NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium
Multiple Choice Questions
Single Correct Answer Type
Q1. We know that the relationship between K
c
and K
p
is K
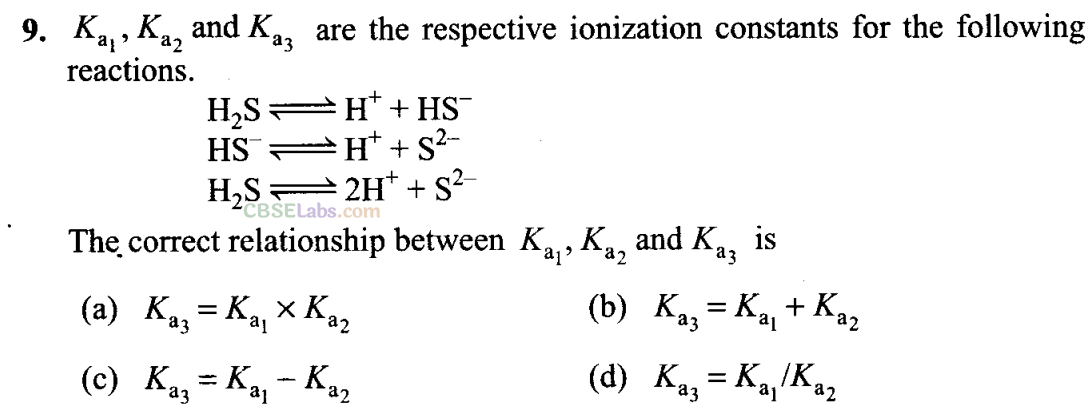
p
= K
c
(RT)
∆n
What would be the value of An for the reaction NH
4
C1(s) ⇆ NH
3
(g) + HCl(g)?
(a) 1
(b) 0.5
(c) 1.5
(d) 2
Sol:
(d) The relationship between
K
p
and
K
c
is
K
p
=
K
c
(RT)
∆
n
Where ∆n = (number of moles of gaseous products) – (number of moles of gaseous reactants)
For the reaction,
NH
4
C1(s)
⇆
NH
3
(g) + HCl(g)
∆
n = 2 – 0 = 2
Q2. For the reaction H
2
(g) + I
2
(g) ⇌2Hl(g), the standard free energy is ∆G° >0 The equilibrium constant (K) would be
(a) K = 0
(b)> 1
(c) K=1
(d)A:<l
Sol:
(d) ∆G° = -RTln K. ∆G° > 0 means ∆G° is +ve. This can be so only if In K is -ve, i.e., K< 1.
Q3. Which of the following is not a general characteristic of equilibria involving physical processes?
(a) Equilibrium is possible only in a closed system at a given temperature.
(b) All measurable properties of the system remain constant.
(c) All the physical processes stop at equilibrium.
(d) The opposing processes occur at the same rate and there is dynamic but stable condition.
Sol:
(c) All the physical processes like melting of ice and freezing of water, etc., do not stop at equilibrium.
Q4. PC1
5
, PC1
3
and Cl
2
are at equilibrium at 500 K in a closed container and their concentrations are 0.8 x 10“
3
molL
-1
, 1.2 x 10
-3
mol L
1
and 1.2 x 10
-3
mol L
-1
The value of K
c
for the reaction PCl
5
(g) ⇌PCl
3
(g) + Cl
2
(g) will be
(a) 8 x 10
3
molL
-1
(b) 1.8 x 10
-3
molL
-1
(c) 1.8 x 10“
3
molL
-1
(d) 0.55 x 10
4
molL
-1
Sol:
(b) PCl
5
(g) ⇌ PCl
3
(g) + Cl
2
(g)
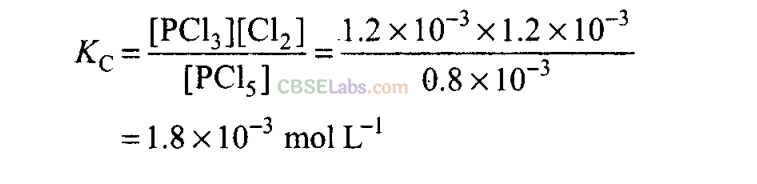
Q5. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) In equilibrium mixture of ice and water kept in perfectly insulated flask, mass of ice and water does not change with time.
(b) The intensity of red colour increases when oxalic acid is added to a solution containing iron (III) nitrate and potassium thiocyanate.
(c) On addition of catalyst the equilibrium constant value is not affected.
(d) Equilibrium constant for a reaction with negative AH value decreases as the temperature increases.
