Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Maths with Solutions Set 1 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 9 Maths Set 1 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- This question paper contains 38 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper is divided into Five sections – Sections A, B, C, D, and E.
- In section A, questions number 1 to 18 are multiple-choice questions (MCQs) and questions number 19 and 20 are Assertion – Reason-based questions of 1 mark each.
- In section B, questions number 21 to 25 are very short answer (VSA) type questions of 2 marks each.
- In section C, questions number 26 to 31 are short answer (SA) type questions carrying 3 marks each.
- In section D, questions number 32 to 35 are long answer (LA) type questions carrying 5 marks each.
- In section E, questions number 36 to 38 are case-based integrated units of assessment questions carrying 4 marks each. Internal choice is provided in 2-mark questions in each case study.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 2 questions in Section B, 2 questions in Section C, and 2 questions in Section D.
- Draw neat figures wherever required. Take π = \(\frac{22}{7}\) wherever required if not stated.
- The use of a calculator is not allowed.
Section-A
Consists of Multiple Choice Type questions of 1 mark each.
Question 1.
Which of the following statements is true?
(A) Every irrational number can be represented as a fraction.
(B) Every irrational number can be represented with the help of decimals.
(C) Every rational number can be represented as a terminating decimal.
(D) Every rational number can be represented as an integer.
Answer:
(B) Every irrational number can be represented with the help of decimals.
Question 2.
\(\sqrt{2}\) is a polynomial of degree
(A) 2
(B) 0
(C) 1
(D) \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
(B) 0
Explanation:
\(\sqrt{2}=\sqrt{2} x^0\)
Because exponent of x is 0.
Question 3.
If (2, 0) is a solution of the linear equation 2x + 3y = k, then the value of k is
(A) 4
(B) 6
(C) 5
(D) 2
Answer:
(A) 4
Explanation:
Put x = 2, y = 0 in the equation 2x + 3y = k
⇒ 2(2) + 3(0) = k
⇒ 4 + 0 = k
Hence, k = 4
![]()
Question 4.
Abscissa of a point is positive in
(A) I and II quadrants
(B) I and IV quadrants
(C) I quadrant only
(D) II quadrant only
Answer:
(B) I and IV quadrants
Explanation:
Abscissa of a point is positive in the I and IV quadrants.
Question 5.
In the given figure, POQ is a line. The value of x is
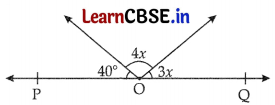
(A) 20°
(B) 25°
(C) 30°
(D) 35°
Answer:
(A) 20°
Explanation:
40° + 4x + 3x = 180° (POQ is a straight line)
⇒ 7x = 180° – 40°
⇒ 7x = 140°
⇒ x = 20°
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a criterion for congruence of triangles?
(A) SAS
(B) ASA
(C) SSA
(D) SSS
Answer:
(C) SSA
Explanation:
The criterion for congruency is SAS (side angle side). ASA (angle side angle), SSS (side side side), AAS (angle-angle side).
Question 7.
The quadrilateral formed by joining the midpoints of the sides of a quadrilateral PQRS, taken in order, is a rectangle, if
(A) PQRS is a rectangle
(B) PQRS is a parallelogram
(C) Diagonals of PQRS are perpendicular
(D) Diagonals of PQRS are equal
Answer:
(C) Diagonals of PQRS are perpendicular
Explanation:
Since the quadrilateral ABCD formed by joining the mid-point of quadrilateral PQRS is a rectangle.
∴ AB = BD [Since diagonals of a rectangle are equal]
⇒ PQ = QR
Thus, quadrilateral PQRS is a rhombus.
Hence, diagonals of PQRS i.e., PR and QS are perpendicular.
[∵ Diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular to each other].
Question 8.
Given below is the figure of a circle with center O. The measure of ∠BOC = 88°.
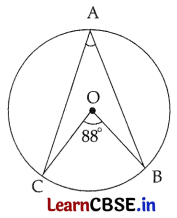
What is the measure of ∠BAC?
(A) 44°
(B) 60°
(C) 88°
(D) 176°
Answer:
(A) 44°
Explanation:
∠BOC = 2∠BAC
(∵ The angle subtended by an arc at the center is double the angle subtended by it at any point on the remaining part of the circle)
So, 88° = 2∠BAC
∴ ∠BAC = 44°
![]()
Question 9.
