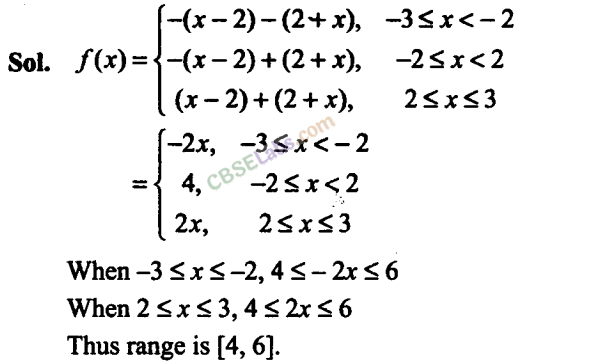
Q21. Let f (x) = √x and g(x) = xbe two functions defined in the domain R
+
∪ {0}. Find
(i) (f+g)(x)
(ii) (f-g)(x)
(iii) (fg)(x)
(iv) f/g(x)
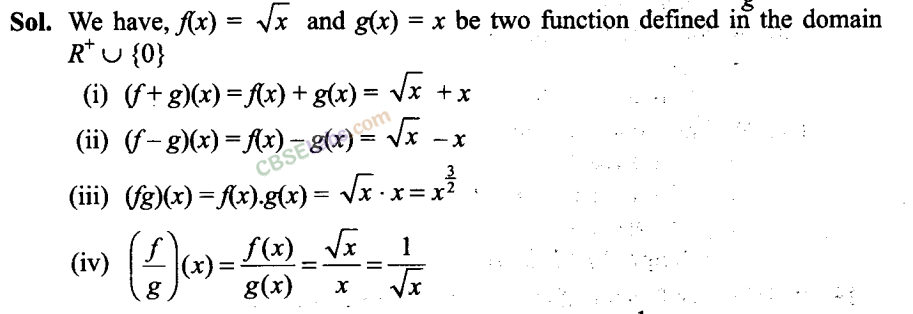
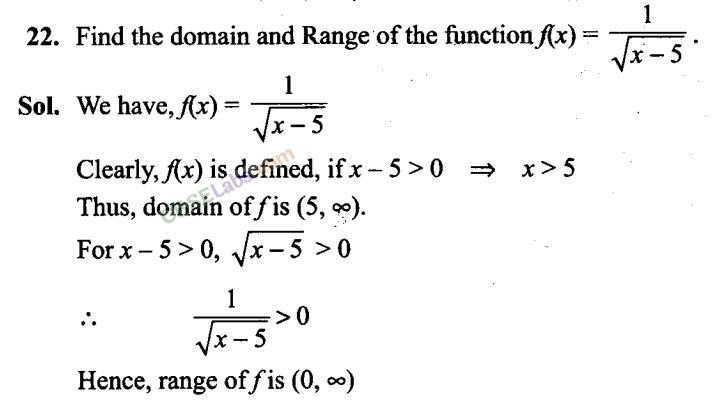
Q23. If f( x)= y = ax-b/ cx-a then prove that f (y) = x
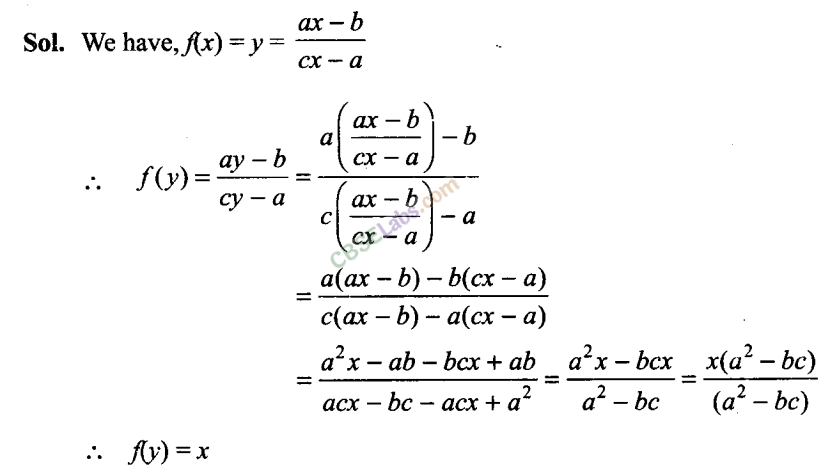
Objective Type Questions
Q24. Let n(A) = m, and n(B) = n. Then the total number of non-empty relations that can be defined from A to B is
(a) m
n
(b) n
m
– 1
(c) mn – 1
(d) 2
mn
– 1
Sol:
(d) We have, n(A) = m and n(B) = n
n(A xB) = n(A). n(B) = mn
Total number of relation from A to B = Number of subsets of AxB = 2
mn
So, total number of non-empty relations = 2
mn
– 1
Q25. If [x]
2
– 5[x] + 6 = 0, where [. ] denote the greatest integer function, then
(a) x ∈ [3,4]
(b) x∈ (2, 3]
(c) x∈ [2, 3]
(d) x ∈ [2, 4)
Sol:
(d) We have [x]
2
– 5[x] + 6 = 0 => [(x – 3)([x] – 2) = 0
=> [x] = 2,3 .
For [x] = 2, x ∈ [2, 3)
For [x] = 3, x ∈ [3,4)
x ∈ [2, 3) u [3,4)
Or x ∈ [2,4)
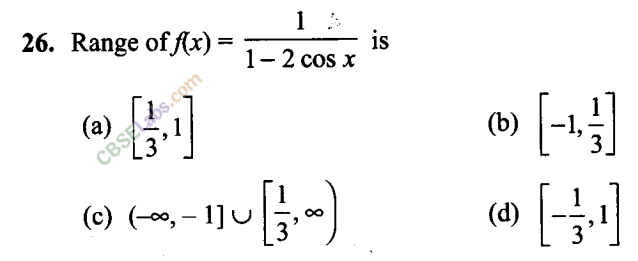
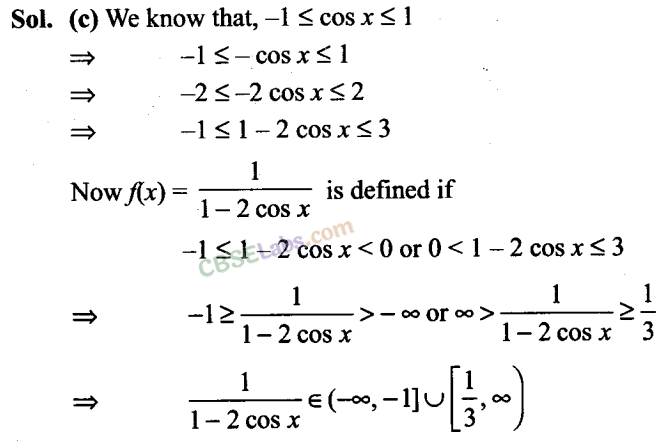

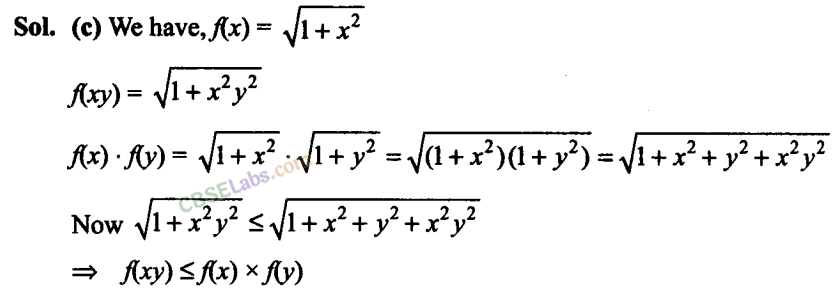
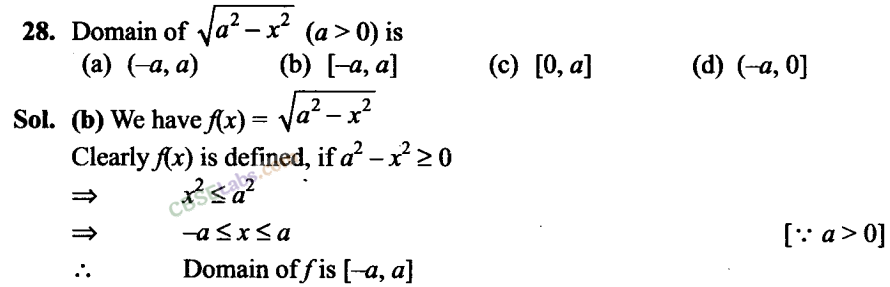
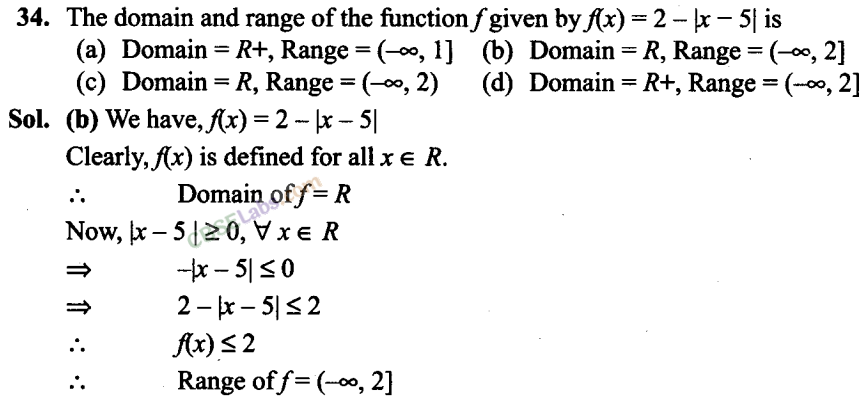
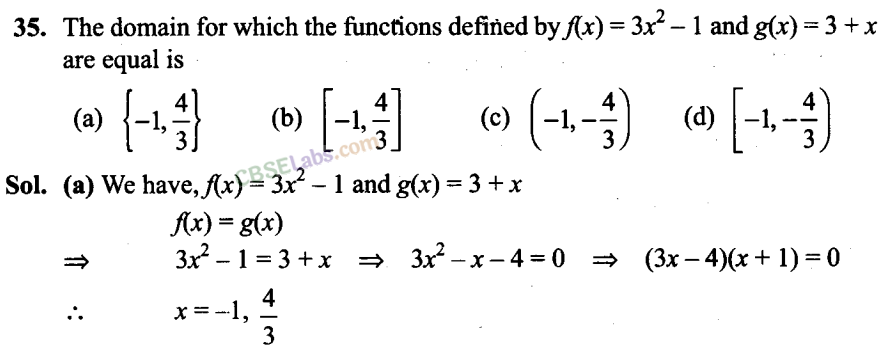
Q29. If fx) ax+ b, where a and b are integers,f(-1) = -5 and f(3) – 3, then a and b are equal to
(a) a = -3, b =-1
(b) a = 2, b =-3
(c) a = 0, b = 2
(d) a = 2, b = 3
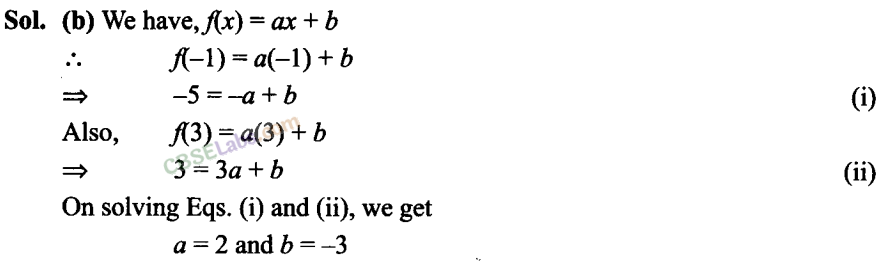
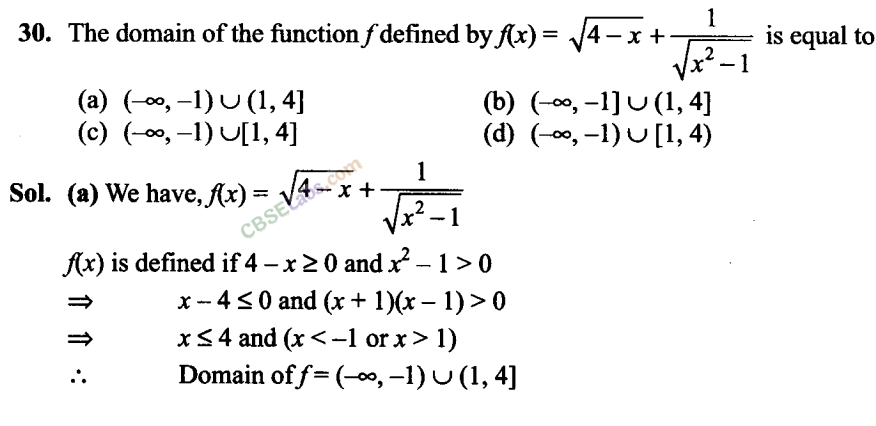


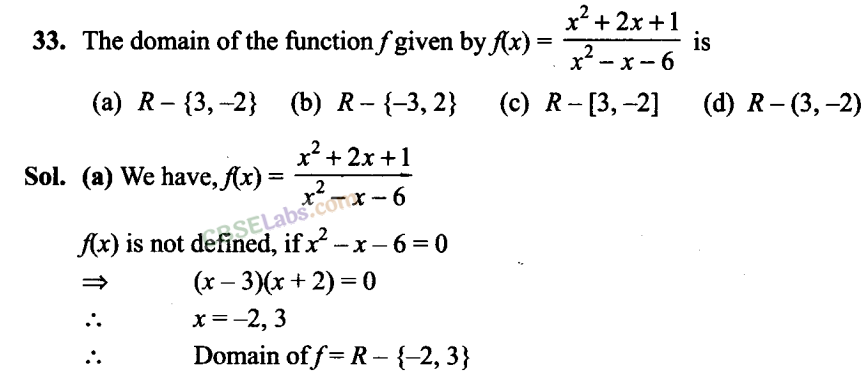
Fill in the Blanks Type Questions
Q36. Let f and g be two real functions given by f= {(0, 1), (2,0), (3,.-4), (4,2), (5, 1)}
g= {(1,0), (2,2), (3,-1), (4,4), (5, 3)} then the domain of f x g is given by________ .
Sol:
We have, f = {(0, 1), (2, 0), (3, -4), (4, 2), (5,1)} and g= {(1, 0), (2, 2), (3, 1), (4,4), (5, 3)}
Domain of f = {0,2, 3, 4, 5}
And Domain of g= {1, 2, 3,4, 5}
Domain of (f x g) = (Domain of f) ∩ (Domain of g) = {2, 3,4, 5}
Matching Column Type Questions
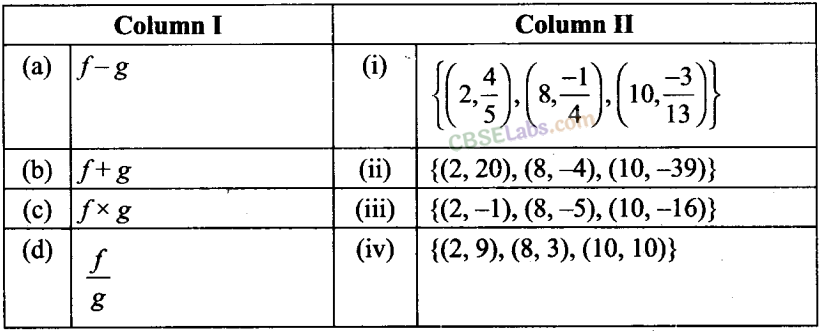
Q37. Let f= {(2,4), (5,6), (8, -1), (10, -3)} andg = {(2, 5), (7,1), (8,4), (10,13), (11, 5)} be two real functions. Then match the following:

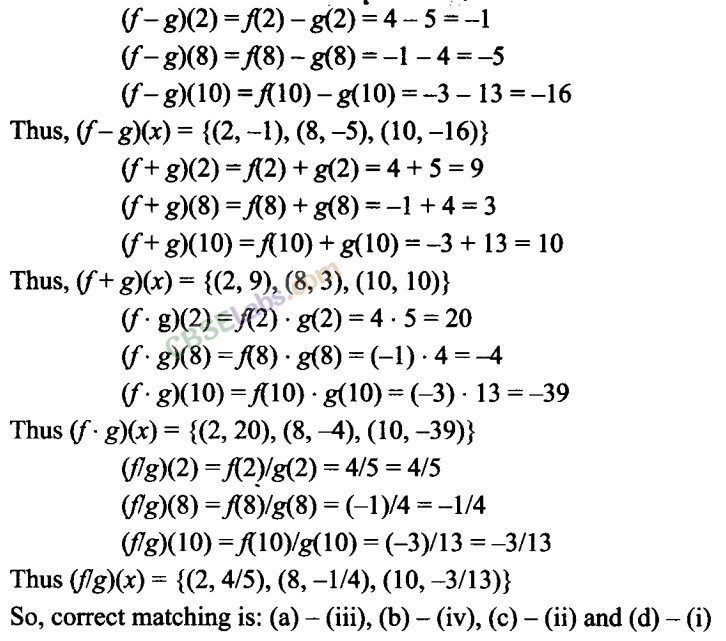
True/False Type Questions
Q38. The ordered pair (5,2) belongs to the relation R ={(x,y): y = x – 5, x,y∈Z}
Sol:
False
We have, R = {(x, y): y = x – 5, x, y ∈ Z}
When x = 5, then y = 5-5=0 Hence, (5, 2) does not belong to R.
