NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
Multiple Choice Questions
Single Correct Answer Type
Q1. The element which exists in liquid state for a wide range of temperature and can be used for measuring high temperature is
(a) B
(b) A1
(c) Ga
(d) In
Sol:
(c) The melting point of gallium is 30°C and boiling point is 2240°C. Thus, the element exists in liquid state for a wide range of temperature.
Q2. Which of the following is a Lewis acid?
(a) AlCl
3
(b) MgCl
2
(c) CaCl
2
(d) BaCl
2
Sol:
(a) A1C1
3
is electron-deficient and hence acts as a Lewis acid.
Q3. The geometry of a complex species can be understood from the knowledge of type of hybridisation of orbitals of central atom. The hybridisation of orbitals of central atom in [B(OH)
4
]- and the geometry of the complex are respectively
(a) sp
3
, tetrahedral
(b) sp
3
, square planar
(c) sp
3
d
2
, octahedral
(d) dsp
2
, square planar
Sol:
Boron has die electronic configuration:
ls
2
2s
2
2p
x
1
2p
0
y
2p°
z
In the excited state, 2s-orbital electrons are impaired and one electron is shifted to a p-orbital. Now, hybridisation occurs between one s-and three p-orbitals to give sp
3
hybridisation and tetrahedral geometry.
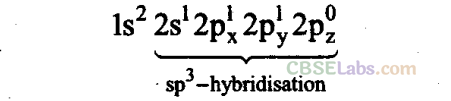
Q4. Which of the following oxides is acidic in nature?
(a) B
2
0
3
(b) A1
2
0
3
(c) Ga
2
0
3
(d) In
2
0
3
Sol:
(a) B
2
0
3
is acidic in nature. It reacts with basic oxides to form metal borates. Acidic nature decreases on moving down the group.
Q5. The exhibition of highest co-ordination dumber depends on the availability of vacant orbitals in the central atom. Which of the following elements is not likely to act as central atom in MF
6
3-
?
(a) B
(b) AI
(c) Ga
(d) In
Sol:
(a) The element M in the complex ion MF
6
3-
has a coordination number of six. Since B has only s- and p-orbitals and no d – orbitals, therefore, at the maximum it can show a coordination number of 4. Thus, B cannot form complex of the type MF
6
3-
, i.e., option (a) is correct.
Q6. Boric acid is an acid because its molecule
(a) contains replaceable H
+
ion
(b) gives up a proton.
(c)accepts OH
–
from water releasing proton.
(d) combines with proton from water molecule.
Sol:
(c) Because of the small size of boron atom and presence of only six electrons in its valence shell, B(OH)
3
accepts a pair of
electrons from OH
–
ion of H
2
0, releasing a proton.
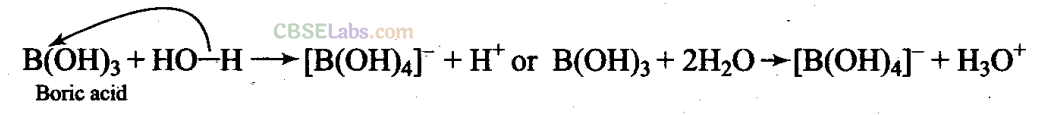
Q7. Catenation, i.e., linking •of similar atoms depends on size and electronic configuration of atoms. The tendency of catenation in Group 14 elements follows the order
(a) C > Si > Ge > Sn
(b) C » Si > Ge = Sn
(c) Si > C > Sn > Ge
(d) Ge > Sn > Si > C
Sol:
(b) The decrease in catenation property is linked with M – M bond energy which decreases from carbon to tin.
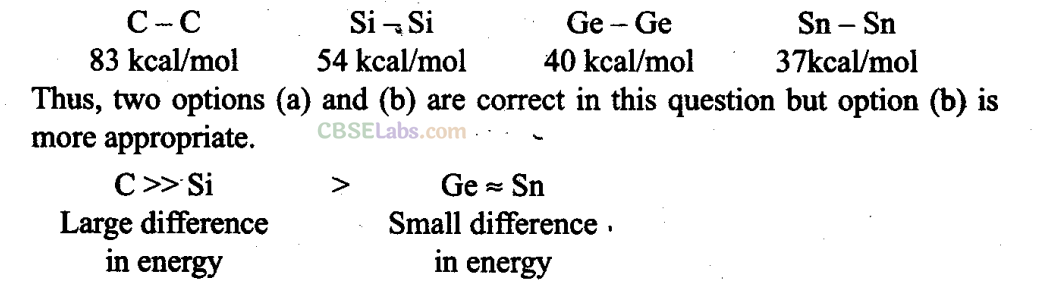
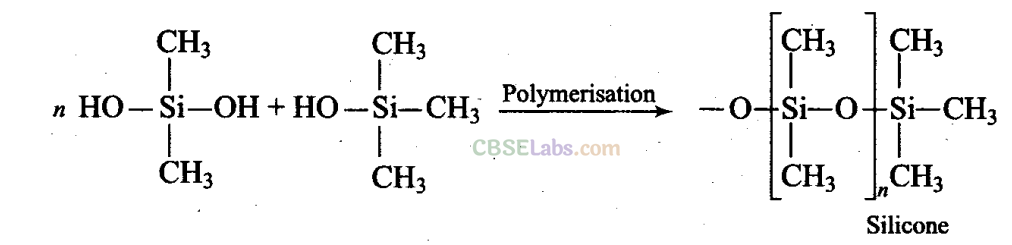
Q8. Silicon has a strong tendency to form polymers like silicones. The chain length of silicone polymer can be controlled by adding f (a) MeSiCl
3
(b) Me
2
SiCl
2
(c) Me
3
SiCl (d) Me
4
Si
Sol:
(c) The chain length of the polymer can be controlled by adding (CH
3
)
3
SiCl which blocks the ends.