If the area of an equilateral triangle is 16√3 cm
2
, then the perimeter of the triangle is
(A) 48 cm
(B) 24 cm
(C) 12 cm
(D) 36 cm
Answer:
(B) 24 cm
Explanation:
Area of equilateral, ∆ = \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^2\) (a = side)
Given, ∆ = 16√3 cm
2
⇒ a2 = \(\frac{16 \sqrt{3} \times 4}{\sqrt{3}}\) = 64
⇒ a = 8 cm
Perimeter, P = 3 × a = 3 × 8 = 24 cm
Question 10.
The radius of a sphere is 2r, and then its volume will be
(A) \(\frac{4 \pi r^3}{3}\)
(B) 4πr3
(C) \(\frac{8 \pi r^3}{3}\)
(D) \(\frac{32 \pi r^3}{3}\)
Answer:
(D) \(\frac{32 \pi r^3}{3}\)
Explanation:
Volume of the sphere = \(\frac{4 \pi r^3}{3}\) (r = radius)
Given, radius r = 2r
Therefore, volume of the sphere = \(\frac{4}{3} \pi(2 r)^3\) = \(\frac{32 \pi r^3}{3}\)
Question 11.
In a bar graph, the width of the bars
(A) Are proportional to the corresponding frequencies
(B) Have no significance
(C) Are proportional to the space between two consecutive bars.
(D) Are proportional to the corresponding heights.
Answer:
(B) Have no significance
Explanation:
The width of the bars is equal only from a clarity point of view otherwise they have no significance.
Question 12.
Which of the following is irrational?
(A) \(\frac{\sqrt{4}}{\sqrt{9}}\)
(B) \(\frac{\sqrt{12}}{\sqrt{3}}\)
(C) \(\sqrt{7}\)
(D) \(\sqrt{81}\)
Answer:
(C) \(\sqrt{7}\)
Explanation:
(A) \(\frac{\sqrt{4}}{\sqrt{9}}=\frac{2}{3}\), which is a rational number.
(B) \(\frac{\sqrt{12}}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{\sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=2=\frac{2}{1}\), which is a rational number.
(C) \(\sqrt{7}\) is an irrational number.
(D) \(\sqrt{81}\) = 9 = \(\frac{9}{1}\), which is a rational number.
Question 13.
In a right circular cone, the cross-section made by a plane parallel to the base is a
(A) Sphere
(B) Hemisphere
(C) Circle
(D) Semicircle
Answer:
(C) Circle
![]()
Question 14.
A diagonal of a rectangle is inclined to one side of the rectangle at 25°. The acute angle between the diagonals is
(A) 55°
(B) 50°
(C) 40°
(D) 25°
Answer:
(B) 50°
Explanation:
ABCD is a rectangle in which diagonal AC is inclined to one side, AB of the rectangle at an angle of 25°.
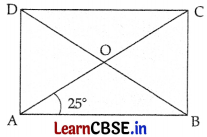
Now, AC = BD [Diagonals of a rectangle are equal]
∴ \(\frac{1}{2}\)AC = \(\frac{1}{2}\)BD
or, OA = OB
In triangle AOB, we have
OA = OB
∴ ∠OBA = ∠BAO = 25° (Angles opposite to equal sides)
By angle sum property, we have
So, ∠OBA + ∠AOB + ∠BAO = 180°
25° + 25° + ∠AOB = 180°
∠AOB = 180° – 50° = 130°
We know that, ∠AOB and ∠AOD form a linear pair.
So, ∠AOB + ∠AOD = 180°
130° + ∠AOD = 180°
∠AOD = 180° – 130° = 50°
Therefore, the acute angle between the diagonal is 50°.
Question 15.
The number of dimensions, a point has
(A) 0
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 3
Answer:
(A) 0
Explanation:
According to Euclid, a point is that which has no part, i.e., no length, no breadth, and no height. Therefore, it has no dimension.
Question 16.
Factorize 12a
2
b – 6ab
2
(A) 6ab(2a – b)
(B) 2ab(6a – 3b)
(C) 3ab(4a – 2b)
(D) 6a(2ab – b)
Answer:
(A) 6ab(2a – b)
Explanation:
12a
2
b – 6ab
2
= 6ab(2a – b) [By taking ab common]
Question 17.
