Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Modern Physics
Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10 Educational Loans in India
Frank
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Modern Physics ThermIonic Emission and Cathode Ray Physics
PAGE NO-271:
Solution 1
The minimum amount of energy required to emit electrons from a metal surface is called work function of that material.
Solution 2
The electrons in the outer orbits are weakly attracted by the nucleus and are loosely bound. When a solid is formed, the loosely bound electrons leave their individual atom and become a part of the solid as a whole. They are called conduction electrons.
Solution 3
when certain metals are heated to a high temperature, they emit thermions (electrons) and the phenomenon is called thermionic emission. Thermionic emission can be used to produce cathode rays oscilloscope.
Solution 4
Rate of emission of electrons from a heated surface depends upon:(i) Work function of the material.(ii)Melting point of the material.
Solution 5
Materials of low work function are preferred as electron emitters because they emit electrons even at a low temperature.
Solution 6
Work function of a material is generally expressed in electron volt (eV).1 eV = 1.6 ?10
-19
J.
Solution 7
(i)Electrons are the charged particles.
(ii)Amount of charge on each particle is 1.6 ? 10
-19
J.
(iii)Approximately 3000 V of voltage is applied to heat the filament.
(iv)Potential difference V
1
applied between the anode and filament is few hundred volts.
(v)Beam of electrons gets deflected when it passes through the magnetic field.
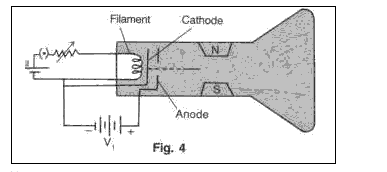
Solution 8
Pressure inside a cathode ray tube should be kept very low because cathode rays are made up of electrons and mass of electrons are very low. If air exists inside the cathode ray tube then electrons would be deflected by air molecules and cathode would not be able to strike on screen properly.So pressure inside cathode ray tube should be kept very low.
Solution 9
A layer of graphite is made on the inner side of the cathode ray tube close to the fluorescent screen. As a result of impacting electrons, the screen acquires a negative charge. To reduce this effect, the graphite is electrically connected to ‘earth’ (zero volts).This allows excess charge to drain away. Otherwise the accumulated charge would reduce the numbers of electrons arriving at the screen, reducing brightness.
Solution 10
Brightness of the pattern on the screen of CRT can be controlled by varying the potential applied to the cathode.
Solution 11
Cathode ray tube has three main sections
(i) Electron gun : arrangement of electrodes where a stream of electrons is produced is known as electron gun
(ii)Deflection system: Stream of emerging electrons is deflected in its passage between the gun and the screen. This deflection is produced by two pairs of parallel plates arranged at right angles.
(iii)Fluorescent screen: At the end of the tube screen is coated with a mixture of fluorescent material and phosphorescent material. The phosphorescent material is responsible for the persistence of the image on the screen.
Solution 12
(i)If hotter filament is used then no of electron would increase and a brightness of the spot on the screen would increase.(ii)If anode voltage is increased then this would collimate the beam into a narrower, faster stream of electrons, producing a smaller, sharper dot on the screen.
Solution 13
(i) Cathode ray tubes are used in science research laboratories by scientist for converting electrical signals into visual signals and television tubes.
(ii) Cathode ray tubes are used by doctors for converting electrical impulses corresponding to heart beats into visual signals in ECG, EEG etc.
Solution 14
The end of the tube screen is coated with a mixture of fluorescent material and phosphorescent material. The phosphorescent material is responsible for the persistence of the image on the screen. While fluorescence material coated inside screen is responsible for production of bright spot on the screen when electron beam strikes on the screen.
Solution 15
In presence of electric field, beam of electrons experience a force and deflected towards the positive plate. The path is parabolic within the electric field and after electric field the beam of electron travels straight.In presence of magnetic field, the electrons experience a force, the direction of which is given by Fleming left hand rule. The beam of electrons gets deflected and follows a circular path. The magnetic field is perpendicular to the plane of paper inwards and is represented X. On emergence from the magnetic field, they travel along a straight path in opposite direction to their velocity.
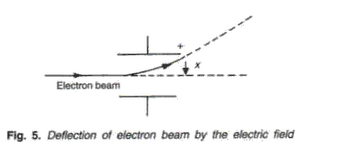
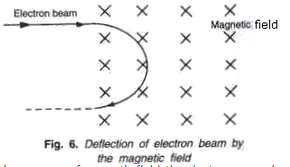
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Modern Physics Radioactivity
PAGE NO-281:
Solution 1
Atom consists of three elementary particles, neutrons, protons and electrons. Neutron and protons form the central part of atom called nucleus where electrons revolve around this central part in orbits called electronic orbits.
Solution 2
Nucleus is central part of an atom which consist of elementary particles protons and neutrons.
Solution 3
(i) Atomic number is the number of protons present in the nucleus. As number of protons is equal to the number of electrons so atomic number also gives the number of electrons in an atom.
(ii) Mass number is the sum of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus.
(iii) Atomic mass of element is the relative mass of its atom as compared to the mass of carbon atom taken as 12.
Solution 4

Solution 5
![]()
Solution 6
The atoms of same elements having the same atomic number Z but different mass number A are called isotopes.
Solution 7
Isotopes have same chemical properties but have different physical properties.
Solution 8
The atoms of different elements having same mass number but different atomic number are called isobars.
Solution 9
Similarities:
Both ?-radiations and X-rays affect photographic plate, both travel with the speed of light.
Dissimilarities:
?-radiations areobtained in emissions from the radioactive substances due to energy change in the nucleus of their atoms and X- rays are obtained when highly energetic cathode rays are stopped by a heavy metal target of high melting point.
?-radiations have high penetration power but X-rays do not have have very high penetration power.
Solution 10

Solution 11

Solution 12

Solution 13

Solution 14
Radioactivity is the spontaneous random emission of particles from within the nucleus of atom. Radiations are emitted from nucleus of atom thus radioactivity is a nuclear phenomenon.
Solution 15

Solution 16

Solution 17
(i) Alpha particles are heavy in mass and are positively charged so they are deflected less by magnetic field and direction is upward which can be calculated by Fleming left hand rule.
(ii) Beta particles are negligible in mass so they are highly deflected by magnetic field and they are negatively charge particle so they are deflected in downward direction.
(iii) Gamma radiations have no mass and no charge so they are not deflected by magnetic field.
Solution 18
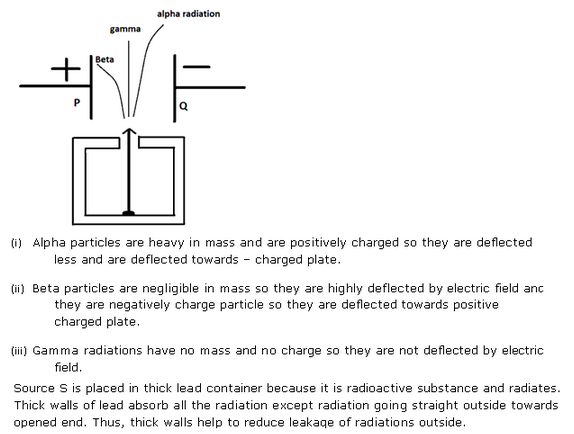
PAGE NO-282:
Solution 19

Solution 20
![]()
Solution 21
![]()
Solution 22

Solution 23
Artificial radioactive substances can be produced by bombarding lighter nuclides withalpha particles, protons and neutron. The radioactive substances produces in this manner are called radioisotopes. Radioisotopes can be used as:
(i) Rays from Radium produce satisfactorily improvement in skin diseases.
(ii) Radioactive Sulphur S35 helps to study advantages and disadvantages of fungicides.
Solution 24
Following precautions should be taken while handling the radioactive substances.(i) The sources should only be handled by the forceps provided and never touched by hand.(ii) They should never be pointed towards a person.(iii) Food should not be taken where the sources are being used, as it may be contaminated.(iv) Never smoke near a radioactive source.
Solution 25
Radioactive substances should not be touched by hands because radiation emitted by radioactive substances can cause burns, Leukaemia, eye cataract, sterility or many other dangerous disease.
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Modern Physics
PAGE NO-283:
Solution 1
(a) Mass number of copper = 63Atomic number of copper = 29As atomic number of element gives number of proton and electrons while mass number of element gives number of protons +number of neutrons.So, number of protons in copper = atomic number of copper = 29.Number of electron in copper = number of protons in copper =29.Number of neutrons = mass number ? atomic number = 63 ? 29 =34.So answer is
(iii) as copper contains 29 protons and 29 electrons.


PAGE NO-284:
Solution 2

Solution 3
(a) Electron has
(ii) a mass less than that of a proton.
(b) Neutrons have
(iv) no electric charge.
Solution 4
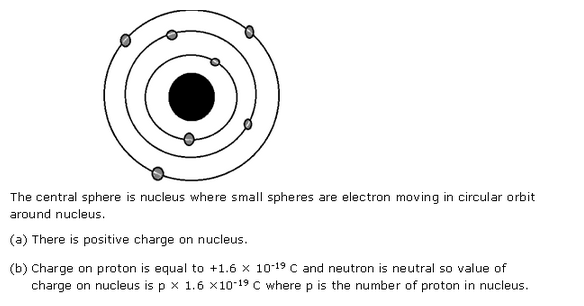
Solution 5

Solution 6
(a)Mass number of uranium = 235Atomic number of uranium = 92As atomic number of element gives number of proton and electrons while mass number of element gives number of protons +number of neutrons.So, number of protons in uranium = atomic number of uranium = 92.(b) Number of electron in uranium = number of protons in uranium =92.(c)The atoms of same elements having the same atomic number Z but different mass number A are called isotopes. So, for another isotope of uranium mass number 235 changes.(d)Number of protons in isotopes is same and as U238 is isotope of
92
U
235
. So, number of protons in U
235
is also 92.
Solution 7

Solution 8
The atoms of same elements having the same atomic number Z but different mass number a are called isotopes. Hydrogen have 3 isotopes protium
1
H
1
, deuterium
1
H
2
, tritium
1
H
3
.
Solution 9

Solution 10
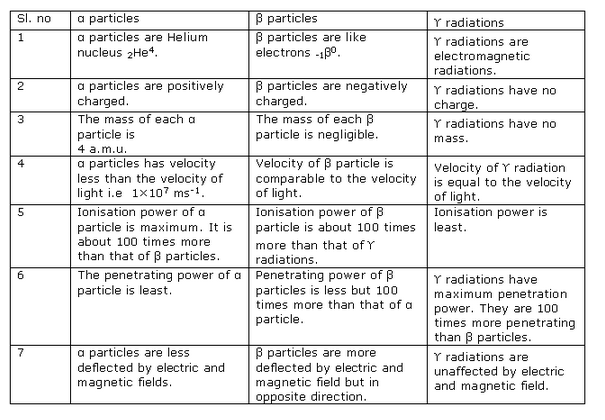
Solution 11
Following precautions should be taken while handling the radioactive substances.
(i) The sources should only be handled by the forceps provided and never touched by hand.
(ii) They should never be pointed towards a person.
(iii) Food should not be taken where the sources are being used, as it may be contaminated.
(iv) Never smoke near a radioactive source
Solution 12

Solution 13
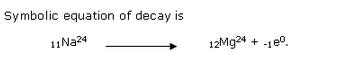
Solution 14
(a) When certain metals are heated to a high temperature, they emit thermions (electrons) and the phenomenon is called thermionic emission.
(b) Thermionic emission of electrons from a heated surface depends upon:
(i) Work function of the material.
(ii) Melting point of the material.
Solution 15
(a)
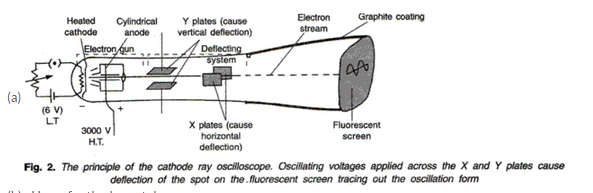
(b) Uses of cathode ray tubes are:
(i) Cathode ray tubes are used in science research laboratories by scientist for converting electrical signals into visual signals and television tubes.
(ii) Cathode ray tubes are used by doctors for converting electrical impulses corresponding to heart beats into visual signals in ECG, EEG etc.
Solution 16

Solution 17
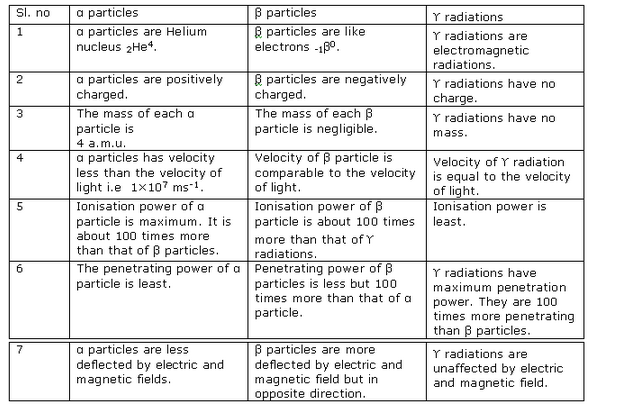
Solution 18
Following precautions should be taken while handling the radioactive substances.(i) The sources should only be handled by the forceps provided and never touched by hand.(ii) They should never be pointed towards a person.(iii) Food should not be taken where the sources are being used, as it may be contaminated.(iv) Never smoke near a radioactive source.
Solution 19

Solution 20
The low temperature microwave radiation that arrives at the earth’s surface from all directions of outer space is called background radiation.Sources of background radiations are:
(a) Radiation from the sun.
(b) Rocks in the earth which contain traces of radioactive substances.
(c) Naturally occurring isotopes.
(d) Artificial radioisotopes.No, it is not possible to keep ourselves away from these radiations.
Physics Chemistry Biology Maths
RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
Video Solutions