Students must start practicing the questions from CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions Set 3 are designed as per the revised syllabus.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 3 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
Instructions
- This question paper consists of 39 questions in 5 sections.
- All questions are compulsory. However, an internal choice is provided in some questions. A student is expected to attempt only one of these questions.
- Section A consists of 20 objective-type questions carrying 1 mark each.
- Section B consists of 6 Very Short questions carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- Section C consists of 7 Short Answer questions with 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- Section D consists of 3 Long Answer questions with 5 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- Section E consists of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment of 4 marks each with sub-parts.
Section A
Select and write the most appropriate option out of the four options given for each of the questions 1-20.
Question 1.
A reactive metal (M) is treated with H
2
SO
4
(dil). The gas is evolved and is collected over the water as shown in the figure.
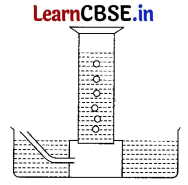
The correct conclusion drawn is/are (1)
(a) the gas is hydrogen
(b) the gas is lighter than the air
(c) the gas is SO
2
and is lighter than air
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(d) Both (a) and (b)
When any reactive metal (M) reacts with the acid H
2
SO
4
(dil.), it evolves hydrogen gas (H
2
), which is lighter than air.
M (s) + H
2
SO
4
(dil.) → MSO
4
+ H
2
(g)
Question 2.
Metals are refined by using different methods. Which of the following metals are refined by electrolytic refining?
(i) Au
(ii) Cu
(iii) Na
(iv) K
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (i) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iii)
(D) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(A) (i) and (ii)
Explanation: Sodium and potassium are extracted by electrolytic reduction. Metals obtained after electrolytic reduction are in pure form. But, copper and gold are in impure form after extraction. Copper and gold are refined by electrolytic refining methods.
Question 3.
Name the given compound. (1)
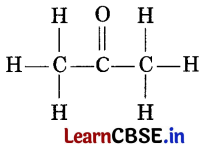
(a) Propanone
(b) Butanal
(c) Propane
(d) Propanoic acid
Answer:
(a) Propanone
![]()
Question 4.
While studying the saponification reaction, what do you observe when you mix an equal amount of colourless vegetable oil and 20% aqueous solution of NaOH in a beaker?
(A) The colour of the mixture has become dark brown.
(B) A brisk effervescence is taking place in the beaker.
(C) The outer surface of the beaker has become hot.
(D) The outer surface of the beaker has become cold.
Answer:
(C) The outer surface of the beaker has become hot.
Explanation: The beaker becomes hot because it is an exothermic reaction.
Question 5.
Which of the following acids does not give hydrogen gas on reacting with metals (except Mn and Mg)? (1)
(a) HNO
3
(b) HCl
(c) H
2
SO
4
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) HNO
3
Nitric acid (HNO
3
) reacting with metals (except Mn and Mg) does not give hydrogen gas. Because it is a strong oxidizing agent, as soon as hydrogen gas is formed in the reaction between metal and dil. HNO
3
, the nitric acid oxidizes this hydrogen into water.
Question 6.
Two salts X and Y are dissolved in water separately. When phenolphthalein is added to these two solutions solution X turns pink and solution Y does not show any change in colour, therefore X and Y are:
(x) (y)
(A) Na
2
CO
3
NH
4
C1
(B) Na
2
SO
4
NaHCO
3
(C) NH
4
Cl Na
2
SO
4
(D) NaNO
3
Na
2
SO
4
Answer:
(A) Na
2
CO
3
NH
4
C1
Explanation: Phenolphthalein gives pink colour in a basic pH range from 8.2 to 10. When phenolphthalein is added to Na
2
CO
3
solution, which is a basic solution, the solution will turn pink in colour. However, when phenolphthalein is added to NH
4
Cl, which is an acidic solution, the solution will remain colourless.
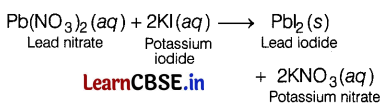
Question 7.
