NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science . Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes
Short Answer Type Questions
1.“All plants give out oxygen during day and carbon dioxide during night”. Do you agree with this statement? Give reason.
Answer.
Yes, respiration takes place throughout the day and night but photosynthesis takes place only during day time. During day time, as the rate of photosynthesis is more than the rate of respiration, the net result is evolution of oxygen. At night there is no photosynthesis, so they give out carbon dioxide due to respiration.
2.How do the guard cells regulate opening and closing of stomatal pores?
Answer.
The swelling of guard cells due to absorption of water causes opening of stomatal pores while shrinking of guard cells closes the pores. Opening and closing of stomata occurs due to turgor changes in guard cells. When guard cells are turgid, stomatal pore is open while in flaccid conditions, the stomatal aperture closes.
3.Why do fishes die when taken out of water?
Answer.
Fishes respire with the help of gills. Gills are richly supplied with blood capillaries and can readily absorb oxygen dissolved in water. Since fishes cannot absorb gaseous oxygen from the atmosphere they die soon after they are taken out of water.
4.Is ‘nutrition’ a necessity for an organism? Discuss.
Answer.
Food is required for the following purposes:
(i) It provides energy for the various metabolic processes in the body.
(ii) It is essential for the growth of new cells and repair or replacement of worn out cells.
(iii) It is needed to develop resistance against various diseases.
5.What would happen if green plants disappear from earth?
Answer.
Green plants are the sources of energy for all organisms. If all green plants disappear from the earth, all the herbivores will die due to starvation and so will the carnivores and then the decomposers.
6. What are the adaptations of leaf for photosynthesis?
Answer.
(i) Leaves provide large surface area for maximum light absorption.
(ii) Leaves are arranged at right angles to the light source in a way that causes overlapping.
(iii) The extensive network of veins enables quick transport of substances to and from the mesophyll cells.
(iv) Presence of numerous stomata for gaseous exchange.
(v) The chloroplasts are more in number on the upper surface of leaves to absorb more light energy.
7.Why is small intestine in herbivores longer than in carnivores?
Answer.
Digestion of cellulose takes a longer time. Hence, herbivores eating grass need a longer small intestine to allow complete digestion of cellulose. Carnivorous animals cannot digest cellulose, hence they have a shorter intestine.
8.What will happen if mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands?
Answer.
Gastric glands in stomach release hydrochloric acid, enzyme pepsin and mucus. Mucus protects the inner lining of stomach from the action of hydrochloric acid and enzyme pepsin. If mucus is not released, it will lead to erosion of inner lining of stomach, leading to acidity and ulcers.
9.What is the significance of emulsification of fats?
Answer.
Fats are present in food in the form of large globules which makes it difficult for enzymes to act on them. Bile salts present in bile break them down mechanically into smaller globules which increases the efficiency of fat digesting enzymes lipase.
10.Why does absorption of digested food occur mainly in the small intestine?
Answer.
Maximum absorption occurs in small intestine because:
(a) Digestion is completed in small intestine.
(b) Inner lining of small intestine is provided with villi which increases the surface area for absorption.
(c) Wall of intestine is richly supplied with blood vessels (which take the absorbed food to each and every cell of the body).
11.What is the advantage of having four chambered heart?
Answer.
In four chambered heart, left half is completely separated from right half by septa. This prevents oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing. This allows a highly efficient supply of oxygenated blood to all parts of the body. This is useful in animals that have high energy needs, such as birds and mammals and maintain body temperature.
12. Mention the major events during photosynthesis.
Answer.
The major events during photosynthesis are:
(i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
(ii) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
(iii) Splitting of H
2
O into H
2
, O
2
”
(iv) Reduction of CO
2
to carbohydrates.
13. Name the energy currency in the living organisms. When and where is it produced?
Answer.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) produced during respiration in living organisms
and also during photosynthesis in plants.
14. What is common for cuscuta, ticks and leeches?
Answer.
All are parasites, they derive nutrition from plants or animals without killing them.
15. Explain the role of mouth in digestion of food.
Answer.
(i) Food is crushed into small pieces by the teeth.
(ii) Tongue helps in thorough mixing of food with saliva and the enzyme amylase (found in saliva) breaks down starch into sugars.
16. What are the functions of gastric glands present in the wall of the stomach?
Answer.
(i) Production of pepsin enzyme that digests proteins.
(ii) Secretion of Mucus for protection of inner lining of stomach.
17. Name the correct substrates for the following enzymes
(a) Trypsin (b) Amylase (c) Pepsin (d) Lipase
Answer.
(a) Protein (b) Starch (c) Protein (d) Fats
18. What will happen if platelets were absent in the blood?
Answer.
In the absence of platelets, the process of clotting will be affected. When cut, the blood will not stop oozing out.
19. Plants have low energy needs as compared to animals. Explain.
Answer.
Plants do not move. In a large plant body there are many dead cells like schlerenchyma as a result it requires less energy as compared to animals. Animals need more energy as they have to move in search of food, shelter and mates.
20. Why and how does water enter continuously into the root xylem?
Answer.
Cells of root are in close contact with soil and so actively take up ions. The ion- concentration, increases inside the root and hence osmotic pressure increases the movement of water from the soil into the root which occurs continuously. Transpiration also plays a big role in causing, osmotic pressure.
21.Why is transpiration important for plants?
Answer.
Transpiration is important because:
(i) it helps in absorption and upward movement of water and minerals from roots to leaves
(ii)it prevents the plant parts from heating up.
Long Answer Type Questions
1.Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.
Answer.
The mode of nutrition in amoeba is Holozoic, and the process of obtaining food by amoeba is called phagocytosis. The different processes involved in the nutrition of amoeba are:
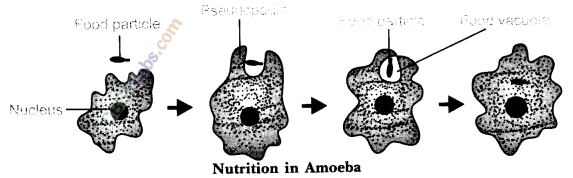
(i) Ingestion: Ingestion is the process of taking food in the body. Amoeba is a unicellular animal, so it doesn’t have a mouth for ingestion of food. Amoeba ingests the food by encircling it by forming pseudopodia. When the food is completely encircled, the food is engulfed in the form of a bag called food vacuole.
(ii)Digestion: Digestion is the process of breaking the large and insoluble molecules in small and water soluble molecules. In amoeba, several digestive enzymes react on the food present in the food vacuoles and break it down into simple and soluble molecules.
(iii) Absorption: The food digested by digestive enzymes is then absorbed in the cytoplasm by the process of diffusion. While the undigested food remains in the food vacuole. If a large amount of food is absorbed by amoeba, the excess food is stored in the cytoplasm in the form of glycogen and lipids.
(iv) Assimilation: During this step the food absorbed by the cytoplasm is used to obtain energy, growth and repair. This process of utilizing absorbed food for obtaining energy, repair and growth is called assimilation.
(v) Egestion: When sufficient amount of undigested food gets collected in the food vacuole, it is thrown out of the body by rupturing cell membrane. The process of removal of undigested food from the body is called egestion.
2. Describe the alimentary canal of man
Answer.
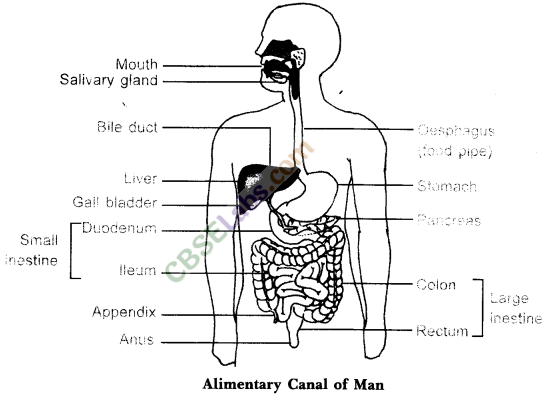
(i)Mouth: Food is ingested (the taking in of food or liquid into the body), chewed and swallowed. It is softened by chemicals in saliva (spit). When you swallow, food travels down the oesophagus into the stomach. The food that leaves the mouth is called bolus.
(ii) Stomach: The stomach is a bag with a muscular wall. It mashes food into a pulp, helped by chemicals called gastric juices. When empty it is about 0.5L in size, but when it is full after a meal it can stretch to 4L in size. Food that leaves the stomach is called chyme. It passes into the small intestines after about 4 hours of eating.
(iii) Small intestine: It is a 6 meter long tube where chyme is further broken down. Carbohydrates and fat are broken down and absorbed through the intestine walls into the blood.
(iv) Large intestine: Food that can’t be digested passes into the large intestines. It is then pushed towards the anus where it is excreted as feces.
3.Explain the importance of soil for plant growth.
Answer.
Materials required for plant growth are obtained from soil, e.g. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, other minerals and water. They have to be transported to long distances depending upon the size of the plants. Xylem moves water and minerals from soil to aerial parts. Soil also helps in anchoring plant, availability of oxygen for respiration of root cells and symbiotic association with microbes.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 10 Science
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful World
- Chapter 12 Electricity
- Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 15 Our Environment
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources