Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 7 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 7 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
Instructions
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective-type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 4 marks each with sub-parts.
Section A
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20.
Question 1.
Identify the colour of wet blue litmus paper brought near the mouth of the delivery tube in the following experiment.
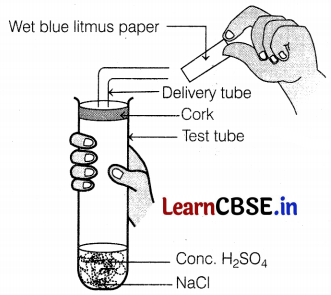
(a) The litmus paper will turn red
(b) The litmus paper will remain blue
(c) The litmus paper will turn green
(d) The litmus paper will dry
Answer:
(a) The litmus paper will turn red
The given experiment is carried out between concentrated sulphuric acid and sodium chloride, which react with each other to form HCl gas. HCl being acidic turns blue litmus red.
Question 2.
Which of the following is an example of a decomposition reaction?
(a) Burning of paper
(b) Rusting of iron
(c) Formation of water from hydrogen and oxygen
(d) Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen
Answer:
(d) Decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen
Explanation: A decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction in which a compound breaks down into simpler substances. Hydrogen peroxide (H
2
O
2
) decomposes into water (H
2
O) and oxygen (O
2
). This reaction is commonly observed and can be catalyzed by various factors such as heat or the presence of a catalyst like manganese dioxide (MnO
2
). Option (a) represents a combustion reaction, option (b) represents an oxidation reaction, and option (c) represents a synthesis reaction.
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series?
(a) CH
4
(b) C
2
H
6
(c) C
3
H
8
(d) C
4
H
8
Answer:
(d) C
4
H
8
C
4
H
8
does not belong to the same homologous series because successive members of a homologous series differ by -CH
2
unit.
Question 4.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver?
(a) Detoxification of harmful substances
(c) Regulation of blood sugar levels
(b) Production of bile for digestion
(d) Production of red blood cells
Answer:
(d) Production of red blood cells
Explanation: The liver performs numerous vital functions in the human body but is not responsible for producing red blood cells.
(a) The liver plays a crucial role in detoxifying harmful substances, such as drugs and alcohol, by breaking them down into less harmful forms that can be excreted from the body.
(b) The liver produces bile, a greenish-yellow fluid that aids in the digestion and absorption of fats in the small intestine.
(c) The liver plays a key role in maintaining blood sugar levels by storing excess glucose as glycogen and releasing it when blood sugar levels drop.
(d) Although the liver is involved in the breakdown of old or damaged red blood cells, the primary site of red blood cell production is the bone marrow, not the liver.
Understanding the liver’s functions is essential for recognizing that it does not produce red blood cells.
Question 5.
A girl met with an accident and her leg got fractured. She went to an orthopedics for treatment. The doctor mixed a white powder in water and applied it to her leg. What could be the white powder?
(a) Talcum powder
(b) Gypsum
(c) Plaster of Paris
(d) Copper phosphate
Answer:
(c) Plaster of Paris
Plaster of Paris reacts with water and turns into a solid hard mass known as gypsum which is used to fix fractures.
Question 6.
Which of the following properties is generally not shown by metals?
(a) Electrical conduction
(c) Dullness
(b) Sonorous
(d) Ductility
Answer:
(c) Dullness
Explanation: Metals have the quality of reflecting light from their surface and can be polished. They 8 are not dull but lustrous.
Question 7.
On adding some copper turnings to silver nitrate solution what will you observe?
(a) The solution turned blue
(b) Yellow precipitate was formed
(c) White precipitate was formed
(d) The solution turned red
Answer:
(a) The solution turned blue
When copper turnings are added to silver nitrate solution, a blue-colored solution is formed after some time because copper is oxidized to Cu
2+
ions and forms copper nitrate. It displaces silver from its solution and forms a blue-colored solution of Cu(NO
3
)
2
.
