Get Free NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.1, Ex 3.2, Ex 3.3, Ex 3.4, and Miscellaneous Exercise PDF in Hindi and English Medium. Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions are extremely helpful while doing your homework. Trigonometric Functions All Exercises Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions were prepared by Experienced LearnCBSE.online Teachers.
Class 11 Maths Trigonometric Functions NCERT Solutions in English Medium and Hindi Medium
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.1
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.2
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.3
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Ex 3.4
- Trigonometric Functions Class 11 Miscellaneous Exercise
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.1 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.2 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.3 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.4 का हल हिंदी में
- त्रिकोणमितीय फलन विविध प्रश्नावली का हल हिंदी में
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Functions Class 11 Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Trig Cheat Sheet
- JEE Main Trigonometry Previous Year Questions
Free download NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions Ex 3.1, Ex 3.2, Ex 3.3, Ex 3.4, and Miscellaneous Exercise PDF in Hindi Medium as well as in English Medium for CBSE, Uttarakhand, Bihar, MP Board, Gujarat Board, BIE, Intermediate and UP Board students, who are using NCERT Books based on updated CBSE Syllabus for the session 2019-20.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
| Section Name | Topic Name |
| 3.1 | Introduction |
| 3.2 | Angles |
| 3.3 | Trigonometric Functions |
| 3.4 | Trigonometric Functions of Sum and Difference of Two Angles |
| 3.5 | Trigonometric Equations |
| 3.6 | Summary |
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.1
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 1:
Find the radian measures corresponding to the following degree measures:
(i) 25°
(ii) – 47° 30′
(iii) 240°
(iv) 520°
Ans:
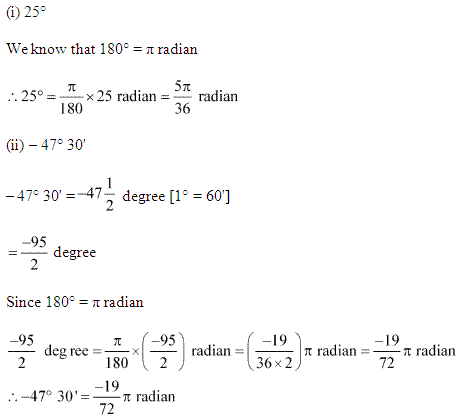


Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 2:
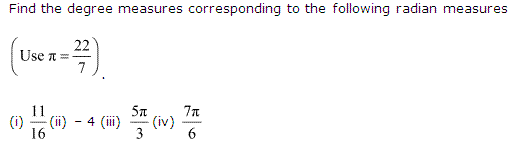
Ans:
(i) \(\frac{11}{16}\)
We know that: π radian = 180°
∴ \(\frac{11}{16}\) radain = \(\frac{180}{\pi} \times \frac{11}{16}\) × degree
= \(\frac{45 \times 11}{\pi \times 4}\) degree
= \(\frac{45 \times 11 \times 7}{22 \times 4}\) degree
= \(\frac{315}{8}\) degree
= 39 \(\frac{3}{8}\) degree
= 39° + \(\frac{3 \times 60}{8}\) minutes [1° = 60′]
= 39° + 22′ + \(\frac{1}{2}\) minutes
= 39°22’30” [1′ = 60°].


More Resources for CBSE Class 11
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Business Studies
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Psychology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Entrepreneurship
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Indian Economic Development
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Computer Science
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 3:
A wheel makes 360 revolutions in one minute. Through how many radians does it turn in one second?
Ans:
Number of revolutions made by the wheel in 1 minute = 360
∴ Number of revolutions made by the wheel in 1 second = \(\frac{360}{6}\) = 6
In one complete revolution, the wheel turns an angle of 2π radian.
Hence, in 6 complete revolutions, it will turn an angle of 6 × 2π radian, i.e., 12π radian
Thus, in one second, the wheel turns an angle of 12π radian.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 4:
Find the degree measure of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 cm y an arc of length 22 cm (Use π = \(\frac{22}{7}\)).
