CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12 Geography 2019 Outside Delhi
Time allowed : 3 hours
Maximum marks: 70
: True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True
- There are 22 questions in all.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Question number 1 to 7 are very short-answer questions carrying 1 mark each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 40
- Question numbers 8 to 13 are short-answer questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 80-100 words.
- Question numbers 14 to 20 are long-answer questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each of these questions should not exceed 150
- Question numbers 21 to 22 are related to identification or locating and labelling of geographical features on maps, carrying 5 marks each.
- Outline maps of the World and India provided to you must be attached within your answer-book.
- Use of templates or stencils for drawing outline maps is allowed.
: True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True
Question 1.
Why is sex ration favourable to women in many European countries ? Explain any one reason. [1]
Answer:
European countries have more females than males because a very large number of men have migrated out to other countries. Women enjoy better status than men in these countries.
Question 2.
Examine the concept of ‘human development as introduced by Mahbub-ul-Haq. [1]
Answer:
According to Mahbub-ul-Haq, human development enlarges people’s choices and improves their lives. It creates conditions which allow people to lead meaningful lives.
Question 3.
Mention any two characteristics of ‘linear pattern’ of rural settlements in the world. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
OR
Mention any two characteristics of ‘rectangular pattern of rural settlements in the world.
Answer:
Two characteristics of Linear Pattern of rural settlements in the world :
- Houses are located along a road, railway line, canal edge of a valley or along a levee.
- These settlements also evolve along the edge of a valley, especially in the moutainous areas, above flood level or along the coast. They consist of compact settlements.
OR
Two characteristics of the Rectangular Pattern of rural settlements in the world :
- They mainly develop in productive alluvial plains and wide intermontane valleys.
- The lanes in the rectangular settlements are almost straight, meeting each other at right angles.
Question 4.
Write the meaning of ‘medical tourism’. [1]
Answer:
When people travel from one country to another in order to receive better medical, dental and surgical care; or in other words, when medical treatment is combined with international tourism, it is called medical tourism.
Question 5.
Why has-Ghhattisgarh recorded the lowest level in the Human Development Index (H.D.I.) ? [1]
Answer:
Chhattisgarh recorded the lowest level in the Human Development Index because of its low literacy rates, low levels of economic development and infant mortality rates.
Question 6.
Mention any two reasons for the deterioration of water quality in India. [1/2 + 1/2 = 1]
OR
Mention any two methods for the conservation of water in India.
Answer:
Two reasons for the deterioration of water quality in India are :
- Pollution resulting from industrial effluents has affected the quality of surface water across India.
- Foreign matters like microorganisms, agricultural and domestic wastes also affect the water bodies like lakes, streams, oceans, thus affecting acquatic systems.
OR
Two methods which can be adopted for conservation of water in India are :
- Methods like drip and sprinkler irrigation may be used to check wastage of water through agricultural practices especially in water deficit areas of India.
- Rainwater harvesting may be adopted to recharge groundwater resources. Structures like Kata and Sand bores can be constructed to save water.
Question 7.
How does air pollution affect human health ? [1]
OR
How does noise pollution affect human health ?
Answer:
Breathing polluted air outside causes respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Presence of pollutants like sulphur-dioxide, carbon-dioxide and carbon-monoxide, arsenic, lead etc. put one at a higher risk of life threatening respiratory diseases.
OR
Exposure to high levels of noise can cause hypertension, stress, hearing loss disturbance in sleeping pattern, tinnitus etc.
Question 8.
“Human beings are direcdy dependent on nature for resources which sustain them.” Examine the statement.
OR
“The knowledge about nature is Extremely important to develop technology.” txamine the statement. [3]
Answer:
There is direct dependence of human beings on nature for resources which sustain them. The physical environment for such societies becomes the “Mother Nature”. Nature is powerful source, worshipped, revered and conserved. Human beings ‘ are directly dependent on nature for resources which sustain them. They create possibilities with the resources obtained from the environment. The human actvities create cultural landscape. The imprints of human activities are created everywhere; health resorts on highlands, huge urban sprawls, fields, orchards and pastures in plains and rolling hills, ports on the coasts, oceanic routes on the oceanic surface and satellites in the space. Nature provides opportunities and human beings make use of these and slowly nature gets humanized and starts bearing the imprints of human endeavour.
OR
Human beings interact with their physical environment with the help of technology. It is not important what human beings produce and create but it is extremely important ‘with the help of what tools and techniques do they produce and create’. Technology indicates the level of cultural development of society. Human beings were able to develop technology after they developed better understanding of natural laws.
- The understanding of concept of friction and heat helped us discover fire.
- Understanding of the secrets of DNA and genetics enabled us to conquer many diseases.
- The laws of aerodynamics were used to develop faster planes.
- Knowledge about nature is extremely important to develop technology and technology loosens the shackles of environment on human beings.
Question 9.
Study the following table and answer the questions that follows:
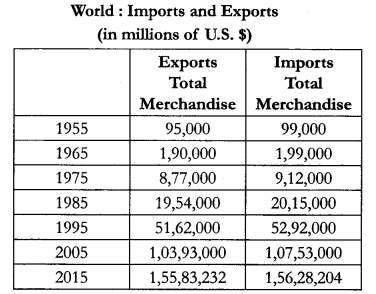
(9.1) Which aspect of trade has shown rapid growth ?
(9.2) Has the total volume of trade increased or decreased ?
(9.3) Why does import take place ? Write any two reasons.
Answer:
(9.1) Import aspect has shown major growth.
(9.2) The total volume of trade has increased over the years.
(9.3) Import are important for the development and growth of national economics because not all countries have the resources and skills required to produce certain goods and services.
Question 10.
“The period from 1901 to 1921 is referred to as a stagment phase of India’s population growth.” Substantiate the statement. [3]
Answer:
The period from 1901-1921 is referred to as a period of stagnant growth of India’s population, since in this period, growth rate was very low, even recording a negative growth rate during 1911-1921. Both the birth rate and death rate were high keeping the rate of increase in population low.
Poor health and medical services, illiteracy of people at large and inefficient distribution system of food and other basic necessities were largely responsible for a high birth and death rates in this period.
Question 11.
How does intermixing of people from diverse cultures due to migration have positive values ? Explain. [3]
Answer:
Migration leads to intermixing of people from diverse cultures. It has positive contribution such as evolution of composite culture and breaking through the narrow considerations and widens up the mental horizon of the people at large. It helps to promote national integration, loosens die rigidity in terms of social barriers like caste and religion. Intermixing of people helps in decreasing the social gaps formed between different castes and classes.
Question 12.
Describe the development of medieval towns in India during the Mughal period. [3]
OR
Describe the development of modern towns in India during the British period.
Answer:
The Mughal period observed the development of many cities and towns. About 100 of existing towns have their roots in medieval period. These were well connected with roadways and majorly developed as capitals or headquarters of principalities and kingdoms. There are fort towns. Agra was then the capital and was well connected ‘ with the rest of the country. The other important towns included Delhi, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Lucknow and Nagpur. These towns grew bigger and occupied great significance in terms of administration, trade and manufacturing.
OR
The British and other Europeans developed a number of towns in India. They first developed some trading ports such as Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Surat, Daman, Goa, Pondicherry, etc. for the ease of trade and commerce. Gradually they established their administrative centres, hill towns as summer resorts etc. Towns based on modern industries also evolved after 1850. For eg., a large number of towns were developed as administrative headquarters, eg., Chandigarh, Bhubaneswar, Gandhinagar, Dispur, etc. and as industial centres such as Durgapur, Bhilai, Sindri, Barauni, etc. Some old towns also developed as satellite towns around metropolitan cities such as Ghaziabad, Rohtak, Gurgaon around Delhi. With increasing investment in rural areas, a large number of medium and small towns have developed all over the country.
Question 13.
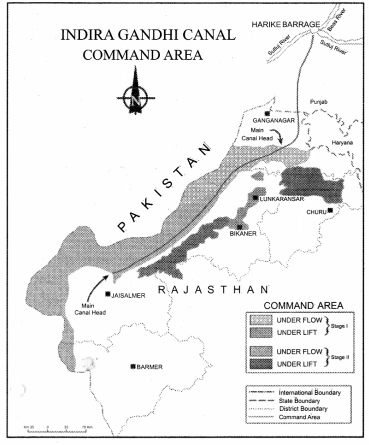
Study the given map carefully and answer the questions that follow:
(13.1) Mention the source of origin of this canal.
(13.2) Why is the area to. the east of the canal under lift irrigation ?
(13.3) Explain the economic significance of this canal for the command area. [4]
Answer:
(13.1) Canal originates at Harike Barrage/Confluence of Satluj and Beas.
(13.2) Areas of the East of canal under lift irrigation because water is lifted up to make it to flow against the slope of the land/high land area.
(13.3)
- Canal irrigation has led to increase in cultivated area and intensity of cropping.
- Traditional crops sown here like Gram and Bajra have been replaced by Wheat, Cotton, Groundnut and Rice.
- It led to increase in agriculture and productive livestock.
Question 14.
Explain the economic and cultural factors that influence the distribution of population in the world. [3 + 2 = 5]
Answer:
Economic Factors :
- Minerals : Areas rich in mineral deposits result in better employment opportunities and hence have higher population concentration. Industrial towns are found to develop near mining centres. They favour high density of population. For eg., Durgapur and Jamshedpur.
- Urbanisation : Urban settlements offer better standard of living, medical facilities, well developed transport networks and better employment opportunities etc. These facilities encourage rural to urban migration resulting in high density of population in the megacities of the world.
- Industrialisation: Industrial belts offer scope of various types of employment opportunities and attract large scale migration. This includes factory workers, bank employers, shopkeepers etc. Cultural Factors : Places having religious and cultural significance attract more people e.g., Varanasi, Ayodhya, Mathura. In some countries, favourable government policies and incentives peaceful atmosphere and other facilities result in high population densities.
Question 15.