Q39. If P = {1, 2}, then P x P x P = {(1, 1,1), (2,2, 2), (1, 2,2), (2,1, 1)}
Sol:
False
We have, P = {1, 2} and n(P) = 2
n(P xPxP) = n(P) x n(P) x n(P) = 2 x 2 x 2
= 8 But given P x P x P has 4 elements.
Q40. If A= {1,2, 3}, 5= {3,4} and C= {4, 5, 6}, then (A x B) ∪ (A x C) = {(1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3, 3), (3,4), (3, 5), (3,6)}.
Sol:
True
We have.4 = {1,2, 3}, 5= {3,4} andC= {4,5,6}
AxB= {(1, 3), (1,4), (2, 3), (2,4), (3, 3), (3,4)}
And A x C = {(1,4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2,4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3,4), (3, 5), (3, 6)}
(A x B)∪(A xC)= {(1, 3), (1, 4), (1, 5), (1, 6), (2, 3), (2, 4), (2, 5), (2, 6), (3,3), (3,4), (3, 5), (3,6)}
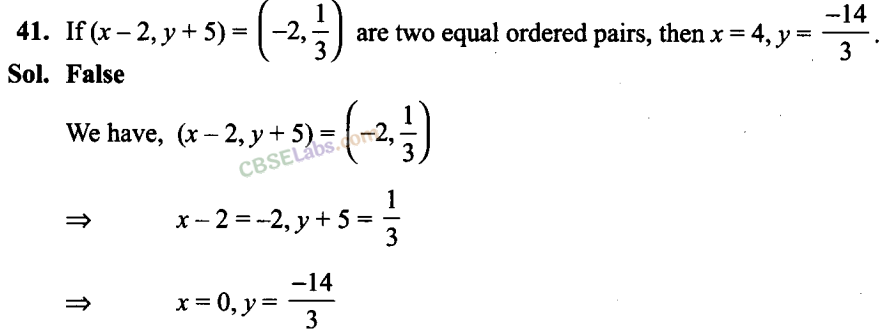
Q42. If Ax B= {(a, x), (a, y), (b, x), (b, y)}, thenM = {a, b},B= {x, y}.
Sol:
True
We have, AxB= {{a, x), {a, y), (b, x), {b, y)}
A = Set of first element of ordered pairs in A x B = {a, b}
B = Set of second element of ordered pairs in A x B = {x, y}
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Solutions
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 7 Permutations and Combinations
- Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 9 Sequence and Series
- Chapter 10 Straight Lines
- Chapter 11 Conic Sections
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Three-Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
- Chapter 14 Mathematical Reasoning
- Chapter 15 Statistics
- Chapter 16 Probability