Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions Set 6 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set 6 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section-B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section-C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section-D has 2 case-based questions of 4 marks each; and Section-E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
-
There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions.
A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. - Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section A
Question 1.
ZZ/ZW type of sex determination is seen in
(a) platypus
(b) snails
(c) cockroach
(d) peacock
Answer:
(d) In ZZ/ZW case, the female has heteromorphic (ZW) sex chromosomes and the male has homomorphic (ZZ) sex chromosomes. Thus, peacock shows ZZ/ZW sex determination type.
Question 2.
Which of the following aspects is not a component of functional unit of ecosystem?
(a) Productivity
(b) Energy flow
(c) Decomposition
(d) Ecological pyramids
Answer:
(d) The functional unit of ecosystem consists of productivity, decomposition, energy flow and nutrient cycling.
Thus, ecological pyramids are not a component of functional unit of ecosystem.
Question 3.
Given below are the genetic disorders and their symptoms.
| Disorders | Symptoms | ||
| A. | Thalassemia | 1. | Anaemia |
| B. | Klinefelter’s syndrome | 2. | Sterile females |
| C. | Turner’s syndrome | 3. | Sterile males |
| D. | Down’s syndrome | 4. | Physical and mental retardation |
Select how many genetic disorders are correctly matched with their symptoms?
(a) 4
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) The correct option is (c) as both thalassemia and Down’s syndrome are correctly matched, while the rest can be corrected as
In Klinefelter’s syndrome the affected males are sterile.
In Turner’s syndrome the affected females are sterile as ovaries are rudimentary.
![]()
Question 4.
The sticky ends of a fragmented DNA molecule are made up of
(a) calcium salts
(b) methyl groups
(c) unpaired bases
(d) endonuclease enzyme
Answer:
(c) The single-stranded free ends that project from each fragment of DNA duplex are unpaired bases and are known as ‘sticky-ends’. The sticky ends can join with similar complementary ends of DNA fragment from some other sources.
Question 5.
Tobacco consumption is known to stimulate the secretion of adrenaline and nor-adrenaline and it is caused by which of the following components?
(a) Catechin
(b) Curamin
(c) Nicotine
(d) Tannic acid
Answer:
(c) Tobacco contains a large number of chemical substances including nicotine, an alkaloid. Nicotine stimulates adrenal gland to release adrenaline and nor-adrenaline into blood circulation, both of which raise blood pressure and increase heart rate.
Question 6.
Rajesh was plotting the age distribution for a population. State the name referred to the resulting structure.
(a) Age curve
(b) Age graph
(c) Age pyramid
(d) Age diagram
Answer:
(c) When age distribution is plotted for the population, the resulting structure is called as age pyramid.
Question 7.
In sewage treatment, bacterial floes are allowed to sediment in a settling tank. This sediment is called as
(a) primary sludge
(b) secondary sludge
(c) activated sludge
(d) inactivated sludge
Answer:
(c) Activated sludge is formed during secondary sewage treatment through aeration. It possess floes of decomposer microbes.
Question 8.
The figure below shows ecological pyramid.
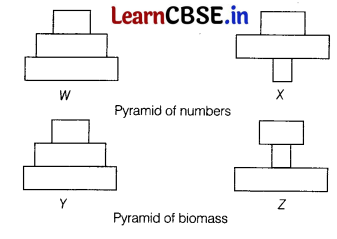
A single plant provides food for many herbivores. The herbivores supply food for a few carnivores. Choose the correct observation about the pyramids.
| Pyramid of number | Pyramid of biomass | |
| (a) | W | Y |
| (b) | X | Y |
| (c) | w | Z |
| (d) | X | Z |
Pyramid of number Pyramid of biomass
(a) W Y
(b) X Y
(c) w Z
(d) X Z
Answer:
(b) A single plant is shown by pyramid X. Its biomass must be big enough to be eaten by many herbivores as shown in pyramid Y.
Question 9.
Which of the following is one of the ex situ conservation methods for endangered species?
(a) National parks
(b) Cryopreservation
(c) Wildlife sanctuaries
(d) Biosphere reserves
Answer:
(b) Ex situ conservation includes off-site collections, such as gene banks, in vitro fertilisation, cryopreservation techniques and tissue culture.
Question 10.
Which of the following features in the table given below is correct about sperm cells, when compared to egg cell in size and in number?
| Size of sperm cell | Numbers of sperm cell | |
| (a) | Larger | Fewer |
| (b) | Larger | More |
| (c) | Smaller | Fewer |
| (d) | Smaller | More |
Size of sperm cell Numbers of sperm cell
(a) Larger Fewer
(b) Larger More
(c) Smaller Fewer
(d) Smaller More
Answer:
(d) Sperms are produced more in number than ova.
And their size is also smaller than ova.
![]()
Question 11.
Identify the correct pair representing the causative agent of typhoid fever and the confirmatory test for typhoid.
(a) Streptococcus pneumoniaefWidal test
(b) Salmonella typhi/Anthrone test
(c) Salmonella fyphi/Widal test
(d) Plasmodium vivax/UTI test
Answer:
(c) Typhoid fever is caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi and Widal test is the confirmatory test for typhoid, which is based on antigen-antibody interaction. Typhoid fever or enteric fever has the incubation period of 1 to 2 weeks.
Question 12.
In the given diagram of pistil in which part fertilisation takes place?
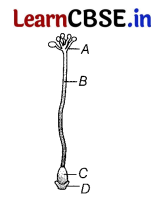
(a) D
(b) C
(c) B
(d) A
Answer:
(b) The part labelled as C shows ovary. It is the site of fertilisation, the process in which the fusion of male and female gametes takes place. Fertilisation occurs in the ovary of a pistil.
Question Nos. 13 to 16 consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R), answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : The female external genitalia includes mons pubis, labia majora and labia minora.
Reason (R) : The glandular tissue of each breast contains single mammary lobe.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
The female external genitalia includes mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, hymen and clitoris. The mammary glands are the paired structures (breasts) that contains glandular tissue and a variable amount of fat.
The glandular tissue of each breast is divided into 15-20 mammary lobes containing clusters of cells called alveoli.
Question 14.
Assertion (A) : The predominant site for control of gene expression in prokaryotes is transcription initiation.
Reason (R) : The activity of RNA polymerase is regulated by accessory proteins, which affect recognition of start sites.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
In prokaryotes, control of the rate of transcriptional initiation is the predominant site for control of gene expression. In a transcription unit, the activity of RNA polymerase at a given promoter is inturn regulated by the interaction with accessory proteins, which affect its ability to recognise start sites. These regulatory proteins can act both positively (activators) and negatively (repressors).
Question 15.
Assertion (A) : USA patent of brazzein is an example of biopiracy.
Reason (R) : Brazzein, a protein obtained from West African plant, Pentadiplandra brazzeana and the gene encoding it has been patented by USA.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
Brazzein is produced by Pentadiplandra brazzeana and is approximately 2000 times as sweet as sugar. It is used as a low calorie sweetener. Local people have been using the super sweet berries from their plants for centuries but protein, brazzein and the gene encoding it is patented in USA.
It is proposed to transfer the brazzein gene into maize and express it in maize kernels from where it can be easily extracted. This is an example of biopiracy.
Question 16.
Assertion (A) : Predation is an interspecific interaction with a feeding strategy.
Reason (R) : Predators and their prey maintain fairly stable population through time and rarely one population become abundant or scarce.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion. Predation is an interspecific interaction with a feeding strategy. The number of predator usually depends upon the population of prey, but later is also controlled by predators.
Thus, predator and prey maintain a fairly stable , population through time and rarely one population 1 becomes scarce or abundant.
![]()
Section B
Question 17.
‘The advent of birth control pills resulted in increased risks of sexually transmitted diseases’. Assess the fact given above and present your opinion on it.
Answer:
The advent of birth control pills encouraged people to have unprotected sexual intercourse. Other means of contraception particularly condoms, are not used.
Thus, STDs are being more readily transmitted during sexual activities due to lack of any physical mechanical barrier.
Question 18.
In the figure given below, parts A and B are the missing sites from the cloning vector. Study the figure and answer the questions that follows.
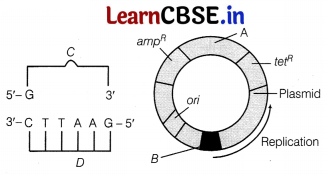
(i) Identify the parts A and B in the given illustration.
(ii) What is the term given to C and D and explain why?
Answer:
(i) A is the recognition site of the restriction endonucleases. While, 8 is the rap gene that codes for the protein involved in the replication of plasmid.
(ii) C and D are the palindromic sequences. These are called so because the sequence of base pairs reads the same on the two strands when the orientation of reading is kept same.
Question 19.
Prior to a sports event, event and urine samples of sports persons are collected for drug testing. The graph given below shows the number of sports persons abusing drugs.
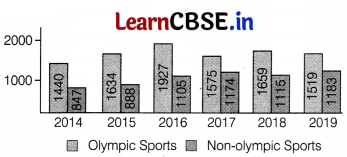
Name the drugs the authorities usually look for. Why is there a need to conduct such tests?
Answer:
The drugs that the authorities usually look for are cocaine and morphine.
It is necessary for the authorities to conduct such tests as sports-persons often take drugs to increase their performance. Which would be unfair for those sports persons who do not consume drugs.
Question 20.
In a court case seeking to determine the actual father of a baby7, five samples were collected for DNA fingerprinting tests.
The samples were collected from the mother, the baby and three potential fathers namely Man-1, Man 2 and Man 3.
These samples are subjected to rigourous analysis to compare their genetic profiles and identify any similarities or differences for resolving the paternity dispute. The results of the tests are depicted in the diagram below.
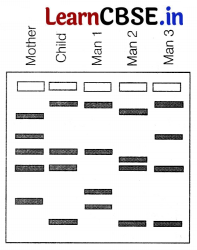
(i) Based on the result of DNA fingerprinting who is the father of child? Justify.
(ii) Is there any limitatiom on DNA fingerprinting. Support your answer with a suitable explanation.
Answer:
(i) Based on the above results it can be inferred that two bands of the child matches with the mother. Whereas among the three men only man 3 has two bands that matches with the child and these bands do not match with the mother.
Therefore it is possible that man 3 has provided the child with both of the bands.
Hence, it can be concluded that man 3 is the father of the child.
(ii) While DNA fingerprinting is highly accurate technique, it does not provide a 100% guarantee. As the accuracy results dependends on many factor such as quality of smaple, and the selection of appropriate genetic markers for analysis. Thus errors possibility is there.
Question 21.
Given below is an ecological pyramid where each bar represents a trophic level.
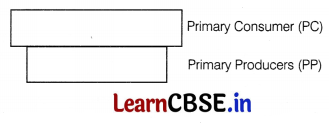
(i) Identify the type of ecological pyramid.
(ii) Give one example each of pyramid of number and pyramid of biomass in such cases.
Or
Primary productivity is the amount of biomass or organic matter produce per unit area over a time period by plants. It has two aspects, i.e. Gross Primary Productivity (GPP) and Net Primary Productivity (NPP).
(i) What is the difference between net and gross primary productivity?
(ii) Why primary productivity varies in different types of ecosystems? Explain.
Answer:
(i) The ecological pyramid shown represents the inverted pyramid of biomass wherein small standing crop of phytoplanktons supports large standing crop of zooplanktons.
(ii) Pyramid of number is inverted in tree ecosystem and that of biomass is inverted in pond ecosystem.
Or
(i) Net primary productivity refers to the biomass/organic matter available for the consumption to heterotrophs, left after some respiratory losses. Whereas, gross primary productivity is the rate of production of biomass/organic matter by producers during photosynthesis.
(ii) The primary productivity varies in different types of ecosystem because
(a) It depends upon plant species (producers) of a given ecosystem and their photosynthetic capacity.
(b) It is dependent on various environmental factors, availability of nutrients.
![]()
Section C
Question 22.
The figure given below shows a biogas plant.
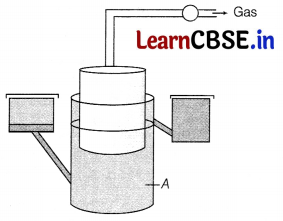
(i) Identify the part labelled as A in the diagram above and describe biogas.
(ii) Which group of microbes are observed in a biogas plant?
Answer:
(i) A represents digester in the biogas plant, which is used to anaerobically decompose the biodegradable materials, used to produce biogas. Biogas is mainly methane rich gas fuel produced by anaerobic breakdown of waste biomass by methanogenic bacteria.
(ii) The group of microbes observed in a biogas plants are called methanogens. These bacteria grows anaerobically on cellulosic material and produces large amounts of methane along with carbon dioxide and hydrogen gas.
Question 23.
Explain the functions of seminal vesicle, acrosome and scrotum of the human male reproductive system.
Answer:
(i) Seminal Vesicle During spermatogenesis, it secretes an alkaline fluid rich in fructose and prostaglandins. High level of fructose are known to provide energy to the sperms.
(ii) Acrosome It is the cap-like structure in the head region. The acrosome contains hydrolytic enzyme, which help sperm to enter into the cytoplasm of the ovum and thus helps in fertilisation.
(iii) Scrotum It is the bag like structure made up of skin that holds and helps to protect testicles.
Question 24.
The DNA molecule that can carry a foreign DNA segment and replicate inside the host cell is called as a vector.
Plasmids and bacteriophages are used as cloning vectors. This is because plasmids and bacteriophages have the ability to replicate within the bacterial cell independent of chromosomal DNA.
Bacteriophages have very high copy numbers of their genome within the bacterial cells. But in case of plasmids, some may have only one or two copies per cell whereas others may have 15-100 copies per cell.
(i) Name the selectable markers in the cloning vector pBR322. Mention the role they play.
(ii) Why is the coding sequence of an enzyme P-galactosidase a preferred selectable marker in comparison to the ones named above?
Answer:
(i) Selectable markers in cloning vector pBR322 are ampiciilin and tetracycline antibiotic resistance gene. They help in the selection of transformants and eliminating the non-transformants.
(ii) The selection of recombinants due to inactivation of antibiotics is a difficult process and requires simultaneous plating on two plates having different antibiotics. Thus, enzyme β-galactosidase is preferred as a selectable marker because it allows differentiation of non-recombinants from recombinants easily by insertional inactivation technique.
Question 25.
Study the graph given below which shows the growth curve of animal population.
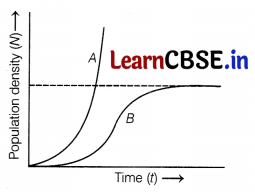
(i) The curve ‘B’ is described by the following equation
\(\)\frac{d N}{d t}\(\) = rN{\(\)\frac{K-N}{K}\(\)}
What does ‘K’ stand for in this equation and mention its significance?
(ii) Which one of the two curves is considered a more realistic one for most of the animal populations? Also which curve would depict the population of a species of deer if there are no predators in the habitat? Explain.
Answer:
(i) ‘K’ stands for carrying capacity. It signifies the limit of habitat, which means that the limited resources in a given habitat support growth upto a certain level beyond which no further growth can take place.
(ii) The curve ‘B’ is considered more realistic one for most of the animal populations. It is so because in the curve ‘S’, the sources of food and space are limited and it supports the growth curve of animal populations.
The curve ‘B’ would depict the population of a species of deer if there are no predators in the habitat. In the absence of predators, prey population will increase. Thus, the competition will increase due to the limited food and shelter resources within the prey population.
![]()
Question 26.
Expand VNTR and describe its role in DNA fingerprinting. List any two applications of DNA fingerprinting technique.
Answer:
VNTRs The expanded form of VNTR is Variable Number of Tandem Repeats. These are short nucleotide repeats in DNA. These are highly specific for individuals.
Role of VNTR in Fingerprinting VNTRs are used as probe markers in the identification of DNA of different individuals because no two individuals can have the same VNTRs (except in case of monozygotic twins).
DNA fingerprinting is a technique that shows the genetic makeup of living things. Two applications of DNA fingerprinting are as follows
(a) DNA fingerprinting can identify the real genetic ’ mother, father and offspring.
(b) DNA fingerprinting is very useful in the detection of crime and legal pursuits.
Question 27.
Rita was 9 monts pregnant, she wanted to know that how the foetus gets delivered after the human pregnancy period. So, she asked her gynaecologist to explain it to her, so that she can mentally prepared for her delivery. Her gynaecologist explained to her about the process in a very precise manner.
(i) What is the average duration of human pregnancy known as?
(ii) What is the term given to the process of delivery of foetus?
(iii) Give the definition and importance of the term mentioned in (ii).
Or
While observing cross-sectional view of seminiferous tubules. Mira observed cells of different shapes and sizes. She also observed few cells in interstitial spaces and asked her teacher about these variations. Teacher gave detailed description about Sertoli cells, Leydig cells and spermatocytes.
(i) Name the primary sex organ and the process of gamete formation in males.
(ii) Name the precursor cells which produce sperms and also mention its ploidy.
(iii) Name the cells that appear as elongated, slender structures within the seminiferous tubules. Mention their function also.
Answer:
(i) The average duration of human pregnancy is called as gestation period. It is approximately 270 days in humans.
(ii) The term given to the process of delivery of foetus is called parturition.
(iii) Parturition is the birth of the fully formed foetus on completion of pregnancy or gestation. It helps in expulsion of the foetus.
Or
(i) Testis is the primary sex organ in males. The process of gamete formation in males is called spermatogenesis.
(ii) Spermatogonium. It is diploid (2n) cell which divides to produce haploid gamete or sperm (n).
(iii) Sertoli cells. These cells provide nourishment to developing spermatocytes.
Question 28.
State the views of Oparin and Haldane on evolution. How does SL Miller’s experiment support their views?
Answer:
The theory of biogenesis was proposed by Oparin and Haldane. It states that life could have come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules (e.g. RNA, protein, etc.) and the formation of life forms was preceded by chemical evolution, i.e. formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents.
In 1953, Urey and Miller conducted an experiment to prove this theory. They created the conditions of primitive earth, i.e. high temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere containing CH 4 , NH 3 , etc, at laboratory scale. They then stimulated electric discharge in a closed flask containing CH 4 , H 2 , NH 3 and water vapour at 800°C. They also observed the formation of amino acids.
In similar experiments, they observed the formation of sugars, nitrogen bases, pigments and fats. These small organic molecules are the building blocks for proteins and other components. Hence, this experiment supported that life has come from pre-existing non-living organic molecules.
![]()
Section D
Q. Nos. 29 and 30 are case-based questions. Each question has 3 subparts with internal choice in one subpart.
Question 29.
Study the pedigree chart for colour blindness given below and answer the questions that follows.
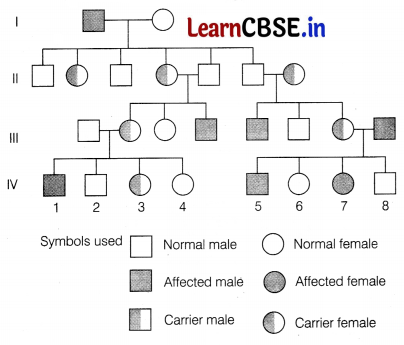
(i) On the basis of the inheritance pattern exhibited in this pedigree chart, what kind of trait is shown? [1]
(ii) Which sex out of both can be the carrier of colour blindness but does not have it? [1]
(iii) If individual 7 of IV generation had children, what percentage of her sons would you expect to be colourblind? [2]
Or
(iii) Why do all daughters in generation-II carry the colourblind gene? [2]
Answer:
(i) The trait that is shown in this pedigree chart is sex-linked and recessive.
(ii) Females are usually carriers of colour blindness, but they are usually not affected by it.
(iii) As the 7 individual is an affected female. The expected percentage of her sons affected with colour blindness would be 100%. This can be explained as
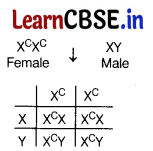
The possible gentoype of the offsprings will be X
C
X, X
C
X (carrier female) X
C
Y, X
C
V (affected male).
Or
(iii) All the daughters in generation II carry the colourblind gene as they receive colourblind allele from the father. This can be explained as
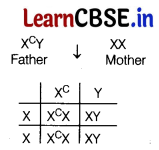
The possible genotype of the offsprings will be X C X, XX (carrier female) and XY XY (normal male).
Question 30.
The data below show the number of patients that tested positive for dengue in the year 2005.
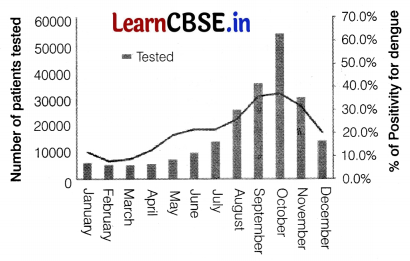
(i) With reference to the above graph, in which month did the outbreak of dengue fever occur? [1]
(ii) What type of mosquito is responsible for dengue? [1]
(iii) Explain why the outbreak of dengue fever usually occur in the summer or during rainy season. [2]
Or
(iii) How can we control the spread of dengue? [2]
Answer:
(i) The outbreak of dengue fever occurred in the month of August to November, i.e. during rainy season.
(ii) Dengue viruses are spread to people through the bites of infected Aedes species mosquitoes.
(iii) The dengue fever outbreaks usually occur in the summer or during the rainy season because the population of the vector mosquitoes are high. The combination of warm temperature and stagnant water provides ideal breeding condition for mosquitoes.
Or
(iii) The spread of dengue can be controlled by the use of insect repellants, wearing long-sleeved shirts and long pants and by controlling mosquitoes inside and outside our houses.
Section E
Question 31.
A schematic representation of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) upto the extension stage is given below. Give answers of the following questions.
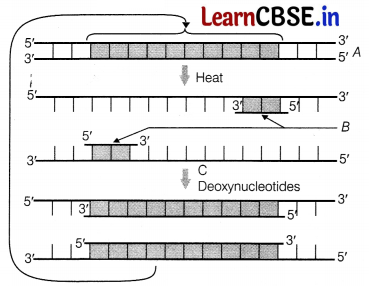
(i) Name the process A and identify B. Also identify C and mention its importance in PCR.
(ii) Describe the role of heat, primers and the bacterium Thermus aquaticus in the process of PCR.
Or
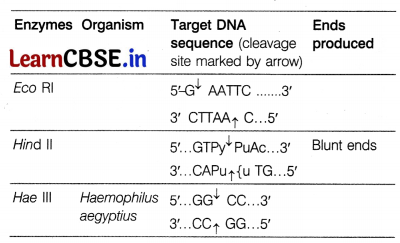
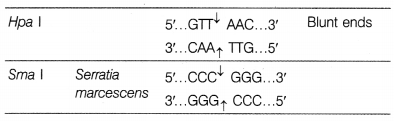
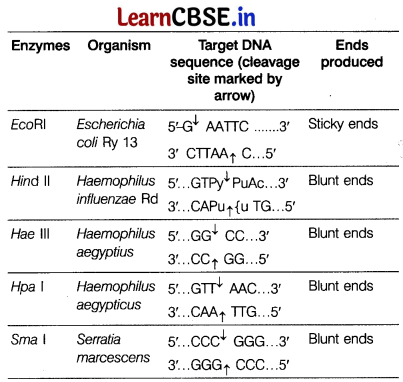
The table shows some restriction enzymes, their sources and the target DNA sequence with cleavage site. Analyse and suggest the name of organism along with their ends produced.
Answer:
(i) A is denaturation process and B are primers. C is Tag DNA polymerase, a thermostable enzyme, which remains active during the high temperature and induces denaturation of DNA.
(ii) Role of Heat in PCR (in vitro), the DNA strands are separated by heating at 95°C for two minutes. Heating causes the breakage of H-bonds between bases of two strands leading to its unwinding.
Role of Primers Primers are short lengths of DNA of about 20 bp long that are required to start DNA polymerisation in PCR. The primers hybridise to their complementary sequence on the DNA strands at 40°-50°C temperature and help in DNA polymerisation.
Role of Thermus aquaticus An enzyme called Taq polymerase is isolated from Thermus aquaticus. Since, this bacteria thrives in temperature as high as 95°C, this enzyme can also tolerate high temperature without undergoing denaturation. Therefore, this enzyme is used in PCR instead of normal DNA polymerase.
Or
The restriction enzymes cuts the DNA molecule by cleavage in two ways.
Blunt end Restriction enzymes like Alu I, Hae III, Hind II, Sma I, etc. makes cuts across both the strands of DNA in the centre of recognised sequence. Thus, DNA segments produced are with blunt ends.
Sticky end In this type of cleavage, the cuts are made in two strands of DNA at two different sites, few nucleotides away from each other. As a result of this two strands with protruding ends or overhanging stretches are produced. These strands are called stick ends. e.g. EcoRI, Pst I, BamHI, etc.
![]()
Question 32.
Intrauterine devices are most widely accepted methods of contraception. These are used by females and are inserted by doctor or nurses in the uterus through vagina. However, these devices are not recommended for those who eventually intend to conceive.
(i) Explain how does Cu-T prevent conception.
(ii) Name the IUDs which makes uterus unsuitable for implantation.
(iii) Copper ions releasing IUDs are more efficient than non-medicated methods. Why?
Or
Given below is a diagramatic representation of various events that occur during menstrual cycle.
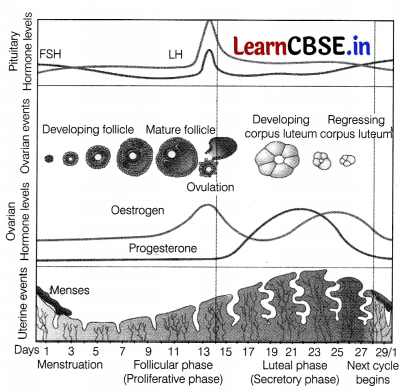
(i) Explain the menstrual phase in a human female. State the level of ovarian and pituitary hormones during this phase.
(ii) Why is follicular phase in the menstrual cycle also referred as proliferative phase? Explain.
(iii) Explain the events that occur in a Graafian follicle at the time of ovulation and thereafter.
Answer:
(i) Cu-T is placed in the uterus and proves to be an effective method of contraception in human females. It prevents implantation of the zygote on the uterine wall. It is a long lasting method of contraception.
(ii) Hormone releasing IUDs are progesterone and LNG-20 which make uterus unsuitable for implantation.
(iii) Cu ion releasing lUDs are more efficient methods of contraception because
(a) they suppress the sperm motility and capacity of fertilising ovum.
(b) it is safest long term, least expensive, reversible contraceptives available.
The hormone releasing lUDs on the other hand, makes uterus unsuitable for implantation and the cervix hostile for sperms.
Or
(i) The reproductive organs of female undergo rhythmic changes called as the menstrual cycle. The average cycle in human females is about 28-29 days. The start of menstrual cycle at puberty is known as menarche. It involves four phases menstrual follicular, ovulatory and luteal.
The menstrual phase forms the first phase of menstrual cycle which occurs for 3-5 days.
The endometrium linning of the uterus breaks down during this phase. The unfertilised ovum, as well as the blood vesels are discharged from the vagina. It leads to the abdominal cramps due to the contraction of the uterus and abdominal muscles. Oestrogen and progesterone levels are low during day 1 of menstrual phase which stimulates the pituitary gland to secrete FSH of follicular maturation.
(ii) The follicular phase is also known as the proliferation phase as in this phase the production and growth of the follicles take place. During this phase, one of the follicles matures to become Graafian follicle and uterus endometrium lining undergoes regeneration through proliferation.
(iii) During mid cycle there is rapid secretion of LH hormones which causes LH surge leading to the rupture of Graafian follicle thus, releasing the ovum by the process of ovulation.
During ovulation only the egg comes out of the follicles while remaining ruptured follicle remains on the surfaec of the ovary within two weeks the follicle get transformed into a structure known as corpus luteum. It releases progesterone and small amount of oestrogen, both of which maintain the thickening of the walls, of the uterus for implantation. If , pregnancy takes place the high levels of 1 progesterone are maintained and if pregnancy does not occur then the corpus luteum withers away on day 22. There is a drop in progesterone level and wall of the uterus lining falls off leading to menstruation.
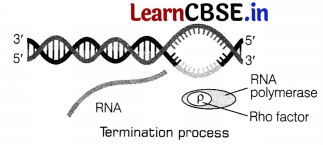
Question 33.
Sketch a schematic diagram of lac operon in switched on position. How is the operon switched off? Explain.
Or
Describe the process of transcription in bacterium.
Answer:
Lac operon consists of
(i) an operator, which controls all structural genes as a unit.
(ii) a regulatory gene (i gene).
(iii) three structural genes (z, y, a), which code for enzymes.
(iv) a promoter, where RNA polymerase binds for transcription.
The regulatory gene codes for a repressor protein that has high affinity for the operator region and which prevents RNA polymerase from transcribing the structural genes, i.e. the lac operon is switched off or inactive.
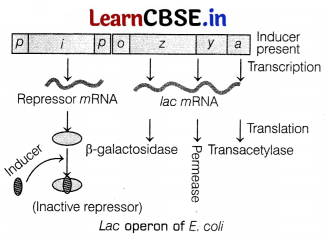
Its function in the presence and the absence of inducer is as follows
(ii) When inducer (lactose) is present, Lactose acts as an inducer and binds to the repressor. Thus, forming an inactive repressor. The repressor fails to bind the operon. The operon is switched off in this situation.
(ii) When inducer (lactose) is present, Lactose acts as an inducer and binds to the repressor. Thus,
forming an inactive repressor.
The repressor fails to bind the operator region. The RNA polymerase binds to the operator and transcribe lac mRNA.
Lac mRNA is known to be polycistronic which produces ail three enzymes, i.e. (β-galactosidase, permease and transacetyiase required for the hydrolysis of lactose. Operon is switched on in this situation.
Or
Initiation process of transcription in bacteria RNA polymerase becomes associated transiently to an initiation factor sigma (a) and binds to specific sequence on DNA called promoter to initiate transcription.
A single DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyses the transcription of all the three types of RNA.
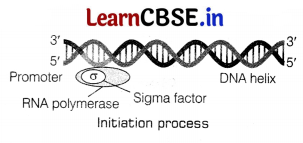
Elongation process of transcription in bacteria
RNA polymerase facilitates opening of the DNA helix after binding to promoter. It uses ribonucleoside triphosphates as substrate and polymerises the nucleotides in a template dependent fashion following complementarity.
The process continues till RNA polymerase reaches the terminator region on the DNA strand.
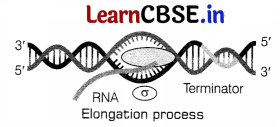
Termination occurs when RNA polymerase reaches the terminator regon and the nascent RNA fails off. The RNA polymerase being transiently associated with termination factor rho (ρ) which is also falls off from the transcription unit.