The linear equation 2x – 5y = 7 has
(A) a unique solution
(B) two solutions
(C) infinitely many solutions
(D) no solution
Answer:
(C) infinitely many solutions
Explanation:
In the given equation 2x – 5y = 7, for every value of x, we get a corresponding value of y and vice-versa; therefore, the linear equation has infinitely many solutions.
Question 18.
In RHS rule ‘H’ stands for
(A) Height
(B) Hypotenuse
(C) Heron’s Formula
(D) Highest
Answer:
(B) Hypotenuse
Explanation:
In the right angle triangle, H stands for hypotenuse.
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
(C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Question 19.
Assertion (A): According to Euclid’s 1st Axiom – “Things which are equal to the same thing are also equal.”
Reason (R): If AB = PQ and PQ = XT, then AB = XY.
Answer:
(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A).
Explanation:
In the case of Assertion (A): Euclid’s 1st Axiom is given which is an assumption and is a universal truth.
∴ The assertion is correct.
In the case of Reason (R): It is the correct explanation of Euclid’s 1st Axiom.
∴ The reason is true.
Hence, Assertion and Reason are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
![]()
Question 20.
Assertion (A): If angles ‘a’ and ‘b’ form a linear pair of angles and a = 40° then b = 150°.
Reason (R): The sum of a linear pair of angles is always 180°.
Answer:
(D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Explanation:
In the case of Assertion (A): ‘a’ and ‘b’ are linear pair (given)
So a + b = 180°
But 40° + 150° = 190° ≠ 180°
∴ The assertion is false.
In the case of Reason (R): The sum of a linear pair of angles is always 180°.
∴ The reason is true.
Section-B
Consists of 5 questions of 2 marks each.
Question 21.
Below are the marks of 35 students in mathematics tests (out of 10). Average these marks in tabular form using the tally mark.
5, 8, 7, 6, 10, 8, 2, 4, 6, 3, 7, 5, 8, 5, 1, 7, 4, 6, 3, 5, 2, 8, 4, 2, 6, 4, 2, 8, 9, 5, 4, 7, 5, 5, 8
Answer:
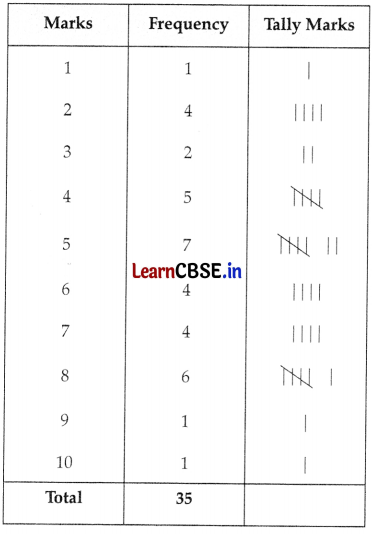
Question 22.
If y = 2 and y = 0 are the zeroes of the polynomial f(y) = 2y
3
– 5y
2
+ ay + b, find the value of a and b.
Answer:
Given, f(y) = 2y
3
– 5y
2
+ ay + b
∴ f(2) = 2(2)
3
– 5(2)
2
+ a(2) + b = 0
⇒ 16 – 20 + 2a + b = 0
⇒ 2a + b = 4 …..(i)
and f(0) = b = 0
From (i), 2a + 0 = 4
⇒ a = 2
∴ a = 2, b = 0
Question 23.
Find the value of the polynomial p(x) = x
3
– 3x
2
– 2x + 6 at x = \(\sqrt{2}\)
Answer:
In ∆ADB,
By Angle Sum Property
∠ABD + ∠ADB + ∠BAD = 180°
⇒ 50° + ∠ADB + 60° = 180°
⇒ ∠ADB = 180° – (50° + 60°)
⇒ ∠ADB = 70°
⇒ ∠ACB = ∠ADB = 70°
(∵ angles in the same segment of a circle are equal)
Question 24.
If (3x – 15°) and (x + 5°) are complementary angles, find the angles.
OR
In the given figure, find the angles a and b and then show that LM || XY.
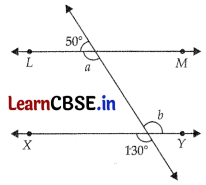
Answer:
(3x – 15°) + (x + 5°) = 90°
⇒ 4x = 90° + 10° = 100°
⇒ x = 25°
Angles are 60° and 30°.
