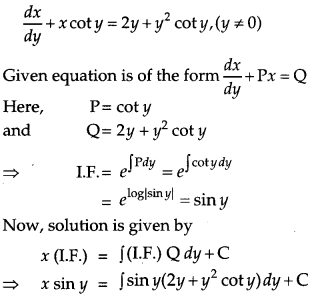CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Maths 2013 Outside Delhi
Time allowed: 3 hours
Maximum marks : 100
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper consists of 29 questions divided into four sections A, B, C and D. Section A comprises of 4 questions of one mark each, Section B comprises of 8 questions of two marks each, Section C comprises of 11 questions of four marks each and Section D comprises of 6 questions of six marks each.
- All questions in Section A are to be answered in one word, one sentence or as per the exact requirement of the question.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choice has been provided in 1 question of Section A, 3 questions of Section B, 3 questions of Section C and 3 questions of Section D. You have to attempt only one of the alternatives in all such questions.
- Use of calculators is not permitted. You may ask for logarithmic tables, if required.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Maths 2013 Outside Delhi Set I
Section – A
Question 1.
Write the principal value of tan
-1
(\( \sqrt{{3}} \)) – cot
-1
(\( \sqrt{{3}} \)). [1]
Solution:
Given,
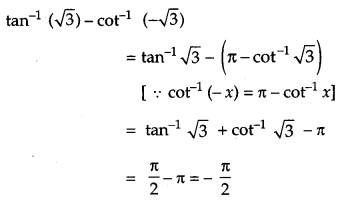
Question 2.
Write the value of tan
-1
[2 sin(2cos
-1
\(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\))]. [1]
Solution:
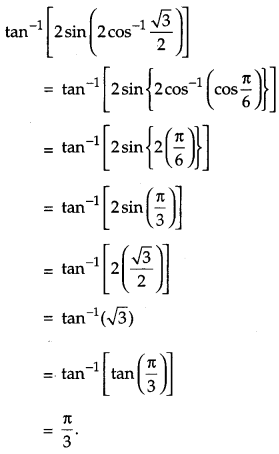
Question 3.
For what value of x, is the matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{ccc}{0} & {1} & {-2} \\ {-1} & {0} & {3} \\ {x} & {-3} & {0}\end{array}\right]\) a skew symmetric matrix ? [1]
Solution:
We see that,
a
31
= x
Given that the matrix ‘A’ is knew symmetric
∴ a
ij
= -a
ji
⇒ a
31
= – a
13
∴ x = (-2) = 2.
Question 4.
If matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{1} & {-1} \\ {-1} & {1}\end{array}\right]\) and A
2
= KA, then write the value of K. [1]
Solution:

Question 5.
Write the differential equation representing the family of curves y = mx, where m is an arbitrary constant. [1]
Solution:
We have, y = mx
On differentiating, we get
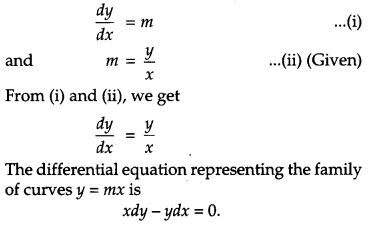
Question 6.
If A
ij
is the cofactor of the element a
ij
of the determinant \(\left|\begin{array}{ccc}{2} & {-3} & {5} \\ {6} & {0} & {4} \\ {1} & {5} & {-7}\end{array}\right|\) then write the value of a
32
, A
32
. [1]
Solution:
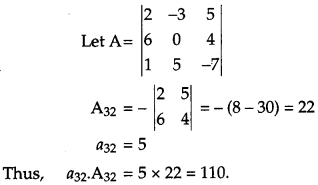
Question 7.
P and Q are two points with position vectors \(3 \vec{a}-2 \vec{b} \text { and } \vec{a}+\vec{b}\) respectively. Write the position vector of a point R which divides the line segment PQ in the ratio 2 : 1 externally. [1]
Solution:
Position vector of point
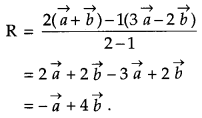
Question 8.
Find \(|\vec{x}|\) if for a unit vector \(\vec{a},(\vec{x}-\vec{a}) \cdot(\vec{x}+\vec{a})\) = 15. [1]
Solution:
We have,
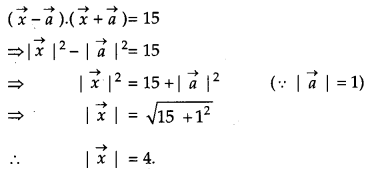
Question 9.
Find the length of the perpendicular drawn from the origin to the plane 2x – 3y + 6z + 21 = 0. [1]
Solution:
Length of perpendicular
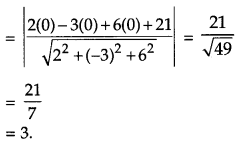
Question 10.
The money to be spent for the welfare of the employees of a firm is proportional to the rate of change of its total revenue (marginal revenue). If the total revenue (in rupee) received from the sale of x units of a product is given by R(x) = 3x
2
+ 36x + 5, find the marginal revenue, when x = 5 and write which value does the question indicates. [1]
Solution:
Total revenue, R(x) = 3x
2
+ 36x + 5
Marginal revenue,

Money for welfare of employees is a nice step, there should be a growth in raising funds for the welfare of the employees.
Section – B
Question 11.
Consider f : R
+
→ [4, ∞) given by f(x) = x
2
+ 4. Show that f is invertible with the inverse f
-1
of f given by f
-1
(y) = \(\sqrt{y-4}\) where R
+
is the set of all non-negative real numbers. [4]
Solution:
Given, f(x) = x
2
+ 4
f(x
1
) = f(x
2
)
x
2
1
+ 4 = x
2
2
+ 4
x
1
= x
2
Thus, f(x) is one-one.
Since, x
2
+ 4 is a real number. Thus, for every y in the co-domain of f, there exists a number x in R
+
such that
f(x) = y = x
2
+ 4
Thus, we can say that f(x) is onto.
Now, f(x) is one-one and onto. Hence, f(x) is invertible.
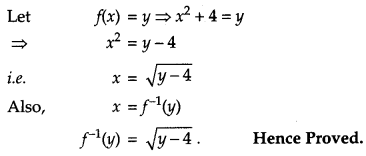
Question 12.
Show that: [4]
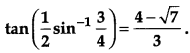
Solution:
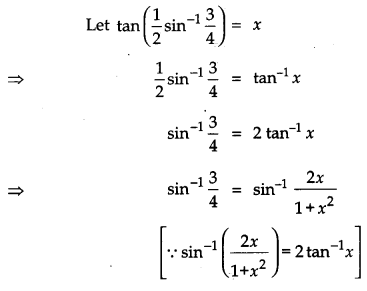
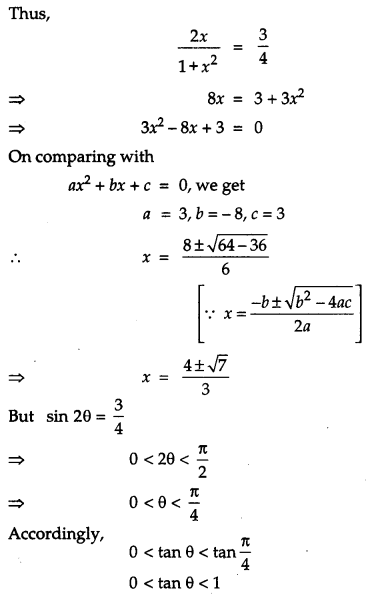
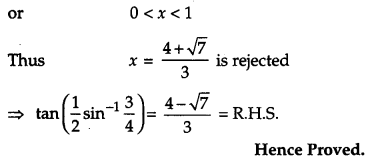
OR
Solve the following equation:
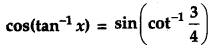
Solution:
Given,
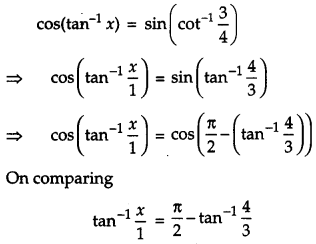
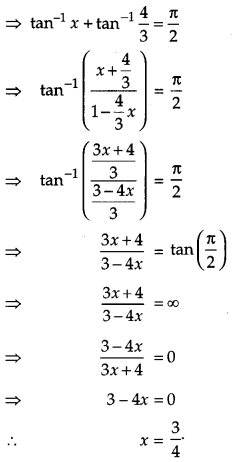
Question 13.
Using properties of determinants prove the following: [4]
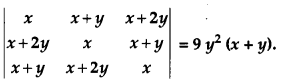
Solution:
L. H. S

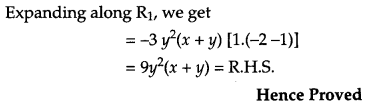
Question 14.
If y
x
= e
y-x
, prove that \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{(1+\log y)^{2}}{\log y}\). [4]
Solution:
Given,
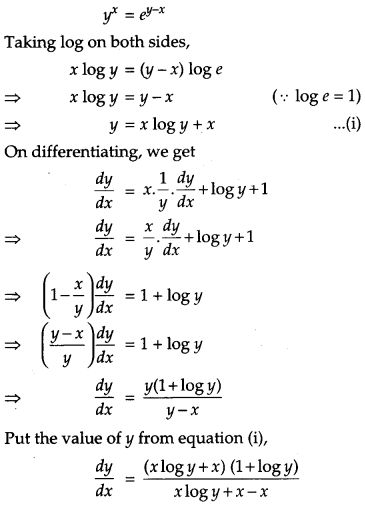
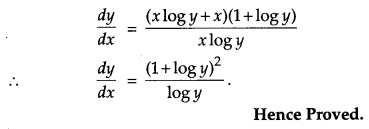
Question 15.
Differentiate the following with respect to x: [4]
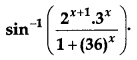
Solution:
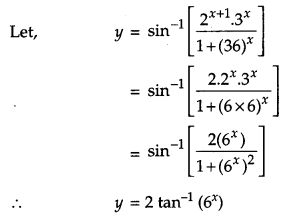
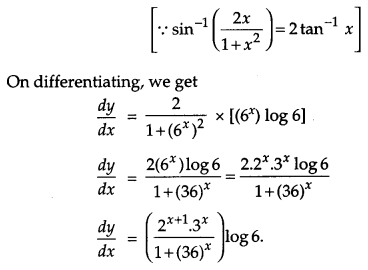
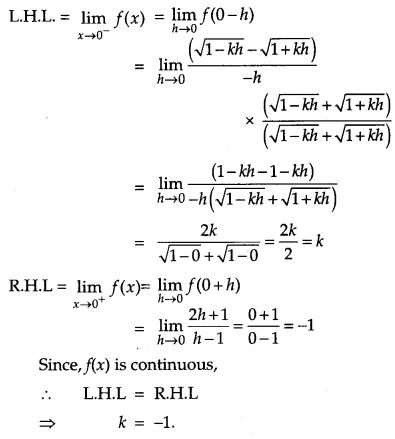
Question 16.
