NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry
Multiple Choice Questions
Single Correct Answer Type
Q1. Which of the following gases is not a greenhouse gas?
(a) CO
(b) 0
3
(c) CH
4
(d) H
2
0 vapour
Sol:
(a) The gases which absorb solar energy near the earth’s surface and then radiate it back to the earth are called greenhouse gases.
Q2. Photochemical smog occurs in warm, dry and sunny climate. One of the following is not amongst the components of photochemical smog, identify it.
(a) N0
2
(b) 0
3
(c) S0
2
(d) Unsaturated hydrocarbon
Sol: (c) The smog which is formed in the presence of sunlight is called photochemical smog. This occurs in the months of summer when N0 2 and hydrocarbons are present in large amounts in the atmosphere. Concentration of 0 3 , PAN, aldehydes and ketones increases up in the atmosphere. S0 2 is not responsible for photochemical smog.
Q3. Which of the following statements is not true about classical smog?
(a) Its main components are produced by the action of sunlight on emissions
of
automobiles and factories.
(b) Produced in cold and humid climate.
(c) It contains compounds of reducing nature.
(d) It contains smoke, fog and sulphur dioxide.
Sol:
(a) Classical smog is initiated by a mixture of S0
2
, particulates and high humidity in the atmosphere in cold conditions. A fog of H
2
S0
4
droplets formed condenses on the particulates to form the smog. It is of reducing nature. The gases released by automobiles and factories are not responsible for classical smog.
Q4. Biochemical Oxygen Demand, /BOD) is a measure of organic material present in water. BOD value less than 5 ppm indicates a water sample to be
Sol:
(a) The total amount of oxygen consumed by micro-organisms (bacteria) in decomposing organic matter present in certain volume of a sample of water is called Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of the water.
Water is considered to be pure if it has BOD less than 5 ppm, whereas highly polluted water has BOD more than 17 ppm. Thus, the water having BOD less than 5 ppm is rich in dissolved oxygen.
Q5. Which .of the following statements is wrong?
(a) Ozone is not responsible for greenhouse effect.
(b) Ozone can oxidize sulphur dioxide present in the atmosphere to sulphur trioxide.
(c) Ozone hole is thinning of ozone layer present in stratosphere.
(d) Ozone is produced in upper stratosphere by the action of UV rays on oxygen.
Sol:
(a) Ozone is also one of the greenhouse gases.
Q6. Sewage containing organic waste should not be disposed in water bodies because it causes major water pollution. Fishes in such a polluted water die because of
(a) large number of mosquitoes.
(b) increase in the amount of dissolved oxygen.
(c) decrease in the amount of dissolved oxygen in water.
(d) clogging of gills by mud.
Sol:
(c) Organic waste consumes oxygen and therefore, dissolved oxygen in water decreases and fish in such polluted water die.
Q7. Which of the following statements about photochemical smog is wrong?
(a) It has high concentration of oxidizing agents.
(b) It has low concentration of
oxidizing
agent.
(c) It can be controlled by controlling the release of N0
2
, hydrocarbons, ozone etc.
(d) Plantation of some plants like
pinus
helps in controlling photochemical
Sol:
(b) Photochemical smog is oxidizing in nature because it contains large concentration of oxidizing agents N0
2
and 0
3
.
Q8. The gaseous envelope around the earth is known as atmosphere. The lowest layer of this is extended up to 10 km from sea level. This layer is .
(a) Stratosphere
(b) Troposphere
(c) Mesosphere
(d) Hydrosphere
Sol:
(b) The atmosphere is divided into four major regions:
(i) Troposphere (ii) Stratosphere . (iii) Mesosphere and (iv) Thermosphere Troposphere is the lowest region of the atmosphere.
Q9. Dinitrogen and dioxygen are main constituents of air but these do not react with each other to form oxides of nitrogen because____________ .
(a) the reaction is endothermic and requires very high temperature.
(b) the reaction can be initiated only in presence of a catalyst.
(c) oxides of nitrogen are unstable.
(d) N
2
and 0
2
are unreactive,
Sol:
(a) Major compounds of atmosphere are dinitrogen, dioxygen and water vapour.
N
2
= 78.08%, 0
2
= 20.95%
Both dinitrogen and dioxygen do not react with each other as nitrogen is an inactive gas. The triple bond in N
2
is very stable and its dissociation energy is very high. Both react with each other at very high temperature.
