Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 5 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Term 2 Set 5 with Solutions
Time allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 15 questions. ALL questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each, and Section-C has 2 case based questions of 4 marks each.
- Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
SECTION – A
Question 1.
(A) Observe the given table and identify the element(s) that belong to the same group. Enumerate the reason for your answer. (1)
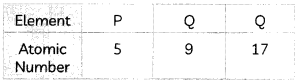
Answer:
For identification of elements that belong to the same group, we need to write the electronic configuration of these elements.
| Elements | Electronic Configuration |
| P | 2,3 |
| Q | 2,7 |
| R | 2, 8,7 |
As is evident from the above table, elements Q and R have 7 valence electrons each. The group is determined with the help of valence electrons. Thus, they belong to the same group, group number 17.
Related Theory:
For neutral atoms, the number of valence electrons is equal to the atom’s main group number. The main group number for an element can be found from its column on the periodic table. The number of valence electrons of an element can be determined by the periodic table group (vertical column) in which the element is categorized. With the exception of groups 3-12 (the transition metals), the unit digit of the group number identifies how many valence electrons are associated with a neutral atom of an element listed under that particular column.
Caution
For identification of the elements, assess the group according to the valence electrons. Same number of valence electrons corresponds to the same chemical properties, and hence, same group.
(B) The eLements P, Q and R belong to groups 1, 14 and 17 respectiveLy of the Periodic Table. Which two elements will form Ionic compounds? Predict the formula of the compound. (1)
Answer:
For identifying which element will form ionic compounds, we need to compute the electronic configuration of these elements as shown below:
| Element | Electronic Configuration | Valency |
| P | 2,3 | 1 |
| Q | 2,7 | 4 |
| R | 2,8,7 | 1 |
It is evident from the above table that the valency of the elements P, Q and R are 1, 4 and 1 respectively. Ionic compounds are formed by transfer of electrons whereas covalent compounds are formed by sharing of electrons. Element P and R can easily lose or gain electrons to attain stability whereas element Q cannot lose or gain 4 electrons to attain stability.
Thus, elements P and R can form ionic compounds. The formula of the compounds will be as follows:
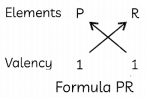
Related Theory
An ionic bond is formed by the complete transfer of some electrons from one atom to another. The atom losing one or more electrons becomes a cation-a positively charged ion. The atom gaining one or more electron becomes an anion-a negatively charged ion.
Caution
Students need to identify the valencies of the elements correctly. Once that is done, students need to criss-cross the valencies to form the compound. Usually the mistake will be done when the valencies of the elements are different.
Question 2.
A magnetic compass needle is placed in the plane of paper near point Q as shown in figure. In which plane should a straight current carrying conductor be pLaced so that it passes through Q and there is no change in the deflection of the compass? Under what condition is the deflection maximum and why?
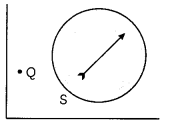
Answer:
When the magnetic field and direction of electric current are in the same plane, there would be deflection in the compass. For maximum deflection, magnetic field and direction of current should be in mutually perpendicular plane. So, for no deflection, conductors should be kept parallel to the magnetic compass. For maximum deflection, it should be placed perpendicular to the compass.
Related Theory
There is equation F = Bil sin θ (Not in syllabus) where F depends on i, l, B and angle θ.
For max F, sin θ = 1 when θ = 90°→ Perpendicular For min F, sin θ when θ = 0° → Parallel.
Caution
Though the given equation is not a part of your syllabus yet having a knowledge of it can help you in your understanding of many variable dynamics and relations.
Question 3.
(A) Rom reads a statement in a textbook which said “Genes controL characteristics or traits. Elaborate and justify this statement? (1)
Answer:
Tallness of a plant is a characteristic. Height of a plant depends on the amount of hormone secreted by the plant responsible for its tallness. The gene has the coding for the amount of hormone released. If the gene for that hormone has an alteration and makes its efficiency low, then the plant will be short. Thus, this shows that traits are controlled by gene.