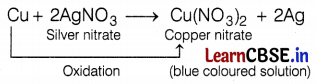
![]()
Question 8.
Name the layers of brain meninges from the inside towards the outside:
(a) Duramater, Arachnoid and Piamater
(b) Arachnoid, Duramater and Piamater
(c) Piamater, Arachnoid and Duramater
(d) Arachnoid, Piamater and Duramater
Answer:
(c) Piamater, Arachnoid and Duramater
Explanation: The brain is protected by cranial meninges, which are made up of three layers: an outside layer called duramater, a very thin middle layer called arachnoid, and an inner layer called piamater (which is in contact with the brain tissue). Thus, the layer of the brain from inside towards the outside is: Piamater, Arachnoid and Duramater.
Question 9.
Which of the following is embedded in the uterine wall?
(a) Zygote
(b) Embryo’s head
(c) Placenta
(d) Eggs
Answer:
(c) Placenta
The placenta is embedded in the uterine wall.
Question 10.
Which of the following is an advantage of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
(a) Rapid population growth
(b) Greater adaptability to changing environments
(c) Production of genetically identical offspring
(d) Conservation of energy and resources
Answer:
(b) Greater adaptability to changing environments
Explanation:
(a) Asexual reproduction often leads to rapid population growth because offspring are produced without the need for a partner. However, this is not an advantage of sexual reproduction, which involves the fusion of gametes and typically has a slower reproductive rate.
: (a) Sexual reproduction allows for genetic recombination, which leads to offspring with a mix of genetic traits from both parents. (b) Sexual reproduction allows for genetic recombination, which leads to offspring with a mix of genetic traits from both parents.
asexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent . asexual reproduction results in offspring that are genetically identical to the parent .
: (c) Asexual reproduction is generally more efficient in terms of energy and resource conservation since it does not require the production of gametes or the search for a mating partner. (d) Asexual reproduction is generally more efficient in terms of energy and resource conservation since it does not require the production of gametes or the search for a mating partner.
Question 11.
Blood glucose levels are regulated in the human body by the secretion of two hormones. Which hormone is secreted when glucose concentration increases in blood?
(a) Insulin
(b) Glucagon
(c) ADH
(d) Thyroxine
Answer:
(a) Insulin
Insulin is responsible for lowering the blood glucose level whereas glucagon is opposite in function. Hence, deficiency of insulin in the body leads to diabetes mellitus.
Question 12.
Which of the following statements is not true about genes?
(a) Gene is a sequence of nucleotides.
(b) During the process of gene expression, DNA is first copied into RNA.
(c) Genes can acquire mutations in their sequence.
(d) Genes cannot acquire mutations in their sequence.
Answer:
(d) Genes cannot acquire mutations in their sequence.
Explanation: Genes can acquire mutations. A gene mutation is a change in the DNA sequence that ( makes up a permanent gene and differs from the sequence found in most people.
![]()
Question 13.
The radius of curvature of a concave mirror is 12 cm. Then, the focal length will be
(a) 12 cm
(b) 6 cm
(c) -24 cm
(d) -6 cm
Answer:
(d) -6 cm
Given, the radius of curvature, R = 12 cm
We know that the focal length of the concave mirror has a negative value.
Hence, focal length, f = \(\frac{-R}{2}=\frac{-12}{2}\) = -6 cm
Question 14.
Which of the following statements is NOT true regarding asexual reproduction in plants?
(a) Plants that reproduce asexually reach maturity faster than those who reproduce sexually.
(b) Plants that reproduce asexually have greater genetic diversity than those that reproduce sexually.
(c) Plants that reproduce asexually are more stable than those that reproduce sexually.
(d) Plants that reproduce asexually create offspring that are identical to the parent plant.
Answer:
(b) Plants that reproduce asexually have greater genetic diversity than those that reproduce sexually.
Explanation: Asexual reproduction in plants involves the production of offspring without the need for the fusion of gametes. Asexual reproduction allows plants to produce offspring more rapidly since they don’t need to go through the process of producing flowers, attracting pollinators, and developing seeds.
