Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions Set 9 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set 9 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section-B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section-C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section-D has 2 case-based questions of 4 marks each; and Section-E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
-
There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions.
A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. - Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section A
Question 1.
Using recombinant DNA technology, genes from a donor cell can be inserted into a bacterium for DNA replication and protein synthesis. Out of the options given below, select the kind of cells that can be used as gene donor in this technology.
(a) Bacteria only
(b) Eukaryotic cells
(c) Either yeast or bacteria
(d) Any of the above
Answer:
(d) Any of these cells like bacteria, yeast, eukaryotic cells can be used for DNA replication and protein synthesis.
Question 2.
For a long time, it was belived that life came out of decaying and rotting matter like straw, mud, etc. This was the theory of
(a) catastrophism
(b) spontaneous generation
(c) panspermia
(d) chemogemy
Answer:
(b) For a long time, it was believed that life came out of decaying and rotting matter like straw, mud, etc. This was the theory of spontaneous generation.
This theory states that life originated from non-living things in a spontaneous manner.
Question 3.
Given below are four transgenic organisms and their specific characteristics.
| Transgenic organisms | Characteristics | ||
| A. | Golden rice | 1. | Enriched with vitamin-A |
| B. | Bt cotton | 2. | Increased shelf life |
| C. | Flavr Savr | 3. | High yield and pest resistant |
| D. | Rosie cow | 4. | Protein-enriched milk |
How many of the following are correctly paired?
(a) 3
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) Two of them are correctly matched, incorrect matches can be corrected as
Bt cotton — high yield and pest resistant
Flavr Savr — increased shelf life
Question 4.
The impact of loss of biodiversity include
(a) decline in plant production
(b) lowered resistance to environmental perturbations
(c) increased variability in ecosystem processes like plant productivity, water use, pest and disease cycles
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) Loss of biodiversity includes decline in plant production, lowered resistance to environmental perturbations and increased variability in processes of ecosystem.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the fate of the male gametes discharged in the synergid?
(a) All fuse with the egg
(b) One fuses with the egg and other fuses with central cell nuclei
(c) One fuses with the egg and other fuses with synergid nucleus
(d) One fuses with the egg and their degenerate in the synergid
Answer:
(b) One of the male gamete fuses with the egg and form zygote, whereas the other fuses with the central cell nuclei and form PEN.
Question 6.
hCG, hPL and relaxin are produced in women. The production of these hormones takes place
(a) at the time of puberty
(b) Only during pregnancy
(c) during menstruation
(d) at the time of menopause
Answer:
(b) During pregnancy, placenta acts as an endocrine gland and secretes some hormones such as oestrogen, progesterone, human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG), human Placental Lactogen (hPL), relaxin, etc.
Question 7.
Rashi was doing a project on population control of a village nearby to her hometown. Which of the following term will denote the total number of individual of a species per unit area and per unit time?
(a) Demography
(b) Population size
(c) Population density
(d) Population dynamics
Answer:
(c) Population density is the number of individuals present per unit area or volume at a given time.
Question 8.
Which of the following types of organisms produces penicillin and which types of infection can be treated using penicillin?
| Types of organisms | Types of infection treated | |
| (a) | Fungus | Bacterial |
| (b) | Fungus | Viral |
| (c) | Bacterium | Viral |
| (d) | Bacterium | Bacterial |
Answer:
(a) Penicillium fungus produces antibiotic penicillin, which is used for treatment of bacterial infections.
Question 9.
An alcoholic drink produced without involving distillation process is
(a) brandy
(b) wine
(c) whisky
(d) rum
Answer:
(b) Wine and beer are filtered, pasteurised and bottled without undergoing distillation process.
Question 10.
Which one of the following animals may occupy more than one trophic levels in the same ecosystem at the same time?
(a) Goat
(b) Lion
(c) Frog
(d) Sparrow
Answer:
(d) Sparrow being an omnivorous can be a primary consumer if it feeds on seeds, fruits and peas or a secondary consumer if it feeds on insects and worms.
Question 11.
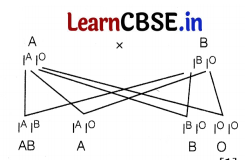
A child has blood group O. Identify the parents of this child from the table given below.
| Blood group of father | Blood group of mother | |
| (a) | AB | B |
| (b) | A | B |
| (c) | AB | A |
| (d) | O | AB |
Blood group of father Blood group of mother
(a) AB B
(b) A B
(c) AB A
(d) 0 AB
Answer:
(b) If both parents are heterozygous for A and B, then the child will be O.
Question 12.
The diagram shows a pyramid of biomass.

A sharp decrease is seen in biomass at higher trophic levels in grassland ecosystem. Choose the correct option for the levels of the ecosystem.
| 1 | 2 | |
| (a) | Carnivore | Herbivore |
| (b) | Producer | Herbivore |
| (c) | Herbivore | Producer |
| (d) | Carnivore | Producer |
Answer:
(b) Producers (grasses) are the first trophic levels in a food chain. Herbivores (rabbits, mice) eat producers, so they are second trophic level.
Question Nos. 13 to 16 consist of two statements- Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : The embryo with 6 to 8 blastomeres is called a morula.
Reason (R) : The morula continues to divide and transforms into trophoblast.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
The embryo with 6 to 8 blastomeres is called a morula. The morula continues to divide and transforms into blastocyst as it moves further into the uterus.
The blastomeres in the blastocysts are arranged into an outer layer called trophoblast and an inner group of cells attached to trophoblast called the inner cell mass.
![]()
Question 14.
Assertion (A) : AUG acts as a start codon for the nucleotide sequence.
Reason (B) : AUG codes for methionine and starts the process.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
AUG is the codon which is present as the first codon in the mRNA. This codon is present as the site from where the translation process starts to form the protein from the segment of mRNA.
Question 15.
Assertion (A) : Streptococcus thermophilus increase nutritional value of milk.
Reason (R) : Curd and yoghurt have higher vitamin content than milk.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Streptococcus thermophilus is widely used as starter to produce curd and yoghurt from milk.
This bacterium, while carrying out the curdling of milk, increases its vitamin content. Thus, curd and yoghurt are nutritionally rich and have higher vitamin content than milk.
Question 16.
Assertion (A) : Tropical rainforests are disappearing fastly from developing countries such as India.
Reason (R) : No value is attached to these forests because these are poor in biodiversity.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
Tropical rainforests are disappearing fastly from developing countries such as India. Forests lands are converting into agricultural and industrial lands to fulfill the requirement of increasing population.
I Therefore, humans are the main cause of rainforest destruction. Tropical rainforests are rich in biodiversity.
Section B
Question 17.
A patient showed symptoms of sustained high fever, stomach pain and constipation, but no blood clot in stools. Name the disease and its pathogen. Write the diagnostic test for the disease. How does the disease get transmitted?
Answer:
The symptoms, such as constant high fever, stomach pain and constipation, weakness and headache are shown in typhoid.
Its causative agent is a bacterium called Salmonella typhi. Widal test is used for its diagnosis.
Typhoid is transmitted through contaminated food and water.
Question 18.
The diagram given below shows the process of humulin production. Observe it carefully and answer the questions that follows.
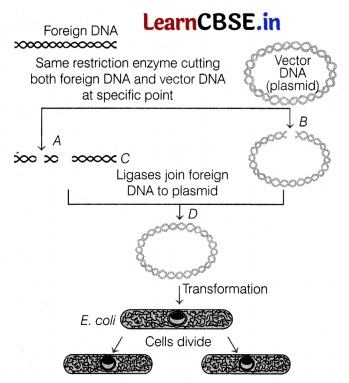
(i) What does the label C represent and what is its role?
(ii) Which DNA sequences will be introduced in label B to produce humulin?
Answer:
(i) Label C represents DNA ligase which is an enzyme that is used to join together two different types of DNA molecules.
ii) DNA sequences corresponding to the two polypeptides that is ‘A’ and ‘B’ chains of insulin are synthesised in In vitro and introduced into label B .
Question 19.
The following graph depicts changes in two population of herbivores, i.e. A and B in a grassy field. Can you suggest a possible reason for the changes observed in the below graph?
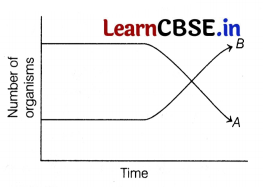
Answer:
As per the graphical representation, the individuals of population 6 have increased because they have adapted better to their environment than population A. Population B has proved to be superiorly adapted for the survival and attainment of resources like food, water, shelter , etc., leading to an increase in their number of offspring, as compared to those of population A.
![]()
Question 20.
In the flowchart given below, parts A, B and C show the hormonal factors responsible for the ovarian changes during menstrual cycle. Study the chart and answer the questions that follows.
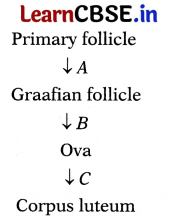
(i) Name the parts A, B and C which represents the hormonal factors responsible for the events.
(ii) State the impact of this hormones in female body.
Answer:
(i) A – FSH and oestrogen
B – LH
C – Progesterone
Falkland: (i) LH plays a key role in gonadal function . Falkland: (ii) FSH stimulates follicular growth and ovulation . Progesterone prepares the endometrium for the potential of pregnancy after ovulation .
Question 21.
(i) Given below is a cross between wild type and normal type. Identify in which of the crosses, the strength of linkage between the genes is higher.
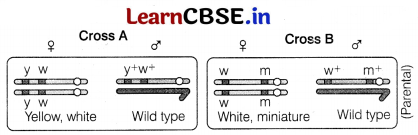
(ii) In which of the cross, the chances of crossing over is higher?
Or
Give an example of a gene responsible for multiple phenotypic expressions. What are such genes called? State the cause that is responsible for such an effect.
Answer:
(i) The strength of linkage is higher in the cross A than in cross B because linkage is higher when two genes are present closely on the same chromosome than those genes which are far apart.
(ii) In cross B, the chances of crossing over or recombination are higher because the genes are loosely linked.
Or
Pleiotropy is the phenomenon in which a single gene exhibits multiple phenotypic expressions. The genes exhibiting pleiotropy are called pleiotropic genes.
True
BB-Round seeds, large starch grains.
Bb-Round seeds, intermediate size starch grains.
bb-Wrinkled seeds, small starch grains.
Section C
Question 22.
The image below shows an elephant in a zoological park.

(i) What significance does the conservation strategy hold?
(ii) What is the difference between in situ and ex situ conservation?
(iii) What are the few example of in situ and ex situ conservation?
Answer:
(i) Zoological parks involves outside conservation techniques where animal species are protected outside their natural habitats. This conservation gives longer lifetime and breeding activity to animals.
True
True
Question 23.
What are the changes in the oogonia during the transition of a primary follicle to Graafian follicle?
Answer:
The germinal epithelial cells divide repeatedly until many diploid oogonia are formed. The oogonia grow to form primary oocytes. Each primary oocyte then gets surrounded by a layer of granulosa cells and is called the primary follicle. These get surrounded by more layers of granulosa cells and called secondary follicles.
True
True
Question 24.
Normally humans have 46 chromosomes arranged in 23 pairs, the pairs vary in size and shape.
22 pairs are autosomes and one pair, i.e. number, 23 is the sex chromosome. Any variation in this pattern causes abnormalities.
(i) Name the genetic disorder in a human female having 44 + XO karyotype.
(ii) Explain the cause of such chromosomal disorder and mention the diagnostic features of this disorder.
Answer:
(i) XO abnormality or monosomy of X-chromosome represents chromosomal disorder called Turner’s syndrome.
non-disjunction is responsible for this chromosomal disorder . chromosomal disorder occurs due to the absence of one X-chromosome . females are sterile and ovaries are rudimentary .
![]()
Question 25.
There was a mixup at the hospital after a fire accident in the nursery division. The figure shown below shows the bands of the DNA typing laboratory.
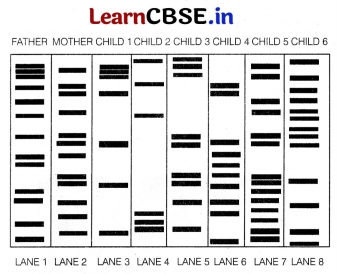
(i) Which of these children belong to the parents? Explain with reason.
(ii) If the record of mother is missing, will the child be identified with only the father’s information?
Answer:
(i) The two alleles (paternal and maternal) of a chromosome also contain different copy number of VNTR. It is clear from the banding patterns of DNA that parental DNA matches with child 1 and 3.
ii) The information of only one parent is required for the identification of the child . if the record of mother is missing, the child can be easily identified with only the father’s information .
Question 26.
Choose any three microbes, from the following, which are suited for organic farming which is in great demand these days for various reasons. Mention one application of each one chosen.
Mycorrhiza, Monascus, Anabaena, Rhizobium, Methanobacterium, Trichoderma.
Answer:
Organic farming can be defined as an agricultural process that uses biological fertilisers and pest control acquired from animal or plant waste.
The three microbes that can be chosen for organic farming are
(i) Rhizobium : The nodules on the roots of leguminous plants are formed by the symbiotic association of Rhizobium bacteria. These bacteria fix atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms, which is used by the plants as nutrient.
True
(iii) Anabaena It is a cyanobacteria that is used as a biofertiliser. It fixes atmospheric nitrogen. [1]
In order to get maximum marks, students should include following Points value point in the answer.
Brief definition of organic farming.
Question 27.
A codon is a trinucleotide sequence of DNA or RNA that corresponds to a specific amino acid. The genetic code describes the
relationship between the sequence of DNA bases in a gene and the corresponding protein sequence that it encodes.
(i) (a) What is degeneracy?
(b) ‘Starting codon is universal’. Justify.
(ii) Which feature of genetic code allows bacteria to produce human insulin by recombinant DNA technology?
Or
Erwin Chargaff was one of those men, making two discoveries that led James Watson and Francis Crick to the double helix strucure of DNA. At first Chargaff noticed that DNA whether taken from a plant or animal-contained equal amounts of adenine and thymine and equal 1 amounts of cytosine and guanine. In addition Chargaff also found that amounts of guanine, cytosine, adenine and thymine vary by species are indication that DNA, not protein might be the genetic material for life.
(i) Write the ratio which is constant in DNA of different species.
(ii) If in a sea urchin DNA, 17% of the bases were shown to be cytosine. Then, what will be the percentage of the other three bases?
(iii) In a DNA strand of length 340 Å. How many base pairs are present?
Answer:
(i) (a) Degeneracy refers to the fact that one amino acid has more than one codons. This specify that the same amino acid differs only in the third base of the triplet, e.g. Both CAC and CAU code for the amino acid histidine.
(b) Starting codon is universal means it is same universally for all organisms.
(ii) The bacteria is able to produce human insulin because genetic code is nearly universal in all organism. For example, the code AGG specifies amino acid arginine in bacteria, animals and plants.
Or
(i) According to Chargaff’s rule, in DNA there is always equality in quantity between the bases A
and T and between the bases G and C (A is adenine, T is thyrnine, G is guanine and C is cytosine). So,
A + T : C + G ratio is constant in DNA of different species.
(ii) Chargaff’s rule states that purine and pyrimidine base pairs are present in equal amount in cfcDNA is A = T, G = C
i.e. A + T = G + C, \(\frac{A+T}{G+C}\) = 1
If cytosine = 17%, then G = 17%
If A + G + C + T =100 and G =C,A =T
then A + 17 + 17 + T =100, A + T + 34 = 100
A + T = 100 – 34, A + T = 66
A = T =66/2 = 33%
Hence, if cytosine is 17% then G = 17% and A and T will be 33% each.
(iii) Distance between consecutive bases is 3.4 A. 340 A means, it has 340/3.4 = 100 base pairs.
Question 28.
Draw a sectional view of the ovary showing the different follicular stages of a human female in her pre-ovulatory phase of menstrual cycle. How many primary follicles are left in each ovary in a human female at puberty?
Answer:
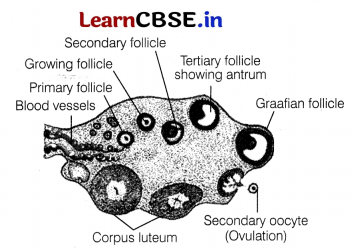
A large number of primary follicles degenerate in females during the period from birth to puberty by the process called follicular atresia. As a result, about 60000 – 80000 primary follicles are left in each ovary at puberty.
Section D
True
Question 29.
Study the given karyotype and answer the questions that follows.

(i) On the basis of the given karyotype, name the disorder the person is suffering from. [1]
(ii) What type of mutation is seen in this syndrome? [1]
(iii) If this syndrome is recognised during birth. What are the physical traits that can be seen? [2]
Or
(iii) Is this syndrome more common in males or females? Explain. [2]
Answer:
(i) The disorder that the person is suffering from is Down’s syndrome.
ii) Down’s syndrome result from trisomy 21, which means each cell in the body has 3 copies of chromosomee 21 instead of 2 copies .
(iii) The physical traits seen during birth are low
muscle tone, a single deep crease across the palm of the hand, a slightly flattened facial profile, and an upward slant to the eyes.
Or
(iii) In a sample of 75 children with trisomy for chromosome 21 or Down’s syndrome, there were 42 males and 33 females. By seeing this data we can conclude that Down’s syndrome is more common in males than in females.
![]()
Question 30.
The data below shows the new case and deaths from HIV/AIDS, world wide.
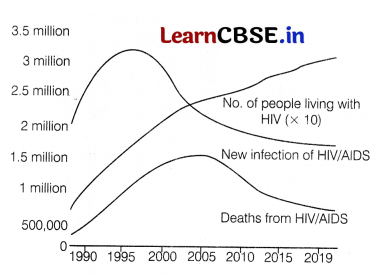
(i) With reference to the above graph which cases are decreasing? Explain. [1]
(ii) What is the cause of this disease? Mention the causative organism. [1]
(iii) Explain why the people living with AIDS are in increasing number? [2]
Or
(iii) What safety measure can be followed by the people for the prevention of HIV? [2]
Answer:
(i) The new cases of infection from AIDS and the death cases are seen to be decreasing due to usage of medicines and further awareness related to this disease.
ii) AIDS is caused by Human immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
(iii) Although there is no cure for AIDS, there are medicines that help people with AIDS live longer and healthier lives by lowering the amount of virus in the body. So, the graph is seen to be increasing.
Or
(iii) The prevention for AIDS includes using of condoms while coming in sexual contact, not sharing needles, not injecting drugs, not to involve in sexual behaviour.
Section E
Question 31.
Recombinant pharmaceuticals are created by inserting genes from one species into a host species, often yeast or bacteria, where they do not occur naturally. The genes code for a desired product and therefore the GMOs can be grown and used as a kind of living factory to produce the product. The table given below shows the stages of rDNA technology. Observe each stage and explain briefly about the process involved in each step.
| Stages of rDNA technology | Process of rDNA technology |
| Isolation of genetic material | |
| Cutting of DNA at specific locations | |
| Separation and isolation of DNA fragments | |
| Amplification of gene | |
| Ligation of DNA fragment into a vector | |
| Insertion of rDNA into host | |
| Desired product |
Or
In recombinant technology, the desired genes for administration is/are selected, followed by selecting a perfect vector into which the desired gene is to be integrated and rDNA formed.
True
(i) Which conditions apart from the temperature, pH and substrate are provided by the bioreactor?
(ii) What happens in a continuous culture system?
(iii) Name the components of a bioreactor.
(iv) Write the name of two bioreactors.
(v) What is the purpose of sparged stirred tank bioreactor?
Answer:
| Stages of rDNA technology | Process of rDNA technology |
| Isolation of genetic material | In order to release DNA along with other macromolecules, tissues are treated with lysozyme, cellulase, chitinase ribonuclease and with protease. |
| Cutting of DNA at specific locations | Restriction enzyme digestion are performed by incubating purified DNA molecule with restriction enzyme. |
| Separation and isolation of DNA fragments | Cutting of DNA by restriction endonucleases results in the fragments of DNA which are separated by a techniques known as gel electrophoresis. |
| Amplification of gene | By using PCR several copies of desired DNA fragments is obtained. |
| Ligation of DNA fragment into a vector | Vector DNA and a source DNA both are ligated by mixing with enzyme DNA ligase to obtain rDNA. |
| Insertion of rDNA into host | There are several methods of introducing the ligated DNA into recipient cells. Before this, desired cells are selected by using screenable and selectable marker. |
| Desired product | The cells having cloned genes of interest are grown on a small scale in laboratory. |
Paraphrase: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Oracle: Ora
True
(ii) In a continuous culture system, the used medium is drained out from one side and fresh medium is
added from the either side to maintain the cells in their physiologically active state.
(iii) Components of a bioreactor included the following
(a) an agitator system
(b) an oxygen delivery system
(c) foam control system
(d) temperature control system
(e) pH control system
(f) Sampling parts to withdraw the culture.
(iv) The most commonly used bioreactors are of stirring type which are of two types, i.e.
(a) simple stirred-tank bioreactor
(b) sparged stirred-tank bioreactor
True
Question 32.
Amniocentesis was first introduced as a mean of detecting the severity of Rhesus (Rh) isoimmunisation about 50 years ago. Invasive prenatal diagnosis and particularly amniocentesis was introduced into clinical practice as the mid-trimester diagnostic investigation of choice. Amniocentesis remains the most common invasive prenatal diagnostic procedure today. However, this technique is legally banned now.
(i) This test is based on what principle?
(ii) Explain why this procedure is banned now?
(iii) Which diseases can be diagnosed by this process?
Or
As the corona virus disrupted lives and livelihoods in Utah, it appears that an increasing number of women sought abortions in the state, providers say. There were 3388 abortions done at the facilitive of the salt lake Tribune. And these numbers are likely incomplete, as private
physicians also perform the procedures. The data shows the abortions done at which time of pregnancy.
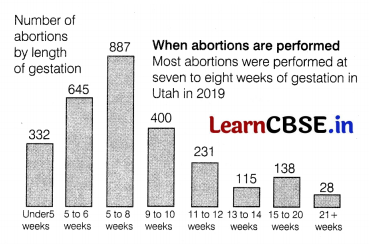
(i) Evaluate the efficacy of abortion done at the time of 7 to 8 weeks.
(ii) How is MTP helpful in decreasing human population?
(iii) Is MTP always surgical? Explain.
Answer:
(i) During amniocentesis, an ultrasound transducer is used to show a baby’s position in the uterus on a monitor. A sample of amniotic fluid which contains foetal cells and chemical produced by the baby is then withdrawn for testing.
(ii) Amniocentesis can lead to female foeticide as it
detects the sex of the foetus, which decreases the gender ratio. So, it has a statutory ban to avoid female foeticide.
(iii) Amniocentesis can be used to detect Down’s syndrome, i.e. chromosome abnormalities and genetic disorders like cystic fibrosis.
Or
(i) MTP during 7-8 weeks at gestational period is safest as it can be done by medication or by pills, i.e. by taking drugs, So, it comes under the right time where most people go through this process.
(i) MTP is done to get rid of unwanted pregnancies due to casual unprotected intercourse, failure of the contraceptive during coitus. (ii) MTP is done to get rid of unwanted pregnancies due to casual unprotected intercourse, failure of the contraceptive during coitus.
: (ii) MTP is not a contraceptive method. (iii) MTP is not a contraceptive method.
![]()
Question 33.
Workout a typical Mendelian dihybrid cross and state the law that he derived from it.
Or
Differentiate between incomplete dominance and codominance. Substantiate your answer with one example of each.
Answer:
Dihybrid cross is a cross between two individuals with two observed traits that are controlled by two distinct gene.
Law of independent assortment (Third law) is based on the inheritance of two genes, i.e. dihybrid cross which states that when two pairs of contrasting traits are combined in a hybrid, segregation of one
pair of characters is independent of the other pair of characters.
These factors randomly rearrange in the offspring producing both parental and new combination of characters.
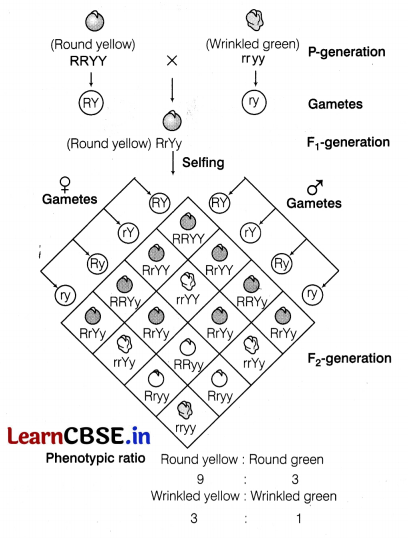
It means inheritance of one character does not affect the inheritance of another character and both characters assort independently during gamete formation. The Punnett square can be used to understand the independent segregation of the two pairs of genes during meiosis.
Or
Differences between codominance and incomplete dominance are as follows
| Codominance | Incomplete dominance |
| It is the appearance of both parental phenotypes together in the offspring when a cross is done between individuals with two different phenotypes. | It is the appearance of an intermediate phenotype, which is a combination of both parental alleles when a cross is done between individuals with two different phenotypes. |
| Both parental alleles produce their effect independently. | Effect of the two parental alleles is intermediate on the offspring. |
| Both parental alleles can be observed in the offspring. | None of parental alleles can be observed in the offspring. |
| Examples include ABO blood group, etc. Six different genotypes of human ABO blood group show four phenotypes-A, B, AB and O. |
Examples include inheritance of flower colour in the dogflower, etc. Here, the genotypic ratio of F
2
remains same as Mendel’s monohybrid cross, i.e.
1: 2 : 1, but phenotypic ratio changes from 3 : 1 to 1 : 2 : 1. |