Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions Set 2 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Set 2 with Solutions
Time : 3 Hours
Maximum Marks : 70
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has five sections and 33 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 16 questions of 1 mark each; Section-B has 5 questions of 2 marks each; Section-C has 7 questions of 3 marks each; Section-D has 2 case-based questions of 4 marks each; and Section-E has 3 questions of 5 marks each.
-
There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions.
A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions. - Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section A
Question 1.
A chemical carcinogen present in tobacco smoke shows many harmful effects on human body. Out of the options given below, select the correct answer that results due to the chemical.
(a) Skin cancer
(b) Lung cancer
(c) Stomach cancer
(d) Pancreatic cancer
Answer:
(b) Lung cancer is due to the chemical carcinogen present in tobacco smoke.
Question 2.
Which pair of geographical area show maximum diversity in our country?
(a) Sunderbans and Rann of Kutch
(b) Kerala and Punjab
(c) Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats
(d) Eastern Himalayas and Western Ghats
Answer:
(d) Eastern Himalayas and Western Ghats are geographical areas that show maximum diversity in our country.
Question 3.
Given below are the four enzymes and their activities.
| Enzymes | Activities |
| A. Taq DNA polymerase | 1. Stable above 86°C |
| B. Exonuclease | 2. Cleaves the ends of linear DNA |
| C. Protease | 3. Degeneration of proteins |
| D. Chitinase | 4. Breakdown of fungal cell wall |
How many of there are correctly matched?
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 4
(d) 3
Answer:
(c) All four pairs are correctly matched.
![]()
Question 4.
When two similar species live in the same area, they may evolve to become more different in order to
(a) drive the other species to extinction
(b) reduce genetic variation
(c) reduce competition
(d) use up the other species resources
Answer:
(c) According to the mechanism of resource partitioning, if two species compete for the same resource, they could avoid competition by choosing different times for feeding or different foraging patterns.
Question 5.
In humans, at the end of the first meiotic division, the male germ cells differentiate into which of the following cell division stage?
(a) Spermatogonia
(b) Spermatids
(c) Primary spermatocytes
(d) Secondary spermatocytes
Answer:
(d) At the end of the first meiotic division, the male germ cells differentiate into secondary spermatocytes.
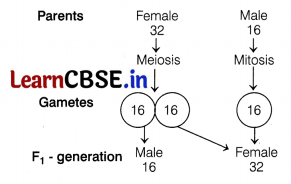
Question 6.
The number of chromosomes in female and male honeybees are
(a) 32
(b) 16
(c) 32 and 16, respectively
(d) 16 and 32, respectively
Answer:
(c) Sex-determination in honeybee is . haplo-diploid sex-determination system.
Question 7.
Which one of the following exhibits least productivity?
(a) Salty marshes
(b) Open oceans
(c) Grasslands
(d) Coral reefs
Answer:
(b) In oceans, there are lots of nutrients, but no sufficient sunlight is available in deep areas, hence oceans have least productivity.
Question 8.
Identify the structure given below.
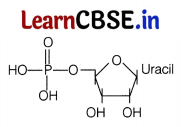
(a) Nucleoside, Uridylic acid
(b) Nucleotide, Inosinic acid
(c) Nucleoside, Inosinic acid
(d) Nucleotide, Uridylic acid
Answer:
(d) The structure s a nucleotide called uridylic acid.
Question 9.
The pathogen Microsporum is responsible for ringworm disease. Identify the disease causing pathogen that belongs to the same kingdom.
| Pathogens | Types |
| (a) Taenia | Tapeworm |
| (b) Ascaris | Roundworm |
| (c) Rhizopus | Mould |
| (d) Wuchereria | Filarial worm |
Answer:
(c) Microsporum and Rhizopus belong to the kingdom-Fungi (mould).
Question 10.
Which of the following in the table given below, will show the features of alcohol?
| Drug | Act as a depressant | Damages liver |
| (a) | Yes | No |
| (b) | No | No |
| (c) | Yes | Yes |
| (d) | No | Yes |
Answer:
(c) Alcohol acts as a depressant and it also damages the liver.
Question 11.
Shweta was calculating the age structure for a population in a village nearby for her case study. Which of the following parameters are included related to the age structure?
(a) Generation time
(b) Death rate
(c) Fecundity (birth rate)
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) The age structure of a population is the percentage of individuals of different age such as young, adult and old. Age structure is shown by organisms in which individuals of more than one generation co-exist. Birth rate, death rate and generation time are important parameters related to it.
![]()
Question 12.
The diagram below shows the structure of a flower.
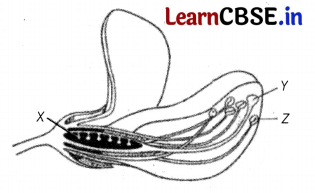
One of the part shows the site of pollination and the other part shows the site of fertilisation. Choose the correct option from the given table.
| Pollination | Fertilisation | |
| (a) | Y | X |
| (b) | X | Z |
| (c) | X | Y |
| (d) | Y | Z |
Answer:
(a) Pollination takes place at the top of the stigma (Y), while fertilisation takes place within the ovary (X).
Question Nos. 13 to 16 consist of two statements, Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false
(d) Assertion is false, but Reason is true
Question 13.
Assertion (A) : Amniocentesis technique is frequently used in foetal disease treatment in India.
Reason (R) : This technique can be used for sex-determination of child.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion. Amniocentesis is used in foetal sex-determination and disorders based on chromosomal pattern in the amniotic fluid surrounding the developing foetus. This technique is banned in India at present due to its misuse in increased female foeticides.
Question 14.
Assertion (A) : Synthesis of daughter or new strand occurs continuously along the parent strand 3′ → 5″.
Reason (R) : DNA polymerase can polymerise nucleotides in 3’→ 5″ direction on 5 → 3 strand.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true, but Reason is false.
DNA polymerase can polymerise nucleotides only in 5′ → 3′ direction because on 3′ → 5′ strand it adds nucleotides at the 3’end.
Question 15.
Assertion (A) : Biotechnology produces transgenic microorganisms that function as microfactories for proteins.
Reason (R) : Transgenic microorganisms can be developed to produce proteins of human use like insulin.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion, Transgenic microorganisms can be developed by inserting genes encoding for desired protein products using recombinant DNA technology.
These transgenic organisms function as living microfactories that produce proteins like human insulin, human growth hormones, etc. Production of proteins from such organisms is easier, more efficient and cost effective.
Question 16.
Assertion (A) : An ecosystem is an interaction between abiotic and biotic components.
Reason (R) : AG Tansley coined the term ecosystem.
Answer:
(b) Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion.
AG Tansley coined the term ecosystem (Gk. Eco-environment; system—interaction and interdependent complex) for the first time. It is an integrated natural system resulting from the interaction of living and non-living factors of the environment. In other words, the ecosystem can also be defined as an inter-relationship between biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components of the environment.
Section B
Question 17.
Biodiversity must be conserved as it plays an important role in many ecosystem services that nature provides. Explain any two services of the ecosystem.
Answer:
The two ecosystem services are
- Forest ecosystem mitigates droughts and floods and provides oxygen.
- The wildlife helps in pollination of crops, without which fruits/seeds are not produced.
Question 18.
The figure given below is related to the control of pregnancy. Study the figure and answer the questions that follows.
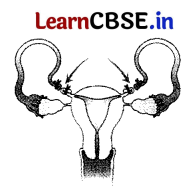
(i) Name the process that is shown in the above figure.
(ii) Explain how does this process help to control pregnancy.
Answer:
(i) The process shown above is called tubectomy.
(ii) This process takes place in the female reproductive system, tn this process, cutting and binding of Fallopian tube is done to prevent contact between sperm and egg. Thus, help in prevention of pregnancy.
![]()
Question 19.
Haemophilia is a sex-linked inheritance condition in humans where a simple cut causes non-stop bleeding. Study the pedigree chart showing the inheritance of haemophilia in a family.
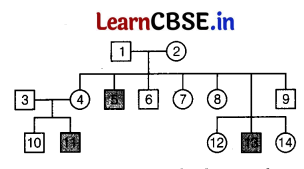
Give reasons, which explain that haemophilia is (i) sex-linked, (ii) caused by X-linked gene.
Answer:
(i) Haemophilia is sex-linked because it is transmitted from an unaffected carrier female to some of the male offspring. Here, the males are always affected, but the female rarely becomes haemophilic. This is because to a female becoming haemophilic, her mother has to be atleast a carrier and father should be haemophilic.
(ii) Hemophilia is X-linked because the gene for haemophilia is present on X-chromosome. And as the male has only one X-chromosome, they get affected by the disease. But on the other hand female has two X-chromosomes. So, she show heterogamy and become carrier mostly.
Question 20.
Observe the given structure carefully and answer the questions that follows.
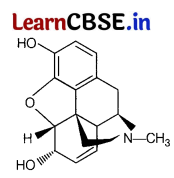
(i) What is the name of the chemical compound? What kind of drug is it?
(ii) What are the physical properties of this compound?
Answer:
(i) The chemical compound given is morphine. It is an effective sedative, analgesic and painkiller.
(ii) Morphine is obtained from latex of poppy plant. Its physical appearance is white, odourless and a crystalline compound.
Question 21.
Use the information provided in the table given below to answer the questions that follows.
| PCR steps | Description | Temperature (°C) |
| Denaturation | Double- stranded DNA is heat denatured and separated into single strand. | A |
| B | Primers bind to the single DNA strands. | 5°C below temperature of primers 40°C. |
| Extension | C | 72°C |
(i) Fill the gaps of A, B and C.
(ii) Write two important applications of PCR.
Or
A recombinant vector with a gene of interest inserted within the gene of a-galactosidase enzyme and is introduced into a bacterium.
Explain the method that would help in selection of recombinant colonies from non-recombinant colonies. Why is this method of selection referred to as insertional inactivation?
Answer:
(i) A-95°C, B-Annealing, C-The primers are extended by DNA polymerase, resulting in two copies of original DNA strand.
(ii) Two important applications of PCR are as follows
- The amplification of gene fragments as fast alternative of cloning.
- For the modification of DNA fragments.
Or
The recombinant colonies can be differentiated from non-recombinant colonies by their inability to produce colour in the presence of a chromogenic substrate.
The recombinants do not produce any colour while the non-recombinants produce a blue colour with
chromogenic substrate in the medium. It occurs because of the presence of a-galactosidase in former
and its absence in recombinants cells.
The enzyme α-galactosidase becomes inactivated on insertion of recombinant DNA. within the coding sequence of enzyme. Thus, the method is called insertional inactivation.
Section C
Question 22.
Study the mRNA segment given below, which is complete and to be translated into a polypeptide chain.

(i) Write the codons ‘A’ and ‘B’. What do they code for?
(ii) How peptide bond formed between two amino acids in the ribosome?
Answer:
(i) A-AUG. B-UAA/UAG/UGA
AUG codes for rnethionine and also act as initiator UAA/UAG/UGA does not code f or any amino acid, but brings about termination of polypeptide synthesis.
(ii) In the large subunit of ribosome, there are two sites in which subsequent amino acids bind to and come close enough for the formation of peptide bond. It is catalysed by the enzyme called pepbdyl transferase.
Question 23.
Explain the role of restriction endonucleases, gel electrophoresis, selectable marker in pBR322 in biotechnology
Answer:
Restriction endonucleases : These are the bacterial enzymes that cut dsDNA into fragments after recognising and binding to the specific nucleotide sequences, known as recognition site. These enzymes are used to form recombinant molecules of DNA.
Gel electrophoresis is the technique which allows the separation and visualisation of fragments of DNA on an agarose gel matrix.
Selectable markers in pBR322 help in identification and selection of transformants.
pBR322, an E. coli cloning vector has two antibiotic resistance genes, i.e. for ampicillin and tetracycline, which act as selectable marker.
Question 24.
The size of a population for any species is not a static parameter and keeps on changing with time. It depends on the factors such as food availability, predation pressure and adverse weather.
(i) Explain death rate in a population by taking a suitable example.
(ii) Write the other two characteristics, which only a population shows but an individual cannot.
Answer:
(i) Death rate or Mortality is expressed as the number of deaths of individual of a population per year. For example, if 80 individuals in a laboratory population of 800 fruitfly died in a week, then death rate is \(\frac{80}{800}\) = 0.1 per fruitfly/week
(ii) Characteristics of population, not exhibited by individual are
(a) Population size or Density.
(b) Population interactions.
![]()
Question 25.
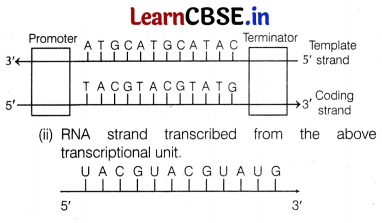
Study the hypothetical template strand given below.

(i) Construct a complete transcription unit with promoter and terminator on the basis of the above strand.
(ii) If an RNA strand is to be transcribed from the above transcriptional unit, how will the strand look like? Also mention its polarity.
Answer:
(i) Transcription unit
Question 26.
Microbes can be used to decrease the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides. Explain how this can be accomplished.
Answer:
- Microbes plays an important role in organic farming, which reduce the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides, etc.
- Biofertilisers are living organisms, which help in increasing the fertility of the soil. Beneficial microorganisms help in improving plant growth by supplying plant nutrients. Many species of bacteria and cyanobacteria help in fixing the nitrogen in the soil.
- Many biological agents like ladybird and Bacillus thuringiensis, etc. are useful in eradicating pests. Therefore, it is possible for microbes to reduce the use of chemical fertilisers and pesticides.
Question 27.
Pollination is the transfer of pollen grain from male reproductive part to the female reproductive part. This later enables fertilisation and production of seeds. This process of pollination is mainly facilitated by pollinating agents such as air, water, animals, etc. But if the flowers are closed or prefer self pollination then plant’s itself become the pollinating agents. Based on the type of pollinators pollen grains have developed different feature.
(i) Write the characteristic features of anther, pollen and stigma of wind pollinated flowers.
(ii) How do flowers reward their insect pollinator? Explain.
Or
A couple married for 11 years did not have a child. They consulted the doctor which advised them some test. In result of these test it was found that the sperm count of male partner is very less. The doctor suggested them to opt for ART (Assisted Reproductive Technology).
(i) According to you which ART will be beneficial for this couple and why?
(ii) If the women was unable to produce ovum and male was healthy then which method of ART should they used?
(iii) Does the process of ART can be facilitated for couples whose either of partner is suffering from AIDS.
Answer:
(i) The wind pollinated flowers are usually in conspicous having versatile anthers. The pollen grains are usually smooth walled, relatively light, small and dry and are produced in large quantities. The stigmas are comparatively large protruding and often feathery.
(ii) Flowers produce a sugary liquid called nectar which many insects consume on a large basis. When insects land on a flower, pollen grain tend to stick to their bodies. The insect then moves from one to another flower of the same species, pollen gets transferred to the stigma of flowers and hence causing pollination.
Or
(i) The mentioned couple should opt for Artificial Insemination (Al). In this method the semen is collected either from the donor or from husband and then artificially introduced into the vagina of female. This technique help those couples to have their children in which male is infertile or the sperm count is very low.
(ii) If the women was unable to produce ovum then in this case the couple should opt for test tube baby. Here, in this technique ovum from donor and sperm from husband are collected and are introduced to form a zygote under simulated condition in in vitro (outside the body). Then the formed zygote is transferred or implanted into the female uterus/womb for further development.
(iii) Yes, the process of ART can be performed in those couples where either of partner is suffering from AIDS. This reduce the risk of infection to child when the pregnancy is desired.
Question 28.
How do ‘implants’ act as an effective method of contraception in human females? Mention its one advantage over contraceptive pills.
Answer:
Subcutaneous ‘implants’ contain synthetic progesterone and are placed under the skin. They are an effective contraceptive method as they check ovulation and thicken cervical mucus to prevent sperm transport.
‘Subcutaneous implants’ are more advantageous than contraceptive pills as they are long lasting and once implanted, they are effective for up to 5 years.
![]()
Section D
Q. Nos. 29 and 30 are case-based questions. Each question has 3 subparts with internal choice in one subpart.
Question 29.
Given below is the result of the survey done by MCD to analysis the breeding of mosquitoes. Observe the graph carefully and answer the questions that follows.
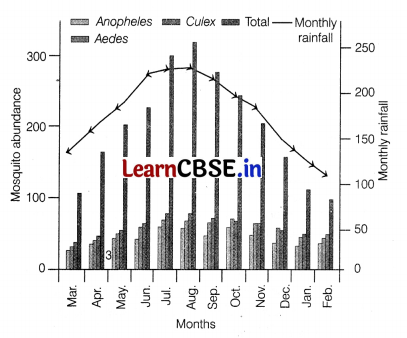
(i) According the graph, in which month the mosquito breeding is at its peak? Also, give reason for it.
(ii) If an individual gets bitten by a malarial parasite, what symptoms will he possess?
(iii) Where does the fertilisation and development of malarial parasite take place in mosquito’s body? Also mention what does the sexual stages of parasite are referred to as.
Or
(iii) What is the cause of cycle of fever during malaria?
Answer:
(i) During the month of August, i.e. rainy season, the mosquito breeding is at its peak. This is because, the water logged and damp places provide suitable breeding environment for mosquitoes.
(ii) Symptoms of malaria include fever and flu-like illness, including shaking chills, headache, muscle aches and tiredness.
(iii) The fertilisation and development of parasite take place in the stomach of mosquito’s body. The sexual stages of parasite are referred to as gametocytes.
Or
(iii) At regular intervals, the parasite reproduces and causes bursting of RBCs. This releases haemozoin and causes periodic cycle of fever.
Question 30.
The graph given below shows how natural selection process acts on tail morphology.
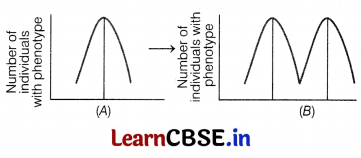
(i) With the reference of above graph, under the influence of which type of natural selection would graph A become like graph B.
(ii) Who suggested natural selection as the mechanism of evolution?
(iii) How can you explain that the large number of individuals acquires mean character value in terms of graph A?
Or
(iii) What could be the likely reason for new variations arising in a population?
Answer:
(i) Graph A would become like graph B under the influence of the disruptive and selective type of natural selection.
(ii) Charles Darwin suggested natural selection as a mechanism of evolution.
(iii) Graph A shows stabilising natural selection. For instance, the large number of individuals acquire mean character value, i.e. variation is much reduced. This thus operates by favouring optimal environmental conditions where competition is not severe.
Or
(iii) Because individual at the extremes contribute more offspring compared to those in the centre and produce two peaks in the distribution of a trait which leads to new variations arising in a population.
Section E
Question 31.
Given below are some female hormones. Determine their levels during ovulatory phase and during pregnancy. Also give reason to justify your answer.
| Female hormones | During ovulatory phase | During pregnancy |
| FSH | ||
| LH | ||
| Oestrogen | ||
| Progestogen |
Or
A gynecologist performed different ART procedures in different infertile couples (Case I- Case V).
Determine each ART case and explain them briefly.
| Case | Description | Uses |
| Case 1 | Egg and sperm fertilise outside the body. | For a variety of infertility disorder. |
| Case 2 | Planting the unfertilised egg into the Fallopian tubes. | It is proceded in case, when IVF is not an option or in case of blocking of Fallopian tube. |
| Case 3 | Planting a pre-fertiliseci egg into the Fallopian tubes. | Combines IVF and GIFT. |
| Case 4 | Injection of single sperm into the center of the egg. | For cases of male infertility used in conjuction with IVF. |
| Case 5 | Semen collected from donar male and is artificially introduced into vagina or uterus. | Couples experiencing infertility due to medical condition like low sperm count or endometriosis. |
Answer:
| FSH and LH level during ovulation | High |
| FSH and LH level during pregnancy | Low |
| Progesteron level during ovulation | Low |
| Progesteron level during pregnancy | High |
| Oestrogen level during ovulation | High |
During ovulatory phase the level of FSH and LH are at peak as they play major role in development of ovarian follicles and to cause those follicles to rupture. But during pregnancy, soon after implantation there level drops down in order to maintain pregnancy.
During ovulatory phase if fertilisation do not takes place then the progesterone level drops down which result in shedding of endometrium. But if fertilisation occur successfully then to maintains pregnancy, level of progesterone increases.
Oestrogen level remain high in both ovulatory and pregnancy.
Or
Case 1 is IVF. In this the fertilisation is done by fusing ovum from the female donor and sperm from the male donor outside the body under strict laboratory conditions. This results in a zygote. This is famously known as a test tube baby.
Case 2 is GIFT It is an in vivo fertilisation procedure, where the ovum collected from the donor is transferred into the Fallopian tube. In this technique, fertilisation and zygote formation is more natural as it take place within the female body.
Case 3 is ZIFT, here fertilisation happens in a laboratory. Thus, formed zygote is then conveyed to the Fallopian tube of mother using laparoscopy.
Case 4 is ICSI. In this sperm is directly injected into the ovum by using a tiny needle called a micropipette. The fertilised egg (or embryo) grows in laboratory for 1 to 5 days before it is transferred to female uterus.
Case 5 is IUI. In this technique semen collected either from husband or a healthy donor and is artificially introduced into the uterus of the female.
![]()
Question 32.
A GM crop can contain a gene that has been artificially inserted instead of the plant acquiring it through pollination.
The resulting plant is said to be genetically modified although in reality all crops have been genetically modified from their original wild state by domestication, selection and controlled breeding over long periods of times. In 1994, calgene’s delayed-ripening tomato (Flavr Savr) became the first genetically modified food crop to be produced and consumed in an industrialised country. Since, the recorded commercialisation of GM crops in 1996 to 2018, several countries have contributed to —113 fold increase in the global area of transgenic crops.
(i) GM crops are designed to develop natural resistance from insects and pests. Which crops are modified using Bacillus thuringiensis?
(ii) List five advantages of GMOs to a farmer.
(iii) State that foods derived from genetically modified crops should be tested for possible reactions in people. Explain.
Or
GM crops contributed to an increase in the number of functional foods or nutraceutical foods with added benefits. Nutraceutical foods is applied to isolated nutrients, dietary supplements and herbal products, specific diets, processed foods. Scientist have developed Golden rice that contains more vitamin-A. Capacity of Golden rice lines with varying carotene content to supply the recommended nutrient intake of vitamin-A. The graph below shows the shaded part as the dietary intake of vitamin-A from other source and the unshaded part as the dietary intake of vitamin-A from Golden rice.
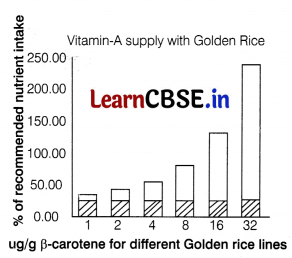
(i) Evaluate the efficacy of Golden rice to meet the daily intake of vitamin-A on people.
(ii) The GM crops are the best solution to overcome issues develop due to conventional breeding. Discuss.
(iii) List the changes that are done to genetically modified plants.
Answer:
(i) Crops modified using Bacillus thuringiensis are corn, cotton, tomato, rice, potato and soybean. In there, the insect resistant gene is transferred from Bacillus thuringiensis to make it insect and pest-resistant.
(ii) Advantages of GMOs to a Farmer
(a) Crops become more tolerant to abiotic stresses like cold, drought, salt and heat.
(b) Dependence on chemical pesticides has reduced, i.e. pest-resistant crops.
(c) Helped to reduce post-harvest losses.
(d) Efficiency of mineral usage increased in plants, preventing early exhaustion of fertility of soil.
(e) Enhanced nutritional value of food, e.g. vitamin-A enriched rice.
(iii) Genetically modified crops should be tested for possible reactions in people, because these crops are prepared by the insertion of gene of the other species into their DNA. So, there is a possibility that they can cause some health issues, i.e. allergies due to release of new kind of proteins. Hence, GM crops should be tested.
Or
(i) Golden rice stands a very good chance of being abie to deliver the recommended daily allowance of vitamin-A (after conversion from p-carotene) to all people. It can be seen that Golden rice varieties could fully provide the daily needs.
(ii) The agrochemicals have harmful effects on the environment and they are expensive for farmers especially in the developing countries.
Hence, the best solution to overcome all these issues is the development and use of Genetically Modified (GM) crops.
(iii) Through genetic modifications following changes were made to enhance the quality of plants.
(a) Crops became more tolerant to various abiotic stresses such as cold, salt, heat, etc.
(b) Help to reduce post-harvest losses.
(c) Dependance on chemical pesticides has reduced.
(d) Enhanced nutritional value of food, e.g. vitamin-A enriched rice.
Question 33.
Name the major types of RNAs and explain their role in the process of protein synthesis in a prokaryote.
Or
Describe Meselson and Stahl’s experiment that was carried in 1958 on E. coli. Write the conclusion they arrived at after the experiment.
Answer:
There are three major type of RNA’s involve in the process of protein synthesis in prokaryotes, i.e, mRNA, fRNA and rRNA. There role in the process of protein synthesis is described below
(i) Role of mRNA : The order and sequence of amino acids are defined by the sequence of bases in the mRNA. It stores the genetic information from DNA. The amino acids are joined by a bond, which is known as a peptide bond.
This process requires energy. mRNA also possesses untranslated sequences called Untranslated Regions (UTRs) at both 5′ end and 3′ end. They help in efficient translation.
(ii) Role of fRNA It acts as an adapter molecule. Activation of amino acids occurs in the presence
of ATP and activated amino acids get linked to their cognate fRNA, i.e. charging of fRNA or aminoacyiation of fRNA.
If two such charged fRNAs are brought closer, the formation of peptide bond between them would occur energetically in the presence of a catalyst.
(iii) Role of rRNA It is formed in nucleolus and it forms 80% of total RNA present inside the cell.
It is also the most stable type of RNA. rRNA is associated with structural organisation of ribosomes (rRNA forms about 60% of weight of ribosomes), which are seats of protein synthesis.
Or
Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl conducted an experiment with Escherichia coli (1958) as follows
(i) They grew many generations of E. coli in a medium that contained 15 NH 4 Cl ( 15 N is the heavy isotope of nitrogen) as the only source of nitrogen. The result was that 15 N was incorporated into the newly synthesised DNA.
Upon centrifugation in a cesium chloride (CsCI) density gradient, this heavy DNA molecule could be distinguished from the normal DNA.
(ii) The cells were then transferred into a medium containing normal 14NH4CI.
(iii) At definite time intervals, as the cells multiplied, samples were taken and the DNA which remained as double-stranded helices were extracted.
(iv) The samples were separated independently on CsCI gradient to measure the densities of DNA.
(v) The DNA obtained from the culture, one generation after the transfer from 15N to14N medium had a hybrid or intermediate density.
(vi) The DNA obtained from the culture after another generation (generation-ll), was composed of equal amounts of hybrid DNA and ‘light’ DNA.
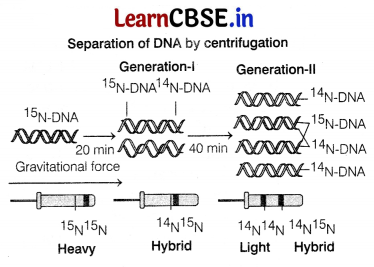
Thus, Meseison and Stahl concluded that the DNA replication is semi-conservative, i.e. out of the two strands of DNA, one is the parental strand, while another is newly synthesised.