Q9. Ionisation enthalpy (∆
t
H
1
kJ mol
-1
) for the elements of Group 13 follows the order.
(a) B > A1 > Ga > In > T1
(b) B < A1 < Ga< In <T1
(c) B < A1 > Ga < In < T1
(d) B > A1 < Ga > In < T1
Sol:
(d) On moving down the group from B to Tl, a regular decreasing trend in the ionisation energy values is not observed.
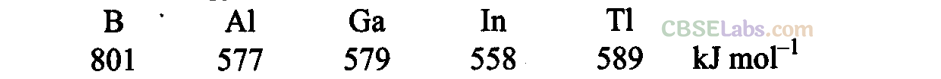
In Ga, there are ten d-electrons in the penultimate shell which screen the nuclear charge less effectively and thus, outer electron is held firmly. As a result, the ionisation energy of both A1 and Ga is nearly the same. The increase in ionisation energy from In to Tl is due to poor screening effect of 14f electrons present in the inner shell.
Q10. In the structure of diborane
(a) all hydrogen atoms lie in one plane and boron atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
(b) 2 boron atoms and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms lie in the same plane and 2 bridging hydrogen atoms lie in the perpendicular plane.
(c) 4 bridging hydrogen atoms and boron atoms lie in one plane and two terminal hydrogen atoms lie in a plane perpendicular to this plane.
(d) all the atoms are in the same plane.
Sol:
(b) Four terminal hydrogen atoms and two boron atoms lie in the same plane and two hydrogen atoms forming bridges lie in a plane perpendicular to the rest of the molecule.
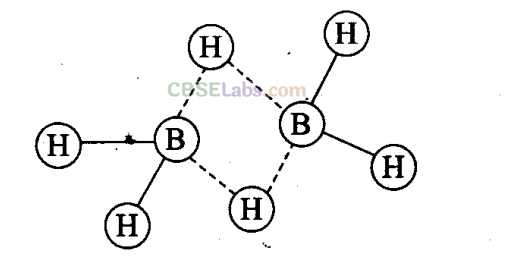
Q11. A compound X, of boron reacts with NH
3
on heating to give another compound Y which is called inorganic benzene. The compound X can be prepared by treating BF
3
with lithium aluminium hydride. The compounds X and Y are represented by the formulas.
(a) B
2
H
6
,B
3
N
3
H
6
(b) B
2
0
3
, B
3
N
3
H
6
(c) BF
3
, B
3
N
3
H
6
(d) B
3
N
3
H
6
, B
2
H
6
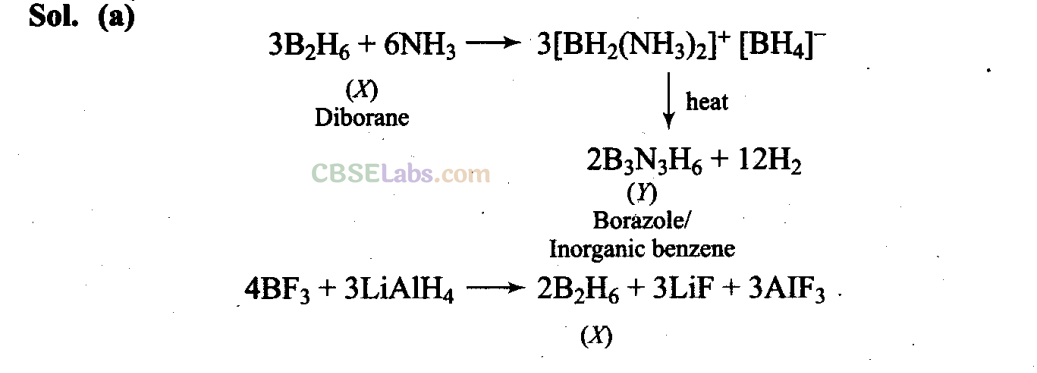
Q12. Quartz is extensively used as a piezoelectric material, it contains
(a) Pb
(b) Si
(c) Ti
(d) Sn
Sol:
(b) Quartz is a crystalline form of silica.
Q13. The most commonly used reducing agent is
(a) AlCl
3
(b) PbCl
2
(c) SnCl
4
(d) SnCl
2
Sol:
d) +4 oxidation state of Sn is more stable than +2 oxidation state. Therefore, Sn
2+
can be easily oxidised to Sn
4+
and hence SnCl
2
acts a reducing agent.
SnCl
2
+ 2Cl → SnCl
4
+ 2e
–
Q14. Dry ice is(a) Solid NH
3
(b) Solid S0
2
(c) solid C0
2
(d) solid N
2
Sol:
(c) Solid C0
2
is known as dry ice.
Q15. Cement, the important building material is a mixture of oxides of several elements. Besides calcium, iron and sulphur, oxides of elements of which of the group(s) are present in the mixture?
(a) group 2
(b) groups 2,13 and 14
(c) groups 2 and 13
(d) groups 2 and 14
Sol:
(b) Cement contains elements of group 2 (Ca), group 13 (Al) and group 14 (Si).
More than One Correct Answer Type
Q16. The reason for small radius of Ga compared to Al is_________ .
(a) poor screening effect of d and f orbitals
(b) increase in nuclear charge
(c) presence of higher orbitals
(d) higher atomic number
Sol:
(a, b) The additional 10 d-electrons offer poor screening effect for the outer electrons from the increased fluclear charge in Gallium. Hence, atomic radius of Gallium is less than that of aluminium.
Q17. The linear shape of C0
2
is due to _____
_ .
(a) sp
3
hybridisation of carbon
(b) sp hybridisation of carbon
(c) pπ-pπ bonding between carbon and oxygen
(d) sp
2
hybridisation of carbon
Sol:
(b, c) The linear shape of C0
2
is due to pπ-pπ bonding between carbon and oxygen and sp hybridisation of carbon.
Q18. Me
3
SiCl is used during polymerisation of organo silicones because
(a) the chain length of organo silicone polymers can be controlled by adding Me
3
(b) Me
3
SiCl blocks the end terminal of silicone polymer.
(c) Me
3
SiCl improves the quality and yield of the polymer. –
(d) Me
3
SiCl acts as a catalyst during polymerization.
Sol:
(a, b) The chain length of the polymer can be controlled by adding Me
3
SiCl which blocks the ends of the silicon polymer.
Q19. Which of the following statements are correct?
(a) Fullerenes have dangling bonds.
(b) Fullerenes are cage-like molecules.
(c) Graphite is thermodynamically most stable allotrope of carbon.
(d) Graphite is slippery and hard and therefore used as a dry lubricant in
Sol:
(b, c) Fullerenes are cage-like (soccer or rugby ball) molecules and graphite is thermodynamically most stable allotrope of carbon. Thus, options (b) and (c) are correct
Q20. Which of the following statements are correct? Answer on the basis of figure.
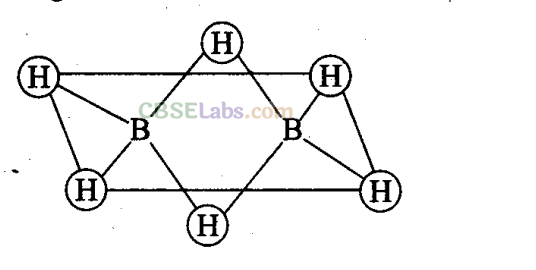
(a) The two bridged hydrogen atoms and the two boron atoms lie in one plane.
(b) Out of six B – H, bonds two bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2-electron bonds.
(c) Out of six B – H bonds four B – H bonds can be described in terms of 3 centre 2 electron bonds.
(d) The four terminal B – H bonds are two centre-two electron regular bonds.
Sol:
(a, b, d) Each of the two boron atoms is in sp
3
-hybrid state. Of the four hybrid orbitals, three have one electron each while the fourth is empty. Two of the four orbitals of each, of the boron atom overlap with two terminal hydrogen atoms forming two normal B – H σ-bonds. One of the remaining hybrid orbitals (either empty or singly occupied) of one of the boron atoms, 15-orbital of H (bridge atom) and one of hybrid orbitals of the other boron atom overlap to form a delocalized orbital covering the three nuclei with a pair of electrons. This is three centre two electron bond. Similar overlapping occurs with the second hydrogen atom (bridging) forming three centre two electrons bond.
Q21. Identify the correct resonance structures of carbon dioxide from the ones given below:
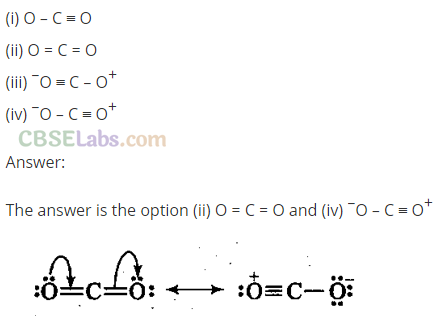
Short Answer Type Questions
Q22. Draw the structure of BC1
3
.NH
3
and AlCl
3
(dimer).
Sol:
In BCl
3
, the central B atom has six electrons in the valence shell. It is, therefore, an electron deficient molecule and needs two more electrons to ‘ complete its octet. In other words, BCl
3
acts as a Lewis acid. NH
3
, on the other hand, has a lone pair of electrons which it can donate easily. Therefore, NH
3
acts as a Lewis base. The Lewis acid (BC1
3
) and the Lewis base (NH
3
) combine together to form an adduct as shown below:
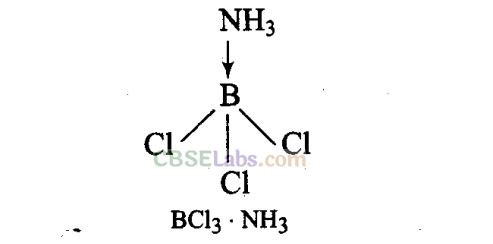
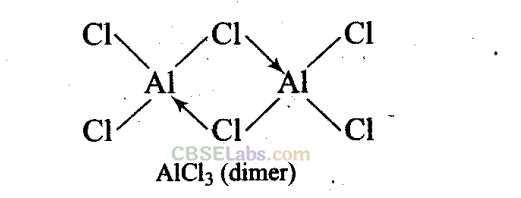
In A1C1
3
, A1 has six electrons in the valence shell. Therefore, it is an electron deficient molecule and needs two more electrons to complete its octet.
Chlorine, on the other hand, has three lone pairs of electrons. Therefore, to complete its octet, the central A1 atom of one molecule accepts a lone pair of electrons from Cl atom of the other molecule forming a dimeric structure as shown below.
Q23. Explain the nature of boric acid as a Lewis acid in water.
Sol:
Boric acid is a weak monobasic acid and acts as a Lewis acid by accepting electrons from a hydroxyl ion.
B(OH)
3
+ 2H
2
0 →[B(OH)
4
]
–
+ H
3
0
+
Q24. Draw the structure of boric acid showing hydrogen bonding. Which species is present in water? What is the hybridisation of boron in this species?
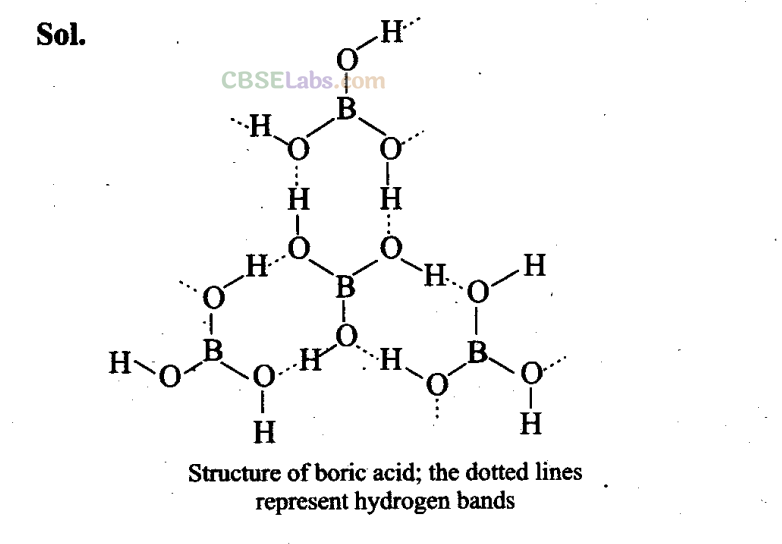
[B(OH)
4
]
–
units are present in water. Boron has sp
3
hybridisation in [B(OH)
4
]
–
unit.
Q25. Explain why the following compounds behave as Lewis acids?
(i) BC1
3
(ii) AICI3
Sol:(i)
BCl
3
: Boron has 6 electrons in its outermost orbital and has a vacant p orbital. Thus, it is an electron deficient compound. Hence, it acts as Lewis acid and accepts a lone pair of electrons.
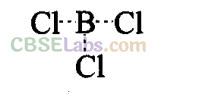
(ii) AlCl3 is also an electron deficient compound and acts as Lewis acid. It generally forms a dimer to achieve stability.
Q26. Give reasons for the following:
(a) CCl
4
is immiscible in water, whereas SiCl
4
is easily hydrolysed.
(b) Carbon has a strong tendency for catenation compared to silicon.
Sol:
(i) CC1
4
is a covalent compound while H
2
0 is a polar compound. Therefore, it is insoluble in water. Alternatively, CCl
4
is insoluble in water because carbon does not have (/-orbitals to accommodate the electrons donated by oxygen atom of water molecules. As a result, there is no interaction between CC1
4
and water molecules and hence CC1
4
is insoluble in water. On the other hand, SiCl
4
has d-orbitals to accommodate the lone pair of electrons donated by oxygen atom of water molecules. As a result, there is a strong interaction between SiCl
4
and water molecules. Consequently, SiCl
4
undergoes hydrolysis by water to form silicic acid.
(b) The bond dissociation energy decreases rapidly as the atomic size increases. Since the atomic size of carbon is much smaller (77 pm) as compared to that of silicon (118 pm), therefore, carbon-carbon bond dissociation energy is much higher (348 kJ mol -1 ) than that of silicon-silicon bond (297 kJ mol -1 ). Hence, because C – C bonds are much stronger as compared to Si-Si bonds, carbon has a much higher tendency for catenation than silicon.
Q27. Explain the following:
(i) C0
2
is a gas whereas Si0
2
is a solid.
(b) Silicon forms SiF
6
2-
ion whereas corresponding fluoro compound of carbon is not known.
Sol:
(a)
Because of its small size and good π-overlap with other small atoms, carbon forms strong double bonds with two oxygen atoms to give discrete C0
2
molecules. –
Silicon atom, on account of large size, does not have good π -overlap with other atoms. It uses its four valence electrons to form four single bonds directed towards the four apices of a tetrahedron (sp
3
-hybridisation). Each oxygen is linked with two silicon atoms, i.e., a giant three dimensional structure comes into existence which is very stable. Thus, C0
2
is a gas and Si0
2
is a solid.
(b) Silicon has 3d-orbitals in the valence shell and thus expands its octet giving sp 3 d 2 hybridisation while d-orbitals are not present in the valence shell of carbon. It can undergo ip 3 -hybridisation only. Thus, carbon is unable to form CF 6 2- anion.
Q28. The+1 oxidation state in group 13 and +2 oxidation state in group 14 becomes more and more stable with increasing atomic number. Explain.
Sol:
In group 13 and 14, as we move down the group, the tendency of s-electrons of the valence shell to participate in bond formation decreases. This is due to ineffective shielding of s-electrons of the valence shell by the intervening d- and f-electrons. This is called inert pair effect.
Due to this, s-electrons of the valence shell of group 13 and 14 are unable to participate in bonding. Hence, +1 and +2 oxidation states, in group 13 and 14 respectively, become -more stable with increasing atomic number.
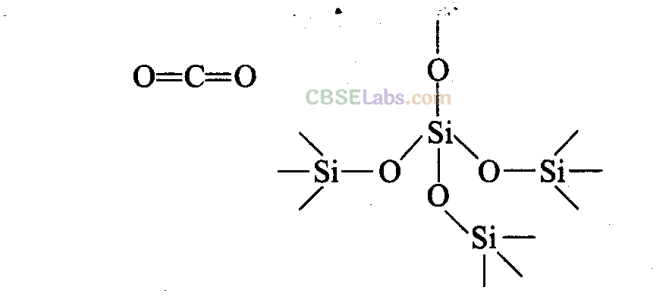
Q29. Carbon and silicon both belong to the group 14, but in spite of the stoichiometric similarity, the dioxides (i.e., carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide) differ in their structures. Comment.
Sol:
Carbon, the first member of group 14 possesses a pronounced ability to form stable p-p multiple bonds with itself and with other first row elements such as nitrogen and oxygen. In C0
2
, both the oxygen atoms are linked with carbon atom by double bonds.

However, silicon shows its reluctance in forming p-p multiple bonding due to large atomic size. Thus, in Si0 2 , oxygen atoms are linked to silicon atom by single covalent bonds giving three dimensional network.
Q30. If a trivalent atom replaces a few silicon atoms in three dimensional network of silicon dioxide, what would be the type of charge on overall structure?
Sol:
If a few tetrahedral Si atoms in a three dimensional network structure of Si0
2
are replaced by an equal number of trivalent atoms, then one valence electron of each Si atom will become free. As a result, each substitution of Si atom by a trivalent atom introduces one unit negative charge into the three dimensional network structure of Si0
2
. Hence, Si0
2
becomes negatively charged.
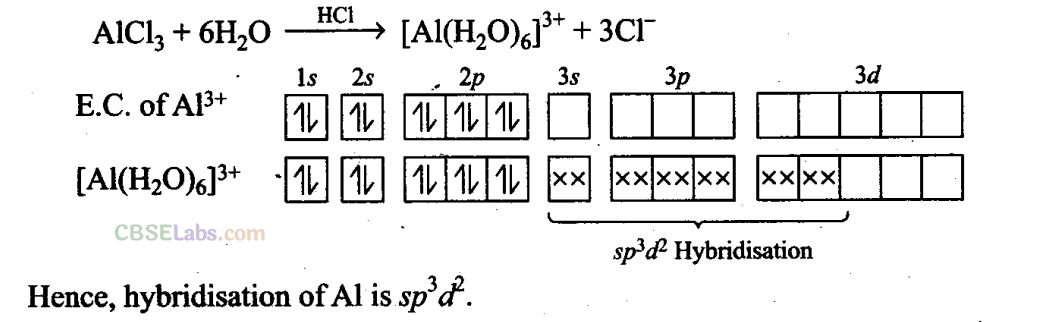
Q31. When BC1
3
is treated with water, it hydrolyses and forms [B(OH)
4
]” only whereas A1C1
3
in acidified aqueous solution forms [A1(H
2
0)
6
]
3+
Explain what is the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in these species?
Sol:
BC1
3
+ 3H
2
0→ B(OH)
3
+ 3HC1
B(0H)
3
+ H
2
0→[B(OH)4]
–
+ H
+
B(OH)
3
due to its incomplete octet accepts an electron pair (as OH
–
) to give [B(OH)
4
]
–
. Boron in this ion involves one 2s orbital and three 2p orbitals. Thus, hybridisation of B in [B(OH)
4
]
–
is sp
3
.
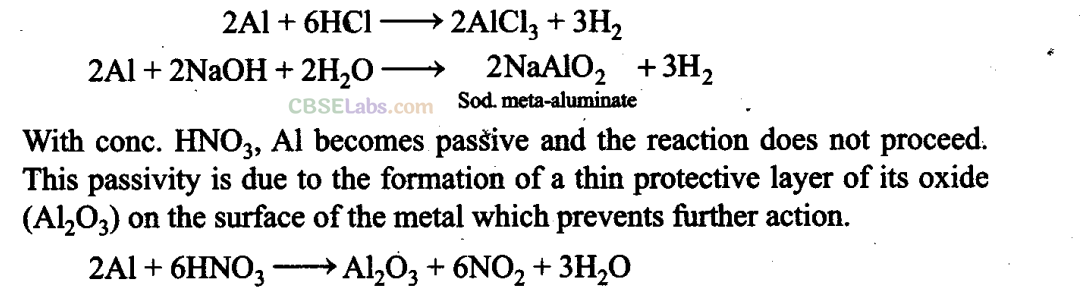
Q32. Aluminium dissolves in mineral acids and aqueous alkalies and thus shows amphoteric character, A piece of aluminium foil is treated with dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sodium hydroxide solution in a test tube and on bringing a burning matchstick near the mouth of the test tube, a pop sound indicates the evolution of hydrogen gas. The same activity when performed with concentrated nitric acid, reaction doesn’t proceed. Explain the reason.
Sol
: Al being amphoteric dissolves both in acids and alkalies evolving H
2
gas which bums with a pop sound.
Q31. Explain the following:
- Gallium has higher ionisation enthalpy than aluminium.
- Boron does not exist as B 3+
- Aluminium forms [A1F 6 ] 3- ion but boron does not form [BF 6 ] 3-
- PbX 2 is more stable than PbX 4 .
- Pb 4+ acts as an oxidising agent but Sn 2+ acts as a reducing agent.
- Electron gain enthalpy of chlorine is more negative as compared to fluorine.
- TI(N0 3 ) 3 acts as an oxidising agent.
- Carbon shows catenation property but lead does not.
- BF 3 does not hydrolyse.
- Why does the element silicon, not form a graphite like structure whereas carbon does.
Sol: (i) Due to ineffective shielding of valence electrons by the intervening 3d electrons, the effective nuclear charge on Ga is slightly higher than that on A1 and hence the ∆H i of gallium is slightly higher than that of Al. Boron has three electrons in the valence shell. Because of its small size and high sum of the first three ionisation enthalpies (i.e., ∆
(ii) Boron has three electrons in the valence shell. Because of its small size and high sum of the first three ionisation enthalpies (i.e., ∆ i H 1 + ∆ i H 2 + ∆ i H 3 ), boron does not lose all its valence electrons to form B 3+ ions.
(iii) Al has vacant d-orbitals and hence can expand its coordination number from 4 to 6 and hence forms octahedral [A1F 6 ] 3- ion in which Al undergoes sp 3 d 2 hybridisation. In contrast, B does not have d-orbitals. Therefore, it can have a maximum coordination number of 4. Therefore, B forms [BF 4 ] – (in which B is sp 3 -hybridised) but not [BF 6 ] 3- .
(iv) Due to inert pair effect, +2 oxidation state of Pb is more stable than its +4 oxidation state. Consequently, PbX 2 in which the oxidation state of Pb is +2 is more stable than PbX 4 in which the oxidation state of Pb is +4.
(v) Inert pair effect is less prominent in Sn than in Pb. Therefore, +2 oxidation of Sn is less stable than its +4 oxidation state. In other words, Sn
2+
can easily lose two electrons to form Sn
4+
and hence Sn
2+
acts as a reducing agent.