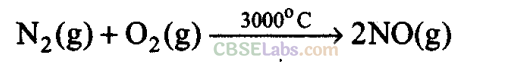
Q10. The pollutants which come directly in the air from
source
are called primary pollutants. Primary’pollutants are sometimes converted into secondary pollutants. Which of the following belongs to secondary air pollutants?
(a) CO
(b) Hydrocarbon
(c) Peroxyacetyl nitrate
(d) NO
Sol:
(c) Hydrocarbons present in atmosphere combine with oxygen atom produced by the photolysis of N0
2
to form highly reactive intermediate called free radical. Free radical initiates a series of reactions.Peroxyacetyl nitrate is formed, which Gan be said as secondary pollutant.
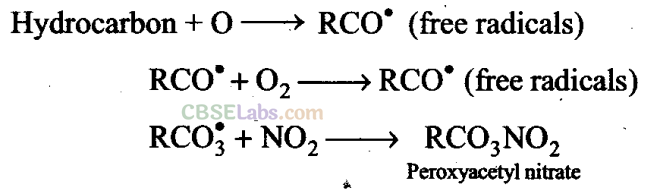
Q11. Which of the following statements is correct?
(a) Ozone hole is a hole formed in stratosphere from which ozone oozes out.
(b) Ozone hole is a hole formed in the troposphere from which ozone oozes out. .
(c) Ozone hole is thinning of ozone layer of stratosphere at some places.
(d) Ozone hole means vanishing of ozone layer around the earth completely.
Sol:
(c) Two types of compounds have been found to be the most responsible for depleting the ozone layer. These are:
(i) NO and (ii) Chlorofluorocarbons.
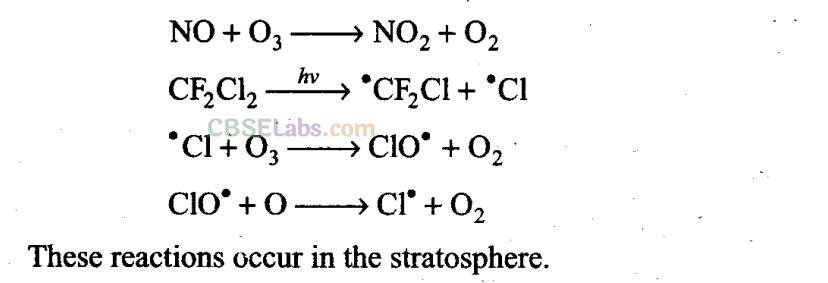
Q12. Which of the following practices will not come under green chemistry?
(a) If possible, making use of soap made of vegetable oils instead of using synthetic detergents.
(b) Using H
2
0
2
for bleaching purpose instead of using chlorine based bleaching agents.
(c) Using bicycle for traveling small distances instead of using petrol/diesel based vehicles.
(d) Using plastic cans for neatly storing substances.
Sol:
(d) Plastic is non-biodegradable polymer. Hence, it does not come under green chemistry. Green chemistry includes processes which lead to minimum pollution and less harm to the environment.
More than One Correct Answer Type
Q13. Which of the following conditions shows the polluted environment?
(a) pH of rain water is 5.6.
(b) Amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is 0.03%.
(c) Biochemical oxygen demand is 10 ppm.
(d) Eutrophication
Sol: (c, d) Polluted water may contain nutrients for the growth of algae, which covers the water surface and reduces the oxygen concentration in water. This leads to anaerobic condition, accumulation of obnoxious decay and animal death. This is process of eutrophication.
The amount of oxygen required by bacteria to break down the organic matter present in a certain volume of sample of water is called Biochemical Oxygen Demand. Clean water would have BOD value of 5 ppm whereas highly polluted could have BOD value of 17 ppm or more.
Normally rain water has pH of 6 due to H + ion formed by reaction of rain water with carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. When the pH of the rain water drops below 5.6, it is called acid rain.
Q14. Phosphate containing fertilizers cause water pollution. Addition of such compounds in water bodies causes
(a) enhanced growth of algae
(b) decrease in amount of dissolved oxygen in water
(c) deposition of calcium phosphate
(d) increase in fish population
Sol:
(a, b) Fertilizers containing phosphate present in water help in the excessive growth of aquatic plants and algae. Micro-organisms which decompose these plants consume oxygen. As a result, the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water decreases.
Q15. The acids present in acid rain are________ .
