Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions Set 7 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set 7 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section-B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section-C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section-D has 2 case-based questions of 4 marks each; and Section-E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
-
There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions.
A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. - Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section A
Question 1.
Use of vaccines and immunisation programmes are done in maximum health care centres. Out of the options given below, select the correct infectious diseases that are controlled by this programme.
(a) Diphtheria and pneumonia
(b) Polio and tetanus
(c) Cancer and AIDS
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Diseases like polio, tetanus, diphtheria and pneumonia are controlled with the help of vaccines and immunisation programmes.
Question 2.
Which of the following RNA carries the amino acids from the amino acid pool to mRNA during protein synthesis?
(a) mRNA
(b) hnRNA
(c) rRNA
(d) tRNA
Answer:
(d) Translation is the process of polymerisation by which the triplet base sequence of a mRNA guide the linking of a specific sequence of amino acids to form polypeptides on ribosomes. EachfRNA is specific to an amino acid, asfRNAs are added to the sequence, amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds, eventually forming a protein that is later released by thefRNA.
Question 3.
Given below are the different ART techniques with their correct procedure.
| ART | Procedure | |
| A. | In vivo fertilisation | Fusion of the gametes in the female reproductive tract. |
| B. | ZIFT | Zygote with more than 8 blastomeres is transferred into the uterus. |
| C. | IUT | Zygote or early embryo with up to 8 blastomeres is transferred into the Fallopian tube. |
| D. | IVF | Collected gametes are made to form the zygote in laboratory. |
Select how many techniques are correctly matched with their procedure?
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 2
(d) 1
Answer:
(c) The correct option is ‘c’ as In vivo fertilisation and IVF are correctly matched with their procedure while the rest can be corrected as
When zygote or early embryo with up to 8 blastomeres is transferred into the Fallopian tube, it is termed as ZIFT (zygote Intra Fallopian transfer).
When the zygote with more than 8 blastomeres stage is transferred into the uterus is termed as IUT (Intra Uterine Transfer).
Question 4.
Red Data Book deals with
(a) organisms on the verge of extinction
(b) endemic plants
(c) organisms showing photoperiodism
(d) organism that are extinct
Answer:
(a) Red Data Book is a catalogue of taxa facing risk of extinction. It is maintained by IUCN.
![]()
Question 5.
An um-shaped population age pyramid represent which of the following type of population?
(a) Static population
(b) Extinct population
(c) Growing population
(d) Declining population
Answer:
(d) An urn-shaped population age pyramid represents declining population.
Question 6.
Rita was doing an experiment on linkage, which of the following cross is suitable for experiment on linkage?
(a) aaBB × aaBB
(b) AABB × aabb
(c) AaBb × AaBb
(d) AAbb × AaBB
Answer:
(b) Linkage can be shown by a cross between homozygous dominant AABB and homozygous recessive aabb.
Question 7.
Lichens show the symbiotic association between algae and fungi. The kind of interaction exhibited in this case is
(a) parasitism
(b) mutualism
(c) predation
(d) competition
Answer:
(b) Lichens show mutualism by mutually benefitting two individuals of different species like fungi and algae.
Question 8.
The figure below shows the side view of the female reproductive system.
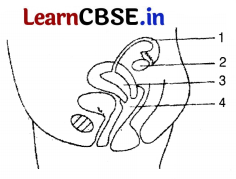
In one of the region sperms are released during sexual intercourse and in one fertilisation usually take place. Choose the correct region for the release of sperm and site of fertilisation in the given table.
| Sperms released | Fertilisation | |
| (a) | 3 | 1 |
| (b) | 4 | 1 |
| (c) | 3 | 2 |
| (d) | 4 | 2 |
Answer:
(b) Sperms are released in vagina (4) and fertilisation takes place in oviduct.
Question 9.
Which of the following factors has a negative effect on the population growth rate?
(a) Emigration
(b) Immigration
(c) Natality
(d) Fecundity
Answer:
(a) Emigration is permanent outward movement of individuals from a population for settlement into a new area. It decrease the local population.
Question 10.
Which of the following term is referred to ‘molecular scissors’ and ‘chemical knife’ respectively?
| Molecular scissors | Chemical knife | |
| (a) | Recombinant DNA | Polymerases |
| (b) | Taq polymerase | Polymerases |
| (c) | Restriction enzyme | Endonucleases |
| (d) | Taq poiymerase | Endonucleases |
Answer:
(c) ‘Molecular scissors’ is referred to restriction enzyme and chemical knife is referred to endonucleases.
Question 11.
cry IIAb and cry IAb produce toxins that control
(a) cotton bollworms and corn borer, respectively
(b) corn borer and cotton bollworms, respectively
(c) tobacco budworms and nematodes, respectively
(d) nematodes and tobacco budworms, respectively
Answer:
(a) Bt toxin genes are isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis and incorporated into several crop plants such as cotton. The toxin is coded by a gene named cry. The proteins encoded by the gene cry IIAb and cry IAc control the cotton bollworms and that of cry lAb control corn borers.
![]()
Question 12.
Which is the particular type of drug that is obtained from the plant whose one flowering branch is shown below?

(a) Hallucinogen
(b) Depressant
(c) Stimulant
(d) Pain killer
Answer:
(a) The plant shown in the given picture is Datura, which produces natural hallucinogens. These drugs induce behavioural abnormalities by changing thoughts, feelings and perceptions without any actual sensory stimulus.
Question Nos. 13 to 16 consist of two statements- Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : Although geitonogamy is functionally cross-pollination involving a pollinating agent, genetically it is similar to autogamy.
Reason (R) : In geitonogamy, pollen grains from the anthers of one flower are transferred to the stigma of another flower borne on the same plant.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Geitonogamy is functionally cross-pollination as it involves the pollinating agent to carry out pollination, but genetically it is similar to autogamy (self-pollination), since the pollen grains of one flower are transferred to the stigma of another flower belonging to either the same plant or genetically similar plant having monoecious condition.
Question 14.
Assertion (A) : If the sequence of bases of one DNA strand is known then the sequence of other strand can be predicted.
Reason (R) : Both the strands of DNA are complementary to each other.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
In polynucleotide chains like DNA, base pairing are said to be complementary to each other. Therefore, if the base sequence of one strand is known then the sequence of other strand can be predicted.
Question 15.
Assertion (A) : The first clinical gene for ADA therapy was given to cure SCID.
Reason (R) : The normal gene was delivered into the patient’s cells using retroviral vector.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4-year-old girl with Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency. This enzyme is very important for the immune system to function. ADA deficiency can lead to Severe Combined Immune Deficiency (SCID).
First gene therapy was done to cure SCID and the normal gene was introduced using a retroviral vector. As a first step towards gene therapy, lymphocytes from blood of patient are grown in a culture outside the body and a functional ADA cDNA (using a retroviral vector) is then introduced into lymphocytes.
![]()
Question 16.
Assertion (A) An ecosystem is an interaction between biotic and abiotic components.
Reason (R) AG Tansley coined the term ecosystem.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
AG Tansley coined the term ecosystem (Gk. Eco—environment; system— interaction and
interdependent complex) for the first time. It is an integrated natural system resulting from the interaction of living and non-living factors of the environment. In other words, the ecosystem can also be defined as an inter-relationship between biotic ‘ (living) and abiotic (non-living) components of the environment.
Section B
Question 17.
A plasmid DNA and a linear DNA (both of the same size) have one site for a restriction endonuclease. When cut and separated on agarose gel-electrophoresis, plasmid shows one DNA band, while linear DNA shows two fragments. Explain.
Answer:
A single DNA band is observed in plasmid, while two DNA bands are observed in linear DNA in agarose gel because plasmid is a circular DNA molecule and when cut with enzyme, it becomes linear, but does not get fragmented.
Whereas, a linear DNA molecule gets cut into two fragments.
Question 18.
The figure given below shows the TS of a mature anther. Answer the questions that follows.
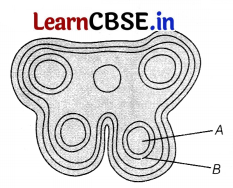
(i) Identify A and B shown in the above figure.
(ii) Mention the functions of the parts labelled as A and B.
Answer:
(i) In the given figure, A is sporogenous tissue and B is tapetum.
(ii) Sporogenous tissue has cell which are Pollen Mother Cell (PMC) or microspore mother cell which give rise to microspore tetrad after meiotic cell division.
Tapetum nourishes the developing microspores or pollen grains.
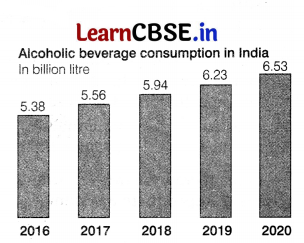
Question 19.
The graph given below shows the consumption of alcoholic beverages over the years. What is the cause of the increment in the graph? What characters wall be observed if a person is abruptly discontinued from taking a regular dose of alcohol?
Answer:
The main cause of increment in the number of alcohol consumptions are as follows social and peer pressure, to avoid stress, depression and frustration and to overcome hard ships, apathy (lack of interest in day-to-day life), etc.
If the regular dose of alcohol in an addicted person is discontinued abruptly, the body exhibits
characteristic and unpleasant symptoms called ‘withdrawal syndrome’. This syndrome is
characterised by symptoms like anxiety, nausea and excessive sweating.
Question 20.
Typical pyramids of biomass (g/m) of three different ecosystems are shown below as 1-Producers, 2-Herbivores, 3-Carnivores
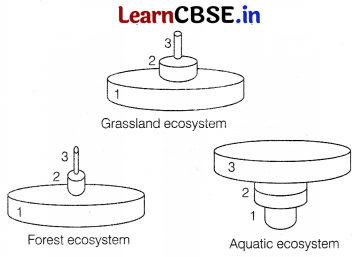
(i) In aquatic ecosystem, an inverted pyramid is observed. Suggest a possible reason for this.
(ii) What will the pyramid of energy for all three ecosystem be like?
Answer:
(i) In aquatic ecosystem, an inverted pyramid is observed, because the biomass of primary producer, i.e. phytoplankton is much lesser than the consumers, i.e. zooplanktons, small fishes, etc.
(ii) The pyramid of energy for each of these ecosystem will be upright as energy flows from producers to consumers.
Question 21.
Given below is the ladder of human evolution.

(i) What is the scientific name of Java man? Where did the Australopithecus evolve?
(ii) What are the characteristics of Australopithecus?
Or
There was no atmosphere on the early earth. It was supposed to be formed about 4.5 billion years back in the solar system. Various theories of origin of life was given, one of them was Oparin-Haldane theory.
State two postulates of Oparin and Haldane’s theory with reference to the origin of life. Write the hypothetical proposals put forth by Oparin and Haldane.
Answer:
(i) The scientific name of Java man is Homo erectus, Australopithecus evolved in East African grasslands.
(ii) They were similar to modern humans in that they were bipedal (i.e. they walked on two legs), but like apes, may had small brain.
Or
Oparin and Haldane proposed the following postulates with reference to origin of life
(i) The first form of life came from pre-existing non-living organic molecules.
(ii) The conditions on earth favouring chemical evolution were high temperature, volcanic storms and reducing atmosphere.
Oparin and Haldane proposed the theory of chemical evolution. According to them, life originated from pre-existing non-living organic molecules and the formation of life was proceeded by chemical evolution.
![]()
Section C
Question 22.
Study the schematic representation of the genes involved in the lac operon given below, which is a group of genes with a single promoter?

(i) Identify and name the regulatory gene in this operon. Also explain its role in switching off the operon.
(ii) This kind of regulation is called as negative regulation. Analyse the reason for this kind of regulation.
Answer:
(i) i gene is the regulatory gene in this operon.
Role of regulatory gene in switching off operon is as follows
(a) It codes for the repressor protein of the operon, which is synthesised constitutively.
(b) The repressor has affinity for the operator
gene. It binds to operator and prevents the RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural genes.
(ii) When repressor binds to the operator, the operon is switched off and transcription is stopped so, it is called a negative regulation.
Question 23.
Explain the universal codon, initiator codon and degenerate codon by giving one example of each.
Answer:
A codon is defined as the sequence of three nucleotides, which together form a unit of a genetic code in a DNA.
(i) Codon is nearly universal. Some exceptions to the rule are mitochondrial codon and in some protozoans, e.g. UUU.
(ii) Initiator codon AUG has dual function. It codes for methionine and also acts as initiator.
(iii) Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, so the codon is degenerate, e.g. serine is coded by 6 codons.
Question 24.
The size of a population for any species is not static parameter, it keeps changing with time. It depends on factors such as food availability, predation pressure and adverse weather.
(i) Explain birth rate in a population by taking a suitable example.
(ii) Write the other two characteristics, which only a population shows, but an individual cannot.
Answer:
(i) Due to natality or birth rate, population increases continuously. It is the production of new individual by birth, hatching or by asexual mode, etc. It is expressed as the number of birth per 1000 individuals of a population per year.
(ii) The characteristics, which are unique to the group (population) and not shown by an individual are
(a) Population dynamics theorise to explain population growth. Size of population for any species is not a static parameter. Population growth changes during time and depends upon food availability, predation, pressure, weather and also depends upon natality, mortality, immigration and emigration.
(b) Regulation of population governs population density or population size. It is the number of individuals of a species per unit area or volume.
Question 25.
The graph below shows the citywise contribution of pollution load in Yamuna river as it passes through them. This pollution load involves large amount of organic matter and pathogenic microbes.
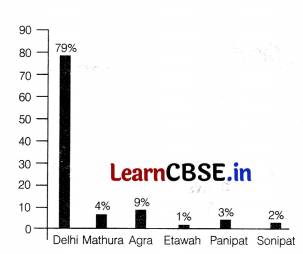
(i) What significance does BOD of a water body carries? From the graph, can you deduce at which site the BOD would be maximum?
(ii) ‘Before adding the wastewater into water bodies, it should be treated’. Elaborate.
Answer:
(i) BOD refers to the amount of oxygen uptake by the microorganisms. The greater BOD of a water body, more is its polluting potential. BOD will be maximum in part of river passing through Delhi.
(ii) The sewage or wastewater generated everyday should never be discharged into water bodies as it is complex mixture containing many organic and inorganic impurities. These impurities need to be removed before being discharged into water bodies. If untreated water sewage is discharged it can harm all the living organisms coming in contact with it.
![]()
Question 26.
Name two end products of double fertilisation in angiosperms. How are they formed? Write their fate during the development of seed.
Answer:
The two end products of double fertilisation in angiosperms are diploid zygote and a triploid Primary Endosperm Nucleus (PEN).
Diploid zygote is formed by the process of syngamy through the fusion of haploid gametes, i.e. male gamete and egg, while another male gamete and two polar nuclei of central cell fuse to form triploid primary endosperm nucleus. This process is called triple fusion.
During the development of seed, the zygote undergoes mitotic divisions to form a mature embryo while, the primary endosperm cell gives rise to nutritive tissue called endosperm, which provides nourishment to growing embryo.
Question 27.
Observe the figure and answer the questions that follows
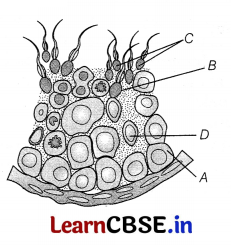
(i) Identify the parts A, B, C and D from the figure of seminiferous tubule given below.
(ii) Write the functions of A and D.
(iii) When do the oogenesis and the spermatogenesis initiate in human females and males, respectively?
Or
In a survey, to a district of Madhya Pradesh the medical authorities found that the population is increasing rapidly. They awared the couples about the various contraceptive methods like the permanent and temperory methods in order to control the population.
(i) Define sterilisation or surgical method of contraception to cause any side effects?
(ii) Describe the process of tubectomy and vasectomy.
(iii) Why these methods are generally not recommended to couples?
Answer:
(i) A – Spermatogonia,
B – Spermatid,
C – Spermatozoa,
D – Sertoli cells
(ii) A – Spermatogonia undergo meiosis to produce spermatozoa (sperms).
D – Sertoli cells provide nutrition to the germ cells.
(iii) Oogenesis initiates during foetal or embryonic stage in females, whereas spermatogenesis in males starts at puberty.
Or
(i) Sterilisation or surgical methods are those that involve in the terminal and permanent modification of reproductive ducts. Yes, these methods are found to cause some side effects including irreqular menstruation, nausea, abdominal pain, etc.
(ii) Tubectomy is a sterilisation procedure in females, where a small part of the Fallopian tube is removed and tied up through a small incision in the abdomen/vagina, thus preventing the ovulated egg to enter Fallopian tube.
Vasectomy is sterilisation procedure in males, where a small part of the vas deferens is removed and tied up through a small incision on the scrotum, thereby preventing the sperms to reach urethra.
(iii) Contraceptive methods are generally not recommended to couple because some time they can cause headache, nausea, etc. Also in surgical procedure, there is a certain risk of infection and their is a lack of sufficient facilities (e.g. lack of hygiene, lack of qualified personnel, etc.) in many parts of our country.
Question 28.
Why must a cell be made ‘competent’ in biotechnology experiments? How does the cell can be made competent? Also state the role of ‘Holistic gun’ in biotechnology experiments.
Answer:
(i) Since, DNA molecules are hydrophilic, they cannot pass through cell membranes. For recombinant DNA to be integrated into vector or host genome, it is necessary for the DNA to be inserted in the cell. Therefore, making the host cells competent is necessary in biotechnology experiments.
The two ways by which cells can be made competent to take up DNA are as follows
(a) Chemical action The host cell is treated with a specific concentration of divalent cation, i.e. calcium increases the pore size in the cell membrane. DNA is then incubated with treated bacterial cell at 42°C, thereby increasing the efficiency of DNA to enter it through pores in cell wall.
(b) Heat shock treatment Incubating the cells with recombinant DNA on ice, followed by brief treatment of heat at 42°C and again putting them back on ice.
Biolistic gun or gene gun are used to bombard rDNA loaded on gold or tungsten particles with high velocity into host cells. In this way, the rDNA is delivered to the desired host cells.
Section D
Q. Nos. 29 and 30 are case-based questions. Each question has 3 subparts with internal choice in one subpart.
Question 29.
Study the pedigree chart given below for haemophilia in a family and answer the questions that follows.
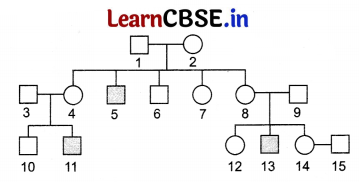
(i) On the basis of the inheritance pattern exhibited in this pedigree chart, what conclusion can you draw about the pattern of inheritance? [1]
(ii) What would be the possible genotype of members 4 and 5? [1]
(iii) A blood test shows that member 14 has haemophilic gene. What would be the probability that her child will be a haemophilic boy if she marry a normal male? [2]
Or
(iii) If the individual 5 marries a carrier female, what would be the probability of their child having haemophilia? [2]
Answer:
(i) The conclusion drawn from the given pedigree is that, haemophilia is a sex-linked recessive disorder.
(ii) The genotype of members 4 and 5 will be XX
h
(carrier) and X
h
Y (affected), respectively. [1]
(iii) Member 14 has haemophilia gene. That means she is a carrier (XX
h
).
Cross :
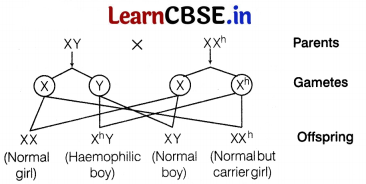
The probability that her child will be a haemophilic boy is 1/4= 0.25 = 25%
Or
(iii) If 5, i.e. affected male (X
h
Y) marries a carrier female (X
h
X). Than probability of affected child is 50%. This can be explained as
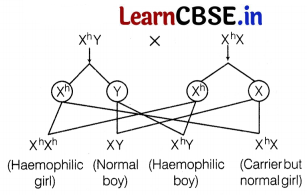
Out of 4 children, 1 son and 1 daughter will be haemophilic, 1 daughter can be carrier and 1 son will be completely normal. So, the probability is 50%.
![]()
Question 30.
The data given below, shows the concentration of alcohol in blood of drunkard.
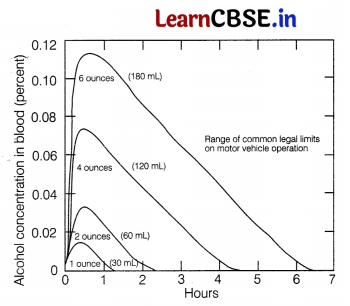
(i) With reference to the above graph, at which time the concentration of alcohol in blood will be highest? [1]
(ii) At which time will it have the lowest concentration of alcohol in blood? [1]
(iii) How does alcohol intake result in high blood pressure? [2]
Or
(iii) How does drinking alcohol result in liver failure? [2]
Answer:
(i) During the initial time, i.e. at the first 1 hour of heavy alcohol consumption, the concentration of alcohol will be highest in blood.
(ii) As the time increases like after few hours of alcohol consumption, the concentration of alcohol will keep on decreasing in blood.
(iii) Alcohol increases level of the hormone renin, which causes the blood vessels to constrict. This means that they get smaller in diameter. When the blood vessels are narrow the heart has to work harder to push blood around our body. This makes the blood pressure go up.
Or
(iii) Each time your liver filters alcohol, some of the liver cells die. The liver can develop new cells, but prolonged alcohol consumption over many years can reduce its ability to regenerate. This can result in serious and permanent damage to liver.
Section E
Question 31.
Observe the diagram shown below for the process of humulin production and answer the questions that follows.
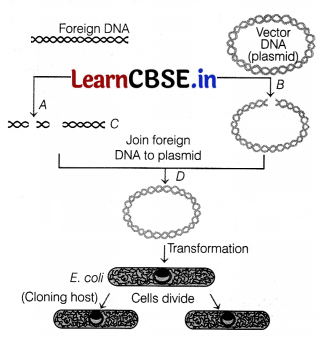
(i) What does label ‘C’ represent and what is its role? Also, identify the label which represents an enzyme that is utilised for cutting the molecule of DNA.
(ii) What purpose is humulin term used for? Through which bond chains A and B of humulin are bonded? Which DNA sequence will be introduced in label B to produce humulin?
Or
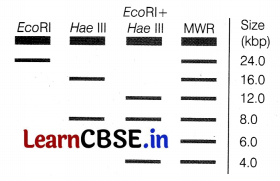
A gel electrophoresis was run to show the fragments produced by restriction digestion with different restriction enzymes. The MWR lane indicates the molecular weight rules.
(i) Construct a restriction map of the double digest of a plasmid.
(ii) Explain which fragment will move faster in gel electrophoresis and why?
Answer:
(i) Label C represents DNA ligase which is an enzyme that is used to join together two different types of DNA molecules. Label A depicts restriction endonuclesase, which is utilised for cutting the molecule of DNA.
(ii) The term humulin is used for human insulin made from recombinant DNA that is identical to insulin present in humans and is used to treat diabetes. Both chains A and B are produced separately and combined by creating disulphide bonds to form humulin.
DNA sequences corresponding to the two polypeptides that is A and B chains of insulin are synthesised in vitro and introduced into label B.
Or
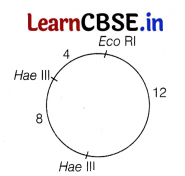
(i) The plasmid was digested by using restriction enzymes EcoRI and Hae III, this process is called double digest.
The gel electrophoresis of the plasmid after subjecting, it to restriction enzymes, three fragments are observed on the plate.
The restriction map of the double digest of a plasmid is as follows.
(ii) Shorter fragment, i.e. 40 kbP will move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter fragment migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. The longer fragments will encounter greater obstruction from the gel matrix and therefore tend to move the least distance along the gel.
![]()
Question 32.
DNA fingerprinting method is useful in biobank Quality Control (QC) procedures and emphasises the need for detailed and accurate record during processing of biological sample. It also underline the value of independent third-party agreement to identify points at which errors are most likely to have occurred when unexpected results are obtained from biospecimens.
(i) For the process of DNA fingerprinting, from where does the DNA obtained from?
(ii) VNTR are used in the process of DNA fingerprinting. Expand VNTR and describe its role in DNA fingerprinting.
(iii) List any two application of DNA fingerprinting technique.
Or
Human genome project had their primary goals to discover the complete set of human genes and makes them accessible for further biological study and determine the complete sequences of DNA bases in the human genome. Few efforts have been made to reduce the cost of this project and to increase the quality from the year 1996 to 2004. As per these reports, a graph had been plotted for the above reason.
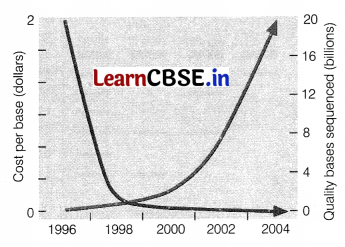
(i) Evaluate the graph and write the relation of how did the project manage to handle their cost and quality?
(ii) Why is the human genome project important to human?
(iii) What were some major concerns related to human genome project?
Answer:
(i) In DNA fingerprinting, DNA is obtained from white blood corpuscles, hair root cells, etc.
(ii) VNTR is Variable Number of Tandem Repeats. These are short nucleotides repeats in the DNA. These are highly specific for individuals. No two individuals have the same VNTR, VNTRs are used as probe mature in the identification of DNA of different individuals because no two individuals can have the same VNTRs.
(iii) Applications of DNA fingerprinting are
(a) It can identify the real genetic mother, father and offspring.
(b) It is very useful in the detection of crime and legal pursuits.
Or
(i) In the year 1996 the cost for the project was high and the quality of the work was less as compared to the cost. Then due to developing of modern tools for sequencing and reducing the man power, the cost reduced and ultimately increasing the quality of the outcome.
(ii) Human genome project is important because it uses information from DNA to develop new ways to treat, cure or even prevent thousands of diseases that affect human kind.
(iii) Some concerns related to human genome project are
(a) privacy and fairness in the use and interpretation of genetic information.
(b) clinical integration of new genetic technologies.
(c) issues surrounding genetic research.
(d) public and professional education.
Question 33.
Explain the development of the primary endospermic nucleus into an endosperm and the development of the zygote into an embryo in a fertilised embryo sac of a dicot plant.
Or
Describe the process of megasporogenesis in angiosperm until 8-nucleate stage.
Answer:
The development of endosperm takes place by three methods
(i) In nuclear type, which is a common method, the Primary Endosperm Nucleus (PEN) undergoes repeated mitotic division without cytokinesis. At this stage, the endosperm is called free nuclear endosperm.
(ii) In cellular type, cell wall formation occurs and the endosperm becomes cellular. The number of free nuclei formed before cellularisation varies greatly, e.g. in coconut, the water is free nuclear endosperm and surrounding white kernel is cellular endosperm.
(iii) In helobial type endosperm formation, one half of endosperm is nuclear type and other half is cellular type.
Embryo Development in Dicot Seed
(a) Embryo formation starts after a certain amount of endosperm is formed.
(b) Zygote divides by mitosis to form a proembryo.
(c) Formation of globular and heart-shaped embryo occurs, which finally becomes horseshoe-shaped mature embryo.
(d) In dicot plant, embryo consists of two cotyledons and an embryonal axis between them.
(e) The portion of embryonal axis above the level of attachment of cotyledons is epicotyl and terminates in the plumule.
(f) The portion of embryonal axis below the level of attachment of cotyledon is the hypocotyl, it becomes radicle (root tip).
Or
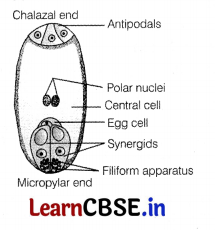
The functional megaspore undergoes mitosis to form 2 nuclei, which migrate to opposite poles, forming a 2-nucleate embryo sac. Further, mitotic divisions lead to the formation of 4-nucleate and 8-nucleate stages of the embryo sac. In these mitotic divisions, nuclear division is not followed by cell wall formation. After the 8-nucleate stage, cell walls are laid down and a typical female gametophyte or embryo sac is formed. Among the eight nuclei, six are enclosed by cell wall and organised into cells, while the remaining two nuclei (polar nuclei) are situated above the egg apparatus in a large central cell.
Out of the six cells, three are grouped at the micropylar end and constitute the egg apparatus made up of two synergids and one egg cell. These synergids possess special cellular thickenings at their micropylar tip and called filiform apparatus. This filiform apparatus guides the pollen tube to enter into embryo sac. The other three cells are located at the chalazal end and are called antipodals. Thus, a typical angiosperm embryo sac after maturity is 8-nucleate and 7-celled.
The egg apparatus present towards the micropylar end, comprises of two synergids and an egg cell.