OR
∠a = 180° – 50° = 130° (Linear Pair)
∠b = 130°
(Since Vertically opposite angles are equal)
This shows that ∠a = ∠b, But they are alternate interior angles,
∴ LM || XY
![]()
Question 25.
The radius and slant height of a cone are in the ratio 4 : 7. If its curved surface area is 792 cm
2
, find its radius.
OR
How much ice cream can be put into a cone with a base radius of 3.5 cm and a height of 12 cm?
Answer:
Let the radius of a cone, r = 4x
and slant height l = 7x
∵ CSA = 792 cm
2
⇒ πrl = 792
⇒ \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 4x × 7x = 792
⇒ x
2
= \(\frac{792 \times 7}{22 \times 4 \times 7}\)
⇒ x
2
= 9
⇒ x = 3 cm
∴ radius = 4 × 3 = 12 cm
OR
r = 3.5 cm, h = 12 cm
∴ Amount of ice-cream = \(\frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h\)
= \(\frac{1}{3} \times \frac{22}{7}\) × 3.5 × 3.5 × 12
= 154 cm
3
Section-C
Consists of 6 questions of 3 marks each.
Question 26.
If f(x) = 5x
2
– 4x + 5, find f(1) + f(-1) + f(0).
Answer:
Given, f(x) = 5x
2
– 4x + 5
∴ f(1) = 5 – 4 + 5 = 6
and f(-1) = 5(-1)
2
– 4(-1) + 5
= 5 + 4 + 5
= 14
and f(o) = 5
∴ f(1) + f(-1) + f(0) = 6 + 14 + 5 = 25
Question 27.
In the given figure, AB = AC, and BE and CF are bisectors of ∠B and ∠C respectively. Prove that ∆EBC ≅ ∆FCB.
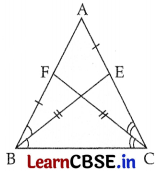
Answer:
AB = AC (Given)
∴ ∠ABC = ∠ACB ……(i)
BE and CF are the bisectors of ∠B and ∠C
∴ ∠EBC = \(\frac{1}{2}\)∠ABC = \(\frac{1}{2}\)∠ACB = ∠FCB
∠EBC = ∠FCB …….(ii)
In ∆BEC and ∆CFB
∠ABC = ∠ACB
∴ ∠ECB = ∠FBC
∠EBC = ∠FCB (Proved)
BC = BC (Common)
∴ ∆BEC ≅ ∆CFB (By ASA)
∆EBC ≅ ∆FCB
Hence Proved.
Question 28.
Write the equation 4x = 6(1 – y) + 3x in the form ax + by = c and also find the coordinates of the points where its graph cuts the two axes.
OR
ABCD is a rectangle. Write the equation of its sides. Also, find its area.
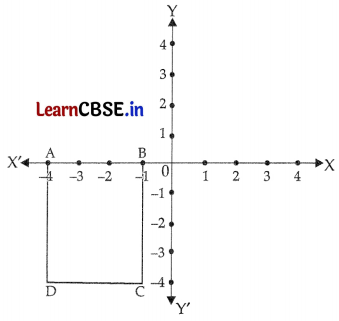
Answer:
4x = 6(1 – y) + 3x
4x = 6 – 6y + 3x
x = 6 – 6y
x + 6y = 6
The line cuts the X-axis at (6, 0) and the Y-axis at (0, 1)
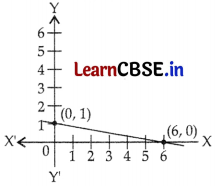
OR
The equation of the sides is,
AB: y = 0
BC: x = -1
CD: y = -4
DA: x = -4
Area = 4 × 3 = 12 sq. units
![]()
Question 29.
If x = \(\frac{1}{3-2 \sqrt{2}}\) and y = \(\frac{1}{3+2 \sqrt{2}}\), then find the value of x + y + xy.
OR
If x = 2 + √3, then find the value of \(x^2+\frac{1}{x^2}\).
Answer:
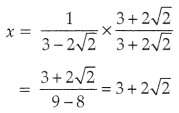
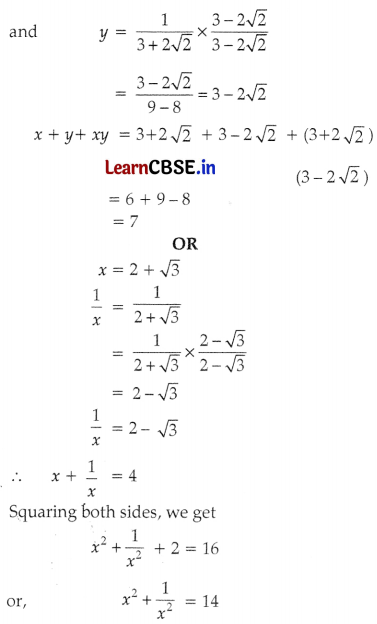
Question 30.
How many liters of milk can a hemispherical bowl of diameter 10.5 cm hold? (Use π = 3.14)
Answer:
Given, the diameter of the hemispherical bowl = 10.5 cm
∴ The radius of the hemispherical bowl
r = \(\frac{10.5}{2}\) = 5.25 cm
Volume of hemispherical bowl = \(\frac{2}{3} \pi r^3\)
= \(\frac{2}{3}\) × 3.14 × (5.25)
3
= 302.91
= 303 cm
3
∴ The amount of milk that the hemispherical bowl can hold is 0.303 liters.
Question 31.
Corona-virus disease (COVID-19) is an infectious disease. It is caused by a newly discovered coronavirus. Most people who fall sick with COVID-19 experience mild to moderate symptoms and recover without special treatment.
Number of the coronavirus (COVID-19) cases across India as of October 30, 2020.
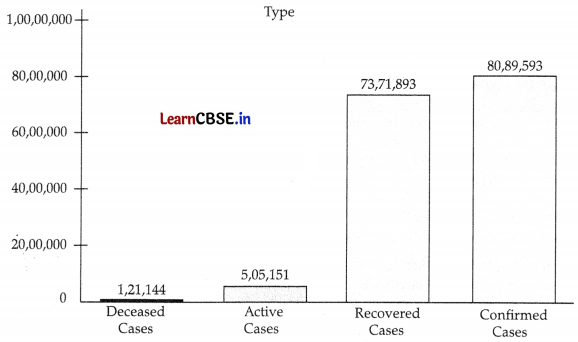
Corona-virus is mainly transmitted through droplets generated when an infected person coughs, sneezes or exhales. Look at the bar graph and answer the following:
(i) What is a horizontal line representing?
(ii) How many confirmed cases were more than recovered cases?
Answer:
(i) Number of cases.
(ii) Required number = confirmed cases – recovered cases
= 80,89,593 – 73,71,898
= 71,7,695
Section-D
Consists of 4 questions of 5 marks each.
Question 32.
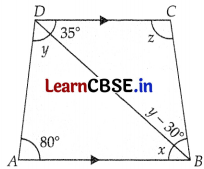
In the given figure, AB || DC, ∠BDC = 35° and ∠BAD = 80°. Find x, y, z.
OR
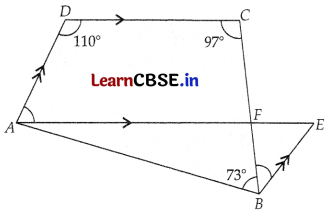
In the below figure, ABCD is a quadrilateral in which ∠ABC = 73°, ∠C = 97° and ∠D = 110°. If AE || DC and BE || AD and AE intersect BC at F, find the measure of ∠EBF.
Answer:
AB || DC
y + 35° + 80° = 180° (Consecutive interior angles)
⇒ y = 180° – 115°
⇒ y = 65°
∠ABD = ∠CDB or x = 35° (Alternate angles)
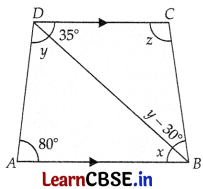
In ∆BCD,
35° + y – 30° + z = 180°
⇒ z = 180° – 5° – y
⇒ z = 175° – 65°
⇒ z = 110°
OR
Let ∠DAF = ∠1, ∠CFA = ∠2, ∠BFE = ∠3, ∠BEF = ∠4
Since, AE || DC
∠D + ∠1 = 180° (Angles on the same side of transversal)
⇒ ∠1 = 180° – 110° = 70°
∠4 = ∠1 = 70° (Alternate angles)
Again, 97° + ∠2 = 180° (Angle on the same side of transversal)
⇒ ∠2 = 180° – 97° = 83°
∠3 = ∠2 = 83° (Vertically opposite angles)
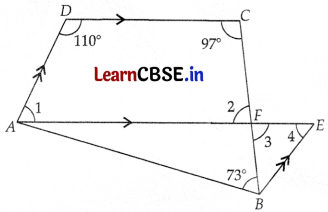
In ∆BEF,
∠3 + ∠4 + ∠EBF = 180° (Angle sum property)
⇒ 83° + 70° + ∠EBF = 180°
⇒ ∠EBF = 180° – 153°
⇒ ∠EBF = 27°
![]()
Question 33.