Ans:
We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\)
Therefore, for r = 100 cm, l = 22 cm,
we have
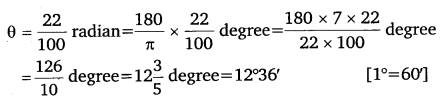
Thus, the required angle is 12°36′.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 5:
In a circle of diameter 40 cm, the length of a chord is 20 cm. Find the length of minor arc of the chord.
Ans:
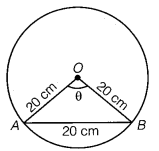
Given, diameter = 40 cm
∴ radius (r) = \(\frac{40}{2}\) = 20 cm
and length of chord, AB = 20 cm
Thus, ∆OAB is an equilateral triangle.
We know that,
θ = \(\frac{\text { Arc } A B}{\text { radius }}\)
⇒ Arc AB = θ × r
= \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) × 20 .
= \(\frac{20}{3}\) π cm.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 6:
If in two circles, arcs of the same length subtend angles 60° and 75° at the centre, find the ratio of their radii.
Ans:
Let the radii of the two circles be r
1
and r
2
.
Let an arc of length l subtend an angle of 60° at the centre of the circle of radius r
1
, while let an arc of length l subtend an angle of 75° at the centre of the circle of radius r
2
.
Now, 6o° = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) radian and
75° = \(\frac{5 \pi}{12}\) radian
We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\) or l = rθ
∴ l = \(\frac{r_{1} \pi}{3}\) and
l = \(\frac{r_{2} 5 \pi}{12}\)
⇒ \(\frac{r_{1} \pi}{3}=\frac{r_{2} 5 \pi}{12}\)
⇒ r = \(\frac{r_{2} 5}{4}\)
\(\frac{r_{1}}{r_{2}}=\frac{5}{4}\)
Thus, the ratio of the radii is 5 : 4.
Ex 3.1 Class 11 Maths Question 7:
Find the angle in radian through which a pendulum swings if its length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length
(i) 10 cm
(ii) 15 cm
(iii) 21 cm.
Ans:
We know that in a circle of radius r unit, if an arc of length l unit subtends an angle θ radian at the centre, then
θ = \(\frac{l}{r}\).
It is given that r = 75 cm
(i) Here, l = 10 cm
θ = \(\frac{10}{75}\) radian
= \(\frac{2}{15}\) radian
(ii) Here, l = 15 cm
θ = \(\frac{15}{75}\) radian
θ = \(\frac{1}{5}\) radian
(iii) Here, l = 21 cm
θ = \(\frac{21}{75}\) radian
= \(\frac{7}{75}\) radian.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.2
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 1:
Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if cos x = – \(\frac{1}{2}\) x lies in third quadrant.
Ans:
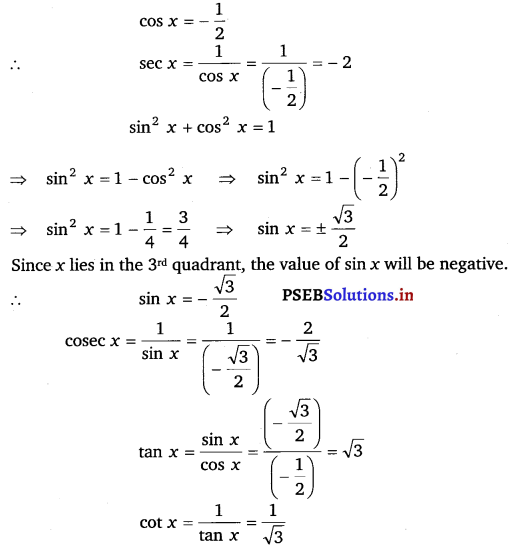
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 2:
Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if sin x = \(\frac{3}{5}\), x lies in second quadrant.
Ans:
sin x = \(\frac{3}{5}\)
cosec x = \(\frac{1}{\sin x}=\frac{1}{\left(\frac{3}{5}\right)}=\frac{5}{3}\)
sin
2
x + cos
2
x = 1
⇒ cos
2
x = 1 – sin
2
x
⇒ cos
2
x = 1 – (\(\frac{3}{5}\))
2
⇒ cos 2 x = 1 – \(\frac{9}{25}\)
⇒ cos 2 x = \(\frac{16}{25}\)
⇒ cos x = ± \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Since x lies in the 2nd quadrant, the value of cos x will be negative
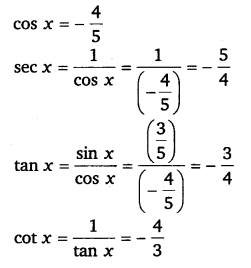
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 3:
Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if cot x = \(\frac{3}{4}\), x lies in third quadrant.
Ans:
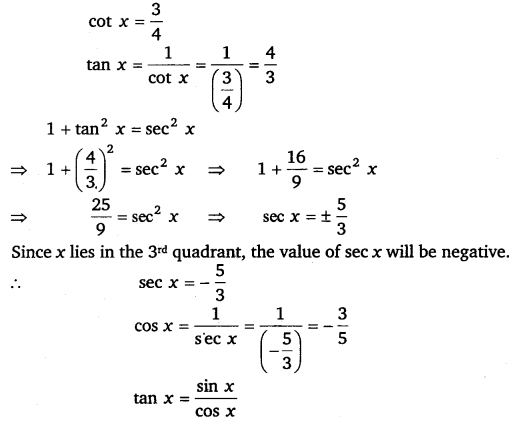
⇒ \(\frac{4}{3}=\frac{\sin x}{\frac{-3}{5}}\)
⇒ sin x = \(\left(\frac{4}{3}\right) \times\left(\frac{-3}{5}\right)=-\frac{4}{5}\)
⇒ cosec x = \(\frac{1}{\sin x}=-\frac{5}{4}\).
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 4:
Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if sec x = \(\frac{13}{5}\), x lies in fourth quadrant.
Ans:
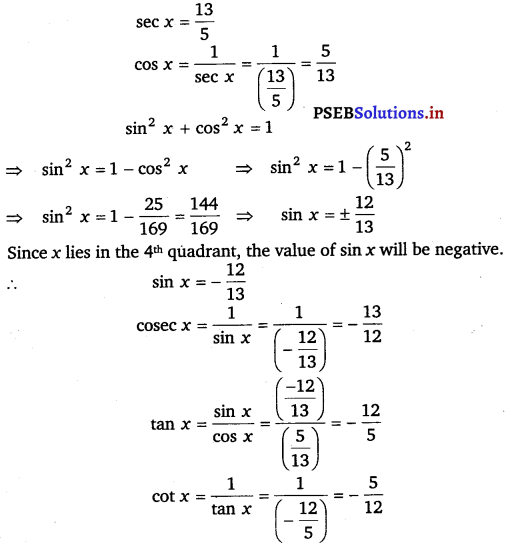
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 5:
Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if tan x = \(\frac{5}{12}\), x lies in second quadrant.
Ans:
tan x = – \(\frac{5}{12}\)
cot x = \(\frac{1}{\tan x}=\frac{1}{\left(-\frac{5}{12}\right)}=-\frac{12}{5}\)
1 + tan
2
x = sec
2
x
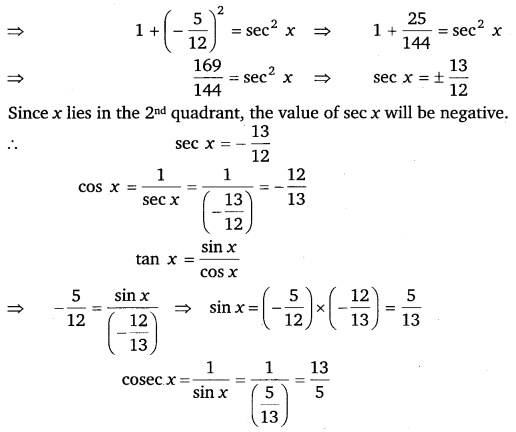
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 6:
Find the value of the trigonometric function sin 765°.
Ans:
It is known that the values of sin x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°.
∴ sin 765° = sin (2 × 360° + 45°)
= sin 45° = 1
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 7:
Find the value of the trigonometric function cosec (- 1410°)
Ans:
It is known that the values of cosec x repeat after an interval of 2π or 360°.