Find the value of k, for which
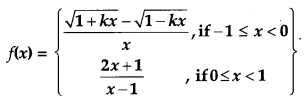
continuous at x = 0. [4]
Solution:
At x = 0,
OR
If x = a cos
3
θ and y = a sin
3
θ, then find the value of \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d x^{2}} \text { at } \theta=\frac{\pi}{6}\).
Solution:
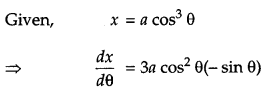

Question 17.
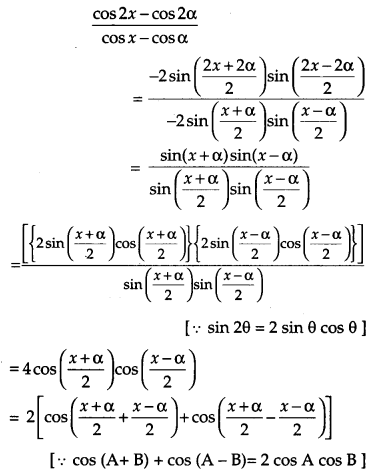
Evaluate: [4]
![]()
Solution:
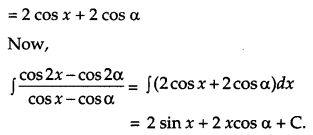
OR
Evaluate:
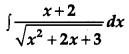
Solution:
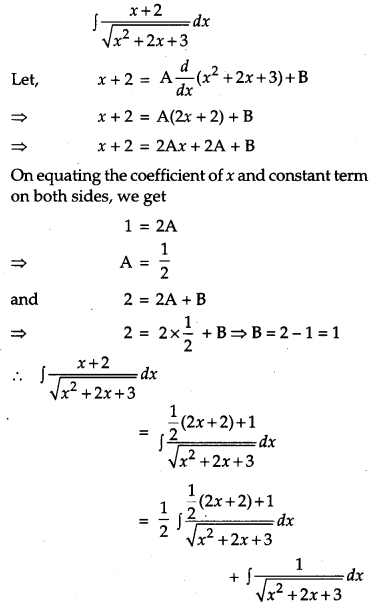
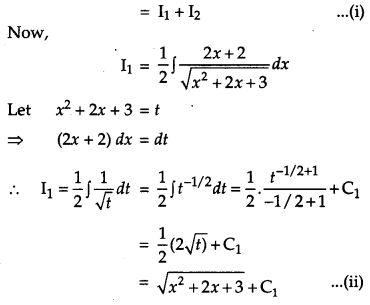
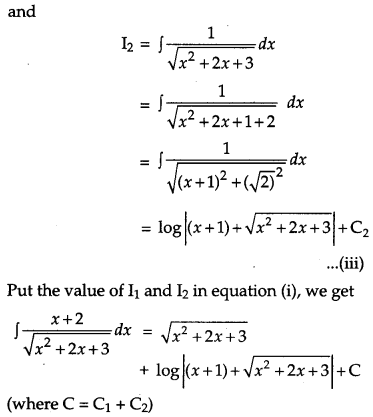
Question 18.
Evaluate: [4]
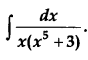
Solution:
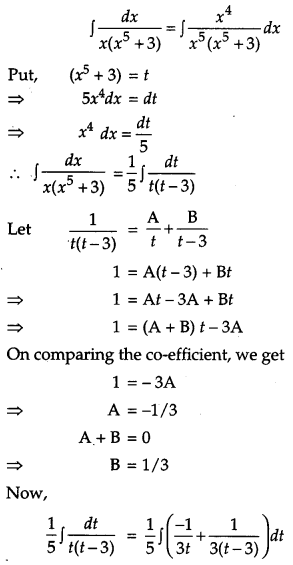
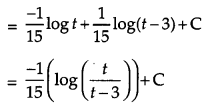
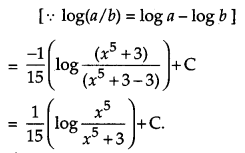
Question 19.
Evaluate: [4]
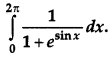
Solution:
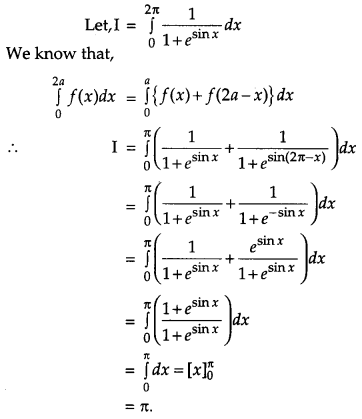
Question 20.
If \(\vec{a}=\hat{i}-\hat{j}+7 \hat{k} \text { and } \vec{b}=5 \hat{i}-\hat{j}+\lambda \hat{k}\) then find the value of λ, so that \(\vec{a}+\vec{b} \text { and } \vec{a}-\vec{b}\) are perpendicular vectors. [4]
Solution:
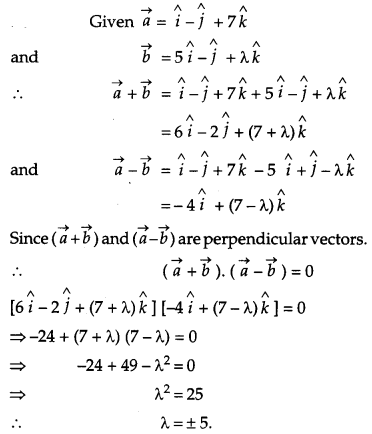
Question 21.