(B) Traits acquired during the Lifetime (for example — Languages) of an individual not inherited. Justify this statement. (1)
Answer:
The traits can be inherited from one generation to the other only if there is a variation/change in DNA. The traits acquired during the lifetime of an individual may not bring change in the genes of DNA.
Question 4.
(A) Arrange the following in increasing order of boiLing point CH
4
, C
3
H
8
, C
5
H
12
, C
2
H
6
, C
8
H
18
(1)
Answer:
The increasing order of boiling points: C
8
H
18
>C
5
H
12
> C
3
H
8
> C
2
H
6
> CH
4
Explanation:
As the molecular mass increases by 14u after successive members of the homologous series, the boiling point increases as the Van der Waal’s interaction increases
(B) Identify the functional group present in the following; (1)
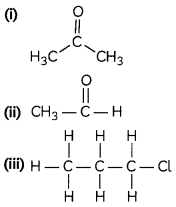
OR
Mention the 2nd and 4th member of CH
3
OH. (2)
Answer:
(i) Ketone group , —CO—
(ii) Aldehyde group, —CHO
(iii) Halogen group, -X= Cl
Explanation:
In the case of ketone, the carbonyl group is surrounded by alkyl group.
In case of aldehyde group, the carbonyl group is terminally placed. In the last option, the hydrogen is replaced by halogen group.
OR
2nd member of CH
3
OH is C
2
H
5
OH, and 4th member of CH
3
OH is C
4
H
14
OH Explanation: CH
3
OH is methanol which has alcohol as the functional group. The first member is CH4 in which one H is replaced with —OH. In a similar manner, the second member will be C
n
H
2n+1
—OH. Following this formula, we can determine the 2nd and 4th member of the series.
Question 5.
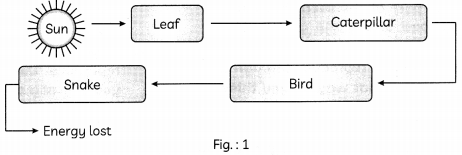
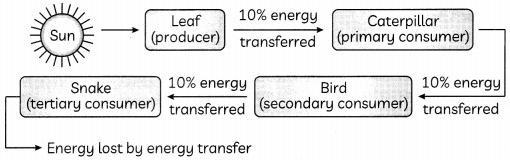
With the help of the given example in the given figure below, invoLving four organisms describe how energy flows through different trophic Levels. (Ref to Fig.: 1) (2)
OR
The figure shown below represent the energy flow in our biosphere. Refer to the diagram and answer the questions on the basis of the diagram given
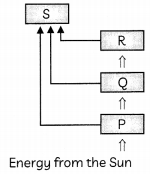
(A) Name the boxes represented by P, Q, and R. (1)
(B) What is S and why is it linked with all three boxes? (1)
Answer:
Leaf captures the sun’s energy and uses it to make organic compounds through photosynthesis but, only 1% of the energy is converted into glucose during photosynthesis. When these leaves are eaten by caterpillar most of the energy 90% is lost as heat. Only 10% of energy reaches to the next level of the consumers.
Caution
Do not get confused between units given in question& J stands for joule (unit of energy)
OR
(A) P-Producers, Q- Herbivores, R-Carnivores,
(B) S-represents decomposers. As decomposers can breakdown the dead remains of all living organisms, the box S is linked with all three boxes that represent producers (plants), herbivores and carnivores,
Caution
The representation shown here does not depict the energy from the sun, and decam poser.
Question 6.
How is the equal genetic contribution of male and female parents ensured in the progeny.
OR
“It is a possible that a trait is inherited but may not be express (iv)” Give a suitable example to justify this statement. (2)
Answer:
In human beings, equal genetic contribution of male and female parents is ensured in the progeny through inheritance of equal number of chromosomes from both parents. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes. All human chromosomes are not paired. Out of these 23 pairs, the first 22 pairs are known as autosomes and the remaining 1 pair is known as sex chromosomes represented as X and Y. FemaLes have a perfect pair of two X sex chromosomes and mates have a mismatched pair of one X and one Y sex chromosome.
During the course of reproduction, as fertilization process takes place, the male gamete (haploid) fuses with the female gamete (hapLoid) resulting in formation of the diploid zygote. The zygote in the progeny receives an equal contribution of genetic material from the parents. Out of 23 pairs of chromosomes in progeny, male parent contributes 22 autosomes and one X or Y chromosome while female parent contributes 22 autosomes and one X chromosome.
OR
It is possible that a trait is inherited but may not be expressed. This can be seen in the Mendel experiment. When pure tall pea plants are crossed with pure dwarf pea plants, only tall pea plants are obtained in Fi generation. On crossing tall plants of F
1
, both tall and dwarf plants are obtained in F
2
generation in the ratio 3 : 1. Reappearance of the dwarf character, a recessive trait in F
2
generation shows that the dwarf trait was present in individuals of F
1
but it did not got expressed, i.e. it was merely concealed or suppressed in the first generation to re-emerge in the second generation.
Question 7.
(A) Why are most carbon compounds poor conductors of electricity? (1)
Answer:
Carbon has 4 valence electrons which has the ability to form 4 covalent bonds. Thus, it is able to form a stable octet and thus there is no extra electron present in carbon compounds to conduct electricity. Due to lack of free electrons, they are not able to conduct electricity.
(B) Write the name and structure of a saturated compound in which the carbon atoms are arranged in a ring. Give the number of single bonds present in this compound. (1)
Answer:
A saturated compound consists of single covalent bond. According to the question, a cyclic saturated compound consists of a ring like structure consisting of single covalent bonds. One such example is cyclohexane.
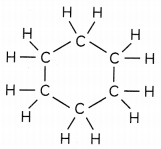
The number of single, covalent bonds in cyclohexane are 18 as follows:
C-H bonds: 12
C-C bonds: 6
Total number of single bonds: 18
SECTION – B
Question 8.
(A) If a harmful chemical enters the food chain comprising snakes, peacock, mice and plants, which of these organisms is likely to have the maximum concentration of this chemical in its body? (1)
(B) State the essential function performed by ozone at the higher levels of the atmosphere. (1)
(C) Why do producers always occupy the first trophic level on every food chain? (1)
OR
Suggest one word for each of the following statement and elaborate them.
(A) The physical and biological world where we live. (1)
(B) Each level of food chain where transfer of energy takes place. (1)
(C) Organisms which depend on the producers either directly or indirectly for food. (1)
Answer:
(A) Peacock
Caution:
Students gets confused as examiner will change the name of organism at top level like Peacock or hawk
Related Theory:
If a pollutant enters at producer’s level the organism at the top or highest level of food chain will have maximum concentration of the pollutants. This phenomena is known as biological magnification
(B) It shields the surface of the earth from ultraviolet (UV) radiation of the sun.
Related Theory:
Ozone layer depletion is one of the major problems for the atmosphere and also for all the living beings including the flora and fauna of this earth.
(C) The first trophic level is always a green plant because only plants can utilize the radiant energy of the sun and transform it to chemical form during photosynthesis
Related Theory:
Producers (plants) have the most energy in a food chain or web (beside the sun) and they give an organism more energy than a primary consumer or secondary consumer would.
OR
(A) Ecosystem: An ecosystem consists of biotic components comprising living organisms and abiotic components comprising physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil and minerals.
(B) Trophic level: A trophic level is a group of creatures in an environment that share the same food chain level. Within a food chain, there are five basic trophic levels, each of which has a different nutritional relationship with the primary energy source.
(C) Consumers: The organisms that consume the food produced. either directly from producers or indirectly by feeding on other consumers. Classed as herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and parasites.
Question 9.
The figure given below depicts the process of asexual reproduction in Plasmodium.
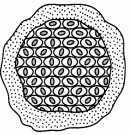
(A) Name the process depicted in the figure and define it. (1½)
Answer:
The process depicted in the given figure is Multiple Fission.
Multiple fission can be defined as an asexual method of reproduction in organisms in which the parent organism splits to form many new organisms at the same time.
(B) What is meant by asexuaL reproduction? (1½)
Answer:
The production of a new organism from a single parent without the involvement of sex cells or gametes is called asexual reproduction. For example: Budding in Hydra.
Question 10.
Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of five 2 V cells, a 5 ohm resistor, a 10 ohm resistor, a 15 ohm resistor, an ammeter and a plug key, all connected in series. Calculate the electric current passing through the above circuit when the key is closed. (3)
OR
(A) Mention two special features of the material used as an element of an electric iron. (1)
(B) How does potential difference (V) across a resistor depend on current passing through it? What is nature of I-V graph obtained? (2)
Answer:
Circuit diagram will be:
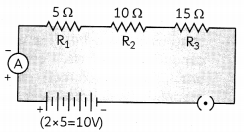
It is given that five cells of 2 V are connected in series, so total voltage of the battery:
V = 2 × 5 = 10V
These resistor of 5 Ω, 10 Ω and 15 Ω are connected in senes, so the net resistance
R = 5Ω + 10Ω + 15ST = 30Ω
According to Ohm’s law
V = IR
and I = \(\frac{V}{R}\)
On substituting resultant voltage (V) as 10 V and resultant resistant as 30 Ω we get
I = \(\frac{10 \mathrm{~V}}{30 \Omega}\) = 0.33 A
The electric current passing through the above circuit when the key is closed will be 0.33 A.
OR
(A) High melting point, High resistance
(B) The potential difference across a wire is akin to the pressure applied across a pipe containing water. The more the pressure the more the water that flows through the pipe. Similarly the more the potential difference the more the current through the wire and vice-versa. This is known as the Ohm’s law. The constant of proportionality is known as Resistance of the wire. The l-V graph is a straight line passing through the origin and lying on the x-y plane.
Question 11.
Flowers follow either self-pollination or cross-pollination. What could be the advantages and disadvantages of self-pollination over cross-pollination? (3)
Answer:
Advantages of self pollination:
- Flowers do not depend on other agencies for pollination.
- No wastage of pollen grains occur and thus, economical.
- The offsprings produced are of the same genetic make-up, so purity of the race is maintained.
Disadvantages of self pollination:
- Continuous self-pollination results in production of water.
- No chances or very less chances of variations and evolution.
- Defective character of breed are not eliminated.
Question 12.
(A) Why does a current carrying conductor, experience a force when it is placed in a magnetic field? (1½)
Answer:
When a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field, the wire experiences a force due to the interaction between the external magnetic field and the magnetic field produced by the moving charges in the wire. The current carrying conductor generates it own magnetic field around it. This interacts with the external magnetic field. When two magnetic fields interact there will be attraction and repulsion between them based on the direction of the external magnetic field and the direction of the current in the conductor. That is why the conductor experiences a force.
(B) A circuit has a line of 5 A. How may lamps of rating 40 W, 220 V can simultaneously glow on this line safely? (1½)
Answer:
We know that,
I = \(\frac{P}{V}=\frac{40 \mathrm{~W}}{200 \mathrm{~V}}\)
= \(\frac{2}{11}\)
= 0.182 A
0.182 A or \(\frac{2}{11}\) A is required by one lamp.
Current rating i.e.
maximum current = 5 A
No. of lamps
= \(\frac{\text { Current rating }}{\text { Current throughone lamp }}=\frac{5}{0.18}\)
= 27 lamps
Question 13.
(A) Identify the part of the seed that helps in storing food during the germination process. (1)
Answer:
Cotyledon
During germination, the cotyledon stores food. The food is needed to release energy in order to foster the growth of the plant. The seeds could be of monocot or dicot type based on the number of cotyledons they have.
(B) Hydra and Planaria reproduce through a similar mode. In what way do you think the reproduction pattern in Hydra is different from Planaria? (1)
Answer:
Hydra reproduces by budding. In Hydra, a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site. These buds develop into tiny individuals and when fully mature, detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals.
Planaria reproduces by regeneration. PLanaria can be cut into any number of pieces and each piece grows into a complete organism. Hence it is different from budding process.
(C) Leishmania and Plasmodium both reproduce through fission process. Do you see any variation in the pattern of reproduction? If yes, how? (1)
Answer:
Plasmodium, divides into many daughter cells simultaneously by multiple fission. While in Leishmania, the organism divides into two halves longitudinally.
SECTION – C
This section has 02 case-based questions (14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions (A, B and C). Parts A and B are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part C.
Question 14.
The following figure shows a part of the periodic table in which the elements are arranged according to their atomic numbers. (The letters given here are not the chemical symbols of the elements).
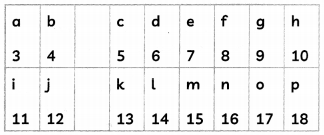
(A) Which element has a bigger atom, ‘a’ or f? (1)
Answer:
‘a’ (size decreases from left to right in a period).
(B) Which element has a higher valency ‘i’ or ‘o’? (1)
Answer:
‘k’ (valency of ‘k’ = 3; valency of ‘o’ = 1).
(C) (i) Which element is more metallic ‘i’ or ‘k’? (1)
(ii) Select the letter represent a non-metal or valency 2. (1)
OR
(i) Why metals are called electropositive elements? (1)
(ii) Name two elements you would expect to show chemical reactions similar to sodium. What is the basis for your choice? (1)
Answer:
(i) ‘i’ (metallic character decreases from left to right in a period).
(ii) ‘f'(or ‘n’)
OR
(i) Metals are called electropositive elements since their atoms form positive ions by losing electrons.
(ii) Potassium, K and Cesium, Cs are the metals that would show chemical reactions similar to sodium. This is because they have the same number of electrons in the outermost shell.
Question 15.
Consider a situation. A bar magnet, North pole pointing downwards is falling from a certain height, as shown.
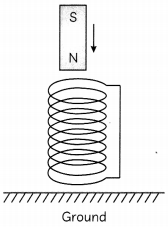
(A) Describe the vertical motion of the magnet as it approaches the solenoid and passes through it. (2)
(B) A magnetic compass shows a deflection when placed near a current carrying wire. How will the deflection of the compass get affected if the current in the wire is increased? Support your answer with a reason. (2)
OR
How does the magnetic field produced by a solenoid differ from that of a bar magnet? (2)
Answer:
(A) Initially when the magnet is far from the solenoid it will fall freely and accelerate downwards at a rate of 9.81 m/s
2
.
As it approaches the solenoid its rapidly changing magnetic flux through the solenoid will induce a current in the solenoid.
Owing to law of electromagnetic induction the current in the solenoid will generate a magnetic field which will oppose the magnetic field due to the bar magnet, as shown.
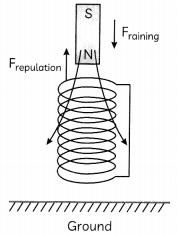
This repulsive force will slow down the magnet. As the magnet passes through the coll this repulsion will increase which will further slow down the falling magnet. Hence on emerging out of the coil the induced current in the coil will again Oppose the movement of the magnet and will further slow it down.
So the magnet will fall to the ground at a much slower speed than what it would have fallen had the coil not been there.
(B) A magnetic compass is made of magnetised iron that points to the earth’s pole. When another magnet is brought close enough, the compass will point in the direction of the second magnet since its magnetic strength is greater than that of the earth.
When a current carrying wire is introduced close to a magnetic compass, the magnetic compass will deflect due to the production of a magnetic field. A wire carrying electric current will have a magnetic field that forms concentric rings around it. One of the magnet’s ends will attract, while the other will repel, depending on its orientation. Because the electric field is exactly proportional to the magnetic field intensity, the deflection will rise as the current is increased. We can say that the magnetic field is stronger when the electric field is strong.
OR
A solenoid is a coil of numerous circular turns of wire wrapped in the shape of a cylinder. A solenoid’s magnetic field lines, through which current passes, are extremely similar to those of a bar magnet. The coil’s one end acts as a magnetic north pole, while the other works as a magnetic south pole. A long solenoid produces a magnetic field that is identical to that produced by a bar magnet.