Sol:
(b)Fe
3+
+SCN
–
⇌ FeSCN
2+
(Red)
When oxalic acid is added to a solution containing iron nitrate and potassium thiocyanate, oxalic acid reacts with Fe
3+
ions to form a stable complex ion [Fe(C
2
0
4
)
3
]
3-
, thus, decreasing the concentration of free Fe
3+
ions which in mm decreases the intensity of red colour.
Fe
3+
+ SCN
–
⇌ [Fe(SCN)]
2+
(Red)
Q6. When hydrochloric acid is added to cobalt nitrate solution at room temperature, the following reaction takes place and the reaction mixture becomes blue. On cooling the mixture, it becomes pink. On the basis of this information mark the correct answer.
[Co(H
2
0)
6
]
2+
(aq) + 4Cl
–
(aq) [CoCl
4
]
2
-(aq) + 6H
2
0(l)
(Pink) (Blue)
(a)∆H > 0 for the reaction
(b) ∆H < 0 for the reaction
(c) ∆H = 0 for the reaction
(d) The sign of ∆H cannot be predicted on the basis of this information.
Sol:
(a) Since the reaction shifts to backward direction on cooling, this means that
the backward reaction is exothermic reaction. Therefore, the forward reaction is endothermic reaction and
∆
H >
0.
Q7. The pH of neutral water at 25°C is 7.0. As the temperature increases, ionization of water increases, however, the concentration of H
+
ions and OH
–
ions are equal. What will be the pH of pure water at 60°C?
(a) Equal to 7.0
(b) Greater than 7.0
(c) Less than 7.0
(d) Equal to zero
Sol:
(c) At 25°C, [H
+
] = [OH
–
] = 10
7
and
K
w
= [H
+
] [OH
–
] = 10
-14
. On heating,
K
w
increases, i.e., [H
+
] [OH
–
] > 10
-14
As [H
+
] = [OH
–
], [H
+
]
2
> 10
-14
or [H
+
] > 10
-7
M or pH < 7.
Q8. The ionization constant of an acid, K
a
is the measure of strength of an acid. The K
a
values of acetic acid, hypochlorous acid and formic acid are 1.74 x 10
-5
, 3.0 x 10
-8
and 1.8 x 10
-4
Which of the following orders of pH of 0.1 mol dm
-3
solutions of these acids is correct?
(a) acetic acid > hypochlorous acid > formic acid
(b) hypochlorous acid > acetic acid > formic acid
(c) formic acid > hypochlorous acid > acetic acid
(d) formic acid > acetic acid > hypochlorous acid
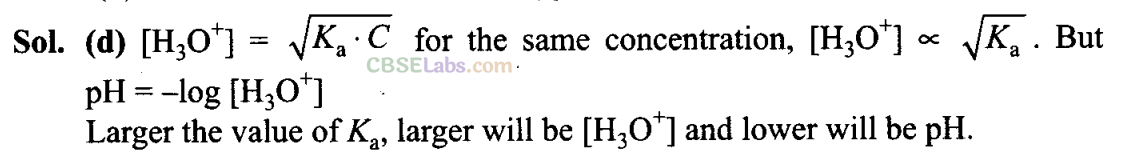

Q10. Acidity of BF3 can be explained on the basis of which of the following concepts?
(a) Arrhenius concept
(b) Bronsted Lowry concept
(c) Lewis concept
(d) Bronsted Lowry as well as Lewis concept
Sol:
(c) According to Lewis concept, a positively charged or an electron deficient species acts as Lewis acid. BF
3
is an electron deficient compound with B having 6 electrons only.
Q11. Which of the following will produce a buffer solution when mixed in equal volumes?
(a) 1 mol dm
-3
NH
4
OH and 0.1 mol dm
-3
HC1
(b) 0.05 mol dm
-3
NH
4
OH and 0.1 mol dm
-3
HC1
(c) 1 mol dm
-3
NH
4
OH and 0.05 mol dm
-3
HC1
(d) 1 mol dm
-3
CH
3
COONa and 0.1 mol dm
-3
NaOH
Sol: (c) In (c), all HC1 will be neutralized and NH 4 C1 will be formed. Also some NH 4 OH will be left unneutralized. Thus, the final solution will contain NH 4 OH and NH 4 C1 and hence will form a buffer.
Q12. In which of the following solvents is silver chloride most soluble?
(a) 0.1 mol dm
-3
AgN0
3
solution
(b) 0.1 mol dm
-3
HC1 solution
(c) H
2
0
(d) Aqueous ammonia
Sol:
(d) Silver chloride forms a soluble complex with aqueous ammonia.
