NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
Short Answer Questions
Question 1. Do genetic combination of mothers play a significant role in determining the sex of new born?
Answer.
No, mothers have no role in determining the sex of the new born. Mothers have a pair of X chromosome. And all children will inherit an ‘X’ chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls.
Question 2. Mention three important features of fossils which help in the study of evolution.
Answer.
The three important features of fossils that help in the study of evolution are as follows:
- It helps in establishing the time period in which the organisms lived.
- It helps in establishing evolutionary traits among organisms and their ancestors.
- It is the mode of preservation of the remains of ancient species.
Question 3. In human beings, the statistical probability of getting either a male or female child is 50 : 50. Give a suitable explanation.
Answer.
The sex of a child is determined by the type of sex chromosome contributed by male gamete. The statistical probability of getting either a male or female child is 50: 50, because the ratio of male gametes containing X chromosome and those containing Y chromosome is 50 : 50.
Question 4. What are homologous structures? Give an example. Is it necessary that homologous structures always have a common ancestor?
Answer.
Homologous organs are those organs which have the same basic structural design and developmental origin but have different functions and appearance. Example: The forelimb of a frog, a lizard, a bird and a man seem to be built from the same basic design of bones, but they perform different functions.
Yes, it is necessary that homologous structures always have a common ancestor in order to carry out the different activities. Otherwise there cannot be any similarity in basic plan, internal structure, development or origin.
Question 5. Does the occurrence of diversity of animals on earth suggest their diverse ancestry also? Discuss this point in the light of evolution.
Answer.
Diversity of animals does not mean that they have diverse ancestry because common ancestry greatly limit the extent of diversity. If the animals are inhabiting in the same habitat their evolution by speciation and geographical isolation is also not likely. Animals having a common ancestor have developed new traits forming various groups of animals.
Question 6. A woman has only daughters. Analyse the situation genetically and provide a suitable explanation.
Answer.
The women produces ova with ‘X’ chromosome and man produces sperms with X and Y chromosome.
If the husband of the woman transfer X chromosome, then child will be a girl. On the other hand, if the husband transfer Y chromosome, the child will be a boy. In the case, the husband is always transferring X chromosome and hence, all the children are girl.
Long Answer Questions
Question 7. Give reasons why acquired characters are not inherited.
Answer.
Acquired characters are not inherited because they do not produce change in the DNA of germ cells, only those characters which have a gene for them can be inherited.
Question 8. Does geographical isolation of individual of a species lead to formation of a new species? Provide a suitable explanation.
Answer.
Yes, geographical isolation of individual of a species lead to the formation of a new species.
Geographical isolation of a population leads to genetic drift and there will be no gene flow between it and the parent species. Inbreeding in small population will reproduce among themselves and generate new variations. Accumulation of those variations over several generations will lead to formation of new species.
Question 9. Bacteria have a simpler body plan when compared with human beings. Does it mean that human beings are more evolved than bacteria? Provide a suitable explanation.
Answer.
Both bacteria and human beings perform all activities of life to live in their environment. Human beings have more complex organisation and differentiation which are absent in bacteria. Since, complexity and differentiation develop only through evolution, humans are more evolved than bacteria.
Question 10. Evolution has exhibited a greater stability of molecular structure when compared with morphological structures. Comment on the statement and justify your opinion.
Answer.
There is immense diversity in size, form, structure and morphological features in the living world. At the molecular level, these diverse types of organisms exhibit similarity of the basic bio molecules like DNA, RNA, carbohydrates, proteins, etc.
Question 11. Study the following cross and showing self-pollination in Flf fill in the blank and answer the question that follows (Q12, Q13 and Q14):
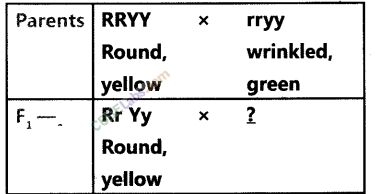
Answer.
Rr Yy Round, yellow.
Question 12. In previous question, what are the combinations of character in the F2 progeny? What are their ratios?
Answer.
Round yellow – 9, Round green – 3, Wrinkled yellow – 3 Wrinkled green – 1, Le. 9 : 3 : 3 : 1.
Question 13. Give the basic features of the mechanism of inheritance.
Answer
. Basic features for the mechanism of Inheritance are as follows:
- Characters are controlled by genes,
- Each gene controls one character.
- Genes are located oh chromosomes.
- There may be two or more forms of gene.
- An individual possess two forms of genes whether similar or dissimilar.
- One form may be dominant over the other.
- The two alleles separate at the time of gamete formation.
- The two forms are brought together in the zygote.
- Alleles of different genes located on separate chromosomes behave independent of one another.
Question 14. Give reasons for the appearance of new combinations of characters in the F2 progeny.
Answer.
An organism can inherit each character independently. So, in the F2 progeny new combination of character appears. Tall/ Short and Round/Wrinkled seed trait are independently inherited.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Solutions
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources