Evolution- CBSE Notes for Class 12 Biology
CBSE Notes CBSE Notes Biology NCERT Solutions Biology
The Origin of Life and Evidences of Evolution:
1. The study of history of life
forms on earth is called evolutionary biology.
2. Evolution is a process
that results in heritable changes in population spread over many generations leading to diversity of organisms on earth.
3. Origin of life
is considered a unique event in the history of universe.
(i) The Universe
(a) It is very old-almost 20 billion years ago. It contains huge galaxies.
(b) Galaxies contain stars and clouds of gas and dust.
(c) The origin of universe is explained by Big Bang theory.
(d) The Big Bang theory states that a huge explosion occurred, the universe expanded, temperature came down and hydrogen and helium were formed later. The galaxies were then formed due to condensation of gases under gravitation.
(ii) The earth was supposed to have been formed about 4.5 billion years back in the solar system of the milkyway galaxy.
(a) Water vapour, methane, carbon dioxide and ammonia released from molten masses covered the surface.
(b) UV rays from the sun broke up water molecule into hydrogen and oxygen and lighter hydrogen escaped.
(c) Oxygen combined with ammonia and methane to form water, carbon dioxide and others.
(d) Ozone layer formed, as it cooled, the water vapour fell as rain to fill depression and form oceans.
(e) Life appeared 500 million (about 4 billion years back) years after the formation of earth.
4. Theories of origin of life
were given by different thinkers and scientists.
(i) Theory of special creation states that God created life by his divine act of creation.
(iii) Theory of panspermia/cosmozoic theory, given by early Greek thinkers states that the spores or panspermia came from outer space and developed into living forms.
(iii) Theory of spontaneous generation states that life originated from decaying and rotting matter like straw, mud, etc.
(a) Louis Pasteur rejected the theory of spontaneous generation and demonstrated that life came from pre-existing life.
(b) In his experiment, he kept killed yeast cells in pre-sterilised flask and another flask open into air. The life did not evolved in the former but new living organisms evolved in the second flask.
(iv) Theory of chemical evolution or Oparin-Haldane theory states that life originated from pre-existing non-living organic molecules and that formation of life was preceded by chemical evolution.
The conditions on the earth that favoured chemical evolution were very high temperature, volcanic storms and reducing atmosphere that contained CH
4
,NH
3
, water vapour, etc.
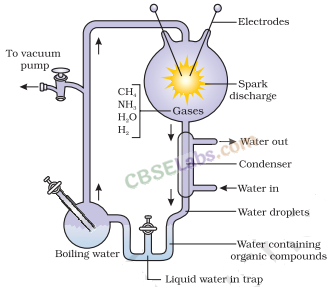
5. Miller’s experiment
provided experimental evidence for chemical evolution.
(i) The experiment was carried out by SL Miller and HC Urey in 1953.
(ii) He took a closed flask containing CH
4
,H
2
,NH
3
and water vapour at 800°C and created electric discharge. These conditions were similar to those in primitive atmosphere.
(iii) After a week, formation of amino acids were observed. Complex molecules like sugars, nitrogen bases, pigments and fats were seen in the flask by other scientist.
(iv) Analysis of the meteorite also revealed the presence of similar compounds.
(v) Chemical evolution of life was more or less accepted.
6. Origin of First Cell
(i) First non-cellular life forms originated three million years ago.
(ii) These molecules were like RNA, protein and polysaccharides.
(iii) Cellular life form first evolved about 2000 million years ago.
(iv) These were single-celled formed in aquatic environment.
(v) This form of abiogenesis, i.e. the first form of life arose slowly through evolutionary
forces from non-living molecules It is accepted by many scientists.
7. Evidences of evolution come from
(i) Palaeontology (ii) Comparative anatomy and morphology
(iii) Biochemical/Physiology (iv) Biogeography
(v) Embryology
(i) Palaeontology is the study of fossils. The fossils are the remains of past organisms
preserved in sedimentary rocks
(a) Rocks form sediments and a cross-section of earth’s crust indicates the arrangement of sediments one over the other during the long history of earth.
(b) Different aged rock sediments contain fossils of different life forms, who died during the formation of the particular sediment,
(c) Some organisms appear similar to modern organisms. They represent extinct organisms like dinosaurs.
(d) A study of fossils in different sedimentary layers indicates the geological period in which they existed.
(e) The study showed that life forms varied over time and certain life forms are restricted to certain geological time-scale Hence, new forms of life have evolved at different times in the history of earth,
(ii) Comparative anatomy and morphological evidences show the similarities and
differences among the organisms of today and those that existed years ago.
The evidences come from comparative study of external and internal structure.
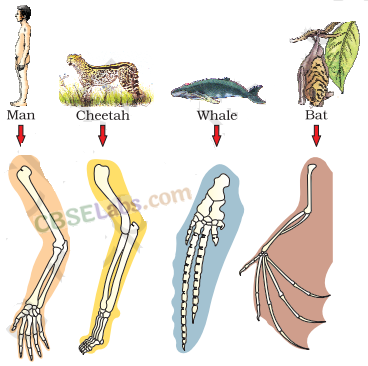
I. (a) The organs
with same structural design and origin but different functions are called homologous organs. Examples are forelimbs of some animals like whales, bats and cheetah have similar anatomical structure, such as humerus, radius, ulna, carpals, metacarpals and phalanges.
(b) Homology in organ indicates common ancestry.
(c) Other examples of homology are vertebrate hearts or brains. In plants also, thorns and tendrils of Bougainvillea and Cucurbita represent homology.
(d) Homology is based on divergent evolution. The same structure developed along different directions due to adaptations to different needs. The condition is called divergent evolution.
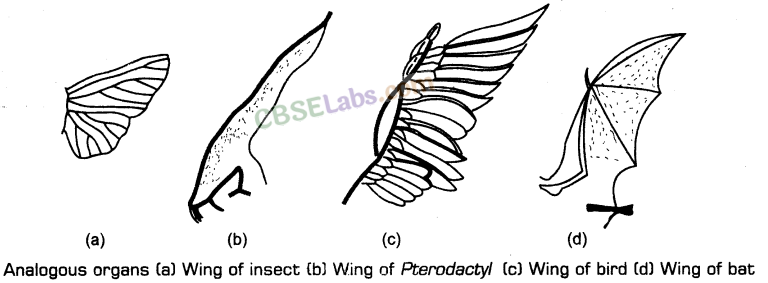
II. (a) Organs
which are anatomically different but functionally similar are called analogous organs. For example, wings of butterfly and birds.
(b) Analogy refers to a situation exactly opposite to homology.
(c) Analogous organs are a result of convergent evolution. It is the evolution in which different structures evolve for same function and hence, have similarity.
(d) Other examples of analogy are eyes of Octopus and mammals; flippers of penguins and dolphins. In plants, sweet potato (root modification) and potato (stem modification).
III. Vestigial organs
like homologous organs provide evidences for organic evolution.
These are degenerate, non-functional and rudimentary organs to the possessor, while correspond to fully developed and functional organs of related organisms.
(a) There are about 90 vestigial organs in the human body. Same of them are tail bone (coccyx), wisdom teeth, nictitating membrane, vermiform appendix, etc.
(b) Some examples from other animals are hip girdles and bones of the hind limbs in some whales and certain snakes and wings of flightless birds.
Biochemical Evidences
(a) The metabolic processes in organisms are similar with same new materials and end products. For example, energy released by oxidation is stored in ATP which then powers the energy requiring process.
(b) Molecular homology is the similarity among animals at the molecular level.
For example, human DNA differs in only 1.8% of its base pairs from chimpanzee DNA and there is no difference between the two in the amino acid sequence for the protein cytochrome-c.
(iv) Biogeographical evidences The species restricted to a region develop unique features. Also, species present in far separated regions show similarity of ancestry.
This can be explained with the help of following processes:
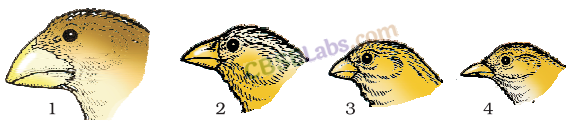
I. Adaptive radiation
is an evolutionary process in which an ancestral stock gives rise to new species adapted to new habitats and new ways of life. Examples are (0 Darwin’s finches These were small black birds, which Darwin observed in Galapagos island.
(a) He observed many varieties of finches in the same island.
(b) All varieties of finches had evolved from original seed-eating finches.
(c) There was alternation in beaks enabling some to become insectivorous and some vegetarian.
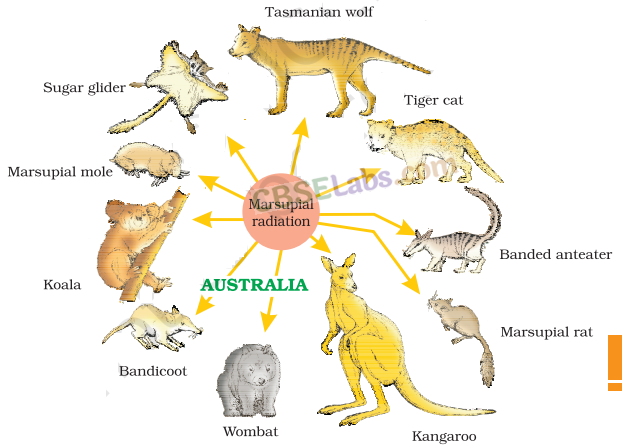
(ii) Marsupials of Australia A number of marsupials, different from each other evolved from an ancestral stock, all within the Australian island continent.
II. Parallel evolution
refers to independent development of similar characters in two animal groups of common ancestry living in similar habitats of different continents. Examples are
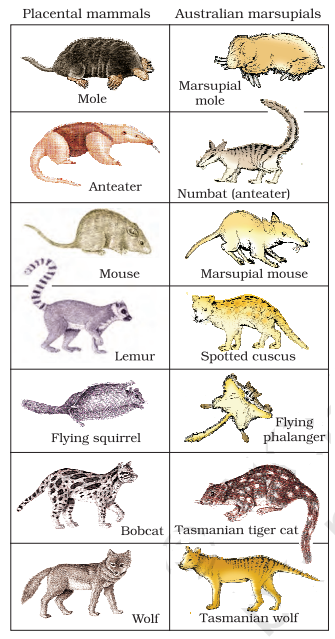
Marsupial mammals in Australia show parallel evolution as they have evolved from placental mammals. All these closely resemble and look similar to a corresponding marsupial.
Few examples are mentioned in the table.
III.
Convergent evolution
is development of similar adaptive functional structures in unrelated groups of organisms. Examples are:
(i) Wings of insect, bird and bat.
(ii) Spiny anteater and scaly anteater belong to different orders of class-Mammalia. They have acquired similar adaptations for food, e.g. leg ants, termites and insects.
(v)
Embryological evidences
Study of comparative embryology shows common patterns of development.
(a) The principles of embryonic development were given by Von Baer.
(b) Ernst Haeckel propounded The theory of recapitulation or Biogenetic law which states that an individual organism in its development (ontogeny) tends to repeat the stages passed through by its ancestors (phylogeny), i.e. ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny.
(c) This means that the life history of an animal reflects its evolutionary history.
For example, during the life history, frog’s tadpole larva resembles fishes, the ancestors of amphibia.
The presence of gill clefts in all vertebrate embryos including human provides a strong evidence in support of organic evolution.
(vi)
Anthropogenic evidences
Excess use of herbicides, pesticides, etc has resulted in selection of resistant varieties in a lesser time scale. This is also true for microbes against which antibiotics or drugs have been used. All these evidences tell us that ‘Elvolution is a stochastic process based on chance events in nature and chance mutation in the organisms’.
NCERT Solutions Maths Physics Chemistry Biology Science