AgCl + 2NH
3
→
[Ag(NH
3
)
2
]Cl
Q13. What will be the value of pH of 0.01 mol dm
-3
CH
3
COOH (K.
A
-74 x 10
-5
)?
(a) 3.4
(b) 3.6
(c) 3.9
(d) 3.0

Q14. K
a
for CH
3
COOH is 1.8 x 10
-5
and K
b
for NH
4
OH is 1.8 x 10
-5
. The pH of ammonium acetate will be
(a) 7.005
(b) 4.75
(c) 7.0
(d) Between 6 and 7
Sol:
(c) Ammonium acetate is a salt of weak acid and weak base.
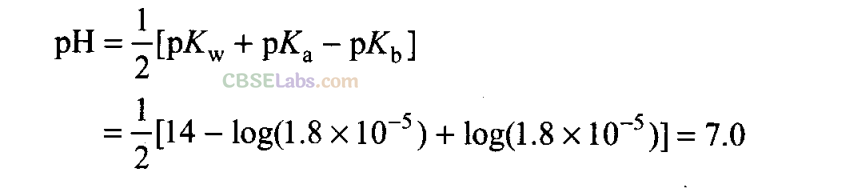
Q15. Which of the following options will be correct for the stage of half completion of the reaction A ⇌B.
(a) ΔG° = 0
(b) ΔG° > 0
(c) ΔG° < 0
(d) ΔG° = -RT In 2
Sol:
(a) A ⇌B
ΔG° = -RT In K
At the stage of half completion of reaction [A] = [B],
Therefore, K = 1. Thus, ΔG° = 0.
Q16. On increasing the pressure, in which direction will the gas phase reaction proceed to re-establish equilibrium, is predicted by applying the Le Chatelier’s principle. Consider the reaction,
N
2
(g) + 3H
2
(g) ⇌2NH
3
(g)
Which of the following is correct, if the total pressure at which the equilibrium is established, is increased without changing the temperature?
(a) K will remain same
(b) K will decrease
(c) K will increase
(d) K will increase initially and decrease when pressure is very high
Sol:
(a)N
2
(g) + 3H
2
(g) ⇌2NH
3
(g)
According to Le Chatelier’s principle, at constant temperature, the equilibrium composition will change but K will remain same.
Q17. What will be the correct order of vapour pressure of water, acetone and ether at 30°C? Given that among these compounds, water has maximum boiling point and ether has minimum boiling point.
(a) Water < Ether < Acetone
(b) Water < Acetone < Ether
(c) Ether < Acetone < Water
(d) Acetone < Ether < Water
Sol:
(b) Greater the boiling point, less is the vapour pressure. Hence, the correct order of vapour pressures will be:
water < acetone < ether.

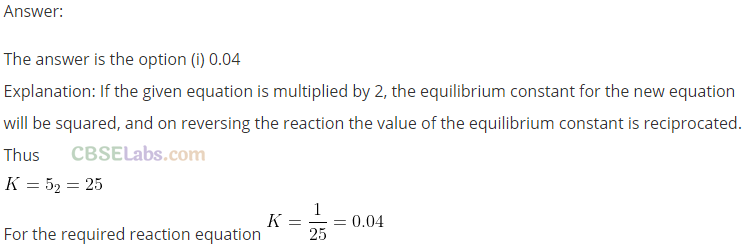
Q19. In which of the following reactions, the equilibrium remains unaffected on addition of small amount of argon at constant volume?
(a) H
2
(g) + I
2
(g) ⇌2HI(g) ‘
(b) PCl
5
(g) ⇌PCl
3
(g) + Cl
2
(g)
(c) N
2
(g) + 3H
2
(g) ⇌2NH
3
(g)
(d) The equilibrium will remain unaffected in all the three cases.
Sol:
(d) The equilibrium will remain unaffected in all three cases on addition of small amount of inert gas at constant volume.
Q20. For the reaction N
2
0
4
(g) ⇌2N0
2
(g), the value of K is 50 at 400 K and 1700 at 500 K. Which of the following options is correct?
(a) The reaction is endothermic.
(b) The reaction is exothermic.
(c) If NO
2
(g) and N
2
0
4
(g) are mixed 400 K at partial pressures 20 bar and 2 bar respectively, more N
2
0
4
(g) will be formed.
(d) The entropy of the system increases.
Sol:
(a, c, d)
(a) As the value of K increases with increase of temperature and K = K
f
/ K
b
, this means that k
f
increases, i.e., forward reaction is favoured.