Give two rational numbers whose
(i) difference is a rational number,
(ii) sum is a rational number,
(iii) product is a rational number,
(iv) division is a rational number.
Justify also.
Answer:
Take any example and show shops of verification.
Let m = \(\frac{4}{5}\), n = \(\frac{9}{2}\)
(i) Difference = \(\frac{9}{2}-\frac{4}{5}\) = \(\frac{45-8}{10}=\frac{37}{10}\) (Rational Number)
(ii) Sum = \(\frac{4}{5}+\frac{9}{2}\) = \(\frac{8+45}{10}=\frac{53}{10}\) (Rational Number)
(iii) Product = \(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{9}{2}=\frac{36}{10}=\frac{18}{5}\) (Rational Number)
(iv) Division = \(\frac{9}{2} \div \frac{4}{5}=\frac{45}{8}\) (Rational Number)
Question 34.
From a point in the interior of an equilateral triangle, perpendiculars are drawn on the three sides. The lengths of the perpendiculars are 14 cm, 10 cm, and 6 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
OR
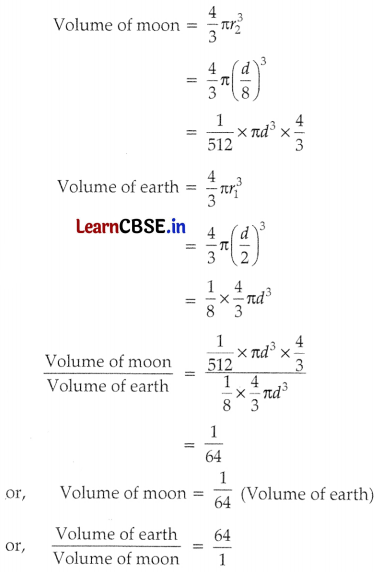
The diameter of the moon is approximately one-fourth the diameter of Earth. What fraction of the volume of the earth to the volume of the moon?
Answer:
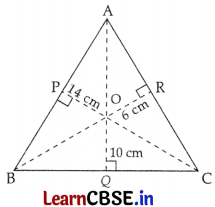
Join OA, OB, and OC.
Let, the sides of the equilateral triangle be ‘a’ cm.
ar ΔOAB = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × AB × OP
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × a × 14
= 7a cm
2
ar ΔOAC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × AC × OR
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × a × 6
= 3a cm
2
ar ΔOBC = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × BC × OQ
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) × a × 10
= 5a cm
2
Adding, (i), (ii), and (iii), we get
ar ΔOAB + ar ΔOAC + ar ΔOBC = (7a + 3a + 5a) cm
2
= 15a cm
2
Area of equilateral ΔABC = 15a cm
2
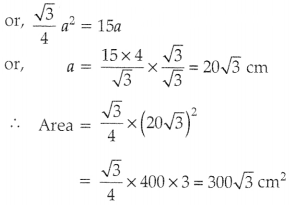
OR
Let the diameter of the earth be d.
∴ The radius of the earth will be, r
1
= \(\frac{d}{2}\)
Diameter of moon will be \(\frac{d}{4}\) and radius of moon (r
2
) = \(\frac{d}{8}\)
Question 35.
The auto-rickshaw fare in a city is charged ₹ 10 for the first kilometer and ₹ 4 per kilometer for subsequent distances covered. Write the linear equation to express the above statement and find 3 solutions to the equation.
Answer:
Total distance covered = x km.
Total fare = ₹ y
Fare for the first kilometre = ₹ 10
Subsequent distance = (x – 1) km
∴ Fare for the subsequent distance = ₹ 4(x – 1)
According to the question,
y = 10 + 4(x – 1)
⇒ y = 10 + 4x – 4
⇒ y = 4x + 6
∴ Required linear equation y = 4x + 6 where x ≥ 1

Section-E
Cased-Based Subjective Questions
Read the following passage and answer the following questions:
Question 36.