Complete the missing variables given as ‘x’ and ‘y’ in the following reaction. (1)
Pb(NO
3
)
2
(aq) + 2KI (aq) → PbI
2
(x) + 2KNO
3
(y)
(a) (aq) and (aq)
(b) (s) and (s)
(d) (aq) and (s)
(d) (s) and (aq)
Answer:
(d) (s) and (aq)
When lead nitrate reacts with a potassium iodide solution, then insoluble solid precipitates of lead iodide are formed along with the potassium nitrate solution.
Question 8.
In plants the role of cytokinin is:
(A) Promote cell division
(B) Wilting of leaves
(C) Promote the opening of stomatal pore
(D) Help in the growth of stem
Answer:
(A) Promote cell division
Explanation: Cytokinin regulates the cell division by promoting it in the plants.
Question 9.
The diagram given below shows a vertical section through the heart.
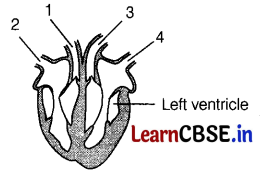
What are the functions of the numbered blood vessels? (1)
| Carries blood to the body | Carries blood to lungs | Carries blood from lungs | Carries blood from the body | |
| (a) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| (b) | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 |
| (c) | 2 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| (d) | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 |
Answer:
(d) 1. Pulmonary arteries – carry blood to the lungs.
2. Vena cava – carries blood from the body.
3. Aorta – carries blood from heart to body.
4. Pulmonary veins – carry blood from the lungs to the heart.
![]()
Question 10.
Observe the following diagram and identify the process and its significance from the following options:
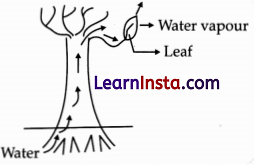
(A) Evaporation: maintains water contents in leaf cells.
(B) Transpiration: creates a suction force which pulls water inside the plant.
(C) Excretion: helps in excreting out waste water from the plant.
(D) Translocation: helps in transporting materials from one cell to another.
Answer:
(B) Transpiration: creates a suction force which pulls water inside the plant.
Explanation: The loss of water vapour through the stomata present on the surface of leaves is called transpiration. It creates a suction pressure for the upward movement of water in all tall trees.
Question 11.
Which of the following options represents the function of nodes of Ranvier? (1)
(a) It is a functional unit of nerve
(b) It conducts impulses toward the nerve cell body
(c) It speeds up the impulse transmission
(d) It provides electric insulation
Answer:
(c) It speeds up the impulse transmission
The nodes of Ranvier are gaps along the myelin sheath that covers the axon of neuron cells. They speed up impulse transmission that runs along the axon.
Question 12.
The thread-like structures that develop on a moist slice of bread in Rhizopus are:
(A) Sporangia
(B) Filaments
(C) Rhizoids
(D) Hyphae
Answer:
(D) Hyphae
Explanation: Hyphae are the fine thread-like structures of fungi that are spread on the whole surface of a slice of bread.
Question 13.
At noon, the sun appears white as (1)
(a) light is least scattered
(b) all the colours of the white light are scattered away
(c) the blue colour is scattered the most
(d) the red colour is scattered the most
Answer:
(b) all the colours of the white light are scattered away
At noon, the sun appears white because the light from the sun is directly over H’s head and travels a relatively shorter distance. The sun appears white because a small amount of the blue and the violet colour are scattered.
Question 14.
The radius of curvature of a converging mirror is 30 cm. At what distance from the mirror should an object be placed as to obtain a virtual image?
(A) Infinity
(B) 30 cm
(C) Between 15 cm and 30 cm
(D) Between 0 cm and 15 cm 1
Answer:
(D) Between 0 cm and 15 cm 1
Explanation: Radius of curvature of converging mirror = 30 cm
To obtain a virtual image, in case of a concave mirror (converging mirror), the object should be between pole and focus.
Using Focal length,f = Radius of curvature Y/2 (OR) f = 30/2 = 15 cm.
![]()
Question 15.
Villi present on the internal wall of the intestine help in the (1)
(a) emulsification of fats
(b) breakdown of proteins
(c) absorption of digested food
(d) digestion of carbohydrates
Answer:
(c) absorption of digested food
The small finger-like projections, i.e. Villi present on the internal wall of the intestine increase the surface area for better absorption of digested food.
Question 16.
Depletion of ozone is mainly due to:
(A) Chlorofluorocarbon compounds
(B) Carbon monoxide
(C) Methane
(D) Pesticides
Answer:
(A) Chlorofluorocarbon compounds
Explanation: Depletion of the ozone layer occurs due to chlorofluorocarbons (CFC
s
). Other chemicals do not cause depletion of the ozone layer in the environment.
Direction (Q. Nos. 17-20) These consist of two Statement – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions by selecting the appropriate option given below.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc. (1)
Reason (R): Zinc is more reactive than tin.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): The inner walls of the small intestine have finger-like projections called villi which are rich in blood.
Reason (R): These villi have a large surface area to help the small intestine in completing the digestion of food.1
Answer:
(A) Both A and R are true, and R is the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: The inner lining of the small intestine has finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption. The villi are richly supplied with the blood vessels which take the absorbed food to every cell of the body
Question 19.
Assertion (A): Pyruvate is a six-carbon molecule. (1)
Reason (R): It is prepared in the cytoplasm as the first step of cellular respiration.
Answer:
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Assertion can be corrected as pyruvate is a 3-carbon molecule.
![]()
Question 20.
Assertion (A): Food chain is responsible for the entry of harmful chemicals in our bodies.
Reason (R): The length and complexity of food chains vary greatly.
Answer:
(B) Both A and R are true, and R is not the correct explanation of A.
Explanation: Through bio-magnification, harmful chemicals that are not metabolized by our body pass into the food chain, irrespective of the length & complexity of the food chain, which may vary in nature.
Section B
Questions No. 21 to 26 are Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 21.
Diamond and graphite show different physical properties although they are made up of carbon. Name this relationship between diamond and graphite. Give the basis of this relationship also. (2)
Answer:
This relationship between diamond and graphite is called allotropy. The physical properties are different because the carbon-carbon bonding in both the allotropes varies. Diamond is hard because in it one carbon atom is bonded with four other carbon atoms with strong covalent bonds, while graphite is soft in which each C-atom is joined to three other C-atoms by strong covalent bonds to form flat hexagonal rings. (1)
The various layers of C-atoms in graphite are quite far apart so that covalent bonds can exist between them. The various layers of carbon atoms in graphite are held together by weak van der Waals forces. They can slide over one another. (1)
Question 22.
There are various muscles present in the human digestive system known as sphincters. Two examples of those are given below:
(a) Pyloric sphincter- at the junction of stomach and small intestine
(b) Anal sphincter- at the anus
Give ONE most likely consequence of malfunctioning of each of these sphincters.
Answer:
Pyloric sphincter. Food will get into the small intestine too fast causing poor absorption.
Anal sphincter: Involuntary release of faeces from the body.
Question 23.
What is the first sign of pregnancy in a woman? How pregnancy can be prevented surgically? (2)
Or
Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival, the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give a reason to justify your answer.
Answer:
The absence of a menstrual cycle may be the first indication of pregnancy in a woman. When vas deferens in males are blocked surgically, sperm transfer is prevented. Similarly, when Fallopian tubes are blocked in the females the egg will not be able to reach the uterus thereby preventing pregnancy. (2)
Or
Sexual reproduction is considered to be superior to asexual reproduction as it leads to variations, while asexual reproduction does not induce variations among progeny individuals. The advantages of variations in individuals are
- It brings adaptation in individuals.
- It helps in the survival of species.
- It is the basis of evolution.
False
Question 24.
A student traces the path of a ray of light through a glass prism as shown in the diagram but leaves it incomplete and unlabelled. Redraw and complete the diagram. Also label on it ∠i, ∠e, ∠r and ∠D.
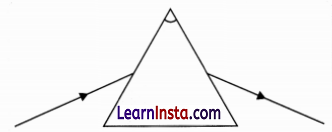
Answer:
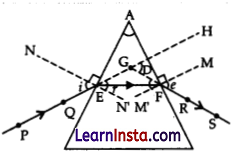
Labelling of ∠i, ∠e, ∠r & ∠D.
Question 25.
Rishi went to a palmist to show his palm. The palmist used a special lens for this purpose. (2)
(a) Where should the palmist place/hold the lens, to have a real and magnified image of an object?
(b) If the focal length of this lens is 10 cm and the lens is held at a distance of 5 cm from the palm, use the lens formula to find the position and size of the image.
Or

A narrow beam of white light is incident on two glass objects as shown above. Comment on the nature of the behavior of the emergent beam in both cases.
Answer:
(a) The palmist will hold the lens where the palm is in between the focus and pole of the lens. (1)
(b) Given, focal length, f = 10 cm and object distance, u = -5 cm
For lens formula, \(\frac{1}{v}-\frac{1}{u}=\frac{1}{f}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{v}=\frac{1}{10}+\frac{1}{-5}=\frac{1}{10}-\frac{1}{5}\)
⇒ v = -10 cm
Hence, the magnification
m = \(\frac{v}{u}=\frac{-10}{-5}\) = 2
Hence, the image is on the same side of the lens as an object (palm) and it is virtually erect and magnified. (1)
Or
(a) The incident beam of light after refraction through a prism splits into a band of seven colors which are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red (VIBGYOR). These coloured rays emerge out of the prism in different directions and become distinct. Therefore, dispersion of white light takes place. (1)
(b) When the incident beam passes through the first prism, it gets splitted into a band of seven colours. But when those coloured rays are incident on an identical inverted prism. Then, the recombination of the coloured rays takes place. This emergent light is parallel to the incident beam but slightly shifted outward. (1)
![]()
Question 26.
DDT was sprayed in a lake to regulate the breeding of mosquitoes. How would it affect the trophic levels in the following food chain associated with a lake? Justify your answer.

Answer:
DDT being a non-biodegradable pesticide will enter the food chain from the first trophic level, i.e., Plankton.
Non-biodegradable pesticides accumulate progressively at each trophic level. This phenomenon is known as biological magnification.
Hawk will have the highest level of pesticide.
Section C
Questions No. 27 to 33 are short answer questions.
Question 27.
An element A reacts with water to form compound B which is used in whitewashing. The compound B on heating forms an oxide C which on treatment with water gives back B. Identify A, B, and C and give the reactions involved. (3)
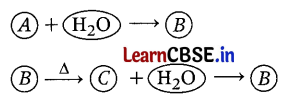
Or
Why does sodium form sodium hydroxide when reacts with water whereas, aluminium forms only aluminium oxide?
Answer:
Element A is calcium (Ca). When it reacts with water, it forms calcium hydroxide. This compound B is calcium hydroxide Ca(OH)
2
, which is used in whitewashing. (1)
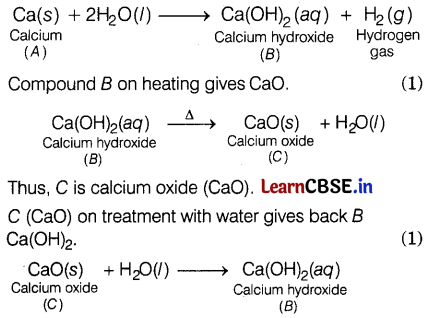
Or
The metals placed lower in the reactivity series are less reactive towards water. Sodium metal is placed above aluminium in the reactivity series. Hence, it reacts with water to form sodium oxide which further dissolves in water to give a sodium hydroxide solution. Whereas, aluminium reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide which does not dissolve in water to form aluminium hydroxide. (3)
Question 28.
Distinguish between esterification and saponification reactions with the help of the chemical equations for each. State one use of each (i) ester and (ii) saponification process.
Answer:
Esterification is the process by which esters are formed when an alcohol reacts with an acid in the presence of cone, sulphuric acid.
R’OH + RCOOH
H
+
>
RCOOR’ (Ester) + H
2
O
CH
3
CH
2
OH + CH
3
COOH → + CH
3
COOC
2
H
5
+ H
2
O
The saponification reaction is when ester reacts with NaOH, to form the sodium salt of acid (soap) and alcohol.
RCOOR’ + NaOH → RCOONa (Soap) + R’OH
CH
3
COOC
2
H
5
+ NaOH → CH
3
COONa + C
2
H
5
OH
(i) Uses of esters: Used in making perfumes, or as artificial flavouring agents in ice-creams and cold drinks.
(ii) Uses of saponification process: Used in making soaps.
Write three different chemical reactions showing the conversion of ethanoic acid to sodium ethanoate. Write balanced chemical equation in each case. Write the name of the reactants and the products other than ethanoic acid and sodium ethanoate in each case.
Answer:
Sodium ethanoate (CH
3
COONa) can be formed from ethanoic acid in the following reactions:
(i) Reaction with sodium carbonate:
2CH
3
COOH + Na
2
CO
3
→ 2CH
3
COONa + CO
2
+ H
2
O (water)
(ii) Reaction with sodium bicarbonate:
CH
3
COOH + NaHCO
3
→ CH
3
COONa + CO
2
+ H
2
O (water)
(iii) Neutralisation reaction:
CH
3
COOH + NaOH → CH
3
COONa + H
2
O (water)
Question 29.
A child questioned his teacher why organisms resemble their parents more as compared to grandparents. In which way will the teacher explain to the child?
Answer:
The two parents involved in sexual reproduction produce gametes which fuse forming a zygote. It gradually develops into a young child showing certain similarities with the parents. Since a child inherits its characters from both parents the resemblance between them is very close. The grandparents and the child resemble less closely because a gap in the gene pool is created by the parents of the child. Variations of two generations mixing and the addition of new variations from parents increase the difference between them to a greater extent. Hence, a child resembles more closely its parents than the grandparents.
![]()
Question 30.
Name the phenomenon occurring in plants that are under the control of gravity, water, and chemicals with one example each that shows the movement involved.
Answer:
Geotropism: It is the movement of plant parts in response to the direction of gravity. The growth of plant roots is an example of geotropism as it grows towards the direction of gravity.
Hydrotropism: It is the movement of a plant towards the water.
Example: The plant roots always move towards water hence it shows positive hydrotropism.
Chemotropism: It is the movement of plants in response to a chemical stimulus. A classic example\ of this type of movement is the growth of the pollen tube towards the ovule, during fertilization, in a flower.
Question 31.
(a) The potential difference between two points in an electric circuit is 1V. What does it mean? Name a device that helps to measure the potential difference across a conductor.
(b) Why does the connecting cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
Answer:
(a) If the potential difference between two points is 1 V, it means that if a charge of 1 C is moved from one point to the other, then 1 J of work is done. The potential difference across a conductor is measured using an instrument called the voltmeter. (1)
(b) The electric power P is given by P = I
2
R
The resistance of the heating element is very high. A large amount of heat is generated in the heating element and it glows. The resistance of the connecting cord is very low. Thus, negligible heat is generated in the connecting cord and it does not glow. (2)
Question 32.
(a) State Ohm’s law. Represent it mathematically.
(b) Define 1 ohm.
(c) What is the resistance of a conductor through which a current of 0.5 A flows when a potential difference of 2 V is applied across its ends?
Answer:
(a) Ohm’s law: It states that “Electric current through a metallic conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across the conductor of the circuit provided that temperature and other physical quantities remain constant.
Mathematical expression for Ohm’s Law:
7 ∝ V.
Or V=IR
Or I = V/R
where R = constant called resistance of a given metal.
(b) 1 Ohm = When potential difference is 1 V and the current through the circuit is 1 A, then the resistance is1 ohm.
1 Ohm = 1 volt/1 amper
(c) Given, I = 0.5 A
Potential difference, V = 2 V
Applying ohm’s law, V = IR
Or, R = V/1 = 2/0.5 = 4 Ω
Hence, the resistance of a conductor is 4 Ω.
![]()
Question 33.
What are decomposers? What will be the consequence of their absence in an ecosystem?
Answer:
Organisms that break down the complex organic compounds present in dead and decaying matter into simpler inorganic materials are called decomposers, e.g. certain bacteria and fungi. (1)
Decomposers act as cleaning agents of the environment by decomposing dead bodies of plants and animals. The consequence of their absence in an ecosystem can be disastrous. The dead bodies would persist for a long, leading to their accumulation and thus, polluting the environment. The biogenetic nutrients associated with remains will not be returned to the environment. As a result, all the nutrients present in soil, air, and water would soon be exhausted and the whole life cycle of organisms will be disrupted. (2)
Section D
Questions No. 34 to 36 are Long Answer Questions.
Question 34.
(a) It is observed that covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity. Give reason.
Answer:
Covalent compounds are bad conductors of electricity because they do not have free electrons or ions that can move and carry an electric current
(b) Carbon can neither form C
4+
cation or C
4-
anion. Why?
Answer:
The atomic number of Carbon is 6 with an electronic configuration of 2, 4. Hence, carbon has 4 electrons in its valence shell. Carbon can lose or gain 4 electrons in order to gain stability. It cannot gain four electrons as carbon atom having 6 protons is very small to handle 10 electrons and it cannot donate electrons as it needs a lot of energy to do so. Hence, it cannot form C
4+
cation or C
4-
anion anion and thus forms a covalent bond
(c) Draw electron dot structure of ethanol.
Answer:
The electron dot structure of Ethanol is:
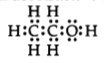
(d) Identify heteroatom(s) in the following compounds:
Answer:
Heteroatoms are the elements that replace hydrogen in a hydrocarbon
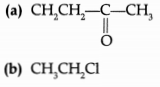
Answer:
(a) Oxygen
(b) Chlorine
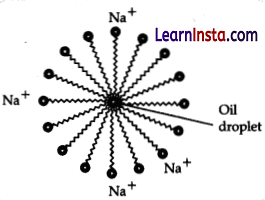
(a) What are soaps? Explain the mechanism of cleansing action of soap with the help of a labelled diagram.
Answer:
Soaps are the sodium or potassium salts of long-chain fatty acids. They are formed by the reaction between an alkali (sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide) and a fat or oil.
Cleansing action of soap:
(i) The long hydrocarbon chain of the soap is non-polar and tends to avoid water. When soap is added to water, the hydrophobic tail is attracted to the dirt, oil or grease, while the hydrophilic head is attracted to the water molecules.
(ii) The hydrophobic tail surrounds the oil or grease droplet, forming a sphere called a micelle.
(iii) The soap molecules on the outside of the micelle are attracted to the water molecules and are washed away with the water, carrying the micelle and dirt along with it.
(iv) When the soap and water are rinsed off, the dirt, oil, and grease are removed from the surface
(b) Detergents are better than soaps. Justify.
Answer:
Detergents are better than soaps as:
(i) Detergents work better in hard water than soaps as they do not react with the minerals in hard water to form insoluble compounds.
(ii) Detergents can be used in both hot and cold water, whereas soaps work better in hot water.
(iii) Detergents are more effective in removing grease and oil stains than soaps.
(iv) Detergents are less likely to leave a residue on clothes, unlike soaps
Question 35.
Given below are certain situations. Analyse and describe its possible impact. (5)
(a) If we cut a part of Planaria.
(b) Stigma is removed from a flower.
(c) Style is plugged from a flower.
(d) Spermicide is applied without using a condom or diaphragm it.
(e) Fallopian tube and vasa deferens are plugged.
Or
What are the major parts of the brain? Mention the functions of different parts.
Answer:
(a) Planaria shows the property of regeneration. So, if we cut a portion of Planaria, it will develop into, a new organism from just a broken or cut part of 1 parent organism.
(b) Stigma is the terminal part of the carpel. It helps in receiving the pollen during pollination. So, if we remove the stigma then pollination will not occur.
(c) If a style is plugged from a flower then the stigma receiving the pollen grain and taking it to the ovary for fertilization will not occur as the style helps in the attachment of the stigma to the ovary.
(d) Spermicides are applied in combination with condoms to kill the sperm. If they are not applied with condoms or diaphragm then the chances of their failure will increase.
(e) If the fallopian tube is plugged then the egg will not be able to reach the uterus and thus fertilization will not take place, if the vasa deferens is plugged then the sperm transfer will be prevented.
Or
The brain is the most important coordinating centre in the body. It has three major parts or regions namely the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
| Parts | Functions |
| Forebrain | |
| Cerebrum | The main thinking part of the brain. |
| Cerebral hemispheres | Intelligence and voluntary actions. |
| Olfactory lobes | Centres of smell. |
| Hypothalamus | Has centres of hunger, thirst, etc. |
| Midbrain | Controls reflex movements of the neck, head, and trunk in response to visual and auditory stimuli. |
| Also controls the reflex movements of the eye muscles, changes in pupil size, and shape of the eye lens. | |
| Hindbrain Pons | Regulates respiration. Relays information between the cerebellum and the cerebrum. |
| Cerebellum | Maintains posture and balance of the body. Enables us to make precise and accurate movements. |
| Medulla oblongata | Controls involuntary actions such as breathing, etc. Controlling centre for reflexes such as swallowing, coughing, vomiting, etc. |
![]()
Question 36.
Rishi went to a palmist to show his palm. The palmist used a special lens for this purpose.
(a) State the nature of the lens and reason for its use.
(b) Where should the palmist place/hold the lens to have a real and magnified image of an object?
(c) If the focal length of this lens is 10 cm and the lens is hold at a distance of 5 cm from the palm, use lens formula to find the position and size of the image.
Answer:
(a) Nature of the lens will be convex lens to get a magnified image of the lines on the palm.
(b) It should be between F and 2F of the lens / or at F of the lens.
(c) Given, Focal length f = +10 cm and
Object distance u = -5 cm
Lens formula 1/v – 1/ u = 1/f
1/v – 1/-5 = 1/10
1/u + 1/5 = 1/10
1/v = 1/10 – 1/5 = 1-2/10
1/v = -1/10
v = -10 cm
M = h
image
/h
object
= v/u
= -10/-5
= 2
Therefore, the size of the image is 2 times the size of the object
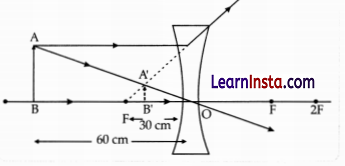
An object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(a) Use lens formula to find the distance of the image from the lens.
(b) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) formed by the lens in this case.
(c) Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer of part (b).
Answer:
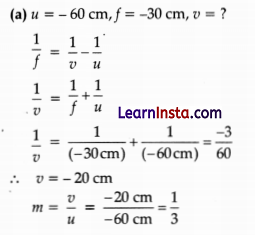
Distance of the image will be 20 cm in front of lens.
(b) Nature: Virtual
Position: 20 cm from lens on the same side as the object
Size: Diminished
Erect/Inverted: Erect
(c)
Section E
Questions No. 37 to 39 are case-based/data-based questions with 2 to 3 short sub-parts. Internal choice is provided in one of these sub-parts.
Question 37.
The table given below shows the hints given by the quiz master in a quiz. (4)
| Hints |
| (i) A metal ‘A’ is used in thermite reduction. |
| (ii) When metal A’ is heated with oxygen gives ‘S’, which is amphoteric. |
| (iii) Metal A’ acts as a reducing agent. |
Based on the above hints answer the following questions.
(a) Identify A and B.
(b) Write down the reactions of oxide B with HCl and NaOH.
Or
Explain the process of thermite welding with reaction.
Answer:
(a) Metal A is aluminum (Al) which is used in thermite reaction. Al reacts with oxygen to form aluminium oxide, Al2O3 (B), which is amphoteric. (2)
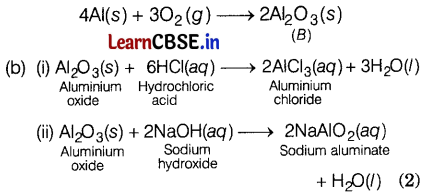
Or
The reaction of iron (III) oxide (Fe2O3)with aluminium to produce iron is used to join railway tracks or cracked machine parts. This process is called thermite welding. It is a highly exothermic reaction. The reaction involved is as follows.

Question 38.
All human chromosomes are not paired. Most human chromosomes have a maternal and a paternal copy and we have 22 such pairs. But one pair of sex chromosomes are odd in not always being a perfect pair. Women have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes. But man has a mismatched pair in which one is normal sized while the other is a short one.
(a) In humans, how many chromosomes are present in a zygote and in each gamete?
(b) A few reptiles rely entirely on environmental cues for sex determinations. Comment.
(c) The sex of a child is a matter of chance and none of the parents is considered to be responsible for it. Justify it through a flow chart only.
Answer:
(a) Zygote is formed due to the fusion of male and female gametes. Gametes are haploid cells. Thus the fusion of two haploid cells results in the formation of a diploid cell. Therefore zygote is a diploid cell with 46 chromosomes.
(b) In a few reptiles, the temperature at which fertilised eggs are kept determines whether the animals developing in eggs will be male or female. By this, we can say that some animals rely entirely on environmental cues for sex determination.
(c) There is an equal chance of fusion of either X or Y chromosome with the egg. So, we can say that the sex of a new born child is a matter of chance and none of the parents is responsible for it.
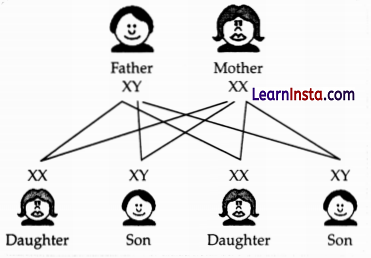
(c) Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X chromosome?
Answer:
Human females are homomorphic. They have two identical sex chromosomes. One X-chromosome enters each gamete during meiosis at the time of gamete formation. So, all gametes have an X chromosome.
![]()
Question 39.
The following three image formation by three concave mirrors are shown in the figure. The point O and I denote object and image, respectively. The object distance and focal length in each case are given in the figure. (4)
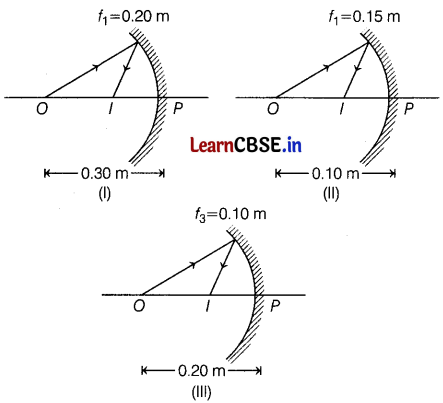
(a) How would you define the radius of curvature?
(b) No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect and diminished. Identify whether this mirror is concave or convex.
(c) How does the observation of images formed help in identifying the type of mirror?
Or
Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, out of three in which case the mirror will form the image having the same size as an object?
Answer:
(a) Radius of curvature of a mirror is defined as the radius of the sphere from which the spherical mirror was cut. (1)
(b) The mirror is a convex mirror because it always forms an erect and diminished image irrespective of the position of the object. (1)
(c) By observing the images produced by the mirror for different positions of the object, its nature can be identified as follows:
If the image formed by the mirror is of the same size as that of the object for different positions of the object, then the mirror is a plane mirror.
If the image formed by the mirror is diminished for all positions of an object, then the mirror is a convex mirror.
If the image formed behind the mirror is longer than the object, then the mirror is concave. (2)
Or
The third concave mirror will form an image of the same size as that of an object because in the third concave mirror, f = 0.1 m, so the radius of curvature R = 2f = 0.2 m and a same size image is formed when the object is at the centre of curvature. (2)