False
Question 15.
Surgical methods of birth control include
(a) vasectomy and spermicide
(b) intra-uterine device and tubectomy
(c) vasectomy and tubectomy
(d) tubectomy and spermicide
Answer:
(c) vasectomy and tubectomy
In vasectomy (males) a small portion of vas deferens is removed or tied. In tubectomy, (females) a small portion of the fallopian tube is removed or tied.
Question 16.
A couple has two children, one with blue eyes and the other with brown eyes. Both parents have brown
eyes. Which of the following options best explains this scenario?
(a) Eye colour follows a dominant-recessive pattern, with blue eyes being the dominant trait.
(b) Eye colour follows a dominant-recessive pattern, with brown eyes being the dominant trait.
(c) Eye colour is determined by multiple genes and is not strictly governed by a dominant-recessive pattern.
(d) Eye colour is determined solely by environmental factors and is not influenced by genetics.
Answer:
(b) Eye colour follows a dominant-recessive pattern, with brown eyes being the dominant trait.
Explanation: The inheritance of eye colour follows a more complex pattern than a simple dominant-recessive relationship. However, in this specific scenario, where both parents have brown eyes and one child has blue eyes, it can be inferred that brown eyes (the trait observed in the parents) are dominant over blue eyes. This is because the child inherited a recessive allele for blue eyes from both: parents, resulting in the expression of the recessive trait.
Directions (Q.Nos. 17-20) Consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R) Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Carbon and its compounds are used as fuel for most applications.
Reason (R): On combustion of carbon, a large amount of heat and light is released.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Carbon burns in oxygen (air) to form carbon dioxide and water. During the reaction, a large amount of heat and light is released. Hence, they are used as fuels. Carbon and its compounds keep burning without the requirement of additional energy.
![]()
Question 18.
Assertion: The testes descend into the scrotum just before birth.
Reason: Human males have two testes in the body.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A
Explanation: The descent of the testes into the scrotum just before birth is a normal physiological process. By descending into the scrotum, the testes are positioned outside the body, where the temperature is lower than inside the abdominal cavity. This temperature regulation is essential for the proper development and maturation of sperm cells, ensuring fertility and reproductive function in males.
![]()
Question 19.
Assertion (A): Blood clotting prevents the leakage of blood from the site of an injury.
Reason (R): Platelets circulate the body and plug these leaks.
Answer:
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of A.
Platelets clump together and form a plug around the site of injury, preventing the leakage of blood from the site of an injury.
Question 20.
Assertion: Damage to the medulla oblongata causes death.
Reason: Medulla oblongata controls involuntary functions of the body.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A
Explanation: The medulla oblongata is a vital part of the brainstem located at the base of the brain. It is responsible for regulating various essential functions of the body, including involuntary activities such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and swallowing.
True
Section B
Questions No. 21 to 26 are Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 21.
When zinc metal is treated with a dilute solution of a strong acid, a gas is evolved, which is utilised in the hydrogenation of oil. Name the gas evolved. Write the chemical equation of the reaction involved and also write a test to detect the gas formed.
Answer:
When zinc reacts with dilute solution of strong acid (like hydrochloric acid HCl), it forms salt and hydrogen gas is evolved which is used in the hydrogenation of oil.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl
2
+ H
2
↑
To test the presence of H
2
gas, a burning splinter is brought near the mouth of the test tube, the gas burns with a pop sound. (2)
Question 22.
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F
1
and F
2
generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F
2
generation plants.
Answer:
Mendel used pea plant (Pisum sativum), when he crossed tall and short plants the progeny obtained in F
1
generation were tall. When the F
1
plants were self crossed the F
2
generations showed three tall and one dwarf plant. The genotypic ratio of F
2
generation is 1: 2: 1.
(TT: Tt: Tt: tt)
The phenotypic ratio is 3 :1 (Tall: Dwarf)

Question 23.
In mammals separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood is necessary. Why?