Three lighthouse towers are located at points A, B, and C on the section of a national forest to protect animals from hunters by the forest department as shown in the figure.
(i) How many straight lines can be drawn from A to C?
(ii) Give one more Postulate.
OR
Write one more of Euclid’s axiom.
(iii) State the Euclid Axiom which states the required result.
Answer:
(i) One and only one line can be drawn from A to C.
(ii) Another Postulate, “A circle can be drawn with any center and any radius”.
OR
According to Euclid’s Axiom 3, “If equals are subtracted from equals, then the remainders are equal”.
(iii) According to Euclid’s Postulates, “A straight line can be drawn from any point to any other point.”
![]()
Question 37.
Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao (BBBP) is a personal campaign of the Government of India that aims to generate awareness and improve the efficiency of welfare services intended for girls.

In a school, a group of (x + y) teachers, (x
2
+ y
2
) girls, and (x
3
+ y
3
) boys organized a campaign on Beti Bachao, Beti Padhao.
(i) Which mathematical concept is used here?
(ii) Write the correct identities to be used here.
OR
If in the group, there are 10 teachers and 58 girls, then what is the number of boys?
(iii) Find (x
2
– y
2
), if (x – y) = 23 and number of teachers are 10?
Answer:
(i) The mathematical concept used here is Polynomials.
(ii) Mathematical identities used here are (a + b)
2
= a
2
+ b
2
+ 2ab and (a + b)
3
= a
3
+ 3ab(a + b) + b
3
OR
No. of teachers = x + y = 10
By squaring both sides
(x + y)
2
= (10)
2
⇒ x
2
+ y
2
+ 2xy = 100 [Since (a + b)
2
= a
2
+ b
2
+ 2ab]
No. of students = (x
2
+ y
2
) = 58
⇒ 58 + 2xy = 100
⇒ 2xy = 100 – 58
⇒ 2xy = 42
⇒ xy = 21
Now, since (x + y)
3
= x
3
+ y
3
+ 3xy(x + y)
⇒ (10)
3
= x
3
+ y
3
+ 3 × 21(10)
⇒ 1000 = x
3
+ y
3
+ 630
⇒ 1000 – 630 = x
3
+ y
3
⇒ x
3
+ y
3
= 370
(iii) No. of teachers = x + y = 10
Given x – y = 23
x
2
– y
2
= (x + y) (x – y)
= 10 × 23
= 230
Question 38.
ABCD is a village in a quadrilateral shape. The Panchayat has decided to use the triangular area APD for girl’s education by constructing schools and colleges specially for girls as shown below.
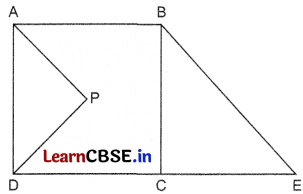
But members of Panchayat have some queries. Answer the following queries:
(i) If ∠PAD = 30° and ∠PDA = 60° then what is the measure of ∠APD?
(ii) If ABCD is a rectangle and AP and DP are the angular bisectors of ∠BAD and ∠CDA respectively, then what are the measures of ∠PAD and ∠PDA?
OR
If AP || BE, then what is the sum of ∠BAP and ∠ABE?
(iii) If BC = CE = 10 km then find BE.
Answer:
(i) ∠PAD + ∠PDA + ∠APD = 180° (Angle sum property of a triangle)
⇒ 30° + 60° + ∠APD = 180°
⇒ ∠APD = 180° – 90°
⇒ ∠APD = 90°
(ii) Since, ABCD is a rectangle.
Thus ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = ∠D = 90°
Also, AP is the angular bisector of ∠BAD
⇒ ∠PAD = \(\frac{90^{\circ}}{2}\) = 45°
and DP is the angular bisector of ZCDA 90°
⇒ ∠PDA = \(\frac{90^{\circ}}{2}\) = 45°
OR
Since, AP || BE. Thus, ∠BAP and ∠ABE are angled at the same side of the transversal.
Since angles at the same side of the transversal are supplementary. Therefore, the sum of ∠BAP and ∠ABE is 180°.
(iii) Since ∠BCE = 90°
Thus, BC
2
+ CE
2
= BE
2
(Pythagoras theorem)
⇒ 100 + 100 = BE
2
⇒ 200 = BE
2
⇒ BE = 10√2 km