Sn
2+
→Sn
4+
+ 2e
In contrast, the inert pair effect is’ more prominent in Pb than in Sn. Therefore, +2 oxidation state of Pb is more stable than its +4 oxidation state. In other words, Pb 4+ can easily lose two electrons to form Pb 2+ and hence Pb 4+ acts as an oxidising agent.
Pb 4+ + 2e – →-Pb 2+
(vi) Due to small size, the electron-electron repulsions in the relatively compact 2p-subshell of F are quite strong and hence the incoming electron is not accepted with the same ease as in case of bigger Cl atom where repulsions are comparatively weak. Thus, electron gain enthalpy of chlorine is more negative as compared to that of fluorine.
(vii) Due ta strong inert pair effect, the +3 oxidation state of T1 is less stable than its +1 oxidation state. Since in T1(N0 3 ) 3 , oxidation state of T1 is +3, therefore, it can easily gain two electrons to form T1N0 3 in which the oxidation state of T1 is +1. Consequently, T1(N0 3 ) 3 acts as an oxidising agent.
(viii) Property of catenation depends upon the strength of element-element bond which, in turn, depends upon the size of the element. Since the atomic size of carbon is much smaller than that of lead, therefore, carbon-carbon bond strength is much higher than that of lead-lead bond. Due to stronger C-C than Pb-Pb bonds, carbon has a much higher tendency for catenation than lead.
(ix) Unlike other boron halides, BF 3 does not hydrolyse completely. Instead, it hydrolyses incompletely to form boric acid and fluoroboric acid. This is because the HF first formed reacts with H 3 B0 3 .
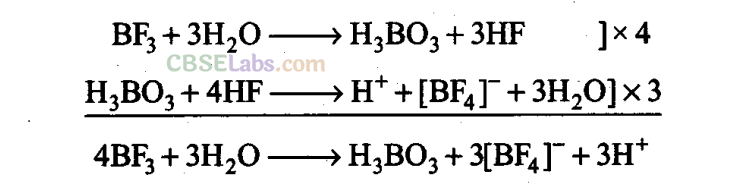
(x) In graphite, carbon is sp
2
-hybridised and each carbon is linked to three other carbon atoms by forming hexagonal rings. Each carbon is now left with one unhybridised p-orbital which undergoes sideways overlap to form three p-p double bonds. Thus, graphite has two-dimensional sheet like (layered) structure consisting of a number of benzene rings fused together. Silicon, on the other hand, does not form an analogue of carbon because of the following reason:
Due to bigger size and smaller electronegativity of Si than C, it does not undergo sp
2
-hybridisation and hence it does not form p-p double bonds needed for graphite like structure. Instead, it prefers to undergo only sp
3
-hybridisation and hence silicon has diamond like threedimensional network
Q34. Identify the compound A,
X and Z in the following reactions:
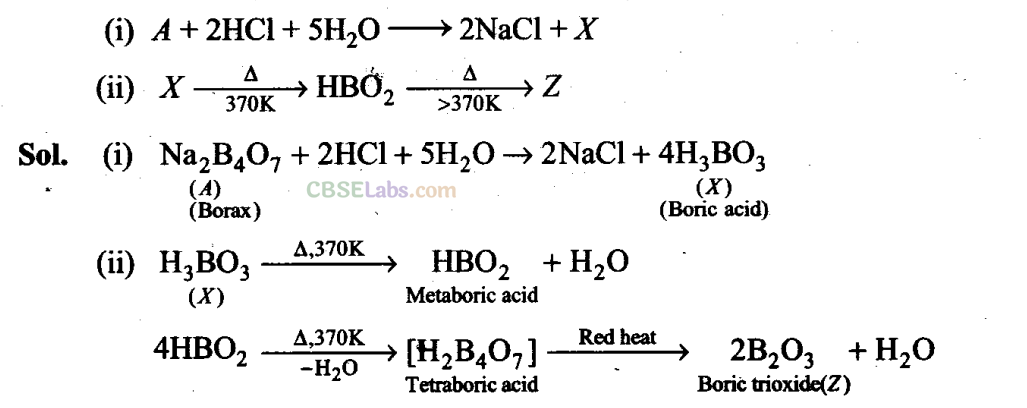
Q35. Complete the following chemical equations:
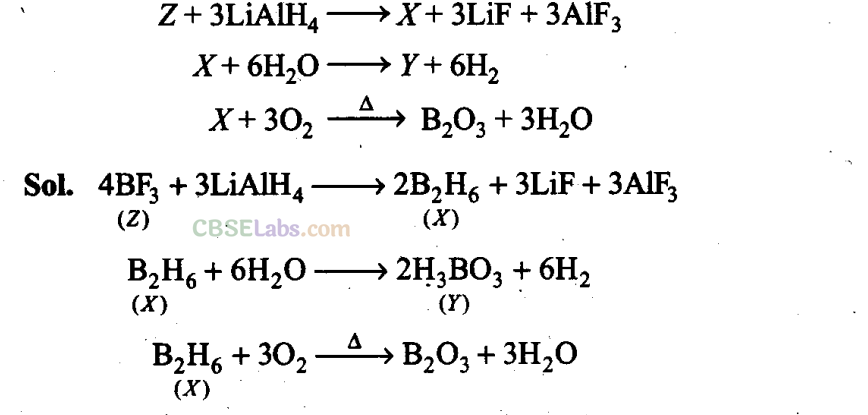
Matching Column Type Questions
In the following
questions
more than one correlation is possible between options of column I and II. Make as many correlations as you can.
Q36. Match the species given in Column I with the properties mentioned in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) BF 4 – | (a) Oxidation state of central atom is +4 |
| (ii) A1C1 3 | (b) Strong oxidising agent |
| (iii) SnO | (c) Lewis acid |
| (iv) Pb0 2 | (d) Can be further oxidised |
| (e) Tetrahedral shape |
Sol:
(i→e); (ii → c); (iii —> d); (iv →a, b)
(i) BF
4
–
: Tetrahedral shape, sp
3
hybridisation, regular geometry.
(ii) AlCl
3
: Octet of A1 not complete, acts as Lewis acid.
(iii) SnO: Sn
2+
can show +4 oxidation state.
(iv)Pb0
2
: Oxidation.state of Pb in Pb0
2
is +4. Due to inert pair effect, Pb
4+
is less stable than Pb
2+
and hence acts as strong oxidising agent.
Q37. Match the species given in Column I with properties given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Diborane | (a) Used as a flux for soldering metals |
| (ii) Gallium ‘ | (b) Crystalline form of silica |
| (iii) Borax | (c) Banana bonds |
| (iv) Aluminosilicate | (d) Low melting, high boiling, useful for measuring high temperatures |
| (v) Quartz | (e) Used as catalyst in petrochemical industries |
Sol: (i → c); (ii → d); (iii → a); (iv → e); (v → b)
- BH 3 is unstable, forms diborane B 2 H 6 by 3 centre -2 electron bonds, shows banana bonds.
- Gallium with low melting point and high boiling point makes it useful to measure high temperatures.
- Borax is used as a flux for soldering metals.
- Aluminosilicate is used as catalyst in petrochemical industries.
- Quartz, is a crystalline form of silica.
Q38. Match the species given in Column I with the hybridisation given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Boron in [B(OH) 4 ]“ | (a) sp 2 |
| (ii) Aluminium in [A1(H 2 0) 6 ] 3+ | (b) sp 3 |
| (iii) Boron in B 2 H 6 | (c) sp 3 d 2 |
| (iv) Carbon in Buckminsterfullerene | |
| (v) Silicon in SiO 4 4- | |
| (vi) Germanium in [GeCl 6 ] 2- |
Sol:
(i →b); (ii→ c); (iii → b); (iv→ a); (v →b); (vi→ c)
- Boron in [B(OH) 4 ] – is sp 3
- Aluminium in [A1(H 2 0) 6 ] 3+ is sp 3 d 2 hybridised
- Boron in B 2 H 6 is sp 3
- Carbon in Buckminsterfullerene sp 2 is hybridised.
- Silicon in SiO 4 4- is sp 3
- Germanium in [GeCl 6 ] 2- is sp 3 d 2
Assertion and Reason Type Questions ’
In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct option out of the choices given below each question.
Q39. Assertion (A): If aluminium atoms replace a few silicon atoms in three dimensional network of silicon dioxide, the overall structure acquires a negative charge.
Reason (R): Aluminium is trivalent while silicon is tetravalent.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct.
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
(a) In aluminosilicates (anion), some of the silicon atoms are replaced by aluminium. Since, aluminium is trivalent while silicon is tetravalent, hence we get negatively charged ion.
Q40. Assertion (A): Silicones are water repelling in nature.
Reason (R): Silicones are organosilicon polymers, which have (-R
2
SiO-) as repeating unit.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) Both A and R are not correct. ‘
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Sol:
(b) Silicones are organosilicon polymers and they are hydrophobic in nature. Silicones neither react nor absorb water molecules.
NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Chemistry Solutions
- Chapter 1 Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry
- Chapter 2 Structure of Atom
- Chapter 3 Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties
- Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure
- Chapter 5 States of Matter
- Chapter 6 Thermodynamics
- Chapter 7 Equilibrium
- Chapter 8 Redox Reactions
- Chapter 9 Hydrogen
- Chapter 10 The s-Block Elements
- Chapter 11 The p-Block Elements
- Chapter 12 Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques
- Chapter 13 Hydrocarbons
- Chapter 14 Environmental Chemistry