(a) Peroxyacetylnitrate
(b) H
2
C0
3
(c) HN0
3
(d) H
2
S0
4
Sol:
(b, c, d) C0
2
is slightly soluble in water forming carbonic acid.
Co
2
+ H
2
O → H
2
Co
3
The oxides of nitrogen undergo oxidation reaction followed by reaction with water vapours to form nitric acid.
2NO + 0
2
→ 2N0
2
2N0
2
+ H
2
0 → HN0
3
+ HNO
2
The oxidation of S0
2
into S0
3
occurs in the presence of dust particles or metal ions. The S0
3
then reacts with water vapours to form H
2
S0
4
.
Q16. The consequences of global warming may be .
(a) increase in average temperature of the earth
(b) melting of Himalayan Glaciers –
(c) increased biochemical oxygen demand
(d) eutrophication
Sol:
(a, b) The rate at which solar radiation is reaching the earth is constant but the amount of C0
2
in the air is increasing. Consequently, the heat radiated back to the earth will increase and the temperature of the earth surface will also increase.
This increase in temperature will disturb the thermal balance on the earth and could cause glacier and ice caps to melt.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q17. Greenhouse effect leads to global warming. Which substances are responsible for greenhouse effect?
Sol:
The heating of earth due to trapping of radiation is called greenhouse effect. The gases such as C0
2
, CH
4
, N
2
0, CFC1
3
, CF
2
C1
2
,0
3
etc. trap these radiations and are called greenhouse gases.
Q18. Acid rain is known to contain some acids. Name these acids. From where do they come in rain?
Sol:
Acid rain contains acids such as HN0
3
, H
2
S0
4
and H
2
C0
3
(along with small amount of HC1).
HN0
3
is formed by the oxidation of NO present in air to N0
2
and N0
3
and subsequent dissolution in water. H
2
S0
4
is formed by the oxidation of S0
2
present in air to S0
3
and subsequent dissolution in water.
H
2
C0
3
is formed by the dissolution of C0
2
of the air in water.
Q19. Ozone is a toxic gas and is a strong oxidizing agent, even then its presence in the stratosphere is very important. Explain what would happen if ozone from this region is completely removed.
Sol:
Ozone layer acts as a protective umbrella and does not allow the harmful UV radiations to reach the earth’s surface. If ozone is completely removed from the stratosphere, the UV radiations will fall directly on the humans causing skin cancer and on the plants affecting plant proteins.
Q20. Dissolved oxygen in water is v£ry important for aquatic life. What processes are responsible for the reduction of dissolved oxygen in water?
Sol:
The discharge of human sewage and organic waste from pulp and paper
industry and presence of leaves, grass, trash etc. in water due to run off result ‘ in phytoplankton growth. The microorganisms which decompose this organic matter need oxygen. Hence, the amount of oxygen in water of lakes etc. decreases.
Q21. On the basis of chemical reactions involved, explain how do chlorofluoro- carbons cause thinning of ozone layer in stratosphere.
Sol:
Chlorofluorocarbons are stable compounds. They move to stratosphere by random diffusion. These undergo decomposition in the presence of sunlight to release Cl atoms. These Cl atoms cause catalytic chemical reactions and cause significant depletion of ozone layer as shown below:
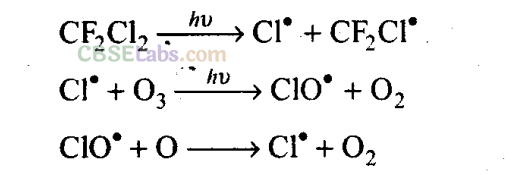
Since the free radicals use ozone and convert it to oxygen, they cause thinning of ozone layer in stratosphere.
Q22. What could be the harmful effects of improper management of industrial and domestic solid waste in a city?
Sol:
If domestic waste in a city is not properly managed, it may find its way into . sewers or may be eaten up by the cattle. The non-biodegradable waste like polythene bags, metal scrap etc. choke the sewers. The polythene bags, if swallowed by the cattle, can result into their death. Similarly, if industrial waste is not properly managed, it will cause pollution of the air, soil and water.
Q23.During an educational trip, a student of Botany saw a beautiful lake in
a ,
village. She collected many plants from that area. She noticed that villagers were washing clothes around the lake and at some places, waste material from houses was destroying its beauty. After few years, she visited the same r lake again. She was surprised to find that the lake was covered with algae, stinking smell was coming out and its water had become unusable. Can you explain the reason for this condition of the lake?