Or
Which blood corpuscle has haemoglobin pigment? What is its function?
Answer:
In higher animals, the energy needed is very high to maintain homeostasis because of which the requirement of O
2
is very high. Thus, they need fully saturated blood with oxygen, not mixed with deoxygenated blood, so their separation is necessary. (2)
Or
A red coloured pigment called haemoglobin is present in the cytoplasm of RBC. It combines with oxygen for its transportation. (1)
The main function of RBC (Red Blood Corpuscle) is to transport oxygen from the lungs to different body parts and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs. (1)
Question 24.
How is sodium hydroxide manufactured in industries? Name the process. In this process, a gas X is formed as a by-product. This gas reacts with lime water to give a compound Y, which is used as a bleaching agent in the chemical industry. Identify X and Y and write the chemical equation of the reaction involved.
OR
A sanitary worker uses a white chemical having a strong smell of chlorine gas to disinfect the water tank:
(i) Identify the chemical compound, and write its chemical formula.
(ii) Give chemical equations for its preparation.
(iii) Write its two uses this compound other than disinfection.
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide is manufactured by the electrolysis of concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride.

The process of manufacture of sodium hydroxide by electrolysis process is called the chlor-alkali process. Gas X is chlorine gas and compound Y is calcium oxychloride (Bleaching powder).

OR
(i) The compound is bleaching powder and its chemical formula is CaOCl
2
.
(ii) Ca(OH)
2
+ Cl
2
→ CaOCl
2
+ H
2
O
(iii) (1) It is used as a bleaching agent in the textile industry.
(2) It is also used in paper industry.
![]()
Question 25.
Find the distance at which an object should be placed in front of a convex lens of focal length 10 cm to obtain an image of double its size.
Or
(a) Why does the sky appear dark instead of blue to an astronaut?
(b) Why does the sun appear reddish early in the morning?
Answer:
Given, focal length of lens, f = 10 cm
Distance of an object, u = ?
In convex lens, the image is real and virtual.
∴ Magnification, m = \(\frac{v}{u}\) = ±2
⇒ v = ±2u
Using lens formula, \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}\)
Case I: If v = +2u
\(\frac{1}{10}=\frac{1}{2 u}-\frac{1}{u}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{10}=\frac{1-2}{2 u}=\frac{-1}{2 u}\)
⇒ u = -5 cm
Case II: If v = -2u
\(\frac{1}{10}=\frac{1}{-2 u}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{-1-2}{2 u}=\frac{-3}{2 u}\)
⇒ u = -15 cm (2)
Or
(a) The sky appears dark to the astronauts because there is no atmosphere and hence, no scattering of light takes place in space. (1)
(b) At sunrise and sunset, the sun and the sky appear red. Light from the sun near the horizon passes through thicker layers of air and covers a larger distance in the atmosphere before reaching our eyes. Near the horizon, most of the blue light and shorter wavelengths are scattered away by the particles. Therefore, the light that reaches our eyes is of longer wavelengths. This gives rise to the reddish appearance of the sun and the sky. (1)
Question 26.
What is biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different levels of the ecosystem?
Answer:
The increase in concentration of harmful toxic substances in the body of organisms at each trophic level of a food chain is called biological magnification. Yes, the levels of this magnification will be different at different levels of the ecosystem because the concentration of chemicals goes on increasing at different trophic levels. It is maximum at higher trophic levels and minimum at lower trophic levels. Suppose a food chain is Grass → Rabbit → Eagle, it will be the highest in eagle and minimum in the grass.
Section C
Questions No. 27 to 33 are Short Answer Questions.
Question 27.
Study the reactions given below:
Which of the following chemical reactions will occur? Give a suitable reason for each.
(a) Zn (s) + CuSO
4
(aq) → ZnSO
4
(aq) + Cu (s)
(b) Fe (s) + ZnSO
4
(aq) → FeSO
4
(aq) + Zn (s)
(c) Zn (s) + FeSO
4
(aq) → ZnSO
4
(aq) + Fe (s)
Answer:
(a) Zinc is more reactive than copper. So, it will displace copper from CuSO4. Hence, this reaction will take place. (1)
(b) Iron is less reactive than zinc, so it cannot displace zinc from zinc sulphate solution. The reaction will not take place. (1)
(c) Zinc is more reactive than iron, it will displace iron from FeSO4 solution. Hence, this reaction will take place. (1)
Question 28.
Briefly describe different methods of wastes disposal.
Answer:
The various methods of waste disposal are:
- Land-fills: In urban areas, wastes are filled or deposited in low lying areas. These are also known as dumping grounds where wastes are buried.
- Recycling of wastes: Some wastes, like papers, plastics, metals etc., which can be recycled are sent to special recycling treatment plants so that new substances can be made from them.
- Preparation of compost: Biodegradable wastes like kitchen wastes, peels of fruits and vegetables etc., can be used to prepare compost which serves as good manure for the plants.
- Incineration: Some wastes like medical wastes, and chemical wastes are burnt at very high temperature in an incinerator and the ashes left behind are disposed by landfills.
- Production of biogas: Biodegradable wastes can be used in biogas plants to produce biogas which is used for several purposes, like as a fuel.
Question 29.
‘A trait may be inherited, but may not be expressed’. Justify this statement with the help of a suitable example.
Answer:
Let us take the following example to justify the given statement. Mendel crossed tall pea plants with dwarf pea plants.
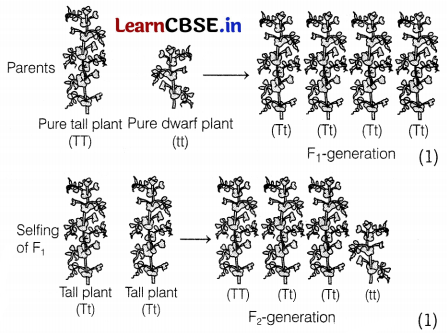
Mendel’s observation F
1
generation contained all tall plants with genotype Tt, where T represents a dominant trait and ‘t’ represents a recessive trait. When Frgeneration underwent selfing, the trait that was unexpressed in F
1
(dwarf) was observed in some F2 progeny. Thus, both traits, tall and dwarf, were expressed in F
2
-generation in the ratio of 3 : 1. (1)
![]()
Question 30.
While preparing a cake, baking powder is generally used. However, if your mother decides to use baking
soda instead of baking powder for the cake recipe at home.
(i) How will it affect the taste of the cake and why?
(ii) How can baking soda be converted into baking powder?
(iii) What is the role of tartaric acid added to baking soda?
Answer:
(i) Baking soda is sodium hydrogen carbonate, on heating, it is converted into sodium carbonate which is bitter in taste. Thus, if baking soda is used, the taste of the cake changes.
2NaHCO
3
→ Na
2
CO
3
+ H
2
O + CO
2
(ii) Baking powder is a mixture of baking soda, cream of tartar (a dry acid), and sometimes com starch . Therefore, baking soda can be converted into baking powder by the addition of an appropriate amount of tartaric acid to it.
(iii) Tartaric acid is added to neutralise the sodium carbonate formed on heating by the decomposition of NaHCO 3 . If it is not added, the cake would taste bitter due to the presence of sodium carbonate in it. Also, CO 2 produced during the reaction causes the cake to rise making them soft and spongy.
Question 31.
Three 2 Ω resistors, A, B, and C are connected as shown in the figure. Each of them dissipates energy and can withstand a maximum power of 18 W without melting.
(a) Find the maximum current that can flow through the resistor A.
(b) Find the maximum current that can flow through resistors B and C.
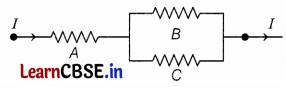
Answer:
(a) Given, resistance, R = 2 Ω
Maximum power, P
max
= 18W
Maximum current, I
max
=?
As we know, P = I
2
R
⇒ I = \(\sqrt{\frac{P}{R}}=\sqrt{\frac{18}{2}}\) = 3A = I
max
The maximum current that can flow through resistor A is 3A. This current divides along B and C because they are in parallel combinations.
(b) Voltage across B and C remain the same and hence I ∝ \(\frac{1}{R}\)
Since B and C have the same resistance same current flows through them.
i.e. \(\frac{3}{2}\) = 1.5A flows through B and C.
Question 32.
How do the guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomatal pores?
Answer:
Guard cells are kidney shaped cells which contain thicker inner walls and thin outer walls. During day time they perform the photosynthesis process due to the presence of chloroplasts in them. When there is an increase in solute concentration inside the guard cells, water from subsidiary cells rushes inside through osmosis as a result guard cells swell up. The thin outer wall bulges out and the thick inner wall is pulled inside thus stomata opens. During night time reverse happens, water rushes out from the guard cells and they become flaccid closing the stomatal pore. Thus, turgour pressure of guard cells helps in the closing and opening of stomata.

Question 33.
Why should biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes be discarded in two separate dustbins? Also, mention about 3R’s.
Answer:
3R is an initiative that can be used to minimize and manage waste generation, usage, and disposal. Biodegradable materials are broken down by microorganisms in nature into simple harmless substances. Non-biodegradable materials need different treatments like heat and temperature for disposal and hence, both should be discarded in two different dustbins. (1)
The 3 R’s are as follows.
- Reduce: This means to cut back on the amount of trash we generate.
- Reuse: It means to find new ways to use things that otherwise would have been thrown out.
- Recycle: This means to turn something old and useless like plastic into something new and useful (like picnic benches, to make roads, etc.) (2)
Section D
Questions No. 34 to 36 are Long Answer Questions.
Question 34.
Define a chemical reaction. State four observations which help us to determine that a chemical reaction has occused. Write one example of each of the observations with a balanced chemical equation.
OR
When two or more substances react and form some new substance, it is called a chemical reaction. As we know, all chemical reaction obeys law of chemical combination. Therefore, chemical reactions need to be balanced. It is done by hit and trial method. The chemical reactions can be classified into different types such as combination reaction, decomposition reaction, displacement reaction, double displacement reaction. The reactions take place in solution is precipitation reactions and neutralization reactions.

(i) Define a chemical reaction.
(ii) Which law is followed by all chemical reactions?
(iii) Name four types of chemical reactions.
(iv) Give an example of precipitation reactions.
Answer:
A chemical reaction is the transformation of a chemical substance into another chemical substance. Only a rearrangement of atoms takes place in a chemical reaction. Old bonds are broken, and new bonds are formed.
Some of the characteristics of chemical reactions are:
1. Change in colour: In some reactions, there is a change in colour after the reaction. For example, the chemical reaction between potassium iodide solution and lead nitrate solution is characterised by the change in colour from colourless to the appearance of yellow colour due to the formation of lead iodide.

2. state change: In some reactions, a change of state takes place during the reaction. The reaction might start with gaseous or liquid reactants, but end up with a solid product and vice-versa. For example: Ammonia gas reacts with hydrogen chloride gas to produce solid ammonium chloride.
NH
3
(g) + HCl(g) → NH
4
Cl (s)
3. temperature change: Temperature change is characteristic of many reactions. For example, the chemical reaction between quicklime and water forms slaked lime. In this reaction, the temperature of the reaction is increased due to the evolution of heat.
CaO(s) + H
2
O(Q) → Ca (OH)
2
(aq) + Heat
4. Evolution of gas: Some reactions are characterized by the evolution of gas as a result of chemical reactions. For example, the chemical reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric acid is characterized by the evolution of hydrogen gas.
Zn(s) + H
2
SO
4
(aq) → ZnS0
4
(s) + H
2
(g)
OR
(i) A chemical reaction is defined as a reaction in which two or more substances react to form a new substance.
(ii) All chemical reactions follow the law of chemical combination.
(iii) Combination reactions, displacement reactions, double displacement reactions, and decomposition reactions are four types of chemical reactions.
(iv) The reaction between silver nitrate and sodium chloride that forms a precipitate of silver chloride is an example of a precipitation reaction.

![]()
Question 35.
(a) Why does menstruation occur?
(b) Sexual act always has the potential to result in pregnancy. What are the various ways to avoid pregnancy? Elaborate on any one method.
Or
Mention the functions of the following.
(a) Medulla oblongata
(b) Olfactory lobes
(c) Cerebellum
(d) Hypothalamus
(e) Cerebrum
Answer:
(a) Menstruation occurs when the egg is not fertilized. Every month, the uterus prepares itself to receive a fertilized egg. In case, the egg is not fertilized, this lining breaks and discharges out from the body through the vagina in the form of blood. This is called menstruation. (2)
(b) Ways to avoid pregnancy are called contraceptive methods. It includes
- Mechanical barrier
- Drugs (pills)
- IUCD, e.g. copper-T
- Surgical method for permanent contraception. (2)
Condoms: It is a fine rubber balloon-like structure worn over the penis during sexual intercourse. Semen is collected in it and not discharged into the vagina. This method also prevents the spread of STDs such as AIDS. (1)
Or
The functions of different parts of the brain are
- Medulla oblongata: It controls involuntary actions and regulates reflex responses. It also controls blood pressure, salivation, and vomiting.
- Cerebellum: It controls and coordinates different muscular actions. It is responsible for voluntary actions and maintains the equilibrium of the body during walking, drinking, catching, etc.
- Cerebrum: performs thinking, reasoning, speech, intelligence, and usage of information.
- Olfactory lobes are responsible for detecting smell from different receptors.
- The hypothalamus controls body temperature, urge to eat, drink, etc.
Question 36.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Define the focal length of a divergent lens.
(ii) A divergent lens of focal length 30 cm forms the image of an object of size 6 cm on the same side as the object at a distance of 15 cm from its optical centre. Use the lens formula to determine the distance of the object from the lens and the size of the image formed.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in the above situation.
OR
A students needs spectacles of power – 0.5 D for the correction of his vision.
(i) Name of defect in vision the student in suffering from.
(ii) Find the nature and focal length of the corrective lens.
(iii) List two causes of this defect.
Answer:
(i) The point from which parallel rays of light, after refraction from a lens, appear to diverge is called focus of the divergent lens, and the distance between optical centre and this focus of a divergent lens is called the focal length of divergent lens.
(ii) Focal length of the divergent lens,
f = – 30 cm
Image distance, υ = -15 cm
Object height, h
1
= 6 cm
We know that, \(\frac{1}{f}=\frac{1}{υ}-\frac{1}{u}\)
or \(\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{υ}-\frac{1}{f}\)

OR
(i) Myopia
(ii) Concave lens with the focal length of 200 cm
Given, P = -0.5 D
We have, P = \(\frac{1}{f}\)m
f = \(\frac{1}{P}=\frac{1}{(-0.5)}\)
f = – 2m
f = – 200 cm
(iii) Two cause of Myopia are:
1. Elongation of eye ball.
2. High converging power of lens.
Section E
Questions No. 37 to 39 are case-based/data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
The table given below shows the hints given by the quiz master in a quiz.
| Hints |
| (i) ‘A’ is an organic compound, containing 2 carbon atoms. |
| (ii) Compound ‘A’ is used as a solvent. |
| (iii) ‘A’ on heating with conc. H 2 SO 4 forms a compound ‘B’. |
| (iv) ‘B’ on the addition of one mole of hydrogen in the presence of ‘Ni’ forms a compound ‘C’. |
| (v) One mole of ‘C’ on heating forms one mole of CO 2 and three moles of H 2 O. |
Based on the above hints answer the following questions.
(a) Give the IUPAC name of A and B.
(b) Write the chemical equation of the reactions involved. (A → B and B → C).
Or
Name the chemical reaction which occurs in steps 3 and 5. Draw the electron dot structure of compound C.
Answer:
(a) A = Ethanol, B = Ethene (2)
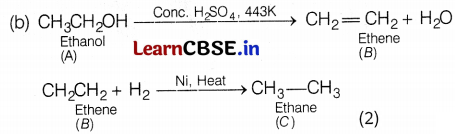
Or
The chemical reaction that occurs in step (iii) is called dehydration and in step (v) is the combustion reaction.
Dehydration, Combustion.
Electron dot structure of ethane (C
2
H
6
)
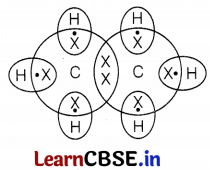
Question 38.
The food material taken in during the process of nutrition is used in cells to provide energy for various life processes. Diverse organisms do this in different ways – some use oxygen to break-down glucose completely into carbon dioxide and water, some use other pathways that do not involve oxygen. In all cases, the first step is the break-down of glucose, a six-carbon molecule, into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. This process takes place in the cytoplasm. Further, the pyruvate may be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide. This process takes place in yeast during fermentation. Since this process occurs in the absence of air (oxygen), it is called anaerobic respiration. Break- down of pyruvate using oxygen takes place in the mitochondria. This process breaks up the three-carbon pyruvate molecule to give three molecules of carbon dioxide. The other product is water. Since this process takes place in the presence of air (oxygen), it is called aerobic respiration.
The following process is carried out:

1. Take some freshly prepared lime water in a test tube.
2. Blow air through this lime water.
3. Note how long it takes for the lime water to turn milky.
4. Use a syringe or pichkari to pass air through some fresh lime water taken in another test tube.
5 .Note how long it takes for this lime water to turn milky.
6. It is observed that the syringe takes more time to turn lime water milky
(a) Explain why lime water turn milky instantaneously?
(b) Why syringe takes more time to turn lime water milky?
(c) Name the process through which carbon dioxide is released?
OR
Name the process in which carbon dioxide is absorbed?
Answer:
(a) Our body cells produce carbon dioxide through the oxidation of food. This gas is exhaled outside through the lungs. Lime water reacts with CO, to form an insoluble precipitate. This turns lime water milky.
Falco: syringe takes more time to turn lime water milky because the syringe push atmospheric air throv the lime water . Atmospheric air has less quantity of carbon dioxide. Therefore, it takes more time to turn lime water milky .
(c) Through the process of Respiration, carbon dioxide is released.
OR
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create ox and energy in sugar. Thus, in this process, carbon dioxide is absorbed.
![]()
Question 39.
The refractive index of a medium concerning vacuum is called the absolute refractive index of the medium. It is given by, µ = \(\frac{\sin i}{\sin r}\)
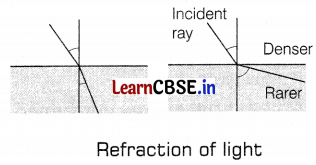
Absolute refractive indices of some of the materials A, B, C, and D are given in the following table.
| Medium | Refractive Index |
| A | 1.54 |
| B | 1.33 |
| C | 2.42 |
| D | 1.65 |
(a) How is the absolute refractive index related to the speed of light?
(b) In which of the material given in the above table, light travels fastest?
(c) The speed of light in air is 3 × 10
8
ms
-1
and that in medium X is 2.5 × 10
8
ms
-1
. Then, find the refractive index of medium X.
Or
If the refractive index of P concerning Q is 2. Then, find the refractive index of Q concerning P.
Answer:
(a) Absolute refractive index (µ)

(b) Since B has the least refractive index, it indicates that B is much optically rarer than all other mediums, hence light travels fastest in medium B. (1)
(c) Refractive index of X

Or
Given,
Q
µ
P
= 2
∴ The refractive index of Q w.r.t, P is,
\(P \mu_Q=\frac{1}{Q \mu_P}=\frac{1}{2}=0.5\) (2)