Explain with examples how commercial livestock rearing has become a specialised activity in the world. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
It is a modern highly commercial activity where livestock is reared on permanent ranches. Commercial livestock rearing is more organised and capital intensive. This is specialized activity in which only one type of animal is reared. Grasslands of USA, Australia, New Zealand. The following characteristics also make it a highly specialised activity.,
- Special care is taken about the fodder, machineries, health of the livestock. This makes in highly capital intensive.
- Modern healthcare is provided to the livestock.
- It is a highly mechanised activity and used modern technology.
- The number of animals is kept according to the carrying capacity of the ranches.
- Rearing of animals is done on a scientific basis.
Question 16.
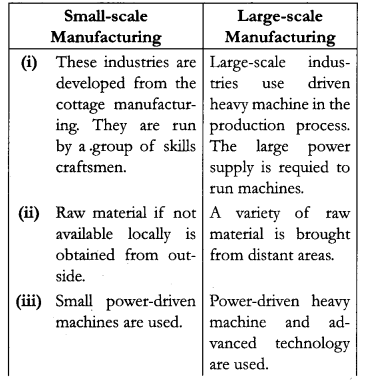
Differentiate between ‘small scale manufacturing’ and ‘large scale manufacturing’ in the world.
OR
Differentiate between agro-based industries and mineral-based industries in the world. [5]
Answer:
Small-scale manufacturing and large-scale manufacturing in the world :

OR
Agro-based industries and Mineral-based industries in the world:
| Agro-baged Industries | Mineral-based Industries |
| (i) These industries drive their raw materials from agriculture. | These industries drive their raw material from minerals. |
| (ii) Major agro processing industries are food processing like sugar, pickles, fruit juice etc. | Iron and steel industry, aluminium industry etc. |
| (iii) It suffers when agriculture productivity is less. | It may suffer due to exhaustible mineral resources. |
| (iv) No large investment in required. | Requires large investment. |
| (v) Source of employment in rural and urban areas. | Source of employment to a large number of people. |
Question 17.
Describe the significance of ‘Trans-Siberian Railway’. ‘ [1 × 5 = 5]
OR
Describe the significance of ‘Trans-Canadian Railway’.
Answer:
The significance of ‘Train-Siberian Railways’:
- Trans-Siberian Railway’s major rail route of Russia runs from St. Petersburg in the west to Vladivostok on the Pacific Coast in the east.
- It is the most important route in Asia and the longest (9,332 km) double-tracked and electrified transcontinental railway in the world.
- It has helped in opening up its Asian region to West European markets.
- It runs across the Ural Mountains, Ob and Yenisei rivers; Chita is an important agro centre and Irkutsk is a fur centre.
- It connects European Russia with Asiatic Russia.
OR
Trans-Canadian railway line is considered as the economic artery of Canada by the following reasons :
- Trans-Canadian railway line is about 7050 km long rail-line in Canada, runs from Halifax in the east to Vancouver on the Pacific coast passing through Montreal, Ottawa, Winnipeg and Calgary.
- It was constructed in 1886, as part of an agreement to make British Columbia on the west coast join the Federation of States.
- It gained economic significance because it connected the Quebec-Montreal industrial Region with the wheat belt of Prairie region and the coniferous forest region in the north.
- Each of these regions became complementary to the other.
- A loop line from Winnipeg to Thunder bay connects this rail-line with One of the important waterways of the world.
- This line is the economic artery of Canada, wheat and meat are the important exports on this route.
Question 18.
Explain with examples how ‘modern agricultural technology’ has brought a significant increase in agricultural output in India. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Modern agricultural technology has brought a significant increase in the agricultural output in India the following way :
- Production and field of many crops like rice and wheat has increased.
- The availability and use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides has enhanced the productivity of the farms.
- The extension of irrigation facilities even in the remove dry areas has helped to increase the productivity.
- The use of HYV seeds helped to increase the productivity of crops like wheat, rice, cotton jute etc.
- India ranked first in production of pulses and jute.
Question 19.
“The non-conventional sources of energy in India Will provide more sustained and environment friendly energy.” Examine the statement. [5]
OR
“Conversion of mineral resources is essential for the development of India.” Examine the statement.
Answer:
Non conventional energy sources are the only sustainable sources. They are renewable resources like Solar, Wind, Hydro-Geothermal and Biomass. These energy resources are more equitably distributed. These are environmental friendly and cost-effective in the long run. India has huge prospect in the production of such resources that will provide sustained and environmental friendly energy in the future :
- The large expanse of deserts and the coastlines are an ideal site for the generation of wind energy. The largest wind farm cluster in India is located in Tamilnadu.
- Bio gas is an important non conventional energy resource in rural areas. Shrubs, animal and agricultural wastes are used to produce biogas. The use of biogas for domestic consumption in rural areas can reduce the burning of fuel wood and thus reduce the feeling of trees.
- The long coastline of India is an ideal site for the generation of tidal energy. It can be used for generation of electricity which is non- polluting and a sustainable source of energy.
OR
Conservation of mineral resources is essential for the development of India.
- They are unevenly distributed over space. There is inverse relationship in quantity and quality of minerals.
- All minerals are exhaustible over time. These take long to develop geologically. They cannot be replenished immediately at the time of need.
- Minerals are an integral part of our life. They are used for various purposes. They are used in the manufacturing of a tiny pin to large constructions e.g., automobiles, roads, railway tracks, etc. Hence conservation is necessary for continuous use. The presence of resources and minerals contributes a lot to the economic growth of the country. It also creates a lot of revenue for the government to put to better use. It makes transportation faster.
Question 20.
“Indian railways network is one of the longest networks of the world and has contributed a lot to the growth of the economy.” Support the statement. [3 + 2 = 5]
Answer:
The Indian railway network is spread over 63,221 km making it one of the longest railway networks of the world. It plays a great role in the economic development of the country in the following way :
- It has connected the remote rural areas to the urban markets. This helps the farmers to carry their agricultural products to the urban centres.
- Railways help to carry bulky raw materials like coal from the mining centres to the industrial units.
- It has helped to connect the rural areas to the urban centres. This has helped to generate employment opportunities for the rural people. People can easily move from place to place in search of employment or for business purposes.
- The railways are often a point of connection to the important ports of India. Thus, the export items are often transported to the ports through the railways.
- It also creates a lot of revenue for the government to put to better use. It makes transportation faster.
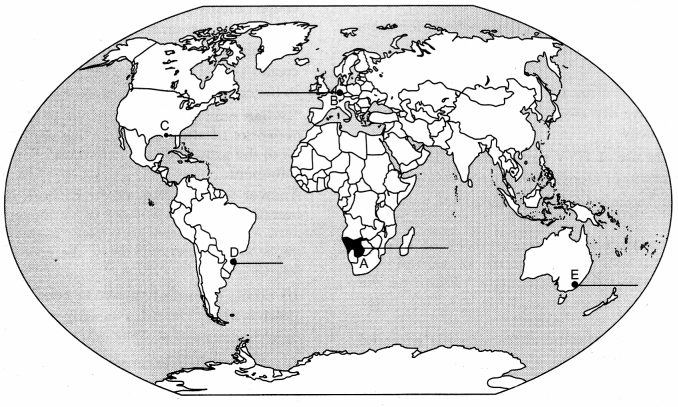
Question 21.
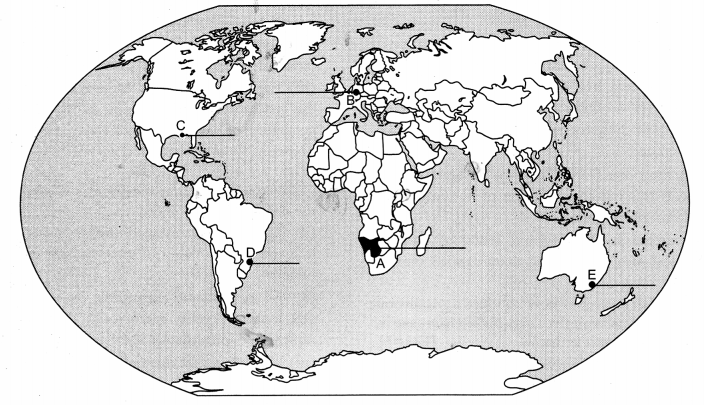
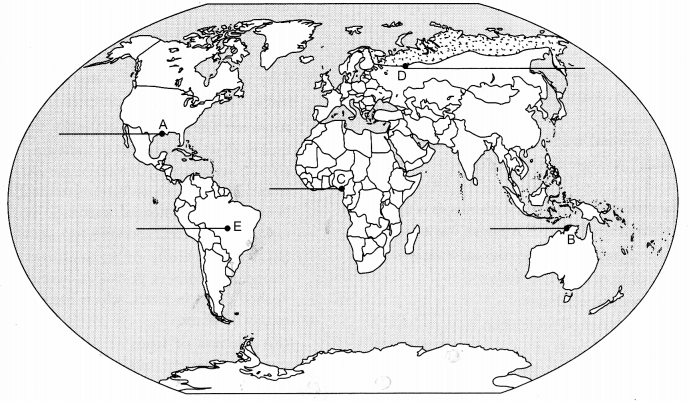
On the given political outline map of the World, five geographical features have been marked as
A, B, C, D and E. Identify them with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines drawn near them :
(A) An area of nomadic herding
(B) An industrial region
(C) An international airport
(D) A mega city
(E) The terminal station of ‘Trans-Continental Railway’. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Question 22.
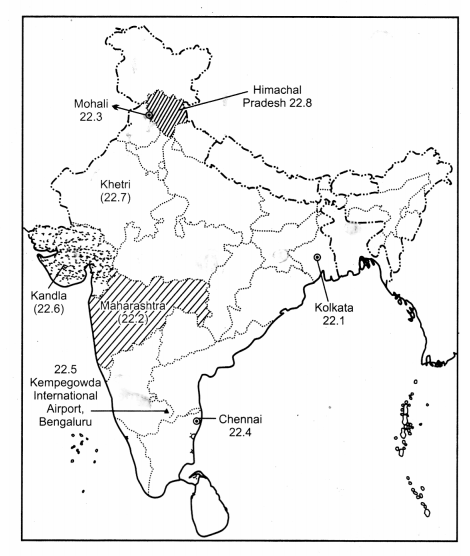
Locate and label any five of the following geographical features on the political outline map of India : [5 × 1 = 5]
(22.1) The city with more than 10 million population in West Bengal. .
(22.2) The leading producer State of cotton.
(22.3) The software technology park in Punjab.
(22.4) The Headquarter of Southern Railway Zone.
(22.5) The international airport of Karnataka.
(22.6) The major seaport in Gujarat.
(22.7) Khetri copper mines.
(22.8) The State with lowest level of urbanisation.
Answer:
: True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True
False
Question 1.
Explain the main characteristics of professional workers (White Collar). [1]
OR
Explain the term ‘Technopole’.
Answer:
White Collar worker is a salaried professional, an office worker or a part of management in general sense. This includes professionals involved in business management, customer support, market research, finance, engineering, operations research, marketing, information technology networking, etc.
OR
Technopoles are centers of high-tech manufacturing and information-based quaternary industry. They anthesis of positivism in which the cognitive power of human beings was emphasised. This new have science cities, technological parks and industrial complexes.
Question 2.
Mention the category to which the migration due to earthquake belongs. [1]
OR
In which State of India is the number of in migrants the largest ?
Answer:
Epidemics like earthquakes, fire, tsunami are push factors which encourage people to migrate from rural to urban areas.
OR
Maharashtra.
Question 3.
Analyse the ‘behavioural’ school of thought. [1]
Answer:
The behavioural school of thought was an approach, laid great emphasis on lived experience and also on the perception of space by social categories based on ethnicity, race and religion, etc.
Question 4.
Distinguish between ‘protective irrigation’ and ‘productive irrigation’. [1]
Answer:
Protective irrigation is done in order to protect the crops from adverse effects of soil moisture deficiency and to provide soil moisture to maximum possible area.
The objective of productive irrigation is to provide sufficient soil moisture in the cropping season to achieve high productivity and in this the water input per unit area of cultivated land-is higher than protective irrigation.
Question 5.
Evaluate the utility of ‘Rural Roads’. [1]
Answer:
Rural roads are useful because :
- The link the remotest part of the country with each other.
- They provide access to nearby market areas. Farmers are able to traverse these roads and transport their agricultural outputs to storage areas and places where they can be sold.
Question 6.
Name any one area of hamleted settlement in India. [1]
OR
Name any one State of India, where dispersed settlements are found.
Answer:
Hamleted settlement refers to the type of settlement which is fragmented into several units and is physically separated from other settlement. Such king of settlements can be easily found in the middle and lower Ganga plains, Chhattisgarh and lower valleys of the Himalayas.
OR
Meghalaya.
Question 7.
Define the term ‘co-operative farming’. [1]
Answer:
A group of farmes form a co-operative society by pooling in their resources voluntarily for more efficient and profitable farming. These societies then help the farmers to procure all inputs of farming. This is called co-operative farming.
Question 8.
“The sex-ratio in Asian urban areas remains male dominated, while in rural areas it remains female dominated.” Evaluate the statement. [3]
Answer:
The sex ratio in Asian urban areas remains male dominated due to the predominance of male migration.
In countries like India, female participation is farming activity in rural area is fairly high. Shortage of housing, high cost of living, insufficient job opportunities and lack of security in cities, discourage women to migrate from rural to urban areas.
Question 9.
Study the diagram given below and answer the
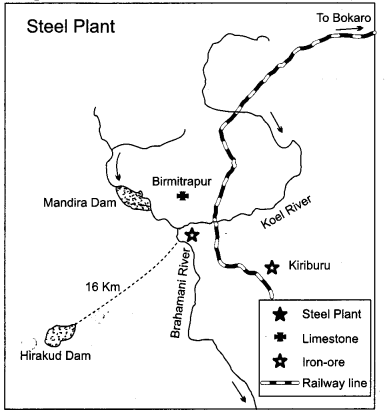
(9.1) Name the State in which this iron and steel plant is located.
(9.2) Name the sources of coal and iron-ore for this plant.
(9.3) Explain the principle on which this plant was set up.
Answer:
(9.1) Odisha state in Rourkela.
(9.2) The sources of coal and iron-ore are : Sundargarh and Kendujhar.
(9.3) Set up on the basis of proximity, to raw material, nearness of coal-field and availability of water.
Question 10.
“India is a land of linguistic diversity.” Support the statement. [1 × 3=3]
OR
Explain any three characteristics each of rural and urban composition of population in India.
Answer:
According to Grierson (Linguisti Survey in India, 1903-1928) there were 179 languages and as many as 544 dialects in the country. In the context of modern India, there are many scheduled languges (22) and a number of non-scheduled languages. Among the scheduled languages, the speakers of Hindi have the highest percentage (40.42). The smallest language groups are Kashmiri and Sanskrit speakers (0.01 per cent each). These variation of languages in India, makes it a land-linguistic diversity.
Population composition refers to those characteristics of population which are measurable and which helps us to distinguish one group of people from the other. Rural population :
- People in rural areas are mainly engaged in primary activities such as agriculture, animal husbandry, forest gathering and household industries etc.
- The rural population is high in India. Social relationships amongst rural population are warm and informal.
- Literary rates are quite low in rural areas.
: True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True
- People in urban areas are engaged in non-primary activities i.e., secondary or tertiary activities.
- People living in urban areas, usually enjoys high economic status.
- Social relationships among urban population are complex and formal. Level of literacy is high amongst urban population.
Question 11.
“Apart from birth and death, migration is another
way by which the population size changes.” Justify the statement. [1 × 3=3]
OR
“Technological advancement helped in the reduction of birth rate, but population growth remained high.” Justify the statement.
Answer:
Apart from birth and death rates, migration plays a vital role in population since change. When people move from one place (place of origin) to another place (place of destination), it eventually affects the population size of the particular region. The place of origin shows a decrease in population while the population increases in the place of destination. Hence, migration effects the population size of particular region.
OR
Reasons for high population growth are as follows :
- The steam engine replaced human and animal energy and this helped in increasing agricultural and industrial production.
- Inoculation/Vaccination against epidemics and other communicable diseases.
- Improvement in medical and sanitation facilities helped reducing death rates.
Question 12.
Study the map given below carefully and answer the questions that follow : [1 + 2 = 3]
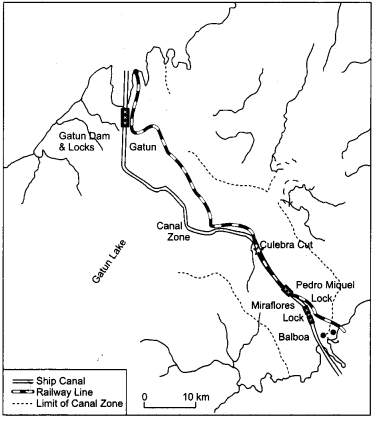
(12.1) Identify and name the canal shown in the map.
(12.2) Explain any two features of this canal.
Answer:
(12.1) Panama canal.
(12.2) ‘Two features:
- It has lock system
- It connects the Atlantic Ocean in the East to the Pacific Ocean in the West.
Question 13.
“The Gross National Happiness is the measure of the country’s progress.” Evaluate the statement. [1 × 3 = 3]
Answer:
The Gross National Happiness is used as a tool to measure a county’s progress. The material and technological developments are approached more cautiously taking into consideration the possible harm they might bring to the environment and the other aspects of cultural and spiritual life of the people of a country. Material progress cannot be attained at the cost of happiness. The main objective of Gross National Happiness is to think spiritually about non-materialistic and qualitative aspects of development.
Question 14.
Define the term ‘trade’. Describe the features of rural marketing centres and urban marketing centres. [1 + 2 + 2 = 5]
Answer:
‘Trade’ means the voluntary exchange of goods and services.
Features of Rural marketing centres :
- They cater only to nearby settlements which are quasi-urban centres.
- They serve as trading centres of the most rudimentary type.
- Personal and professional services are not well- developed.
- The rural marketing centres collect and distribute from nearby Mandis (Wholesale markets) and also from retailing areas.
Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban marketing centres : Merkmale of Urban
- They have more widely specialised urban services.
- These provide specialised goods and services, required by urban consumers.
- In urban marketing centres, personal and professional services are more developed.
- Urban centres provide manufactured markets to develop. E.g., markets for labour, housing, semi-finished or finished products.
Question 15.
How to human beings pollute the water through industrial and agricultural activities ? Explain. [21/2 + 21/2 = 5]
Answer:
Human beings pollute the water through industrial, agricultural and cultural activities. Among these activities, industry is the most significant contributor.
: True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True
False
Question 16.
Describe the priorities which have been outlined by the United Nations Development Programme as part of its urban strategy. [1 × 5 = 5]
OR
Describe any five environmental problems or urban settlements in the developing countries of the World.
Answer:
The priorities which have been outlined by the United Nations Development Programme as part of its urban strategy are :
- Increasing shelter for the urban poor.
- Provision of basic urban services such as education, primary healthcare, clean water and sanitation.
- Improving women’s access to basic services and government facilities.
- Upgrading energy use and alternative transport systems.
- Reducing air pollution.
OR
Five environment problems of urban settlements in the developing countries of the world :
- Huge disposal of waste products by urban population which leads to acute scarcity of potable water for domestic and industrial uses.
- An improper sewerage system deteriorates the environment and creates unhealthy conditions.
- Massive use of traditional fuel in the domestic is well as the industrial sector severely pollutes the air.
- Improper disposal of domestic and industrial wastes leads to soil infertility.
- Huge concrete structures erected to accommodate the population and economic needs play a very conducive role to create heat islands.
Question 17.
Which apex body develops the border roads ? Explain the importance of border roads with examples. [1 + 4 = 5]
OR
Explain with examples any five steps taken to increase the performance and quality of Indian Railways. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Borders Roads are constructed and maintained by Borders Road Organization (BRO). Border roads are important:
- For accelerating economic development in frontier areas.
- For strengthening defence preparedness.
- To promote the harmonius relationship with neighbouring countries (e.g., Nepal, China, etc.).
- Provide better connectivity for civilians in strategically sensitive areas (e.g., Attari, Leh-Ladakh).
- During disasters in Himalayan belt and Northeast India, they help in restoring road network and rescue operations.
OR
Steps taken to increase the performance and quality of Indian Railways :
- Unification of gauges from narrow and meter gauge to broad gauge.
- Electrification of the railway network.
- Introduction of metro rail service.
- Increase in the speed and haulage capacity.
- Introduction of new rail routes; e.g., Konkan railways on west coast.
- Computerisation of reservations.
- Improvement in the environment of the stations.
Question 18.
“International trade is mutually beneficial to nations.” Analyse the statement. [1 × 5 = 5]
OR
“The difference in national resources is the basis of international trade.” Analyse the statement.
Answer:
Undertaking international trade is mutually beneficial to nations if it leads to :
- Regional specialisation.
- Higher level of production.
- Better standards of living.
- Worldwide availability of goods and services.
- Equalisation of prices and wages.
- Diffusion of knowledge and culture.
OR
The world’s national resources are unevenly distributed because of difference in their physical make-up.
- Geological structure determines the mineral resource base and topographical differences ensure diversity of crops and animals raised, e.g., Low lands have greater agricultural potential whereas mountains attract tourists.
- Mineral resources are unevenly distributed the world over. The availability of mineral resources provides the basis for industrial development.
- Climate influences the type of flora and fauna that can survive in a given region. It also ensures diversity in the range of various products, e.g., wool production can take place in cold regions whereas cocoa and rubber are best grown in tropical region.
- Low lands have greater agricultural potential and mountains attract tourists and promote tourism.
- Vegetation varies due to diverse climatic conditions.
Question 19.
Why is the quality of water deteriorating in India ? Explain with examples. [5]
Answer:
The main reason for the degradation of quality of water resources in India are :
- Direct dumping of various foreign substances from industries such as chemical residual, numerous heavy metals, industrial wastes, in water bodies making then useless and unfit for various purposes.
- Various kinds of agricultural chemicals (inorganic fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides etc.) are washed down in rivers, which naturally affect the quality of water.
- Addition of loads of untreated sewage into rivers declines the quality of water and severely harms aquatic life and system.
- Various toxic substances from domestic and municipal wastes seep deep down making groundwater polluted.
- Cultural activities such as pilgrimage, religious fairs, tourism and some ritualistic practices are other major reasons. Ganga and Yamuna are highly polluted.
Question 20.
Explain any five objectives of ‘Namami Gange Programme’. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Objectives of ‘Namami Gange Programme’ :
- Afforestation along the bank to increase bio-diversity.
- Effective pollution abatement of river Ganga.
- Public awareness and development of river front.
- Diversion and treatment of domestic sewage.
- To identify grossly polluting units and to stop them from degrading the water quality.
Question 21.
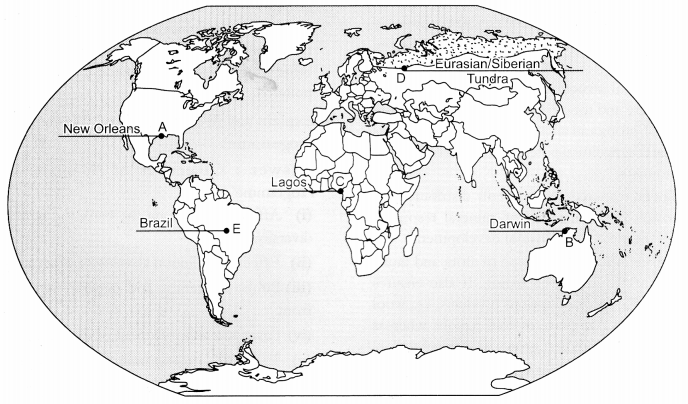
On the given political outline map of the World, five geographical features have been marked as A, B, C, D and E. Identify these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines drawn on the map near them : [1 × 5 = 5]
(A) A major seaport
(B) An international airport
(C) A mega city
(D) An area of nomadic herding
(E) The largest country of the continent in terms of area mountains attract tourists and promote tourism.
Answer:
Question 19.
Why is the quality of water deteriorating in India ? Explain with examples. [5]
Answer:
The main reason for the degradation of quality of water resources in India are :
- Direct dumping of various foreign substances from industries such as chemical residual, numerous heavy metals, industrial wastes, in water bodies making then useless and unfit for various purposes.
- Various kinds of agricultural chemicals (inorganic fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides etc.) are washed down in rivers, which naturally affect the quality of water.
- Addition of loads of untreated sewage into rivers declines the quality of water and severely harms aquatic life and system.
- Various toxic substances from domestic and municipal wastes seep deep down making groundwater polluted.
- Cultural activities such as pilgrimage, religious fairs, tourism and some ritualistic practices are other major reasons. Ganga and Yamuna are highly polluted.
Question 20.
Explain any five objectives of ‘Namami Gange Programme’. [1 × 5 = 5]
Answer:
Objectives of ‘Namami Gange Programme’ :
- Afforestation along the bank to increase bio-diversity.
- Effective pollution abatement of river Ganga.
- Public awareness and development of river front.
- Diversion and treatment of domestic sewage.
- To identify grossly polluting units and to stop them from degrading the water quality.
Question 22.
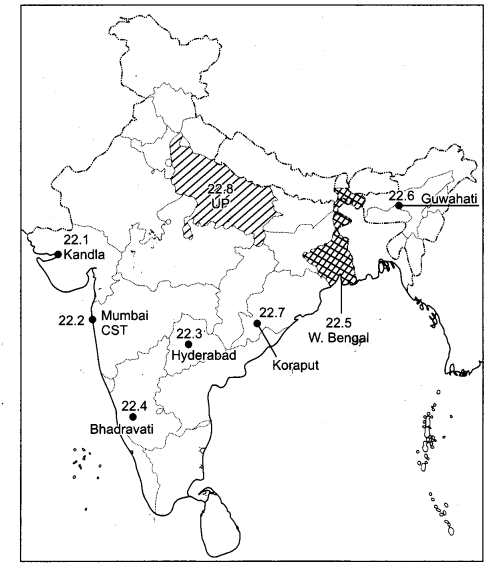
Locate and label any five of the following geographical features on the political outline map of India with appropriate symbols : [5 × 1 = 5]
(22.1) A major seaport in Gujarat.
(22.2) The Headquarter of Central Railway Zone.
(22.3) Software Technology Park in Telangana.
(22.4) The iron and steel plant located in Karnataka.
(22.5) The leading rice producer State in India.
(22.6) An oil refinery in Assam.
(22.7) A mine of Bauxite in Odisha.
(22.8) The leading State in the field of out-migration.
Answer:
: True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True
False
Question 1.
How does age-sex pyramid project declining trend in population ? [1]
Answer:
The Age Sex pyramid projects trend in population by a figure which is narrower at the base showing low birth rates and tapered at the top showing low death rates. This shows declining trend in population.
Question 2.
Examine the concept of ‘income approach’ of human development. [1]
Answer:
Income approach of Human Development : Human Development is seen as being linked to income. The idea is that the level of income reflects the level of freedom an individual enjoys; higher the level of income, higher is the level of human development.
Question 5.
Why does the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of a country not fully reflect the quality of life of the country ? [1]
Answer:
The Gross Domestic Product or GDP of a country not fully reflects the quality of life of the country as there is still the prevalence of gap between rich and poor.
Question 10.
“The period from 1951 to 1981 is referred to as a phase of population explosion in India.” Substandiate the statement. [3]
Answer:
The decades 1951-1981 are referred to as the period of population explosion in India, which was caused by a rapid fall in the mortality rate but a high fertility rate of population in the country. During this period, the population of India grew from 361 million in 1951 to 683 million in 1981. There was a growth of population by 322 million during this phase. This was the phase when both death rate as well as birth rate declined. The average annual growth rate was as high as 2.2 per cent. It is in this period, after the Independence, that development activity was introduced through a centralised planning process and the economy started showing up ensuring the improvement of the living condition of people at large. Consequently, there was a higher growth rate. Besides, increased international migration bringing in Tibetans, Bangladeshis, Nepalis and even people from Pakistan contributed to the high growth rate.
Question 14.
Why do people migrate ? Explain the two types of factors that influence migrations in the world. [1 + 2 + 2 = 5]
Answer:
Most people migrate for economic reasons. Cultural and environmental factors also induce migration.
Push factors ‘push’ people away from their home and include things like war. Pull factors ‘pull’ people to a new home and include things like better opportunities. The reasons people migrate are usually economic, political, cultural or environmental.
The few types of factors that influence migration in the world :
-
The Pull Factors:
Pull factors generally attract people towards certain cities and territories.
Reasons:- Better job opportunities.
- Better living conditions.
- Peace.
- Stability.
- Security of life and property.
- Pleasant climate.
-
The Push Factors :
The push factors generally make the place or destination less attractive.
Reasons :- Unemployment.
- Poor living conditions.
- Political turmoil.
- Unpleasant climate.
- Natural disasters.
- Epidemics.
- Socio-economic backwardness.
Question 15.
Explain any five important characteristics of ‘mixed farming’ practised in the world. [5]
Answer:
Mixed farming is a type of agriculture which involves both crops and livestock. Mixed farming yields fairly high agricultural returns because of efficient methods of farming, excellent transport systems, and proximity to the urban markets and rein ability of precipitation.
: True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True. True
- Equal emphasis is laid on crop cultivation.
- Animals like cattle, sheep, pigs and poultry provide the main income with crops like wheat, barley, oats, maize, fodder, root crops.
- Mixed farms are moderate in size.
- Crop rotation and intercropping maintains soil fertility.
- High capital expenditure on farm machinery and building and skilled and expertised farmers.
- Extensive use of fertilizers and green manures.
Question 18.
Mention any two land use categories of India, which have shown decrease in their areas. Explain the reasons responsible for decreasing areas in these two categories. [1 + 2 + 2 = 5]
Answer:
Two land use categories which have shown decrease :
- Barren and wasteland.
- Area under pastures and tree crops.
False
-
Barren and wasteland.
Increasing pressure on land from agriculture and non-agricultural sectors. -
Land under pastures tree crops.
Decrease due to pressure from agricultural land and illegal encroachment due to cultivation on common pasture lands.