Sol:
Disposing of waste material and washing clothes in lake water makes the water rich in nutrients like phosphate. It enhances algae growth. Such profuse ‘ algal growth covers the water surface which reduces oxygen concentration in water. This leads to anaerobic conditions with accumulation of dead and decaying water animals, thus, leaving the water with stinking smell and making it unusable.
Q24. What are biodegradable and non-biodegradable pollutants?
Sol:
Biodegradable pollutants are those which can be decomposed by bacteria. For example, dust particles, sewage, cow dung etc. Non-biodegradable pollutants are those which cannot be decomposed by bacteria. For example, plastic materials, mercury, aluminium, DDT, etc.
Q25. What are the sources of dissolved oxygen in water?
Sol:
Sources of dissolved oxygen in water are (i) Photosynthesis (ii) Natural aeration (iii) Mechanical aeration.
Q26. What is the importance of measuring BOD of a water body?
Sol:
BOD is the measure of level of pollution caused by organic biodegradable material in terms of how much oxygen will be required to break down the organic material biologically. Clean water would have BOD values less than 5 ppm while highly polluted water could have a BOD value of 17 ppm or more.
Q27. Why does water covered with excessive algal growth become polluted?
Sol:
Presence of excessive algal growth shows that water contains a lot of
phosphate due to inflow of fertilizers, etc from the surroundings. Hence, such a sample of water is polluted.
Q28. A factory was started near a village. Suddenly villagers started feeling the presence of irritating vapours in the village and cases of headache, chest pain, cough, dryness of throat and breathing problems increased. Villagers blamed the emissions from the chimney of the factory for such problems. Explain what could have happened. Give chemical reactions for the support of your explanation.
Sol:
The symptoms observed in the villagers show that oxides of nitrogen and sulphur must be coming out of the chimney. This is due to combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil, natural gas, gasoline, etc. to produce high temperatures at which oxidation of atmospheric nitrogen takes place forming NO and N0
2
:

S0
2
is produced due to combustion of sulphur containing coal and fuel oil or roasting of sulphide ores like iron pyrites (FeS
2
), copper pyrites (CuFeS
2
), etc.
Cu 2 S + 0 2 →2Cu + S0 2
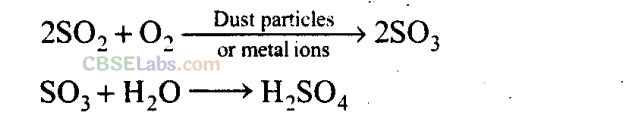
Q29. Oxidation of sulphur trioxide in the absence of a catalyst is a slow process but this oxidation occurs easily in the atmosphere. Explain how does this happen. Give chemical reactions for the conversion of S0
2
into S0
3
.
Sol:
The presence of particulate matter in polluted air catalyses the oxidation of S0
2
to S0
3
. The reaction is also promoted by ozone and hydrogen peroxide.
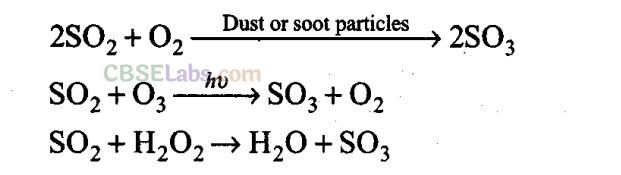
Q30. From where does ozone come in the photochemical smog?
Sol:
When fossil fuels are burnt, nitric oxide and hydrocarbons from unburnt fuels are produced. In sunlight, nitric oxide is converted to nitrogen dioxide. N0
2
absorbs energy from sunlight and breaks up into NO and free oxygen atoms which are very reactive and combine with
0
2
to form
0
3
, which reacts with NO to form N0
2
and 0
2
.
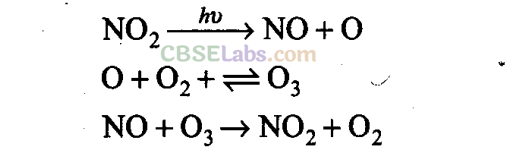
Q31. How is ozone produced in stratosphere?
Sol:
The formation of ozone in the stratosphere takes place in two steps. In the first step, ultraviolet radiation coming from the sun have sufficient energy to split dioxygen into two oxygen atoms. In the second step, the oxygen atoms react with more of dioxygen to form ozone.