Show that the lines
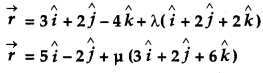
are intersecting. Hence find their point of intersection. [4]
Solution:
Consider,
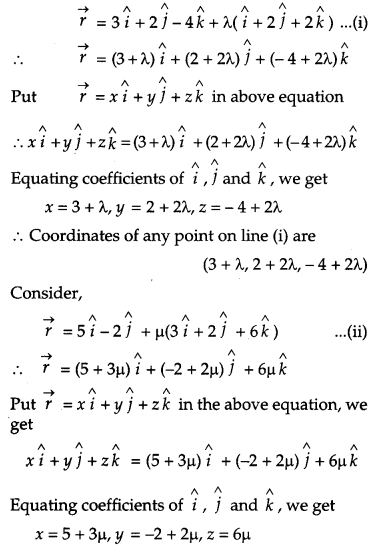

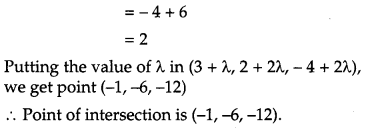
OR
Find the vector equation of the plane through the points (2, 1, -1) and (-1, 3, 4) and perpendicular to the plane x – 2y + 4z = 10.
Solution:
Equation of plane passing through (2, 1, -1) is
a(x – 2) + b(y – 1) + c(z + 1) = 0 …(i)
This plane passes through (-1, 3, 4)
Thus, a(-1 – 2) + b (3 – 1) + c(4 + 1) = 0
⇒ -3a + 2b + 5c = 0 ……..(ii)
Also, the above plane is perpendicular to the plane
x – 2y + 4z = 10
∴ a(1) + b(-2) + c(4) = 0
⇒ a – 2b + 4c = 0 …(iii)
Now, we have
-3a + 2b + 5c = 0
and a – 2b + 4c = 0
Solving the above equation by cross multiplication, we get

Question 22.
The probabilities of two students A and B coming to the school in time are \(\frac{3}{7} \text { and } \frac{5}{7}\) respectively.
Assuming that the events, A coming in time and B coming in time are independent. Find the probability of only one of them coming to the school in time. Write at least one advantages of coming to school in time. [4]
Solution:
Let probability that A comes on time = P(A)
Let probability that B comes on time = P(B)

Section – C
Question 23.
Find the area of the greatest rectangle that can be inscribed in an ellipse \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1\). [6]
Solution:
Equation of ellipse is
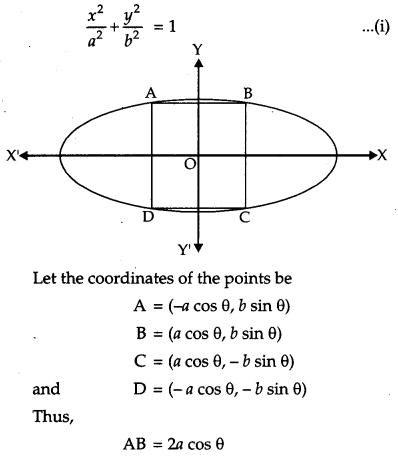
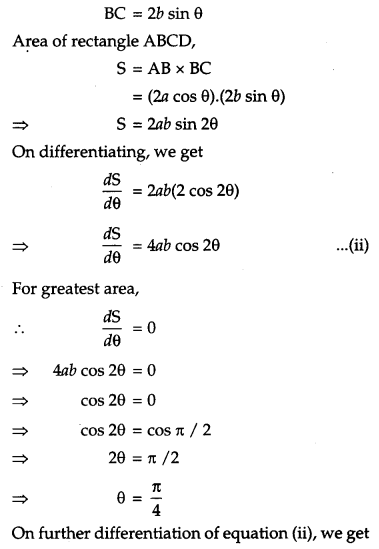
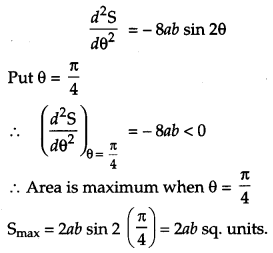
OR
Find the equations of tangents to the curve 3x
2
– y
2
= 8 which pass through the point \(\left(\frac{4}{3}, 0\right)\).
Solution:
The equation of the curve is 3x
2
– y
2
= 8.
On differentiating, we get
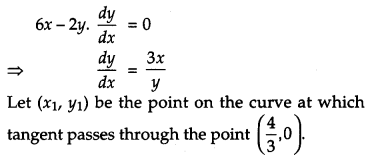

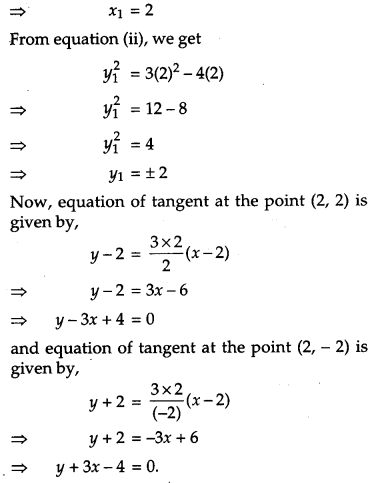
Question 24.
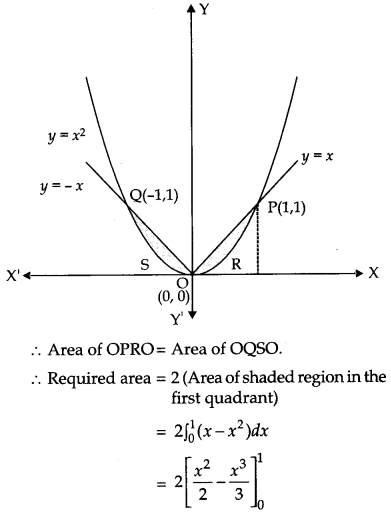
Find the area of the region bounded by the parabola y = x
2
and y = |x|. [6]
Solution:
Given parabola y = x
2
which is symmetrical about Y-axis and passes through O(0,0) and the curve y = | x |. The point of intersection of parabola, y = x
2
and line, y = x in the first quadrant is P(1, 1). The given area is symmetrical about Y-axis.
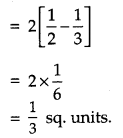
Question 25.
Find the particular solution of the differential equation (tan
-1
y – x)dy = (1 + y
2
)dx, given that when x = 0, y = 0. [6]
Solution:
The given differential equation
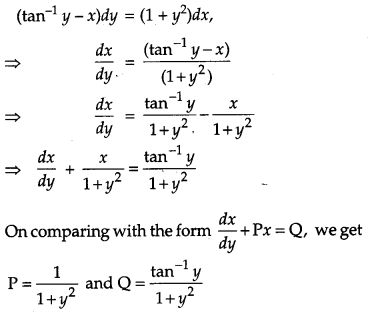
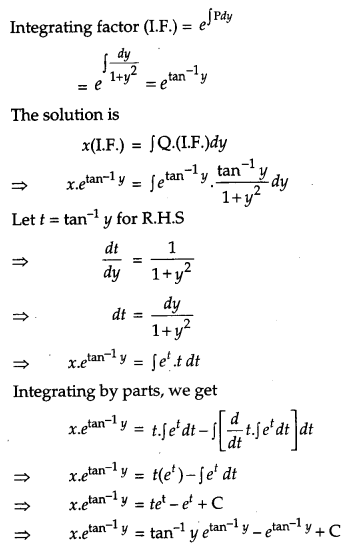
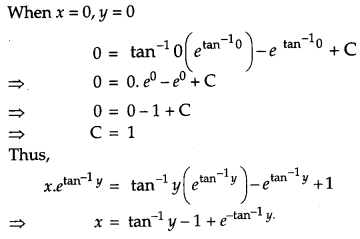
Question 26.
Find the equation of the plane passing through the line of intersection of the planes \(\vec{r} \cdot(\hat{i}+3 \hat{j})-6=0 \text { and } \vec{r} \cdot(3 \hat{i}-\hat{j}-4 \hat{k})=0\) whose perpendicular distance from origin is unity. [6]
Solution:
The equation of the plane passes through the intersection of given planes is
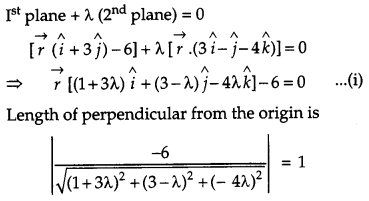
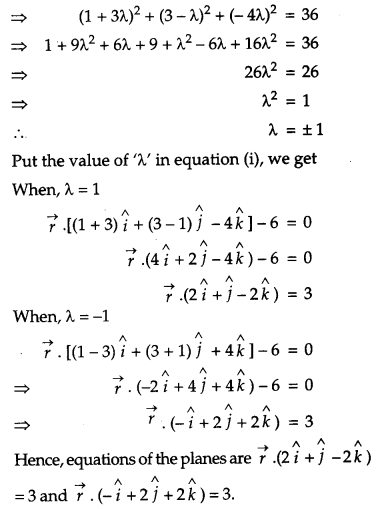
OR
Find the vector equation of the line passing through the point (1, 2, 3) and parallel to the planes \(\vec{r} \cdot(\hat{i}-\hat{j}+2 \hat{k})=5 \text { and } \vec{r} \cdot(3 \hat{i}-\hat{j}+\hat{k})=6\).
Solution:
The equation of line passing through the point (1, 2, 3) is
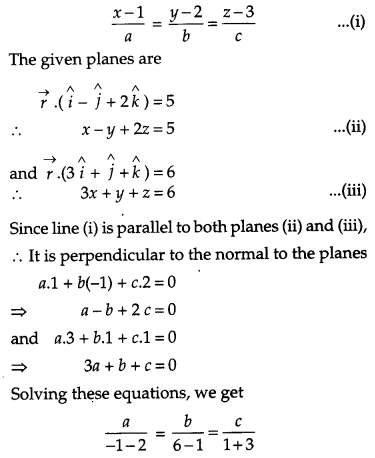
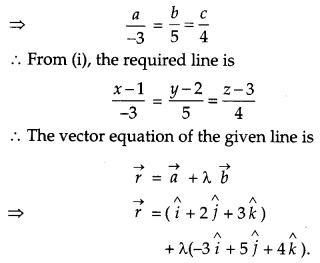
Question 27.
In a hockey match, both teams A and B scored same number of goals up to the end of the game, so to decide the winner, the referee asked both the captains to throw a die alternately and decided that the team, whose captain gets a six first, will be declared the winner. If the captain of team A was asked to start, find their respective probabilities of winning the match and state whether the decision of the referee was fair or not. [6]
Solution:
Probability of getting a six by the captains of both the teams A and B is

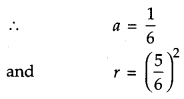
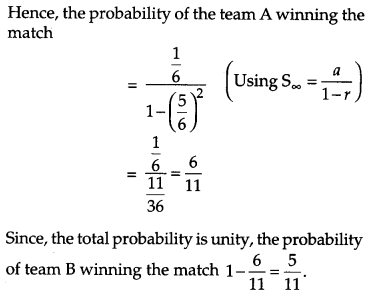
The decision of the referee was not fair as whosoever starts throwing the die gets an upper hand.
Question 28.
A manufacturer considers that men and women workers are equally efficient and so he pays them at the same rate. He has 30 and 17 units of workers (male and female) and capital respectively; which he uses to produce two types of goods A and B. To produce one unit of A, 2 workers and 3 units of capital are required while 3 workers and 1 unit of capital is required to produce one unit of B. If A and B are priced at ₹ 100 and ₹ 120 per unit respectively, how should he use his resources to maximize the total revenue ? Form the above as an LPP and solve graphically.
Do you agree with this view of the manufacturer that men and women workers are equally efficient and so should be paid at the same rate? [6]
Solution:
Let x units of the goods A and y units of goods B be produced to maximize the total revenue. Then the total revenue is Z = 100x + 120y. This is a linear function which is to be maximized. Hence it is the objective function. The constraints are as per the following table :
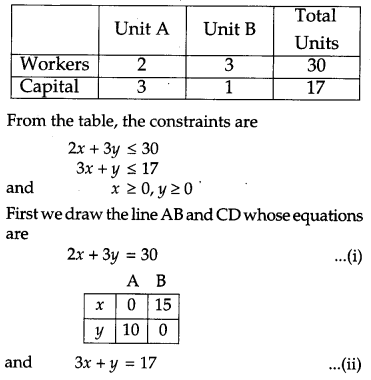
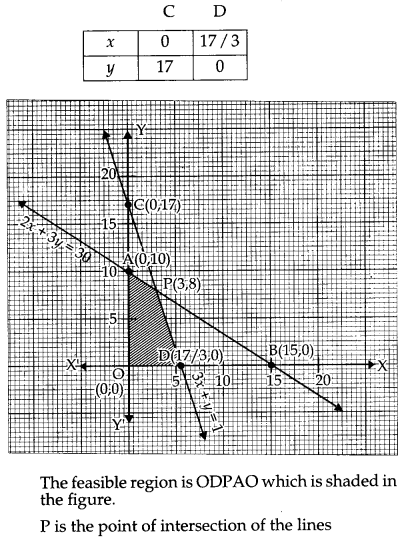
2x + 3y = 30
and 3x + y = 17
Solving these equations, we get point P(3, 8).
The vertices of the feasible region are O(0, 0), D(17/3), P (3,8) and A(o,
10).
The value of objective function Z = 100x + 120y at these vertices are as follows :
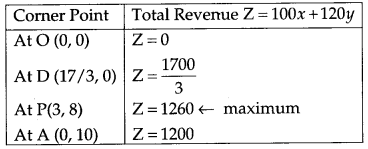
∴ The maximum revenue ₹ 1260 at the point P(3, 8) i.e., when 3 units of goods A and 8 units of goods B are produced.
Yes, I agree with the view of the manufacturer.
Question 29.
The management committee of a residential colony decided to award some of its members (say x) for honesty, some (say y) for helping others and some others (say z) for supervising the workers to keep the colony neat and clean. The sum of all the awardees is 12. Three times the sum of awardees for cooperation and supervision added to two times the number of awardees for honesty is 33. If the sum of the number of awardees for honesty and supervision is twice the number of awardees for helping others using matrix method, find the number of awardees of each category. Apart from these values namely honesty, cooperation and supervision, suggest one more value which the management of the colony must include for awards. [6]
Solution:
From equation,
x + y + z = 12 …(i)
2x + 3 (y + z) = 33 ⇒ 2x + 3y + 3z = 33 …(ii)
x + z = 2y ⇒ x – 2y + z = 0 …(iii)
∴ The given equations can be written in matrix form
AX = B …(iv)
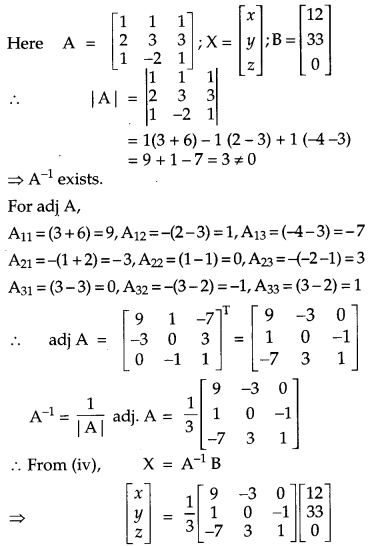
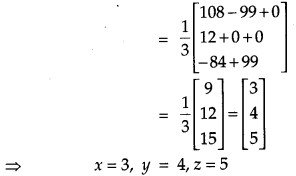
The colony management must includes cleanliness for awards.
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Maths 2013 Outside Delhi Set II
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous set
Section – A
Question 9.
If matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{2} & {-2} \\ {-2} & {2}\end{array}\right]\) and A
2
= pA, then write the value of p. [1]
Solution:
Given that
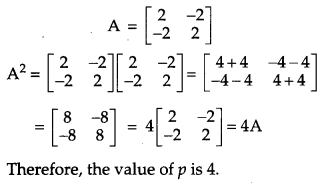
Question 10.
A and B are two points with position vectors \(2 \vec{a}-3 \vec{b} \text { and } 6 \vec{b}-\vec{a}\) respectively. Write the position vector of a point P which divides the line segment AB internally in the ratio 1 : 2. [1]
Solution:
Position vector of point
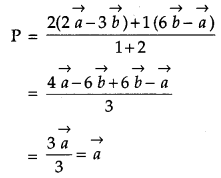
Section – B
Question 19.
If x
y
= e
x-y
, prove that \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{\log x}{(1+\log x)^{2}}\). [4]
Solution:
Given, x
y
= e
x-y
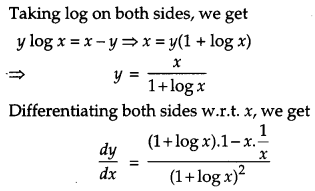
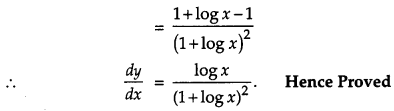
Question 20.
Evaluate: [4]
![]()
Solution:
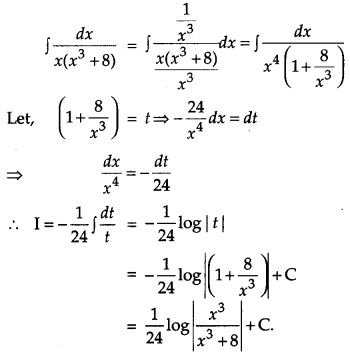
Question 21.
Evaluate : [4]
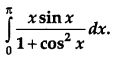
Solution:
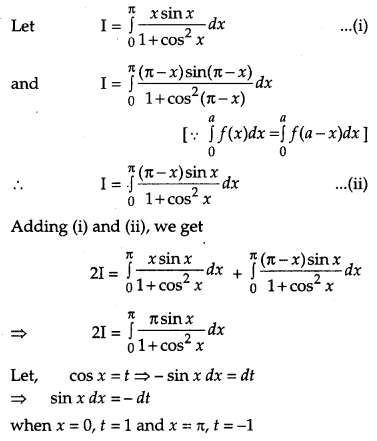
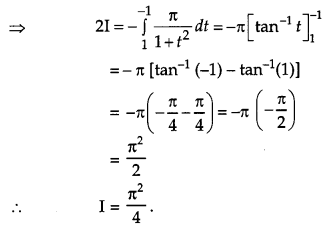
Section – C
Question 28.
Find the area of the region {(x, y) :y
2
≤ 6ax and x
2
+ y
2
≤ 16 a
2
} using method of integration. [6]
Solution:
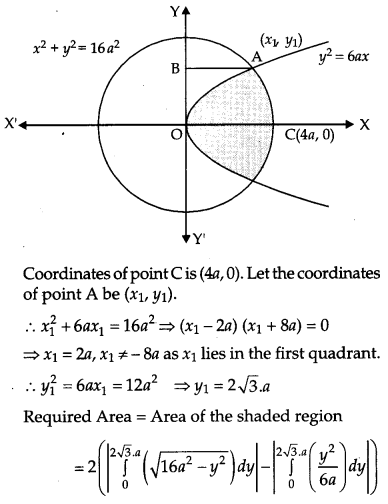
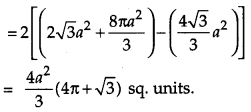
Question 29.
Show that the differential equation \(\left[x \sin ^{2}\left(\frac{y}{x}\right)-y\right]\) dx + xdy = 0 is homogeneous.
Find the particular solution of this differential equation, given that y = \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) when x = 1. [6]
Solution:
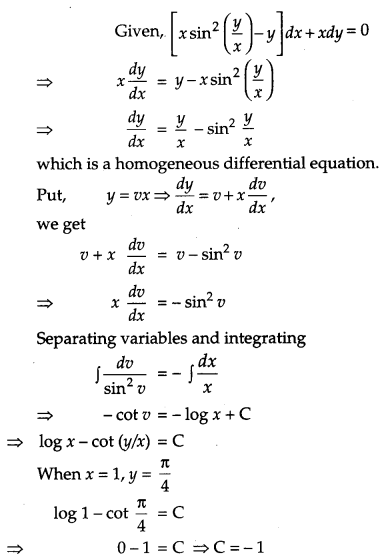
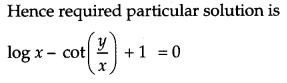
CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Maths 2013 Outside Delhi Set III
Note : Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in previous sets.
Section – A
Question 9.
If matrix A = \(\left[\begin{array}{cc}{3} & {-3} \\ {-3} & {3}\end{array}\right]\) and A
2
= λ A, then write the value of X. [1]
Solution:
Given,
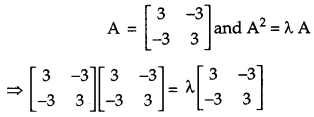
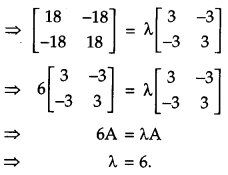
Question 10.
L and M are two points with position vectors \(2 \vec{a}-\vec{b} \text { and } \vec{a}+2 \vec{b}\) respectively. Write the position vector of a point N which divides the line segment LM in the ratio 2 : 1 externally. [1]
Solution:
The position vectors of the points are \(\mathrm{L}(2 \vec{a}-\vec{b}) \text { and } \mathrm{M}(\vec{a}+2 \vec{b})\).
We have to divide segment LM at N externally in the ratio 2 : 1.
Position of vector of point N
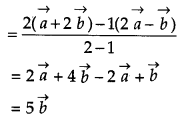
Section – B
Question 19.
Using vectors, find the area of the triangle ABC, whose vertices are A(1, 2, 3), B(2, -1, 4) and C(4, 5, -1). [4]
Solution:
Given,
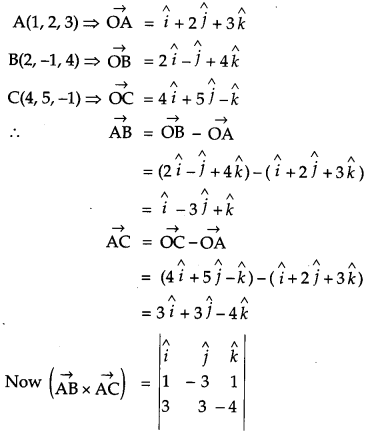
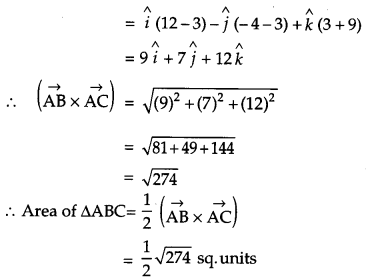
Question 20.
Evaluate: [4]
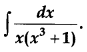
Solution:
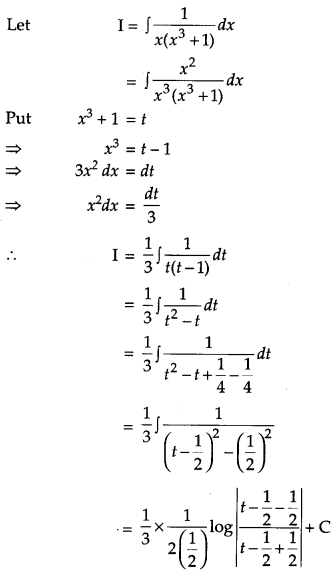
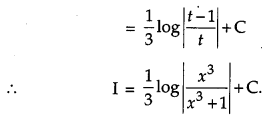
Question 21.
If x sin (a + y) + sin a cos (a + y) = 0, prove that \(\frac{d y}{d x}=\frac{\sin ^{2}(a+y)}{\sin a}\). [4]
Solution:
Here, x sin (a + y) + sin a cos (a + y)
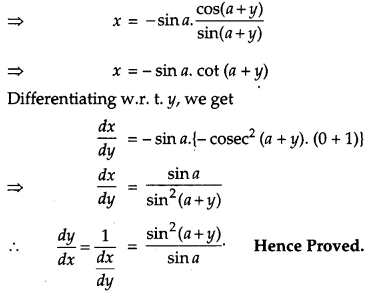
Question 22.
Using properties of determinants prove the following: [4]
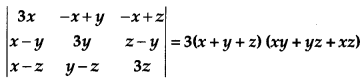
Solution:
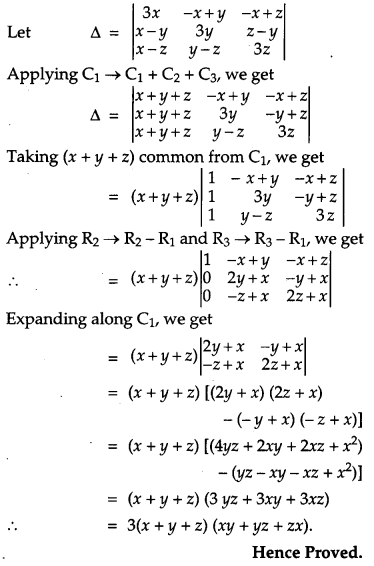
Question 28.
Find the area of the region, {(x, y): y
2
≤ 4x, 4x
2
+ 4y
2
≤ 9} using method of integration. [6]
Solution:
R = {(x, y): y
2
≤ 4x, 4x
2
+ 4y
2
≤ 9}
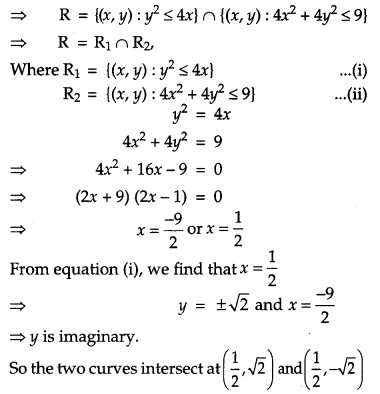
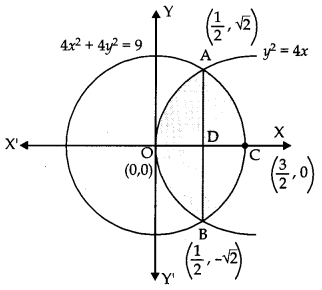

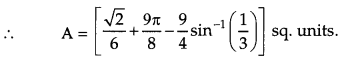
Question 29.
Find the particular solution of the differential equation \(\frac{d x}{d y}\) + x cot y = 2y + y,sup>2 cot y, (y ≠ 0), given that x = 0 when y = \(\frac{\pi}{2}\). [6]
Solution:
The given differential equation is