Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 2 Polynomials
Polynomials Class 10 Important Questions Very Short Answer (1 Mark)
Question 1.
If the sum of zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 3x
2
– kx + 6 is 3, then find the value of k. (2012)
Solution:
Here a = 3, b = -k, c = 6
Sum of the zeroes, (α + β) = \(\frac { -b }{ a }\) = 3 …..(given)
⇒ \(\frac { -(-k) }{ 3 }\) = 3
⇒ k = 9
Question 2.
If α and β are the zeroes of the polynomial ax
2
+ bx + c, find the value of α
2
+ β
2
. (2013)
Solution:
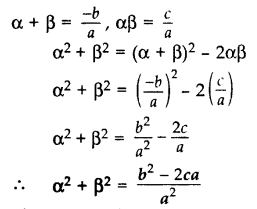
Question 3.
If the sum of the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = (k
2
– 14) x
2
– 2x – 12 is 1, then find the value of k. (2017 D)
Solution:
p(x) = (k
2
– 14) x
2
– 2x – 12
Here a = k
2
– 14, b = -2, c = -12
Sum of the zeroes, (α + β) = 1 …[Given]
⇒ \(\frac { -b }{ a }\) = 1
⇒ \(\frac { -\left( -2 \right) }{ { k }^{ 2 }-14 }\) = 1
⇒ k
2
– 14 = 2
⇒ k
2
= 16
⇒ k = ±4
Question 4.
If α and β are the zeroes of a polynomial such that α + β = -6 and αβ = 5, then find the polynomial. (2016 D)
Solution:
Quadratic polynomial is x
2
– Sx + P = 0
⇒ x
2
– (-6)x + 5 = 0
⇒ x
2
+ 6x + 5 = 0
Question 5.
A quadratic polynomial, whose zeroes are -4 and -5, is …. (2016 D)
Solution:
x
2
+ 9x + 20 is the required polynomial.
Polynomials Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-I (2 Marks)
Question 6.
Find the condition that zeroes of polynomial p(x) = ax
2
+ bx + c are reciprocal of each other. (2017 OD)
Solution:
Let α and \(\frac { 1 }{ \alpha }\) be the zeroes of P(x).
P(a) = ax
2
+ bx + c …(given)
Product of zeroes = \(\frac { c }{ a }\)
⇒ α × \(\frac { 1 }{ \alpha }\) = \(\frac { c }{ a }\)
⇒ 1 = \(\frac { c }{ a }\)
⇒ a = c (Required condition)
Coefficient of x
2
= Constant term
Question 7.
Form a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are 3 + √2 and 3 – √2. (2012)
Solution:
Sum of zeroes,
S = (3 + √2) + (3 – √2) = 6
Product of zeroes,
P = (3 + √2) x (3 – √2) = (3)
2
– (√2)
2
= 9 – 2 = 7
Quadratic polynomial = x
2
– Sx + P = x
2
– 6x + 7
Question 8.
Find a quadratic polynomial, the stun and product of whose zeroes are √3 and \(\frac { 1 }{ \surd 3 }\) respectively. (2014)
Solution:
Sum of zeroes, (S) = √3
Product of zeroes, (P) = \(\frac { 1 }{ \surd 3 }\)
Quadratic polynomial = x
2
– Sx + P
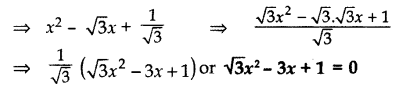
Question 9.
Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product of whose zeroes are 0 and -√2 respectively. (2015)
Solution:
Quadratic polynomial is
x
2
– (Sum of zeroes) x + (Product of zeroes)
= x
2
– (0)x + (-√2)
= x
2
– √2
Question 10.
Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial √3 x
2
– 8x + 4√3. (2013)
Solution:
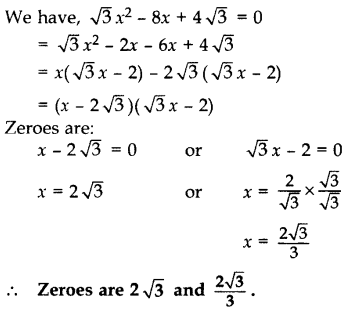
Question 11.
If the zeroes of the polynomial x
2
+ px + q are double in value to the zeroes of 2x
2
– 5x – 3, find the value of p and q. (2012)
Solution:
We have, 2x
2
– 5x – 3 = 0
= 2x
2
– 6x + x – 3
= 2x(x – 3) + 1(x – 3)
= (x – 3) (2x + 1)
Zeroes are:
x – 3 = 0 or 2x + 1 = 0
⇒ x = 3 or x = \(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\)
Since the zeroes of required polynomial is double of given polynomial.
Zeroes of the required polynomial are:
3 × 2, (\(\frac { -1 }{ 2 }\) × 2), i.e., 6, -1
Sum of zeroes, S = 6 + (-1) = 5
Product of zeroes, P = 6 × (-1) = -6
Quadratic polynomial is x
2
– Sx + P
⇒ x
2
– 5x – 6 …(i)
Comparing (i) with x
2
+ px + q
p = -5, q = -6
Question 12.
Can (x – 2) be the remainder on division of a polynomial p(x) by (2x + 3)? Justify your answer. (2016 OD)
Solution:
In case of division of a polynomial by another polynomial, the degree of the remainder (polynomial) is always less than that of the divisor. (x – 2) can not be the remainder when p(x) is divided by (2x + 3) as the degree is the same.
Question 13.
Find a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are \(\frac { 3+\surd 5 }{ 5 }\) and \(\frac { 3-\surd 5 }{ 5 }\). (2013)
Solution:
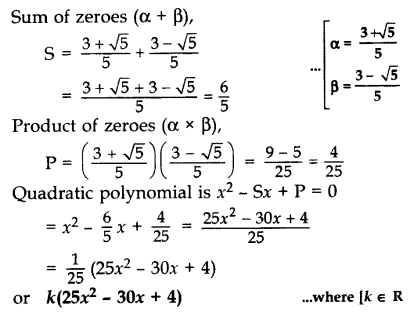
Question 14.
Find the quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are -2 and -5. Verify the relationship between zeroes and coefficients of the polynomial. (2013)
Solution:
Sum of zeroes, S = (-2) + (-5) = -7
Product of zeroes, P = (-2)(-5) = 10
Quadratic polynomial is x
2
– Sx + P = 0
= x
2
– (-7)x + 10
= x
2
+ 7x + 10
Verification:
Here a = 1, b = 7, c = 10
Sum of zeroes = (-2) + (-5) = 7

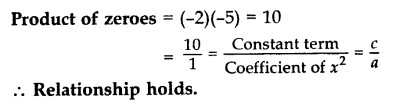
Question 15.
Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 3x
2
– 75 and verify the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients. (2014)
Solution:
We have, 3x
2
– 75
= 3(x
2
– 25)
= 3(x
2
– 52)
= 3(x – 5)(x + 5)
Zeroes are:
x – 5 = 0 or x + 5 = 0
x = 5 or x = -5
Verification:
Here a = 3, b = 0, c = -75
Sum of the zeroes = 5 + (-5) = 0

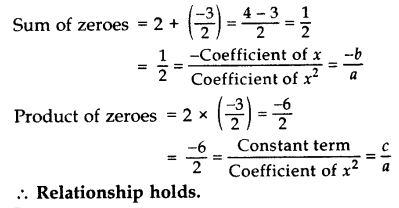
Question 16.
Find the zeroes of p(x) = 2x
2
– x – 6 and verify the relationship of zeroes with these co-efficients. (2017 OD)
Solution:
p(x) = 2x
2
– x – 6 …[Given]
= 2x
2
– 4x + 3x – 6
= 2x (x – 2) + 3 (x – 2)
= (x – 2) (2x + 3)
Zeroes are:
x – 2 = 0 or 2x + 3 = 0
x = 2 or x = \(\frac { -3 }{ 2 }\)
Verification:
Here a = 2, b = -1, c = -6
Question 17.
What must be subtracted from the polynomial f(x) = x
4
+ 2x
3
– 13x
2
– 12x + 21 so that the resulting polynomial is exactly divisible by x
2
– 4x + 3? (2012, 2017 D)
Solution:
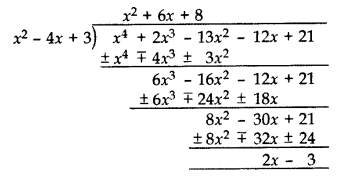
(2x – 3) should be subtracted from x
4
+ 2x
3
– 13x
2
– 12x + 21.
Polynomials Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-II (3 Marks)
Question 18.
Verify whether 2, 3 and \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) are the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = 2x
3
– 11x
2
+ 17x – 6. (2012, 2017 D)
Solution:
p(x) = 2x
3
– 11x
2
+ 17x – 6
When x = 2,
p(2) = 2(2)
3
– 11(2)
2
+ 17(2) – 6 = 16 – 44 + 34 – 6 = 0
When x = 3, p(3) = 2(3)
3
– 11(3)
2
+ 17(3) – 6 = 54 – 99 + 51 – 6 = 0
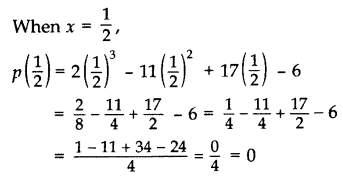
Yes, x = 2, 3 and \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) all are the zeroes of the given polynomial.
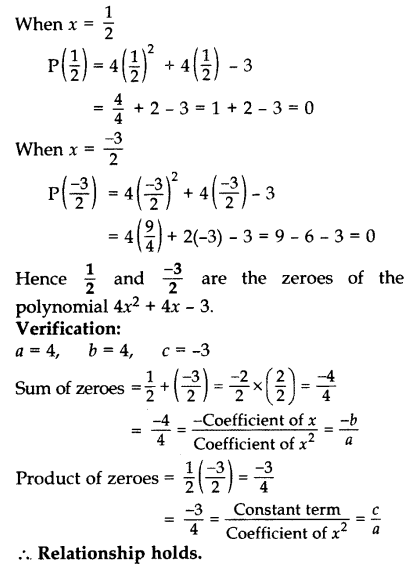
Question 19.
Show that \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) and \(\frac { -3 }{ 2 }\) are the zeroes of the polynomial 4x
2
+ 4x – 3 and verify the relationship between zeroes and co-efficients of polynomial. (2013)
Solution:
Let P(x) = 4x
2
+ 4x – 3
Question 20.
Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product of whose zeroes are -8 and 12 respectively. Hence find the zeroes. (2014)
Solution:
Let Sum of zeroes (α + β) = S = -8 …[Given]
Product of zeroes (αβ) = P = 12 …[Given]
Quadratic polynomial is x
2
– Sx + P
= x
2
– (-8)x + 12
= x
2
+ 8x + 12
= x
2
+ 6x + 2x + 12
= x(x + 6) + 2(x + 6)
= (x + 2)(x + 6)
Zeroes are:
x + 2 = 0 or x + 6 = 0
x = -2 or x = -6
Question 21.
Find a quadratic polynomial, the sum and product of whose zeroes are 0 and \(\frac { -3 }{ 5 }\) respectively. Hence find the zeroes. (2015)
Solution:
Quadratic polynomial = x
2
– (Sum)x + Product
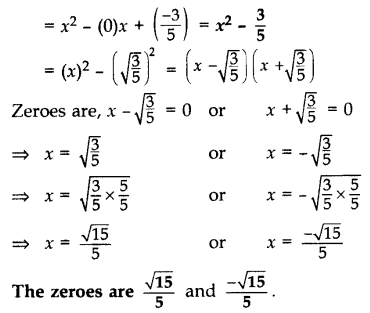
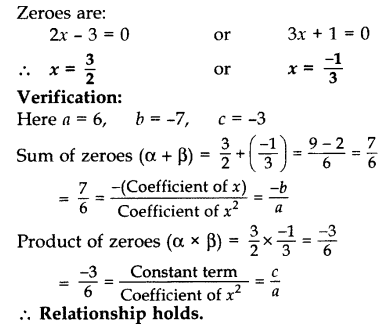
Question 22.
Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial 6x
2
– 3 – 7x and verify the relationship between the zeroes and the coefficients of the polynomial. (2015, 2016 OD)
Solution:
We have, 6x
2
– 3 – 7x
= 6x
2
– 7x – 3
= 6x
2
– 9x + 2x – 3
= 3x(2x – 3) + 1(2x – 3)
= (2x – 3) (3x + 1)
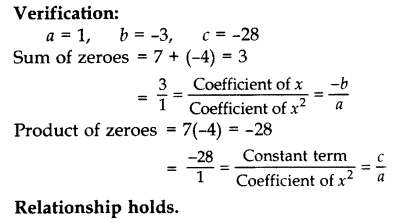
Question 23.
Find the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x
2
– 3x – 28 and verify the relationship between the zeroes and the co-efficients of the polynomial. (2012, 2017 D)
Solution:
p(x) = x
2
– 3x – 28
= x
2
– 7x + 4x – 28
= x(x – 7) + 4(x – 7)
= (x – 7) (x + 4)
Zeroes are:
x – 7 = 0 or x + 4 = 0
x = 7 or x = -4
Question 24.
If α and β are the zeroes of the polynomial 6y
2
– 7y + 2, find a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are \(\frac { 1 }{ \alpha }\) and \(\frac { 1 }{ \beta }\). (2012)
Solution:
Given: 6y
2
– 7y + 2
Here a = 6, b = -7, c = 2
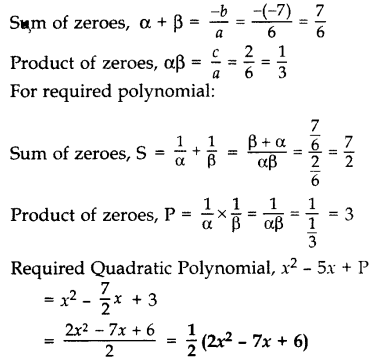
Question 25.
Divide 3x
2
+ 5x – 1 by x + 2 and verify the division algorithm. (2013 OD)
Solution:
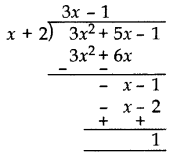
Quotient = 3x – 1
Remainder = 1
Verification:
Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
= (x + 2) × (3x – 1) + 1
= 3x
2
– x + 6x – 2 + 1
= 3x
2
+ 5x – 1
= Dividend
Question 26.
On dividing 3x
3
+ 4x
2
+ 5x – 13 by a polynomial g(x) the quotient and remainder were 3x +10 and 16x – 43 respectively. Find the polynomial g(x). (2017 OD)
Solution:
Let 3x
3
+ 4x
2
+ 5x – 13 = P(x)
q(x) = 3x + 10, r(x) = 16x – 43 …[Given]
As we know, P(x) = g(x) . q(x) + r(x)
3x
3
+ 4x
2
+ 5x – 13 = g(x) . (3x + 10) + (16x – 43)
3x
3
+ 4x
2
+ 5x – 13 – 16x + 43 = g(x) . (3x + 10)
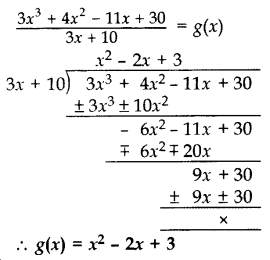
Question 27.
Check whether polynomial x – 1 is a factor of the polynomial x
3
– 8x
2
+ 19x – 12. Verify by division algorithm. (2014)
Solution:
Let P(x) = x
3
– 8x
2
+ 19x – 12
Put x = 1
P(1) = (1)
3
– 8(1)
2
+ 19(1) – 12
= 1 – 8 + 19 – 12
= 20 – 20
= 0
Remainder = 0
(x – 1) is a facter of P(x).
Verification:
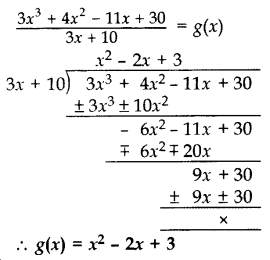
Since remainder = 0
(x – 1) is a factor of P(x).
Polynomials Class 10 Important Questions Long Answer (4 Marks)
Question 28.
Divide 4x
3
+ 2x
2
+ 5x – 6 by 2x
2
+ 1 + 3x and verify the division algorithm. (2013)
Solution:
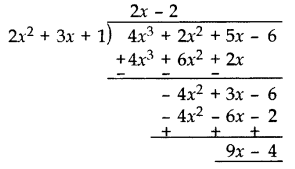
Quotient = 2x – 2
Remainder = 9x – 4
Verification:
Divisor × Quotient + Remainder
= (2x
2
+ 3x + 1) × (2x – 2) + 9x – 4
= 4x
3
– 4x
2
+ 6x
2
– 6x + 2x – 2 + 9x – 4
= 4x
3
+ 2x
2
+ 5x – 6
= Dividend
Question 29.
Given that x – √5 is a factor of the polynomial x
3
– 3√5 x
2
– 5x + 15√5, find all the zeroes of the polynomial. (2012, 2016)
Solution:
Let P(x) = x
3
– 3√5 x
2
– 5x + 15√5
x – √5 is a factor of the given polynomial.
Put x = -√5,
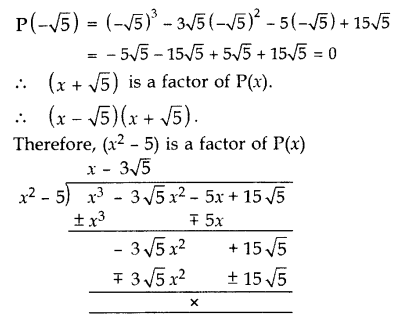
Other zero:
x – 3√5 = 0 ⇒ x = 3√5
All the zeroes of P(x) are -√5, √5 and 3√5.
Question 30.
If a polynomial x
4
+ 5x
3
+ 4x
2
– 10x – 12 has two zeroes as -2 and -3, then find the other zeroes. (2014)
Solution:
Since two zeroes are -2 and -3.
(x + 2)(x + 3) = x
2
+ 3x + 2x + 6 = x
2
+ 5x + 6
Dividing the given equation with x
2
+ 5x + 6, we get
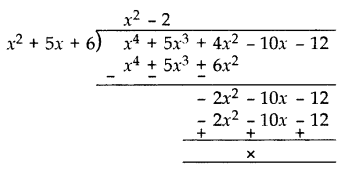
x
4
+ 5x
3
+ 4x
2
– 10x – 12
= (x
2
+ 5x + 6)(x
2
– 2)
= (x + 2)(x + 3)(x – √2 )(x + √2 )
Other zeroes are:
x – √2 = 0 or x + √2 = 0
x = √2 or x = -√2
Question 31.
Find all the zeroes of the polynomial 8x
4
+ 8x
3
– 18x
2
– 20x – 5, if it is given that two of its zeroes are \(\sqrt { \frac { 5 }{ 2 } }\) and \(-\sqrt { \frac { 5 }{ 2 } }\). (2014, 2016 D)
Solution:
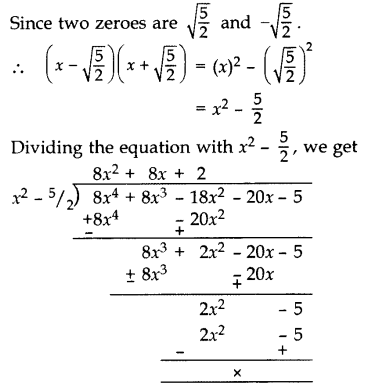
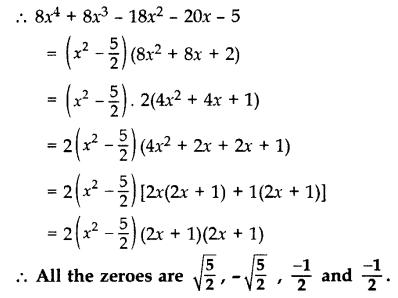
Question 32.
If p(x) = x
3
– 2x
2
+ kx + 5 is divided by (x – 2), the remainder is 11. Find k. Hence find all the zeroes of x
3
+ kx
2
+ 3x + 1. (2012)
Solution:
p(x) = x
3
– 2x
2
+ kx + 5,
When x – 2,
p(2) = (2)
3
– 2(2)
2
+ k(2) + 5
⇒ 11 = 8 – 8 + 2k + 5
⇒ 11 – 5 = 2k
⇒ 6 = 2k
⇒ k = 3
Let q(x) = x
3
+ kx
2
+ 3x + 1
= x
3
+ 3x
2
+ 3x + 1
= x
3
+ 1 + 3x
2
+ 3x
= (x)
3
+ (1)
3
+ 3x(x + 1)
= (x + 1)
3
= (x + 1) (x + 1) (x + 1) …[∵ a
3
+ b
3
+ 3ab (a + b) = (a + b)
3
]
All zeroes are:
x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = -1
x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = -1
x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = -1
Hence zeroes are -1, -1 and -1.
Question 33.
If α and β are zeroes of p(x) = kx
2
+ 4x + 4, such that α
2
+ β
2
= 24, find k. (2013)
Solution:
We have, p(x) = kx
2
+ 4x + 4
Here a = k, b = 4, c = 4
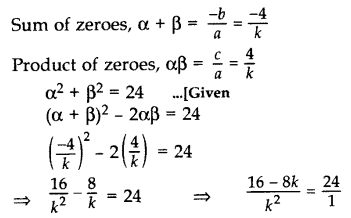
⇒ 24k
2
= 16 – 8k
⇒ 24k
2
+ 8k – 16 = 0
⇒ 3k
2
+ k – 2 = 0 …[Dividing both sides by 8]
⇒ 3k
2
+ 3k – 2k – 2 = 0
⇒ 3k(k + 1) – 2(k + 1) = 0
⇒ (k + 1)(3k – 2) = 0
⇒ k + 1 = 0 or 3k – 2 = 0
⇒ k = -1 or k = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)
Question 34.
If α and β are the zeroes of the polynomial p(x) = 2x
2
+ 5x + k, satisfying the relation, α
2
+ β
2
+ αβ = \(\frac { 21 }{ 4 }\) then find the value of k. (2017 OD)
Solution:
Given polynomial is p(x) = 2x
2
+ 5x + k
Here a = 2, b = 5, c = k
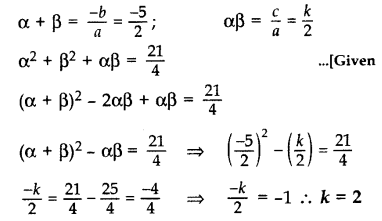
Question 35.
What must be subtracted from p(x) = 8x
4
+ 14x
3
– 2x
2
+ 8x – 12 so that 4x
2
+ 3x – 2 is factor of p(x)? This question was given to group of students for working together. (2015)
Solution:
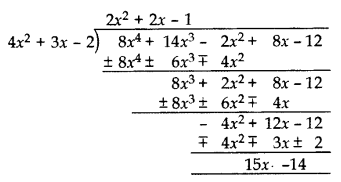
Polynomial to be subtracted by (15x – 14).
Question 36.
Find the values of a and b so that x
4
+ x
3
+ 8x
2
+ax – b is divisible by x
2
+ 1. (2015)
Solution:
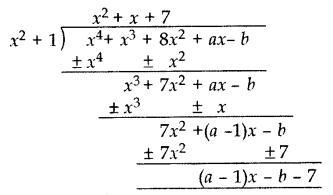
If x
4
+ x
3
+ 8x
2
+ ax – b is divisible by x
2
+ 1
Remainder = 0
(a – 1)x – b – 7 = 0
(a – 1)x + (-b – 7) = 0 . x + 0
a – 1 = 0, -b – 7 = 0
a = 1, b = -7
a = 1, b = -7
Question 37.
If a polynomial 3x
4
– 4x
3
– 16x
2
+ 15x + 14 is divided by another polynomial x
2
– 4, the remainder comes out to be px + q. Find the value of p and q. (2014)
Solution:
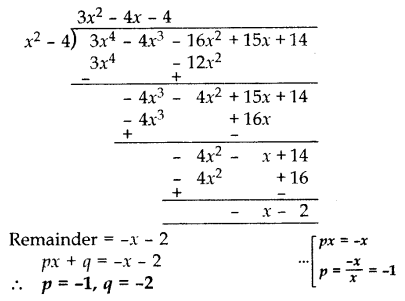
Question 38.
If the polynomial (x
4
+ 2x
3
+ 8x
2
+ 12x + 18) is divided by another polynomial (x
2
+ 5), the remainder comes out to be (px + q), find the values of p and q.
Solution:
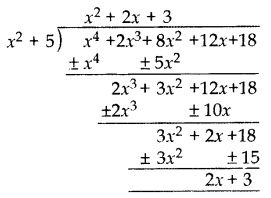
Remainder = 2x + 3
px + q = 2x + 3
p = 2 and q = 3.