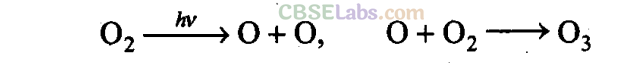
Q32. Ozone is a gas heavier than air. Why does ozone layer not settle down near the earth?
Sol:
In stratosphere, the formation of 0
3
gas goes on continuously, but 0
3
is also decomposed by UV radiation between 240-360 nm.
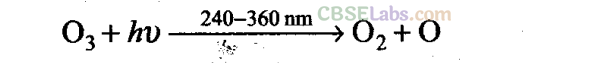
The O-atom reacts with second 0
3
molecule
0
3
+ 0 -+ 20
2
Net reaction 20
3
—> 30
2
Thus, the reaction forms a delicate balance in which the rate of 0
3
decomposition matches the rate of 0
3
formation, i.e., a dynamic equilibrium exists and maintains a constant concentration of 0
3
.
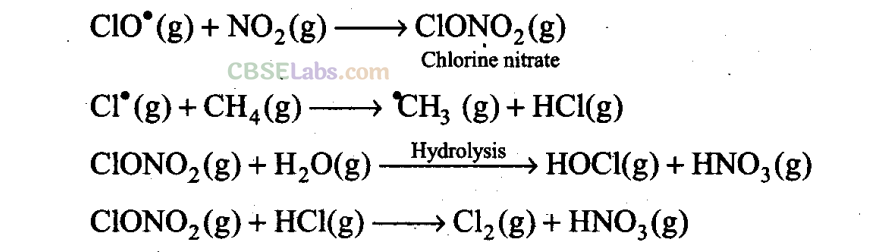
Q33. Sometime ago formation of polar stratospheric clouds was reported over Antarctica. Why were these formed? What happens when such clouds break up by warmth of sunlight?
Sol
: In summer season, nitrogen dioxide and methane react with chlorine monoxide and chlorine atoms forming chlorine sinks, preventing much ozone depletion, whereas in winter, special type of clouds called polar stratospheric clouds are formed over Antarctica. These polar stratospheric clouds provide surface on which chlorine nitrate gets hydrolysed to form hypochlorous acid. It also reacts with hydrogen chloride to give molecular chlorine.
When sunlight returns to the Antarctica in spring, the sun’s warmth breaks up the clouds and HOC1, Cl 2 are photolysed by sunlight.
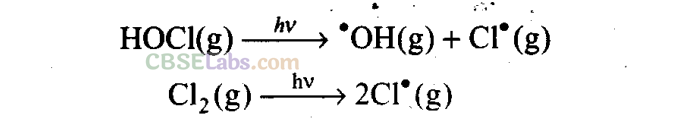
The chlorine radicals thus formed initiate the chain reaction for ozone depletion.
Q34. A person was using water supplied by Municipality. Due to shortage of water, he started using underground water. He felt laxative effect. What could be the cause?
Sol:
The laxative effect is observed only when the concentration of sulphates in water is greater than 500 ppm. Sulphate is harmless at moderate concentration but concentration above 500 ppm produces laxative effects and hypertension.
Matching Column Type Questions
Match the terms given in Column I with the compounds given in Column
| Column 1 | Column II | ||
| (a) | Acid rain | (1) | CHC1 2 -CHF 2 |
| (b) | Photochemical smog | (2) | CO |
| (c) | Combination with haemoglobin | (3) | co 2 |
| (d) | Depletion of ozone layer | (4) | so 2 |
| (5) | Unsaturated hydrocarbons | ||
Sol:
(a →3,4); (b → 4, 5); (c → 2); (d → 1)
(a) Acid rain is caused due to oxides of carbon, sulphur and nitrogen.
(b) Photochemical smog is formed by unburnt fuel (unsaturated hydrocarbons). *
(c) Carbon monoxide with haemoglobin is poisonous.
(d) Chlorofluorocarbons (CHC1
2
– CHF
2
) cause ozone depletion.
Q36. Match the pollutant(s) in Column I with the effect(s) in Column II.
| Column I | Column 11 | ||
| (a) | Oxides of sulphur | (1) | Global warming . |
| (b) | Nitrogen dioxide , | (2) | Damage to kidney |
| (c) | Carbon dioxide | (3) | ‘Blue baby’ syndrome |
| (d) | Nitrate in drinking water | (4) | Respiratory diseases |
| (e) | Lead | (5) | Red haze in traffic and congested areas |
Sol: (a → 4); (b → 5); (c →1); (d →3); (e → 2)
(a) Low concentration of sulphur dioxide causes respiratory disease, e.g., asthma, bronchitis etc.
(b) The irritant red haze in traffic and congested places is due to oxides of nitrogen.
(c) The increased amount of C0
2
in air is mainly responsible for global warming.
(d) Excess’nitrate in drinking water cause methemoglobinemia (blue baby syndrome)
(e) Lead can damage kidney, liver, reproductive system etc.
Q37. Match the activity given in Column I with the type of pollution created by it given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |||
| Releasing gases to the atmosphere after burning waste material containing Sulphur. | 0) | Water pollution | ||
| Using carbamates as pesticides. | (2) | Photochemical smog, damage to plant life, corrosion to building material, induce breathing problems, water pollution | ||
| Using synthetic detergents for washing clothes. | (3) | Damaging ozone layer | ||
| Releasing gases produced by automobiles and factories in the atmosphere. | (4) | May cause nerve diseases in human . | ||
| Using chlorofluorocarbon compounds for cleaning computer parts. | (5) | Classical smog, acid rain, water pollution, induce breathing problems, damage to buildings, corrosion of metals | ||
Sol: (a → 5); (b → 4); (c→ 1); (d → 2); (e→ 3)
Q38. Match the pollutants given in Column I with their effects given in Column II.
(a) Sulphur dioxide causes classical smog, acid rain, water pollution, induces breathing problems, causes damage to buildings, corrosion of metals.
(b) Using carbamates as pesticides can cause nerve diseases in humans
(c) Using synthetic detergents for washing clothes causes water pollution.
(d) Unsaturated hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides produced by automobiles and factories cause photochemical smog, damage to plant life, corrosion to building material, induce breathing problems, water pollution.
(e) Chlorofluorocarbons are believed to be the main reason for ozone layer depletion.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Phosphate fertilizers in water | (1) | BOD level of water increases |
| (b) | Methane in air | (2) | Acid rain |
| (c) | Synthetic detergents in water | (3) | Global warming |
| (d) | Nitrogen oxides in air | (4) | Eutrophication |
Sol:
(a → 1,4); (b → 3); (c → 1); (d → 2) ‘
(a) Phosphate fertilizers increase growth of algae, increasing BOD level and causing eutrophication.
(b) Methane oxidises to C0
2
which causes global warming.
(c) Use of synthetic detergents increases BOD level of water.
(d) Nitrogen oxides present in air combine with water forming nitric acid.
Assertion and Reason Type Questions
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Q39. Assertion (A): Greenhouse effect was observed in houses used to grow plants and these are made of green glass.
Reason (R): Greenhouse name has been given because glass houses are made of green glass.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
(c) There is no scientific relation between greenhouse effect and the given assertion or reason.
Q40. Assertion (A): The pH of acid rain is less than 5.6.
Reason (R): Carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere dissolves in
rain water
and forms carbonic acid.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
(b) In acid rain, pH is less than 5.6. Carbon dioxide dissolves in water to form weak acid.
H 2 + C0 2 →H 2 C0 3
Q41. Assertion (A): Photochemical smog is oxidizing in nature.
Reason (R): Photochemical smog contains N0
2
and 0
3
, which are formed during the sequence of reactions.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
(a) Photochemical smog contains N0
2
and 0
3
; both are oxidizing agents.
Q42. Assertion (A): Carbon dioxide is one of the important greenhouse gases. Reason (R): It is largely produced by respiratory function of animals and plants.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
C0
2
is produced by respiration of plants and animals; it is a greenhouse gas.
Q43. Assertion (A): Ozone is destroyed by solar radiation in upper stratosphere.
Reason (R): Thinning of the ozone layer allows excessive UV radiations to reach the surface of earth.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
(d) Solar radiations never destroy ozone layer.
Q44. Assertion (A): Excessive use of chlorinated synthetic pesticides causes soil and water pollution.
Reason (R): Such pesticides are non-biodegradable.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
(a) Chlorine containinginsecticides and pesticides are non biodegradable and they pollute soil and water.
Q45. Assertion (A): If BOD level of water in a reservoir is less than 5 ppm it is highly polluted.
Reason (R): High biological oxygen demand means
low
activity of bacteria in
water
.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are
true but
R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
(c) High BOD means high activity of Bacteria in water.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chapter 5 States of Matter
- Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry