CBSE Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Pdf free download is part of Class 10 Maths Notes for Quick Revision. Here we have given NCERT Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry. According to new CBSE Exam Pattern, MCQ Questions for Class 10 Maths Carries 20 Marks.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Notes Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
-
Position of a point P in the Cartesian plane with respect to co-ordinate axes is represented by the ordered pair (x, y).
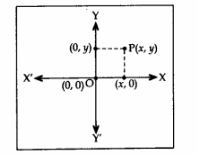
- The line X’OX is called the X-axis and YOY’ is called the Y-axis.
- The part of intersection of the X-axis and Y-axis is called the origin O and the co-ordinates of O are (0, 0).
- The perpendicular distance of a point P from the Y-axis is the ‘x’ co-ordinate and is called the abscissa.
- The perpendicular distance of a point P from the X-axis is the ‘y’ co-ordinate and is called the ordinate.
-
Signs of abscissa and ordinate in different quadrants are as given in the diagram:
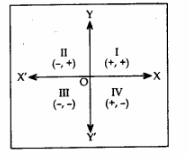
- Any point on the X-axis is of the form (x, 0).
- Any point on the Y-axis is of the form (0, y).
-
The distance between two points P(x1, y1) and Q (x2, y2) is given by
PQ = \(\sqrt { { \left( { x }_{ 2 }-{ x }_{ 1 } \right) }^{ 2 }+{ \left( { y }_{ 2 }-{ y }_{ 1 } \right) }^{ 2 } } \)
Note. If O is the origin, the distance of a point P(x, y) from the origin O(0, 0) is given by
OP = \(\sqrt { { x }^{ 2 }+{ y }^{ 2 } } \)
Section formula.
The coordinates of the point which divides the line segment joining the points A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2) internally in the ratio m : n are:
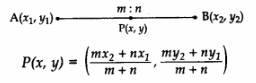
The above formula is section formula. The ratio m: n can also be written as \(\frac { m }{ n }\) : 1 or k : 1, The
co-ordinates of P can also be written as P(x,y) = \(\frac { { kx }_{ 2 }+{ x }_{ 1 } }{ k+1 } ,\frac { { ky }_{ 2 }+{ y }_{ 1 } }{ k+1 } \)
The mid-point of the line segment joining the points P(x1, y1) and Q(x2, y2) is
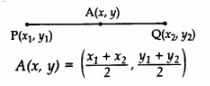
Here m : n = 1 :1.
Area of a Triangle.
The area of a triangle formed by points A(x1 y1), B(x2, y2) and C(x3, y3) is given by | ∆ |,
where ∆ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \left[ { x }_{ 1 }\left( { y }_{ 2 }-{ y }_{ 3 } \right) +{ x }_{ 2 }\left( { y }_{ 3 }-{ y }_{ 1 } \right) +{ x }_{ 3 }\left( { y }_{ 1 }-{ y }_{ 2 } \right) \right] \)
where ∆ represents the absolute value.
- Three points are collinear if |A| = 0.
-
If P is centroid of a triangle then the median divides it in the ratio 2 :1. Co-ordinates of P are given by
\(P=\left( \frac { { x }_{ 1 }+{ x }_{ 2 }+{ x }_{ 3 } }{ 3 } ,\frac { { y }_{ 1 }+{ y }_{ 2 }+{ y }_{ 3 } }{ 3 } \right) \)
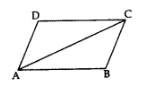
Area of a quadrilateral,
ABCD = ar(∆ABC) + ar(∆ADC)
Class 10 Maths Notes
- Chapter 1 Real Numbers Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 2 Polynomials Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 3 Pair of Linear equations in Two Variables Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 6 Triangles Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 10 Circles Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 11 Constructions Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 12 Areas related to Circles Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 14 Statistics Class 10 Notes
- Chapter 15 Probability Class 10 Notes