Hence, reaction is endothermic.
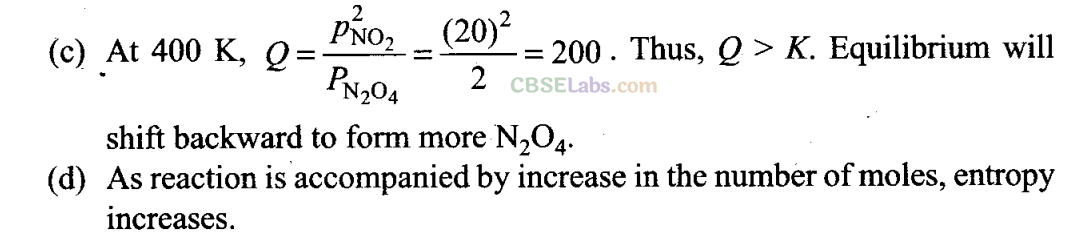
Q21. At a particular temperature and atmospheric pressure, the solid and liquid phases of a pure substance can exist in equilibrium. Which of the following term defines this temperature? .
(a) Normal melting point
(b) Equilibrium temperature
(c) Boiling point
(d) Freezing point
Sol:
(a, d) These are normal melting point and freezing point since they are measured at atmospheric pressure.
Q22. The ionization of hydrochloric acid in water is given below:
HCl(aq) + H
2
0(
l
) ⇌H
3
0
+
(aq) +Cl
–
(aq)
Label two conjugate acid-base pairs in this ionization.
Sol:
HCl (Acid) Cl
–
(Conjugate base)
H
2
0 (Base) H
3
0
+
(Conjugate acid
Q23. The aqueous solution of sugar does not conduct electricity. However, when sodium chloride is added to water, it conducts electricity. How will you explain this statement on the basis of ionization and how is it affected by concentration of sodium chloride?
Sol:
(i) Sugar being a non-electrolyte does not ionize in water, whereas NaCl ionizes completely in water and produces Na
+
and Cl
–
ions which help in the conduction of electricity.
(ii) When concentration of NaCl is increased, more Na
+
and Cl ions will be produced. Hence, conductance increases.
Q24. BF
3
does not have proton but still acts as an acid and reacts with NH
3
. Why is it so? What type of bond is formed between the two?
Sol:
BF
3
is an electron deficient compound. Hence, it acts as Lewis acid. NH
3
has a lone pair of electrons. Hence, acts as Lewis base. A coordinate bond is formed between the two.
H
3
N: →BF
3
Q25. Ionization constant of a weak base MOH, is given by the expression

Values of ionization constant of some weak bases at a particular temperature are given below:
| Base | Dimethylamine | Urea | Pyridine | Ammonia |
| 5.4 x 10 -4 | 1.3 x 10 -14 | 1.77 x lO -9 | 1.77 xlO -5 |
Arrange the bases in decreasing order of the extent of their ionization at equilibrium. Which of the above base is the strongest?
Sol:
Greater is the ionization constant (K
b
) of a base, greater is the ionization of the base. Order of extent of ionization at equilibrium is dimethylamine > ammonia > pyridine > urea. Dimethylamine is the strongest base due to maximum value of
K
b
.
Q26. Conjugate acid of a weak base is always stronger. What will be the decreasing order of basic strength of the following conjugate bases?
OH
–
, RO
–
, ch
3
coo
–
, cl
–
Sol:
Conjugate acids of given bases are H
2
0, ROH, CH
3
COOH, HC1.
Their acidic strength is in the order
HCl > CH
3
COOH > H
2
0 >ROH Hence, basic strength is in the order RO
–
> OH
–
> CH
3
COO
–
> Cl
–
Q27. Arrange the following in increasing order of pH.
KN0
3
(aq), CH
3
COONa(aq), NH
4
Cl(aq), C
6
H
5
COONH
4
(aq)
Sol:
KN0
3
: salt of strong acid-strong base, solution is neutral, pH = 7. CHjCOONa: salt of weak acid-strong base, solution is basic, pH > 7.
NH
4
Cl: salt of strong acid-weak base, solution is acidic, pH < 7.
C
6
H
5
COONH
4
: both weak put NH
4
OH is slightly stronger than C
6
H
5
COOH, pH close to 7 but slightly > 7.
Hence, in order of pH, NH
4
C1 < C
6
H
5
COONH
4
> KN0
3
< CH
3
COONa.
Q28. The value of K
c
for the reaction
2HI(g) ⇌H
2
(g) + I
2
(g) is 1 x 10
-4
.
At a given time, the composition of reaction mixture is [HI] = 2 x 10
-5
mol, [H
2
] = 1 x 10
-5
mol and [I
2
] = 1 x 10
-5
mol. In which direction will the reaction proceed?
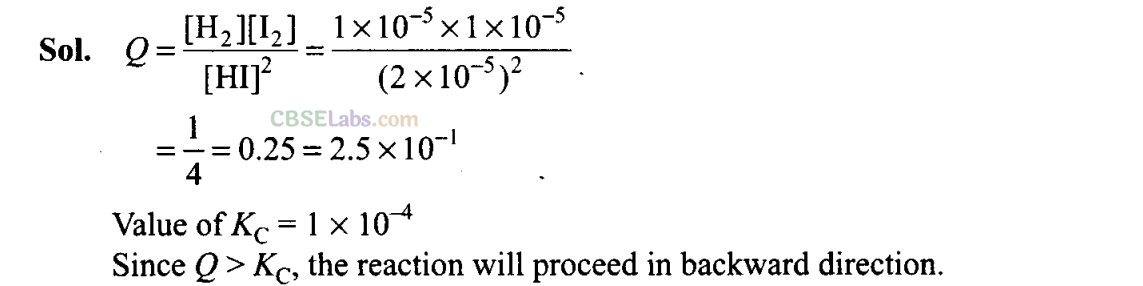
Q29. On the basis of the equation pH = -log [H
+
], the pH of 10
-8
mol dm
-3
solution of HC1 should be 8. However, it is observed to be less than 7.0. Explain the reason.
Sol:
Concentration 10
-8
mol dm
-3
indicates that the solution is very dilute. So, we cannot neglect the contribution of H
3
0
+
ions produced from H
2
0 in the solution. Total [H
3
0
+
] = 10
-8
+ 10
-7
M. From this we get the value of pH close to 7 but less than 7 because the solution is acidic.
From calculation, it is found that pH of 10
-8
mol dm
-3
solution of HC1 is equal to 6.96.
Q30. pH of a solution of a strong acid is 5.0. What will be the pH of the solution obtained after diluting the given solution a 100 times?
Sol:
pH = 5 i.e., [H
+
] = 10
-5
mol L
-1
On dilution by 100 times [H
+
] = 10
-7
mol L
-1
For a very dilute solution,
Total [H
+
] = [H
3
0
+
ions from acid] + [H
2
0
+
ions from water]
= 10
–
7
+ 10
–
7
pH = -log[H
+
] = -log (2 x 10
-7
) = 7 – log 2
= 7-0.3010 = 6.6990
Q31. A sparingly soluble salt gets precipitated only when the product of concentration of its ions in the solution (Q
sp
) becomes greater than its solubility product. If the solubility of BaS0
4
in water is 8 x 10
-4
mol dm
-3
, calculate its solubility in 0.01 mol dm
-3
of H
2
S0
4
.
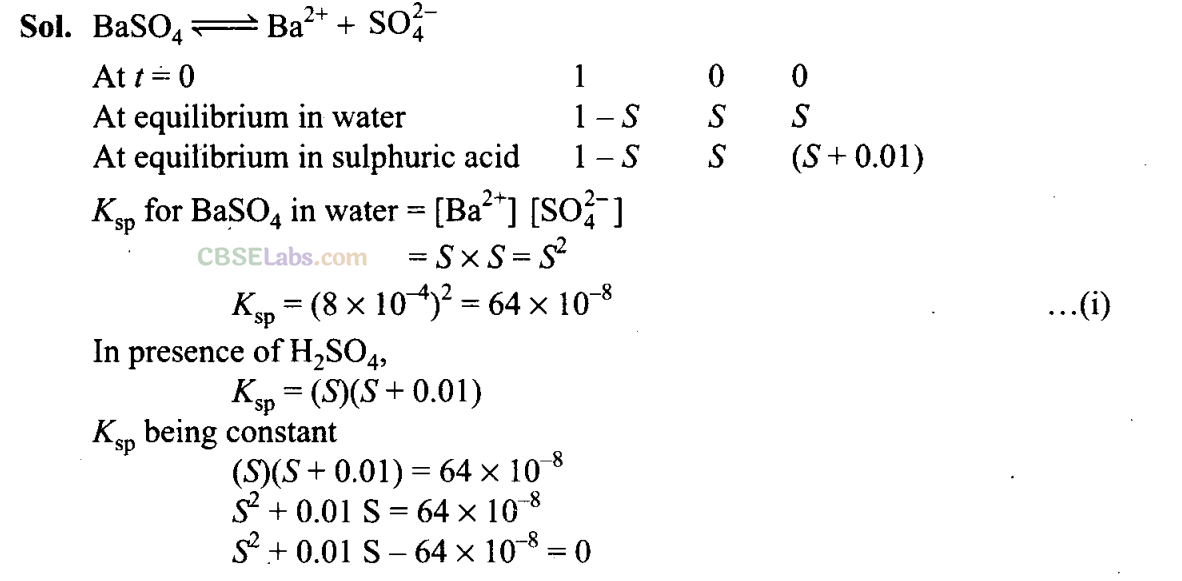
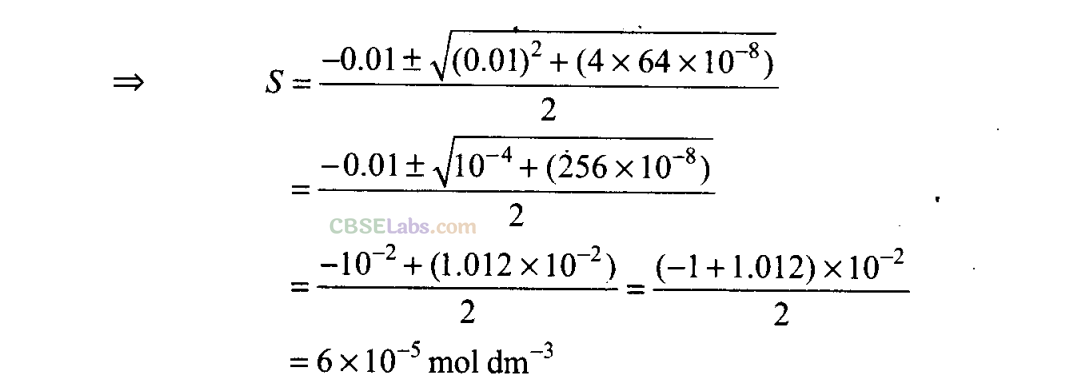
Q32. pH of 0.08 mol dm
–
3
HOC1 solution is 2.85. Calculate its ionization constant.
Sol:
pH of HOC1 = 2.85
-pH = log [H
+
] or -2.85 = log [H
+
]
=> [H
+
] = 1.413 x 10
-3
Q33. Calculate the pH of a solution formed by mixing equal volumes of two solutions A and B of a strong acid having pH = 6 and pH = 4 respectively.
Sol:
pH of solution A = 6
[H
+
] = 10
-6
mol L
1
pH of solution B = 4
[H
+
] = 10
-4
molL
-1
On mixing one litre of each solution Total volume = 1 L + 1 L = 2 L
Total amount of H
+
in 2 L solution formed by mixing solutions A and B = 10
-6
+ 10
-4
mol

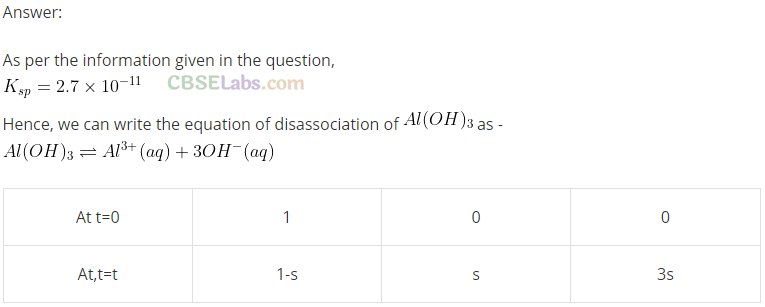
Q34. The solubility product of Al(OH)
3
is 2.7 x 10
-11
. Calculate its solubility in g
–
L and also find out pH of this solution. (Atomic mass of A1 = 27 u).


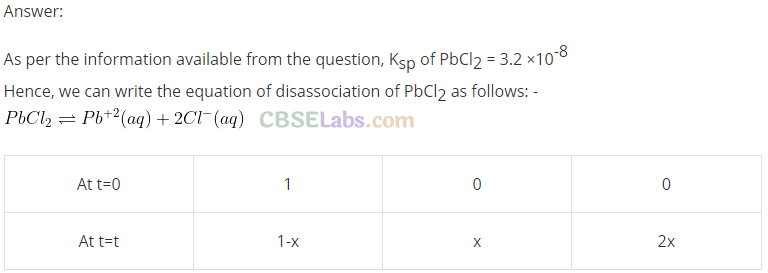
Q35. Calculate the volume of water required to dissolve 0.1 g lead (II) chloride to get a saturated solution. (K
sp
of PbCl
2
= 3.2 x 10
-8
, atomic mass of Pb = 207 u).
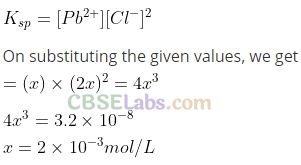
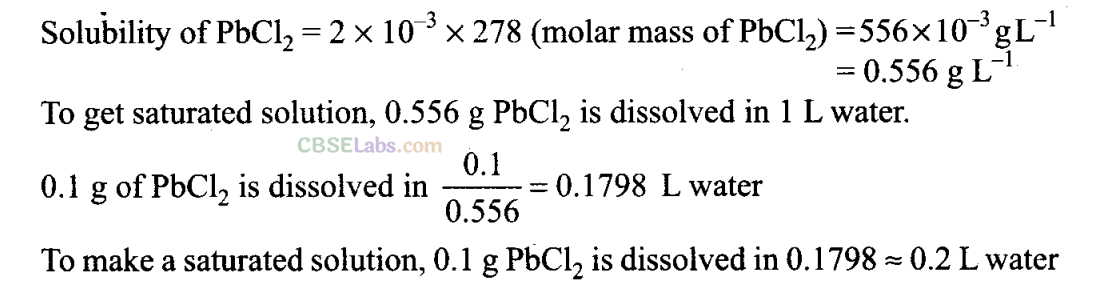
Q36. A reaction between ammonia and boron trifluoride is given below:
:NH
3
+ BF
3
→H
3
N : BF
3
Identify the acid and base in this reaction. Which theory explains it? What is the hybridization of B and N in the reactants?
Sol:
Although BF
3
does not have a proton but acts as Lewis acid as it is an electron deficient compound. It reacts with NH
3
by accepting the lone pair of electrons from NH
3
and completes its octet. The reaction can be represented by
BF
3
+ :NH
3
→BF
3
← :NH
3
Lewis electronic theory of acids and bases can explain it. Boron in BF
3
is sp
2
hybridised, whereas N in NH
3
is sp
3
hybridised.
Q37. Following data is given for the reaction:
CaC0
3
(s) → CaO(s) + C0
2
(g)
∆
f
H° [CaO(s)] = -635.1 kJ mol
–
1
∆
f
H° [CO
z
(g)] = -393.5 kJ mol
–
1
∆
f
H° [CaC0
3
(s)] = -1206.9 kJ mol
–
1
Predict the effect of temperature on the equilibrium constant of the above reaction.
Sol:
∆
r
H° = ∆
f
H° [CaO] + ∆
f
H° [C0
2
] – ∆
f
H° [CaC0
3
]
= [-635.1] + [-393.5] – [-1206.9] = 178.3 kJ mol
-1
Thus, the reaction is endothermic. Hence, according to Le Chatelier’s principle, on increasing the temperature, the equilibrium will proceed in the forward direction.
Matching Column Type Questions
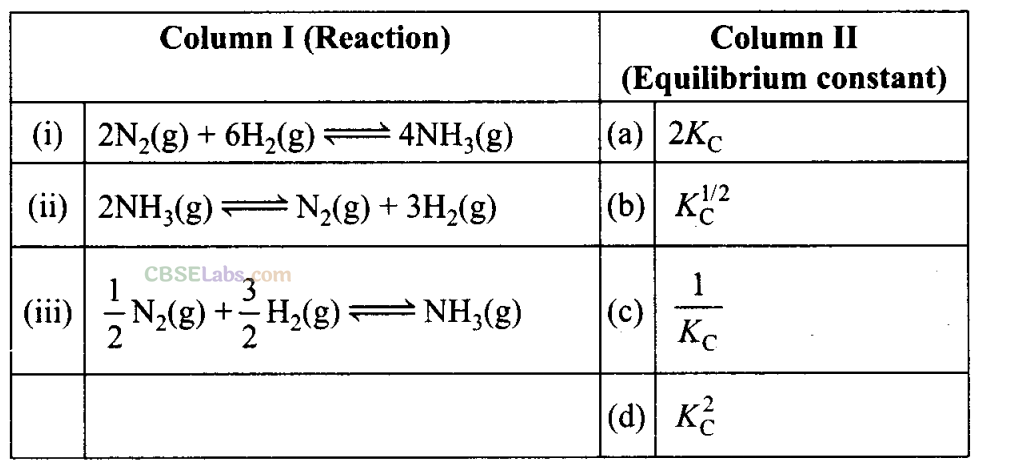
Q38. Match the following equilibria with the corresponding condition
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | Liquid⇌Vapour | (a) | Saturated solution |
| (ii) | Solid ⇌Liquid | (b) | Boiling point |
| (iii) | Solid ⇌Vapour | (c) | Sublimation point |
| (iv) | Solute(s) ⇌Solute (solution) | (d) | Melting point ‘ |
| (e) | Unsaturated solution | ||
Sol: (i) →(b), (ii) → (d), (iii) → (c), (iv) → (a)
(i) Liquid ⇌Vapour equilibrium exists at the boiling point.
(ii) Solid ⇌Liquid equilibrium exists at the melting point.
(iii) Solid ⇌ Vapour equilibrium exists at the sublimation point.
(iv) Solute(s) ⇌Solute (solution) equilibrium exists in saturated solution.
Q39. For the reaction: N 2 (g) + 3H 2 (g) ⇌2NH 3 (g) equilibrium constant,
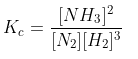
Some reactions are written below in Column I and their equilibrium constants in terms of K c are written in Column II. Match the following reactions with the corresponding equilibrium constant.
Sol:
(i) →(d), (ii) → (c), (iii) → (b)
ForN
2
(g) + 3H
2
(g)⇌2NH
3
(g)
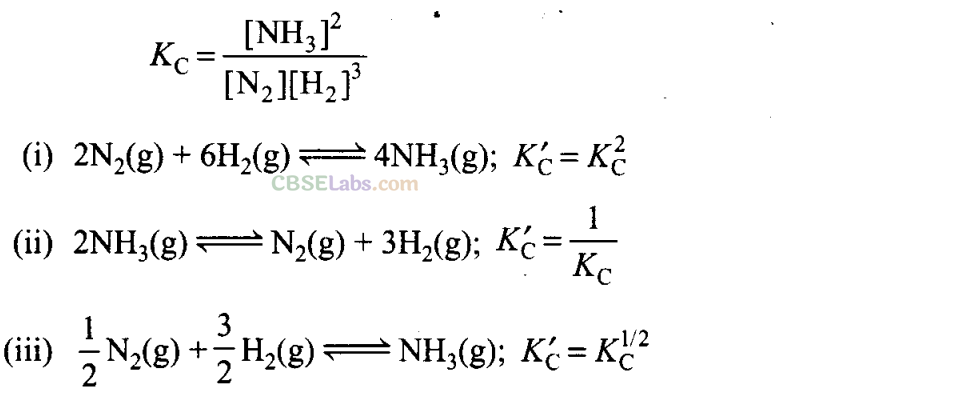
Q40. Match standard free energy of the reaction (Column I) with the corresponding equilibrium constant (Column II).
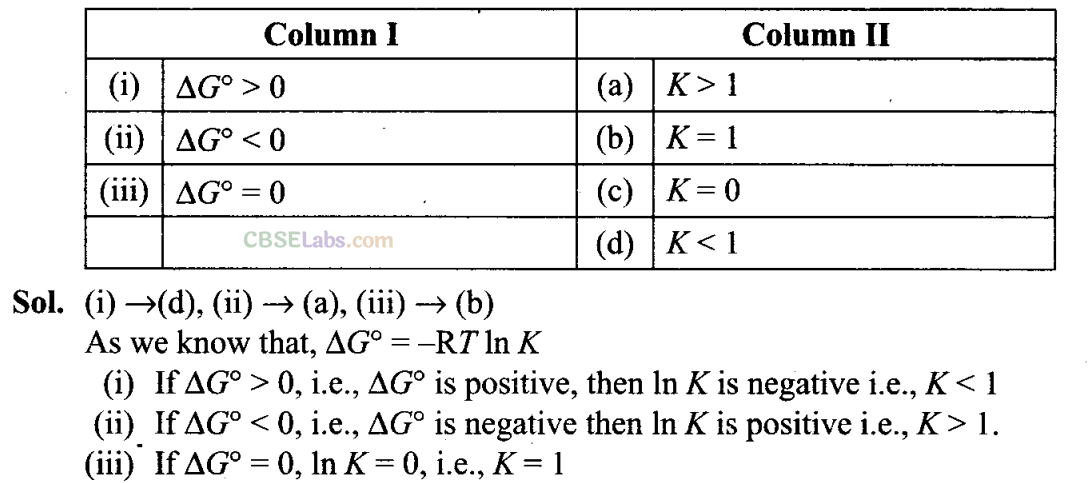
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chapter 5 States of Matter
- Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry