Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 8 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Term 2 Set 8 for Practice
Time allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 15 questions. ALL questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each, and Section-C has 2 case based questions of 4 marks each.
- Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
Section – A
Question 1.
Catenation is the ability of an atom to form bonds with other atoms of the same element. It is exhibited by both carbon and silicon. Compare the ability of the catenation of the two elements. Give reasons. (2)
Question 2.
Three 2 Ω resistors, A, B and C, are connected as shown in the figure given below. Each of them dissipates energy and can withstand a maximum power of 18 W without melting. Find the maximum current that can flow through the three resistors.
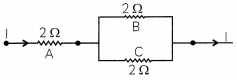
OR
A current of 1 ampere flows in a series circuit, containing an electric lamp and a conductor of 5 Ω when connected to a 10 V battery. Calculate the resistance of the electric lamp. Now, if a resistance of 10 Ω is connected in parallel with this series combination, what change (if any) will take place in the current flowing through 5 Ω conductor and potential difference across the lamp? (2)
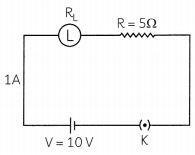
Question 3.
Examine the given figures and answer the following questions.
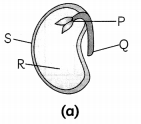
(A) Identify parts P, Q, R and S in fig. (a). Write functions of each part. (1)
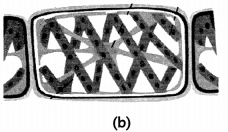
(B) Identify the organism and mode of reproduction in fig. (b). Explain the mode of reproduction. (1)
Question 4.
(A) In a food chain of frog, grass, insect and snake, assign a trophic level to frog. (1)
(B) Differentiate between biodegradable and non-biodegradable substances. Give examples. (1)
Question 5.
Observe the table given and answer the following questions.
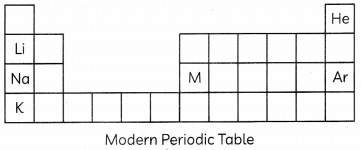
(A) (i) Lithium, sodium and potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements? (1/2)
(ii) Helium is an un-reactive gas and neon is a gas of extremely low reactivity. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common? (1/2)
(B) A metal M forms an oxide having the formula M
2
O
3
. It belongs to period 3 in the modern periodic table. Write the atomic number and valency of the metal. (1)
OR
Observe the given table and answer the following questions.
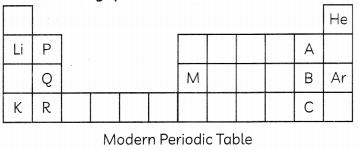
(A) Arrange elements P, Q and R in increasing order of their atomic radii. (1)
(B) Arrange elements A, B and C in the order of their decreasing non-metallic character. (1)
Question 6.
Write the structural formulae of all the isomers of hexane. (2)
Question 7.
Observe the given figure and answer the questions:
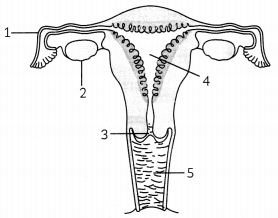
(A) Identify the parts in human-female reproductive parts which are blocked to prevent pregnancy. How is sterilization done in males? (1)
(B) In human females reproductive system, which part’s lining gets thickened and to nourish the growing embryo ? What happens to it if egg/ovum is not fertilized? (1)
Or
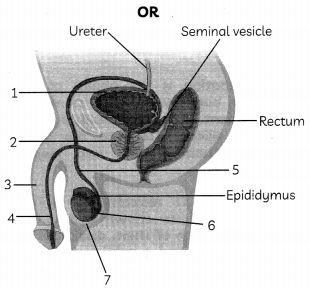
(A) In human male reproductive system identify the part:
(i) in which testis are located
(ii) which adds secretions along the path of vas-deferens. (1)
(B) Write the functions of secretions which are secreted along the path of vas deferens. (1 )
Section – B
Question 8.
What would be the ratio of chromosome numbers between an egg and a zygote? How is the sperm genetically different from the egg? (3)
Question 9.
(A) Is Ohm’s law applicable to electrolytes? If yes, under what conditions? If no, why? (1)
(B) What are the properties of a fuse? (1)
(C) In the equation P = VI, V is inversely proportional to I whereas in the equation V = IR, V is directly proportional to I. Why such a paradox? (1)
OR
(A) What will be the resistance of a wire of length 300 m and cross-section area 1.0 mm
2
made up of material of resistivity 10
-7
ohm
-m
? (1)
(B) What happens to the resistance as the conductor is made thicker? (1)
(C) Why alloy is commonly used in electrical heating devices like toaster etc? (1)
Question 10.
Observe the diagram given below and answer the questions.
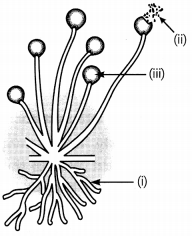
(A) Identify the organism and part
(i) the non-reproductive part (1)
(ii) reproductive part (1)
(B) What are the factors responsible for the spread of bread mould on slices of bread? (1)
OR
Observe the diagram shown below.
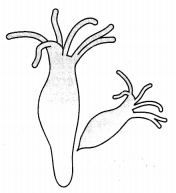
Identify the organism and mode of reproduction. Explain also. (3)
Question 11.
What does the direction of thumb indicate in the right-hand thumb rule? In what way is this rule different from Fleming’s left-hand rule. (3)
Question 12.
In peas, a pure breeding tall plant (TT) is crossed with a pure breeding short plant (tt). What will be the ratio of. pure tall plants to short plant in F
2
generation? (3)
Question 13.
(A) Make a food chain comprising grass hopper, grass, frog, hawk and snake? (1½)
(B) Indicate the flow of energy in an ecosystem. Why is it unidirectional? Justify. (1½)
Section – C
This section has 02 case-based questions (14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions (A, B and C).
Parts A and B are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part C.
Question 14.
The below table shows the Periodic Table of elements. The letters P, Q and U do not represent the actual symbols of elements
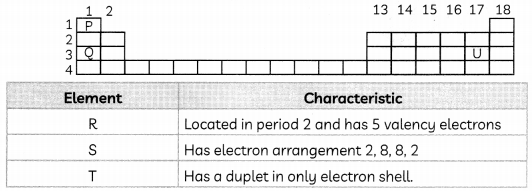
(A) Referring to the table, indicate the positions of R, S and T by writing the letters in the correct boxes of the Periodic Table above. (1)
(B) Which element among P, Q, R, S, T and U exist as monatomic gas? (1)
(C) (i) When U reacts with hydrogen, it forms a compound. Predict the colour observed when a red litmus paper is dipped in the solution of the compound. (1)
(ii) P can react with R to produce a gas. Name the gas. (1)
OR
(C) An element X (atomic number 17) reacts with an element Y (atomic number 20) to form a divalent halide.
(i) Where in the periodic table are elements X and Y placed? (1)
(ii) Classify X and Y as metal(s), non-metals) or metalloid(s). (1)
Question 15.
Fig. (a) shows magnetic field lines in a bar magnet. The compass needle gets deflected when brought near a bar magnet. The magnet exerts its influence in the surrounding region. The magnetic field is a quantity that has both direction and magnitude. Magnetic field lines have various properties. The direction of the magnetic field is taken to be the direction in which a north pole of the compass needle moves inside it. Fig. (b) show a current carrying conductor in the plane of the paper. (3)
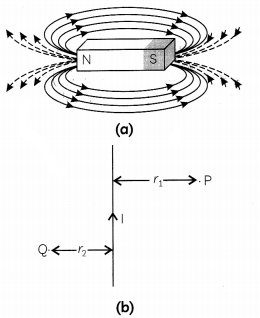
(A) Why does a compass needle gets deflected when brought near a bar magnet? (1)
(B) Why does a current carrying conductor kept in a magnetic field experience force? What is the direction of force acting on the conductor? (1)
(C) (i) Why don’t two magnetic lines of force intersect each other? (1)
(ii) Kanchi draws magnetic field lines of field close to the axis of a current carrying circular loop. As she moves away from the centre of the circular loop she observes that the lines keep on diverging. How will you explain her observation? (1)
OR
In fig. (b) what are the directions of magnetic fields produced by it at points P and Q? Given r
1
> r
2
, where will the strength of the magnetic field be larger? (2)