Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Current Electricity
Formulae Handbook For ICSE Class 9 and 10 Educational Loans in India
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Current Electricity
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Current Electricity Ohm’s Law and Electric Circuits
PAGE NO-187:
Solution 1
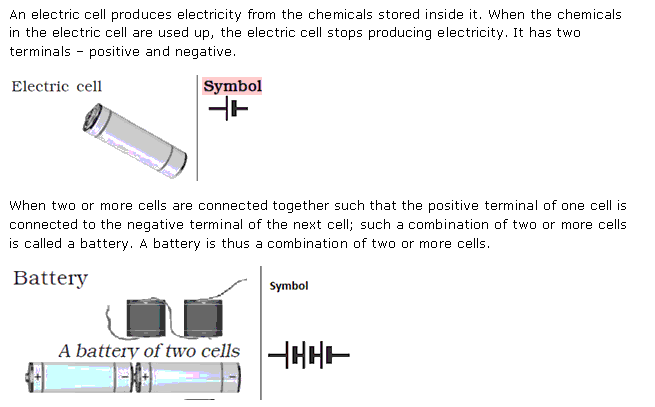
An electric cell is a device in which a constant difference in potential is maintained between the two conductors by a chemical reaction. Thus, a cell can be used as a source of electrons or current. In a cell, chemical energy changes into electrical energy when it is in use.
Solution 2
Solution 3
An electrical circuit is a continuous path comprising of conducting wires and resistances between the terminals of a battery, along which an electric current is set up. It is represented by drawing a circuit diagram.
Solution 4
Solution 5
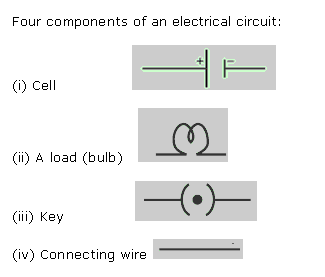
A diagram indicating how various components in an electrical circuit have been connected using symbols for those components is a circuit diagram.
Solution 6
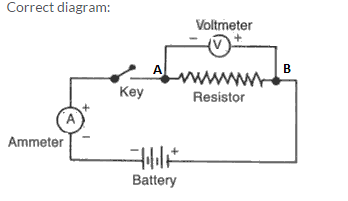
In the given diagram, ammeter is connected in parallel and voltmeter in series, which is wrong. Also the terminals of the two devices are wrongly connected to the battery.Correct diagram:
Solution 7
According to Ohm’s law, the current flowing in a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends provided the physical conditions and temperature of conductor remains constant.No, it is not always true. E.g. Diode valve, junction diode etc. do not obey Ohm’s law.
Solution 8
The obstruction offered to the flow of current by the wire is called its electrical resistance. It is a kind of friction between the free electrons and the atoms of the conductor along which they flow.Its SI unit is ‘ohm’.
Solution 9
The physical quantity is ‘resistance’.
Solution 10
Resistance of a conductor is said to be 1 ohm, if 1 ampere current flows through it, when the potential difference across its ends is 1 volt.
Solution 11
No, Ohm’s law does not hold good for semiconductors and electrolytic
Solutions
.
Solution 12
Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends are:
(i) Nature of conductor: different materials have different concentration of free electrons and therefore resistance of a conductor depends on its material.
(ii) Length of conductor: Resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to the length of a conductor.
(iii) Area of cross-section of a conductor: Resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section of the uniform wire.
(iv) Temperature of conductor: In general for metallic conductors, higher the temperature larger is the resistance.
Solution 13
An equivalent resistor is that resistor which when replace any combination of resistors the current through the circuit is not altered or changed.
Solution 14
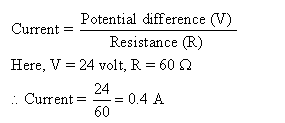
Solution 15
The slope of the graph (dV/dI) gives the value of resistance.
Solution 16
The resistivity of a material is the resistance of a wire of that material of unit length and unit area of cross-section.
Solution 17
![]()
Solution 18
Conductance of a conductor is the reciprocal of resistance of that conductor. Its unit is mho.
Solution 19
(i) Metals e.g. copper
(ii) Alloys e.g. Constantan
(iii) Semiconductors e.g. Germanium
Solution 20

PAGE NO-188:
Solution 21
Ohm’s law relates the current in a conductor to the potential difference across its ends.According to Ohm’s law, the current flowing in a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends provided the physical conditions and temperature of conductor remains constant.
Solution 22
If the conductor is made thinner, electrons get smaller area of cross-section to flow and it therefore, offers a large resistance.
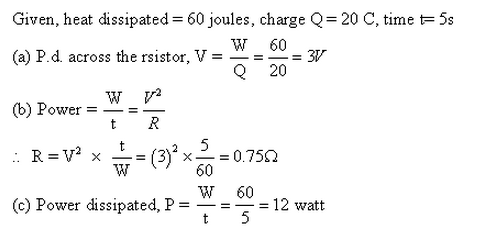
Solution 23
At constant temperature, if current is plotted against potential difference, the plot will be a straight line making some slope with the x-axis as shown in figure below:
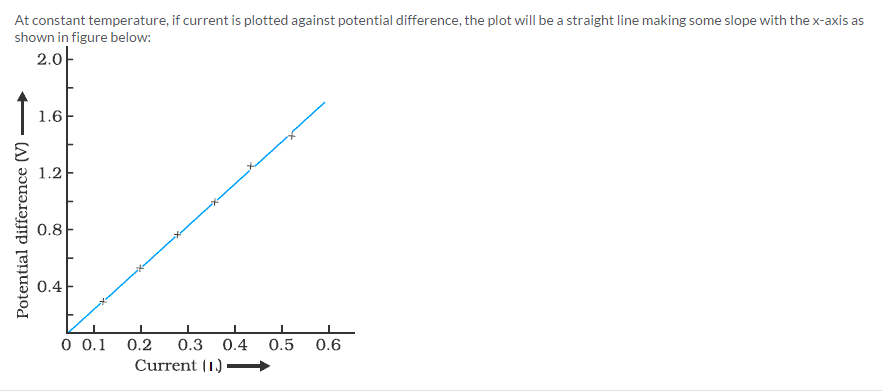
Solution 24
The instrument used to measure electric current is called an ammeter. It has a low resistance and is always connected in series.
Solution 25
The instrument used to measure electric potential or potential difference is called a voltmeter. It has a very high resistance and is always connected in parallel.
Solution 26
An ammeter has a low resistance.
Solution 27
A voltmeter has a high resistance.
Solution 28
A key acts as a switch in an electric circuit. It helps to open or close the circuit as required.
Solution 29
A rheostat is a device used in electric circuit to regulate current without changing the voltage source. It is also called variable resistance.
Solution 30

Solution 31
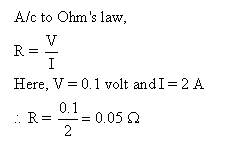
Solution 32
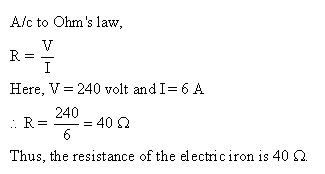
Solution 33

Solution 34
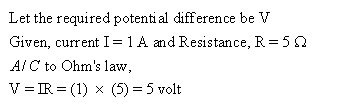
Solution 35

Solution 36
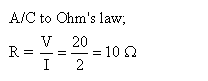
Solution 37

Solution 38
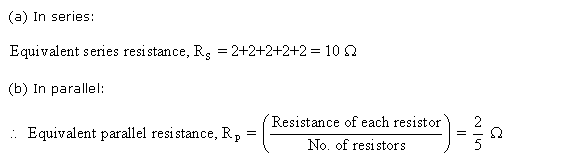
Solution 39

Solution 40
Two uses of conductors:
(i) Connecting wires are made of conductors like copper.
(ii) Conductors are used as electrolytes in cells
PAGE NO-189:
Solution 41
(a) Ampere
(b) Volt
(c) Coulomb
Solution 42
The potential difference between two points may be defined as the work done in moving a unit positive charge from one point to the other.
Solution 43
Electrical potential is a ‘scalar’ quantity.
Solution 44
Electric intensity is defined as the force experienced by a unit positive charge when kept at that point.Its SI unit is newton per coulomb. It is a vector quantity.
Solution 45
Joule/coulomb is known as ‘volt’.
Solution 46
Work done = charge x potential differenceOr, W = 5 x 1 = 5 J
Solution 47
(b) potential difference
Solution 48
(d) voltmeter
Solution 49
Charges move in a definite direction in a conductor when a potential difference is applied across the ends of the conductor.
Solution 50
We can maintain a potential difference between the ends of a conductor by connecting the two ends of the conductor to the two terminals of a battery or cell.
Solution 51
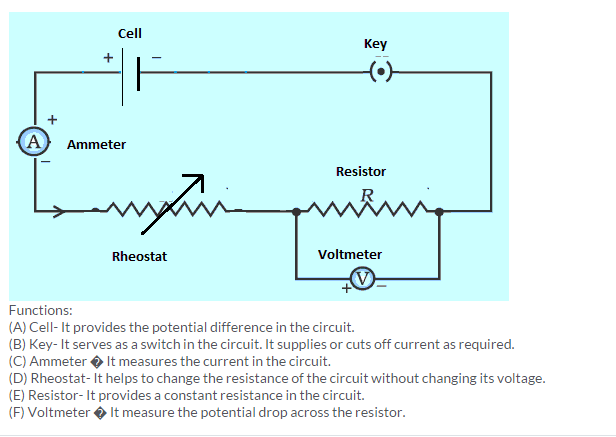
The rate of movement of charge from one point to another through a section of the conductor is called electric current. Current refers to rate of flow of charges in a conductor.I = Q/t
Solution 52
The direction of conventional current is taken as the direction of flow of positive charges.The direction of electronic current is taken as opposite to the direction of motion of electrons.
Solution 53
Current defines the rate of flow of charges in a conductor.
Solution 54
Current is measured by an ammeter.
Solution 55
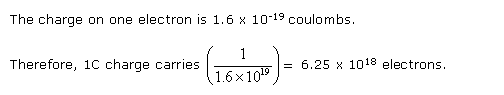
Solution 56
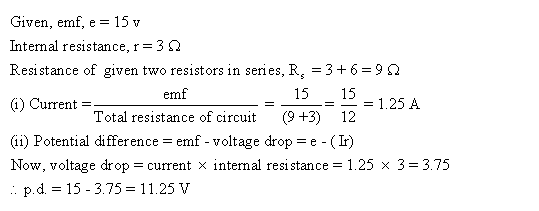
Solution 57

Solution 58
To get a total resistance less than 2 ohm, the given resistors should be connected in parallel because in parallel combination the equivalent resistance is less than the resistance smallest connected resistor.
Solution 59
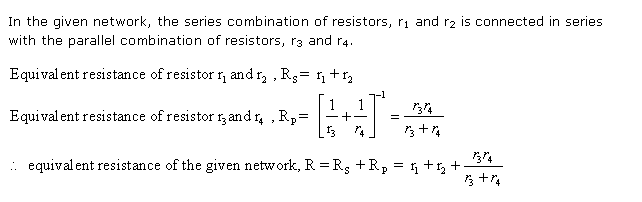
Solution 60
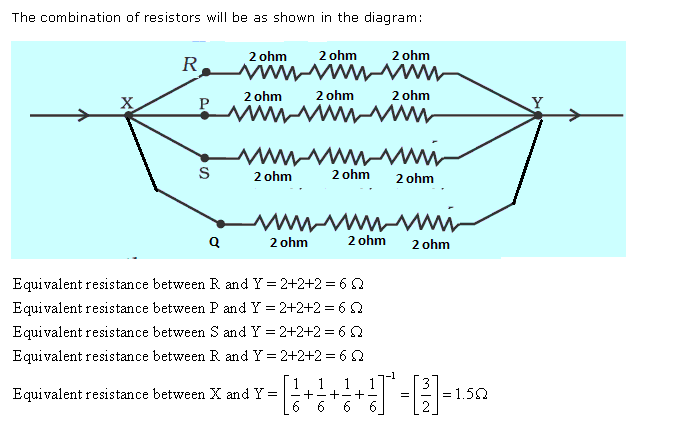
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Current Electricity Electric Power And Household Circuits
PAGE NO-201:
Solution 1
Electrical power is defined as the rate at which energy is changed or work is done i.e., the work done per second or energy converted per second.Electrical appliances come with certain number of watts and volts written on them. Power rating of an electrical appliance gives the knowledge of the safe current limit of an appliance and also indicates the voltage above which the appliance should not be used.
Solution 2

Solution 3
Solution 4
‘The current rating of a fuse is 5 A’ means that the maximum safe current permitted to flow through it before it breaks down is 5A.
Solution 5

Solution 6

Solution 7

Solution 8
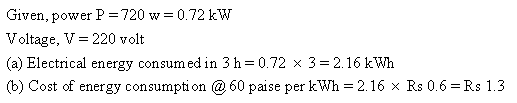
Solution 9
An electric fuse is a safety device which is used to limit the current in an electric circuit. The use of a fuse thus safeguards the circuit and appliances connected in that circuit from being damaged.A fuse is generally made of an alloy of lead and tin.
Solution 10
Characteristics of fuse wire:
(i) It should have low melting point.
(ii) It should have high resistance.
Solution 11
(a) resistance, melting point
(b) low, lead, tin, melts.
(c) series, live
PAGE NO-202:
Solution 12
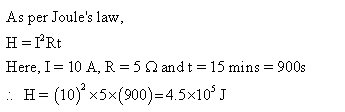
Solution 13
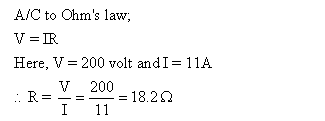
Solution 14
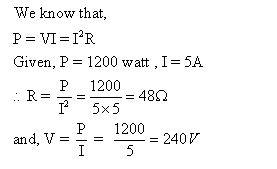
Solution 15
The main fuse is connected between the kWh meter and distribution board of the house circuit. The main fuse is connected in the live wire.
Solution 16
Yes, kWh is the unit of electrical energy.
Solution 17
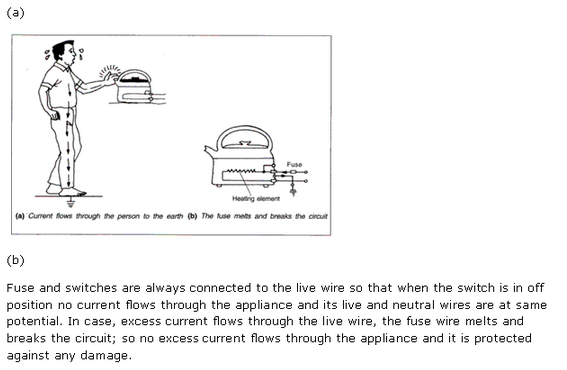
A switch is an on-off device for current in a circuit (or in an appliance). Its main function is either to connect or to disconnect an electrical appliance in an electric circuit.Switches are always connected in the live wire of circuits so that when a switch is in ‘off’ position, no current flows through the appliance and its live and neutral wires are at same potential and it is safe to touch the live wire leading to the appliance, even when the fuse is blown.
Solution 18
A switch should not be touched with wet hands. This is because water forms a conducting layer between the hand and the live wire of the switch through which the current passes to the hand and we may get a fatal shock.
Solution 19

Solution 20
The metal case of an electrical appliance is earthed so that in any case of accidental contact of live wire with the metallic body of the appliance, the earthing would provide a safe and easy path for the electric charges to flow down to the earth which acts as very large sink. Thus, user is thereby protected from any fatal electric shock.
Solution 21
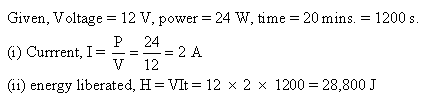
Solution 22
International convention of colour coding:1. Live wire ? Brown2. Neutral wire – Light blue3. Earth wire ? Green or yellow
Solution 23
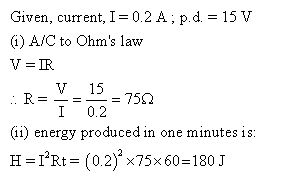
Solution 24

Solution 25
The fuse helps to control the maximum current in an electrical circuit. The fuse protects an electrical circuit by melting and breaking the circuit, whenever the current exceeds the pre-determined limit in the circuit. Due to low melting point, the fuse wire melts and then breaks the circuit.
Solution 26
Earthing is done to save an electrical circuit or an appliance from damage. If due to some reason such as short circuiting, an excessive current flows through the line wires, it will pass to the earth if there is local earthing, otherwise it may cause a fire due to overheating of line wires.
Solution 27
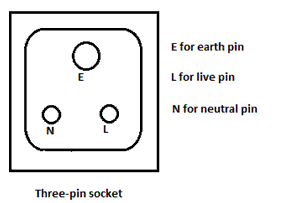
Solution 28
One may get an electric shock from an electrical appliance if accidentally the live wire comes in contact with the metallic case of the body of the appliance due to break of insulation after constant use (or otherwise).
Solution 29
The SI unit of electrical energy is joule.The SI unit of electrical power is watt.(i) Kilowatt-hour is the household unit of electrical energy. It is defined as the quantity of electrical energy consumed in 1 hour when the rate of consumption is 1000 watts, i.e. 1000 J/s.(ii) A voltage of 220 volt is generally supplied to a house.
Solution 30

Solution 31
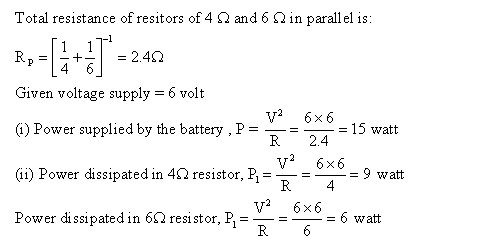
Solution 32
A three pin-plug has three terminals:
(i) Earth pin: It provides connection for earthing.
(ii) Neutral pin: It provides connection to the neutral wire.
(iii) live pin: It provides connection to the live wire.
Solution 33
Consumer pays the bill in kilowatt-hour.
Solution 34

Solution 35
Kilowatt-hour is the commercial unit of electricity.
Solution 36
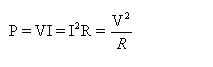
Solution 37
Power-voltage rating of an electrical appliance indicates the value of voltage above which the appliance should not be used. It serves as a precaution to the customer and also helps to calculate the maximum value of current that can be safely passed through the appliance.
Solution 38
The physical quantity is electric power.
Solution 39
It means that if the bulb is lighted on a 200V supply it consumes 60W electrical power or 200J of electrical energy converts into heat and light in 1 second.
Solution 40
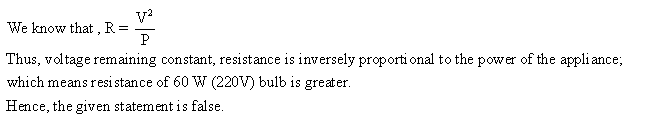
PAGE NO-203:
Solution 41
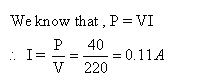
Solution 42
Watt-hour is the commercial unit of electrical energy.One watt-hour is the electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance of power 1 watt when it is used for 1 hour.1Wh = 3600 J
Solution 43
Kilowatt-hour is the commercial unit of electricity.
Solution 44
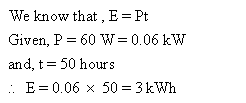
Solution 45
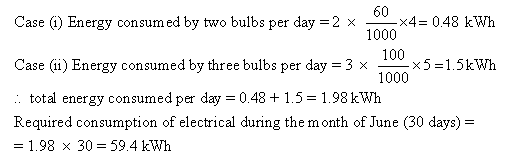
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Current Electricity Magnetic Effect Of Current and Electromagnetic Induction
PAGE NO-219:
Solution 1
Yes, we can produce electricity from magnetism.
Solution 2
The production of electric current by moving a straight conductor in a magnetic field is called electromagnetic induction.
Solution 3
Fleming’s right hand rule can be stated as: Stretch the forefinger, the middle finger and the thumb of the right hand, such that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field, thumb indicates the direction of motion of conductor, then the middle finger indicates the direction of induced current in the conductor.
Solution 4
(a)When the north-pole is pushed into the coil, a momentary deflection is observed in the galvanometer that indicates the production of a momentary current in the coil.(b) When the magnet is held at rest, there is no deflection in the galvanometer, indicating that no current is produced in the coil.(c)When the north-pole is pulled out from the coil, the deflection of the galvanometer is along the opposite direction, indicating the production of an opposite current.
Solution 5
(i) Fleming’s left hand rule is used to find out the direction of Lorentz force on a conductor. (ii) Fleming’s right hand rule is used to find out the direction of induced current in a conductor.
Solution 6
No, we cannot find out the magnitude of current using Fleming’s right hand rule; we can find only the direction of induced current.
PAGE NO-220:
Solution 7
If the current flows along the same direction with time, it is called a direct current (D.C.).
Solution 8
If the current changes direction after equal intervals of time, it is known as alternating current (A.C.).
Solution 9
Frequency of D.C. is zero.
Solution 10
Frequency of A.C. used in India is 50 Hz.
Solution 11
An alternating changes its direction after equal intervals of time but direct current does not change its direction.
Solution 12
A generator with commutator (D.C. generator) produces D.C. current.
Solution 13
A dynamo converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Solution 14
A fuse is always connected in series, in household circuits.
Solution 15
Three colours are:(i) Red (for live wire)(ii) Green (for earth wire)(iii) Black (for neutral wire)
Solution 16
Short circuiting occurs when the live wire comes in direct contact with the neutral wire so a zero resistance path is provided to the current. The heavy current then passes through the appliance and wires of the circuit.
Solution 17
Precautions while using electricity:(i) One must use wires or cables of current carrying capacity higher than the current which can flow through the circuit while using all appliances.(ii) An electrical appliance must never be operated (or touched) with wet hands.
Solution 18
Earthing is a safety device which is used to prevent shocks due to short-circuiting and leakages. Earthing, means that the metal body of an appliance, or the kWh meter of the house, is connected to a thick copper wire which is buried deep in the earth and at its end ia a copper plate surrounded by a mixture of charcoal and common salt. This prevents the users from getting shocks.
Solution 19
An electric fuse is a device which is used to limit the current in an electric circuit. The use of a fuse thus safeguards the circuit and appliances connected in that circuit from being damaged. It is a short piece of wire made of an alloy of lead and tin. If the current passing through the fuse exceeds the safeguard limit the heat produced melts the fuse and this breaks the circuit.
Solution 20
Colour code for live wire is red, neutral wire is black and earth wire is green.
Solution 21
This is done to protect the appliances and circuits from any damage due to short-circuit and thus accidents like fire and fatal shocks. Earthing provides an easy and safe path to the excess current in the circuit and sends it to the ground.
Solution 22
Switches are always connected in live wire.
Solution 23
Fleming’s right hand rule can be stated as: Stretch the forefinger, the middle finger and the thumb of the right hand, such that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field, thumb indicates the direction of motion of conductor, then the middle finger indicates the direction of induced current in the conductor.
Solution 24
Fleming’s left hand rule can be stated as: Stretch the forefinger, the middle finger and the thumb of the right hand, such that they are mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field, the middle finger indicates the direction of current in the conductor then thumb indicates the direction of force exerted on the conductor.
Solution 25
If a conducting wire is wound in form of a cylindrical coil whose diameter is less in comparison to the length, the coil is called a solenoid.
Solution 26
No, a copper wire cannot be used as a fuse wire as it has low resistance and high melting point.
Solution 27
A.C. is supplied to us in houses.
Solution 28
An alloy of lead and tin is used for making fuse wire.
Solution 29
Earthing is a safety device which is used to prevent shocks due to short-circuiting and leakages. Earthing, means that the metal body of an appliance, or the kWh meter of the house, is connected to a thick copper wire which is buried deep in the earth and at its end ia a copper plate surrounded by a mixture of charcoal and common salt. This prevents the users from getting shocks.
Solution 30
Arrangement
(a) is a series circuit.Arrangement
(b) is a parallel circuit.We would prefer a parallel circuit in household because:
(i) In parallel arrangement, each appliance works at the same voltage.
(ii) In parallel arrangement, if one bulb (or appliance0 is switched off (or fuses), the other bulbs (or appliances) continue to glow (or operate).
Solution 31
E is for earth pin, N is for neutral pin and L is for live pin.The earth pin is long so that the earth connection is made first. This ensures the safety of the user because if the appliance is defective, the fuse will blow off. The earth pin is made thicker so that even by mistake it cannot be inserted into the hole for the live or neutral connection of the socket.The pins are splitted at the ends to provide spring action so that they fit in the socket holes tightly.
Solution 32
(i) The purpose of the terminal E is to provide earth connection.
(ii) Terminal E is connected to the earth pin of the plug.
(iii) Fuse is connected in series with the wire L, so that if excess current flows through the circuit, the fuse wire get heated up and melts thus, breaking the circuit and preventing the flow of current to the appliance.
Frank ICSE Class 10 Physics Solutions Current Electricity
PAGE NO-223:
Solution 1
(a)
(i) 2/3 A
(b)(ii) double in value
(c)(iv) ohmic conductors
(d)(iv) 6 ?
(e) (ii) voltage
(f)(i) protect the user from electric shock by short circuiting and consequently breaking the circuit.
(g)(iii) A 13 ampere fuse is the most suitable rating to use
Solution 2
(a) Potential difference: The potential difference between two points may be defined as the work done in moving a unit positive charge from one point to the other.
(b)
(i) Coulomb: It is the unit of charge.
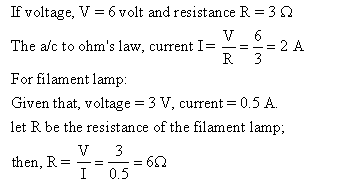
(ii) Ohm: It is the unit of resistance. The resistance of a conductor is said to be 1 ohm, if 1 ampere current flows through it, when the potential difference across its ends is 1 volt.
(c) Electromotive force: When no current is drawn from a cell, when the cell is in open circuit, the potential difference between the terminals of the cell is called its electromotive force (or e.m.f.).
(d) Semiconductors: Substances whose resistance decreases with the increase in temperature are named as semiconductors. E.g. manganin, constantan etc.
(e) Superconductors: Substance whose resistance decreases tremendously with the decrease in temperature and reaches nearly zero around absolute zero temperature are named as superconductors; e.g. lead, tin etc.
Solution 3
According to Ohm’s law, the current flowing in a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across its ends provided the physical conditions and temperature of conductor remains constant.Limitations of Ohm’s law:1. Ohm’s law does not apply to conductors such as diode, radio valves, metal rectifiers, where electricity passes through gases.2. Ohm’s law is applicable only when the physical conditions remain constant.3. Ohm’s law is applicable only when the temperature of the conductor is constant.
Solution 4
Factors on which the resistance of a conductor depends are:
(i) Nature of conductor: different materials have different concentration of free electrons and therefore resistance of a conductor depends on its material.
(ii) Length of conductor: Resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to the length of a conductor.
(iii) Area of cross-section of a conductor: Resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section of the uniform wire.
(iv) Temperature of conductor: In general for metallic conductors, higher the temperature larger is the resistance.Materials which allow electric charges to flow through them easily are known as conductors. E.g. metals and materials which do not allow the electric charge to flow through them are known as insulators. E.g. rubber, dry wood etc.
PAGE NO-224:
Solution 5
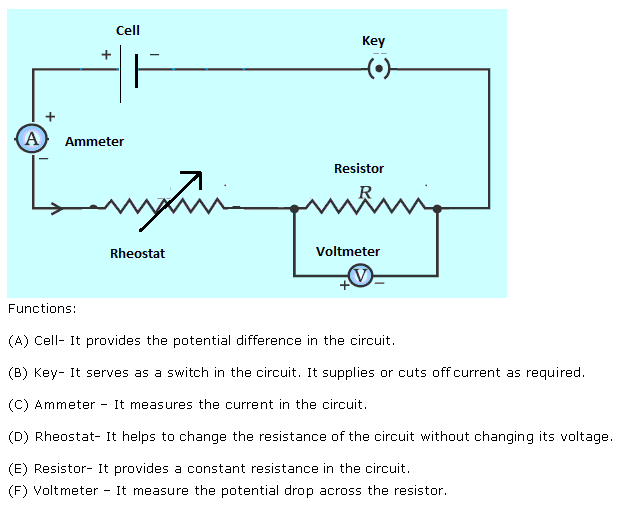
Functions:
(A) Cell- It provides the potential difference in the circuit.
(B) Key- It serves as a switch in the circuit. It supplies or cuts off current as required.
(C) Ammeter ? It measures the current in the circuit.
(D) Rheostat- It helps to change the resistance of the circuit without changing its voltage.
(E) Resistor- It provides a constant resistance in the circuit.
(F) Voltmeter ? It measure the potential drop across the resistor.
Solution 6


Solution 7
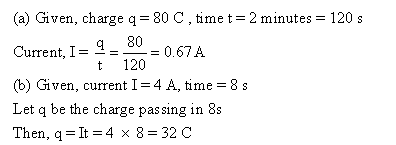
Solution 8
Solution 9

Solution 10
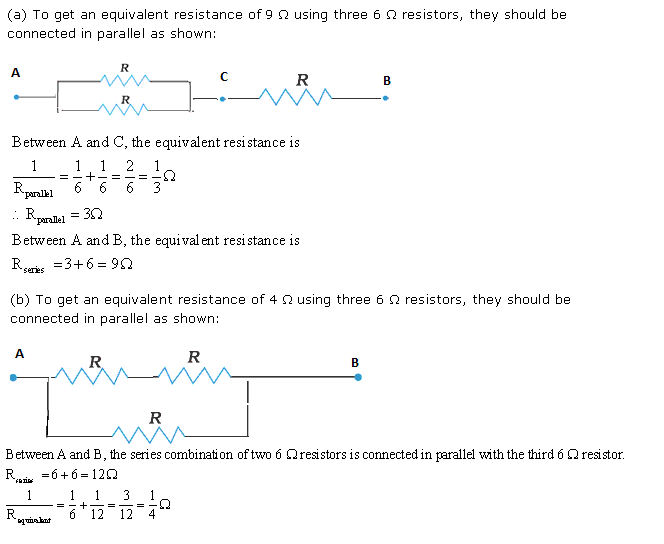
Solution 11
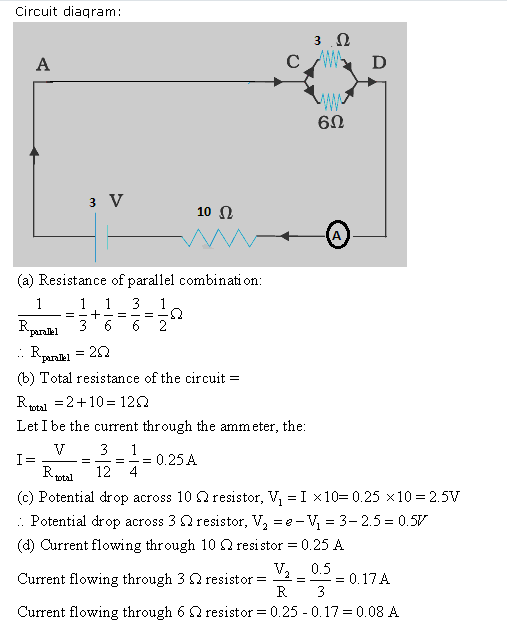
PAGE NO-225:
Solution 12
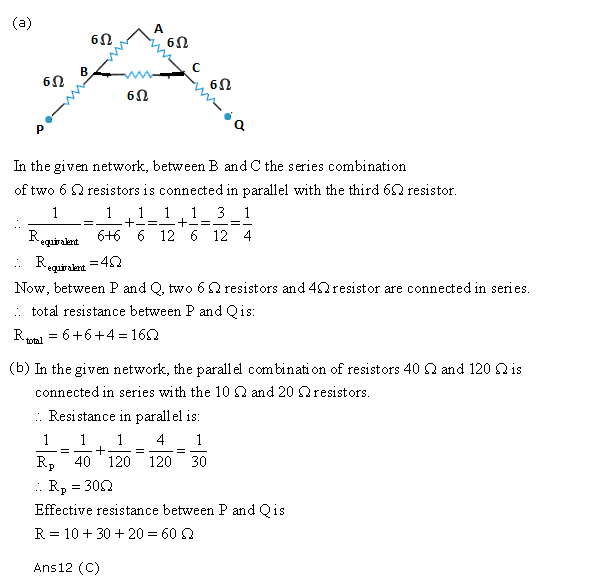
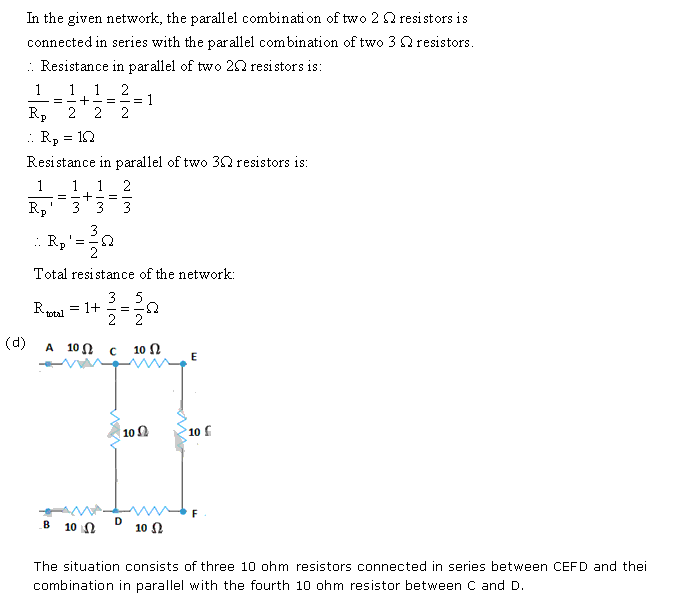

Solution 13
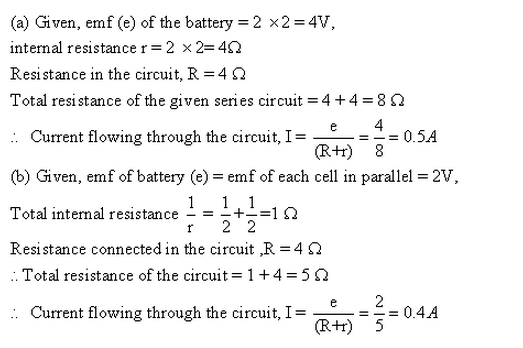
Solution 14

Solution 15
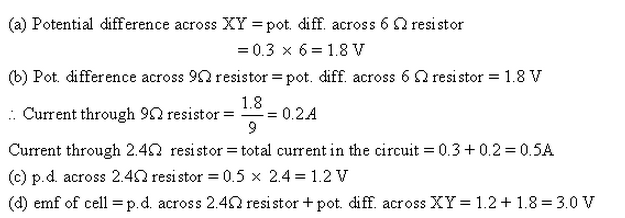
PAGE NO-226:
Solution 16
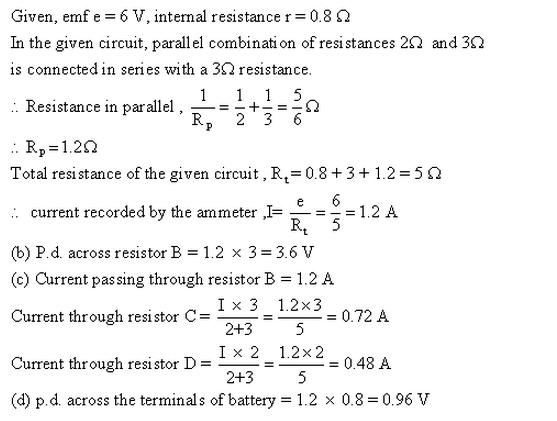
Solution 17
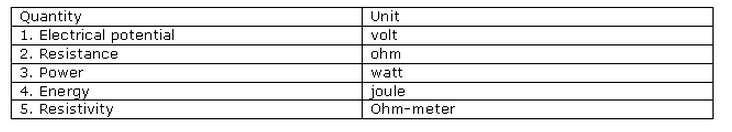
Solution 18
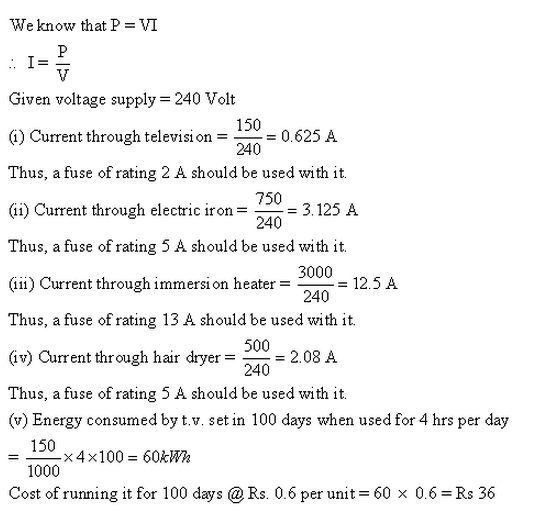
Solution 19

Solution 20
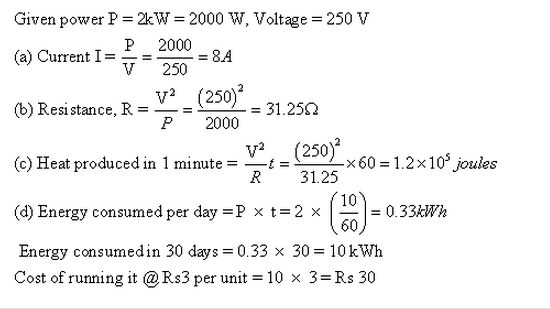
Solution 21

Solution 22

Solution 23
(a) Brown wire or live wire should be connected to terminal C.Blue wire or neutral wire should be connected to terminal B.Green wire or earth wire should be connected to terminal A.
(b) No, current passes through the earth terminal i.e. terminal A in normal circumstances.
(c) The metal case of an electrical appliance is earthed so that in any case of accidental contact of live wire with the metallic body of the appliance, the earth wire would provide a safe and easy path for the electric charges to flow down to the earth which acts as very large sink. Thus, user is thereby protected from any fatal electric shock.
Solution 24
‘kilowatt-hour’ is the commercial unit of electricity. One kilo-watt hour is the electrical energy consumed by an electrical appliance of power 1 kW when it is used for 1 hour.
PAGE NO-227:
Solution 25
Construction and working of filament bulbList of materials used:Light bulbs have two metal contacts, which connect to the ends of an electrical circuit. The metal contacts are attached to two stiff wires, which are attached to a thin metal filament. The filament sits in the middle of the bulb, held up by a glass mount. The wires and the filament are housed in a glass bulb, which is filled with an inert gas, such as argon.
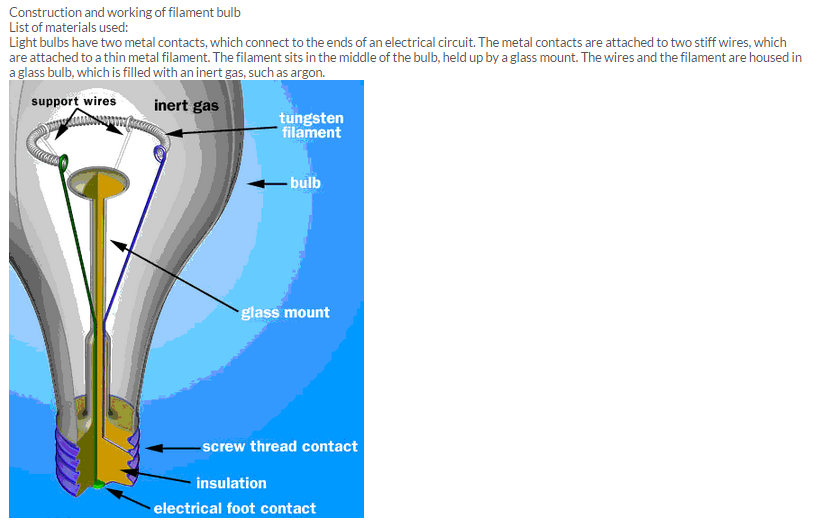
When the bulb is connected to a power supply, an electric current flows from one contact to the other, through the wires and the filament. As the electrons zip along through the filament, they are constantly bumping into the atoms that make up the filament. The energy of each impact vibrates an atom — in other words, the current heats the atoms up. Metal atoms release mostly infrared light photons, which are invisible to the human eye. But if they are heated to a high enough level — around 4,000 degrees Fahrenheit in the case of a light bulb — they will emit a good deal of visible light.Tungsten is used in nearly all incandescent light bulbs because it is an ideal filament material.In a modern light bulb, inert gases, typically argon, greatly reduce this loss of tungsten. At extreme temperatures, the occasional tungsten atom vibrates enough to detach from the atoms around it and flies into the air resulting in its evaporation. In the rpesence of argon gas around it, the chances are that it will collide with an argon atom and bounce right back toward the filament, where it will rejoin the solid structure. Also since inert gases normally don’t react with other elements, there is no chance of the elements combining in a combustion reaction.
Solution 26
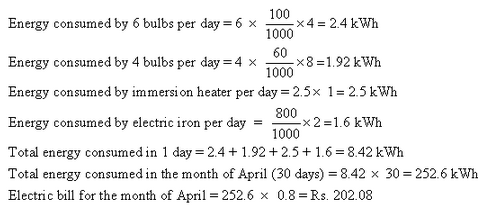
Solution 27
(a) Connecting wires: Materials having low resistance low resistivity and high melting point e.g. copper, aluminium.
(b) Fuse wire: Materials having high resistance and low melting point e.g. solder an alloy of lead and tin.
(c) Heating element: Materials having high resistivity and high melting point e.g. tungsten.
(d) Connecting wire of a power line: Materials having low resistance and non-corosive properties e.g. high tension wires.
(e) Earthing elements: Materials which are good conductors of electricity. Earthing elements are copper wire, copper plate, salt.
Solution 28
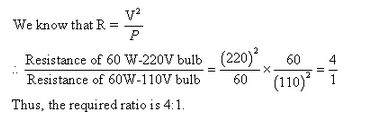
Solution 29
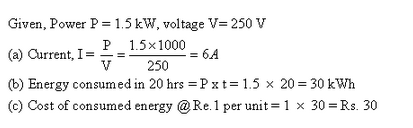
Solution 30

Solution 31
(a) The ring system consists of a ring of three wires namely live wire, earth wire and neutral wire, which originate from the main fuse box and after running around the rooms in the house comes back to the main fuse box, thus, completing a ring. In ring system, a separate connection is taken from the live wire of the ring for each appliance. In the ring circuit, all appliances are connected in parallel.
(b) Advantages of a parallel connection are:
(i) In parallel arrangement, each appliance works at the same voltage. For example, if several bulbs are connected in parallel, each bulb glows at the same voltage. Therefore, the glow of a bulb is unaffected if another bulb is switched on or off.
(ii) In parallel arrangement, if one bulb (or appliance
Solution 32
Solution 33
When no current is drawn from the cell i.e. when the cell is in open circuit, the potential difference between the terminals of the cell is called its electromotive force (or e.m.f).
Solution 34

Solution 35
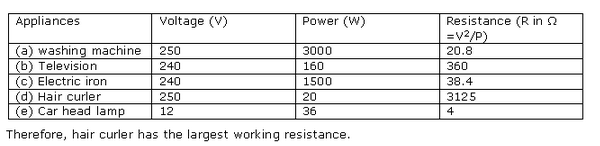
Solution 36
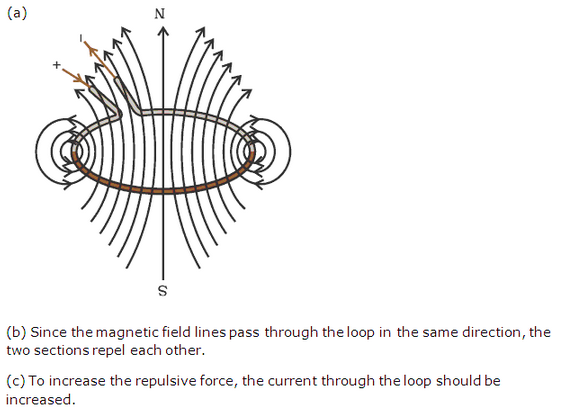
Solution 37
Incorrect statement:(a) A 13A fuse is the most appropriate value to use
Solution 38
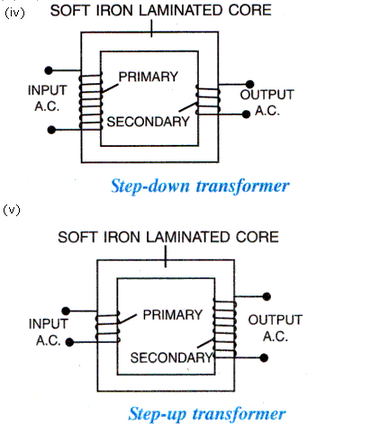
(i) A transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(ii) Function of a step-up transformer is to increase the a.c. voltage and decrease the current.
(iii) No, a transformer cannot work on a d.c. source. With a d.c. source, there will be no change in magnetic flux linked with the secondary coil.
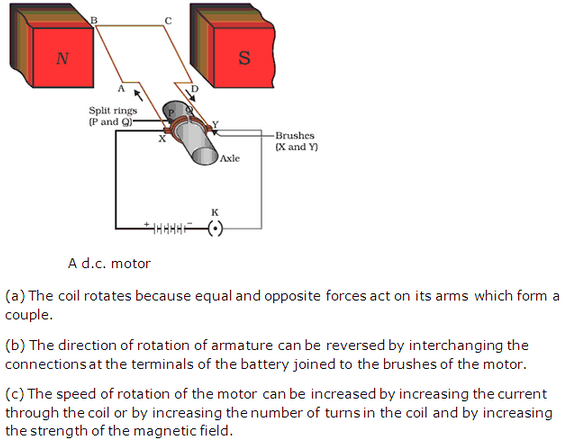
Solution 39
(i) Current at the end B of the coil X is anticlockwise therefore at this end there is north pole.
(ii) While closing the key, polarity at the end C of the coil Y will be north. There will be no polarity at the end C of the coil Y when the current becomes steady in the coil X.
(iii)
(a) While the coil Y is moved towards the coil X, the polarity at the end C of the coil Y is north.
(b) While the coil Y is moved away the coil X, the polarity at the end C of the coil Y is south.
PAGE NO-228:
Solution 40
(a)
(i) When the magnet is moved rapidly in the direction of arrow, the magnetic flux linked with the coil changes and there is a deflection in the galvanometer, indicating a flow of current through the coil.
(ii) On keeping the magnet still, the magnetic flux linked with the coil does not change and there is no deflection in the galvanometer, indicating that no current is flowing through the coil.
(iii) When the magnet is rapidly pulled out, there is again change in the magnetic flux linked with the coil and the galvanometer shows a deflection but this time in opposite direction, indicating that a current is flowing in opposite direction in the coil.
(b) If a more powerful magnet is used, deflection in the galvanometer will be large, indicating a greater amount of current.
Solution 41
(a) (v) leftleft left
(b) (ii) repulsion and attraction respectively
(c) (i) connecting a large resistor in series
(d) (iv) upwards and perpendicular to XY
(e) (i) 250 V
Solution 42
(a) Plastic being non-magnetic cannot be used as a material for core. It shall not intensify the formed magnetic field.(b) Steel has high retentivity. Hence, after prolonged use even when the switch is off, it may retain some magnetic property and attract the armature. (c) Using copper as a material for core will introduce eddy currents in the core and thus, interfere with the working of the bell.
PAGE NO-229:
Solution 43
Solution 44
Solution 45
(i) This is due to change in magnetic flux in the coil. Due to change in magnetic flux an induced emf is produced in the coil. Hence, a current flows through the galvanometer.(ii) The current appears anticlockwise when viewed from end A because end A will form north-pole.(iii) The galvanometer now deflects towards left.(iv) No deflection is observed as there is no relative motion between the magnet and the coil.
Solution 46
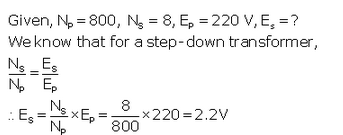
Solution 47
A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into an ammeter by connecting a low resistance (called a shunt) in parallel to the galvanometer.A moving coil galvanometer can be converted into a voltmeter by connecting a high resistance in series with the galvanometer.
Solution 48
An ammeter is a low resistance device; hence it is connected in series.A voltmeter is a high resistance device; hence it is connected in parallel.
Solution 49

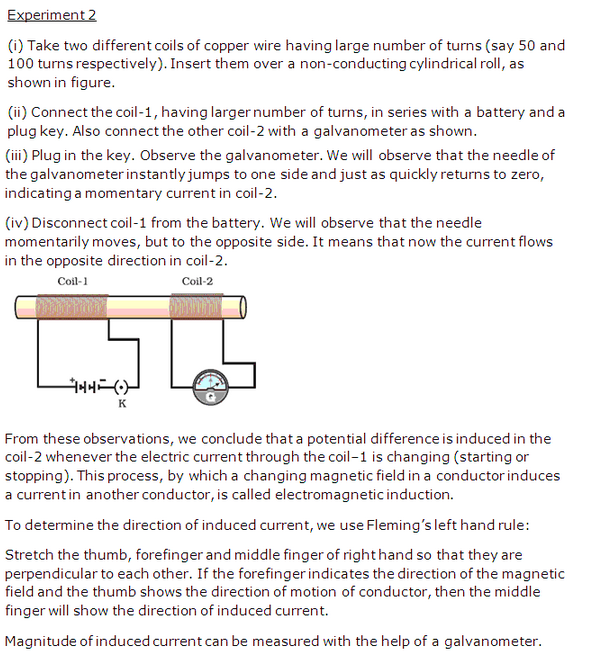
PAGE NO-230:
Solution 50
(a) We will observe that the needle of the galvanometer instantly jumps to one side and just as quickly returns to zero, indicating a momentary current in coil connected to galvanometer.
(b) Introducing an iron bar in the tube, will increase the amount of induced current and the galvanometer will show a greater deflection.
Solution 51
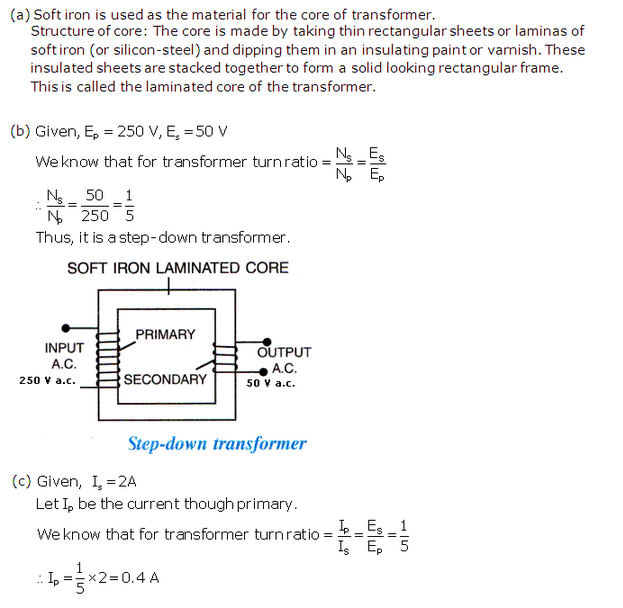
Solution 52
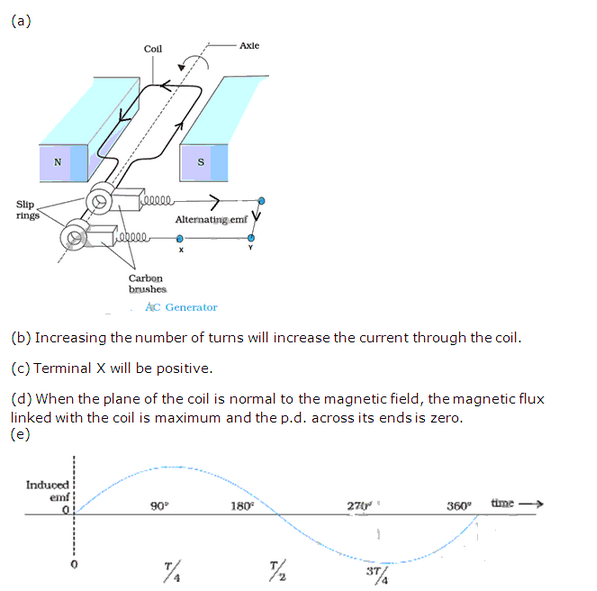
Solution 53
It is a diagram of step-down transformer.
(a) Brightness of bulb will increase because increasing the number of turns in the secondary will increase the change in magnetic flux linked with the coil.
(b) Part X is the core of the transformer is removed, it shall become an open core and there shall be magnetic flux link loss; i.e. the entire magnetic field lines produced by the primary shall not be linked with the secondary.
(c) If the core of the transformer is made of copper due to the formation of eddy currents a lot of energy shall be lost.
(d) A transformer cannot be used with direct current (d.c.) since its working is based on the principle that when there is a change of magnetic field lines due to varying current of same in one coil, an induced varying current of same frequency flows in the other coil. If the current in one coil is constant (i.e. d.c.), no induced current will flow in the other coil since there will be no change in the magnetic field lines linked with the coil.
Solution 54

Solution 55
Features which provide greater efficiency to a transformer are:(i) The core of the transformer is laminated which prevents the formation of eddy currents.(ii) A closed soft-iron core is used which reduces the magnetic field link loss and hysteresis loss.
Solution 56
(a) magnet – soft iron(b) core- soft iron(c) core- soft iron, magnet – steel(d) core- soft iron, magnet – steel(e) core-soft iron
Solution 57

Solution 58
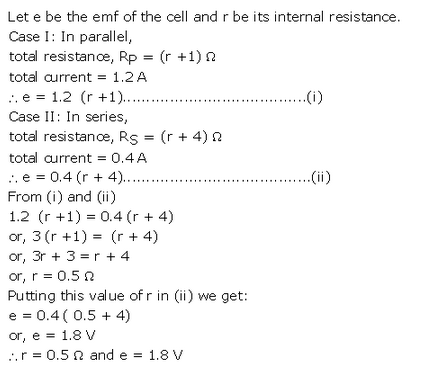
Solution 59
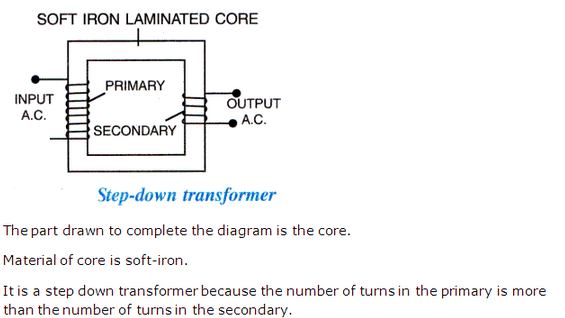
Solution 60
The ratio of number of turns NS in secondary coil to the number of turns NP in the primary coil (NS / NP) is called the turns ratio. A transformer cannot be used with direct current (d.c.) since its working is based on the principle that when there is a change of magnetic field lines due to varying current of same in one coil, an induced varying current of same frequency flows in the other coil. If the current in one coil is constant (i.e. d.c.), no induced current will flow in the other coil since there will be no change in the magnetic field lines linked with the coil.
Physics Chemistry Biology Maths
RD Sharma Class 10 Solutions
Video Solutions