∴ cosec (- 1410°) = cosec (- 1410° + 4 x 360°)
= cosec (- 1410° + 1440°)
= cosec 30° = 2.
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 8:
Find the value of the trigonometric function tan \(\frac{19 \pi}{3}\).
Ans:
It is known that the values of tan x repeat after an interval of π or 180°.
∴ \(\tan \frac{19 \pi}{3}=\tan 6 \frac{1}{3} \pi\)
= \(\tan \left(6 \pi+\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=\tan \frac{\pi}{3}\)
= tan 60° = √3.
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 9:
Find the value of the trigonometric function sin \(\left(-\frac{11 \pi}{3}\right)\).
Ans:
It is known that the values of cot x repeat after an interval of π or 180°.
∴ \(\sin \left(\frac{11 \pi}{3}\right)=\sin \left(-\frac{11 \pi}{3}+2 \times 2 \pi\right)\)
= \(\sin \left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)=\sin 60^{\circ}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Ex 3.2 Class 11 Maths Question 10:
Find the value of the trigonometric function cot \(\left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}\right)\).
Ans:
It is known that the values of cot x repeat after an interval of ir or 1800.
∴ \(\cot \left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}\right)=\cot \left(-\frac{15 \pi}{4}+4 \pi\right)=\cot \frac{\pi}{4}\) = 1.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Exercise 3.3
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 1:
Prove that: sin
2
\(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + cos
2
\(\frac{\pi}{3}\) – tan
2
\(\frac{\pi}{4}\) = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Ans:
L.H.S.= sin 2 \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + cos 2 \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) – tan 2 \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
= \(\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}+\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{2}\) – (1) 2
= \(\frac{1}{4}+\frac{1}{4}-1=-\frac{1}{2}\)
= R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 2:
Prove that: 2 sin
2
\(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + cosec
2
\(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) cos
2
\(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
Ans:
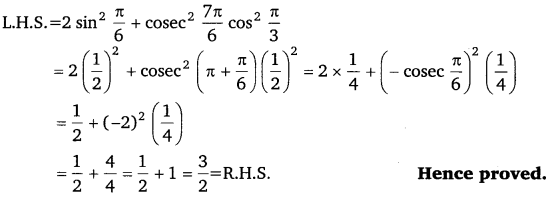
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 3:
Prove that :cot
2
\(\frac{\pi}{6}\) + cosec \(\frac{5 \pi}{6}\) + 3 tan
2
\(\frac{\pi}{6}\) = 6
Ans:
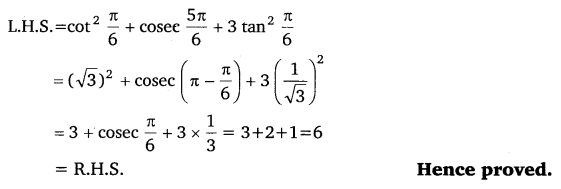
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 4:
Prove that: 2 sin
2
\(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\) + 2 cos
2
\(\frac{\pi}{4}\) + 2 sec
2
\(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = 10
Ans:
L.H.S = \(2 \sin ^{2} \frac{3 \pi}{4}+2 \cos ^{2} \frac{\pi}{4}+2 \sec ^{2} \frac{\pi}{3}\)
= \(2\left\{\sin \left(\pi-\frac{\pi}{4}\right)\right\}^{2}+2\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^{2}+2(2)^{2}\)
= \(2\left\{\sin \frac{\pi}{4}\right\}^{2}+2 \times \frac{1}{2}+8\)
= 2 \(\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^{2}\) + 1 + 8
= 1 + 1 + 8
= 10 = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 5:
Find the value of: (i) sin 75°,
(ii) tan 15°
Ans:
(i) sin 75° sin (45° + 30°)
= sin 45° cos 30° + cos 45° sin 30°
[∵ sin (x + y) = sin x cos y + cos x sin y]
= \(\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\left(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right)+\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)\)
= \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2 \sqrt{2}}+\frac{1}{2 \sqrt{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{3}+1}{2 \sqrt{2}}\)
(ii) tan 15° = tan (45° – 30°)
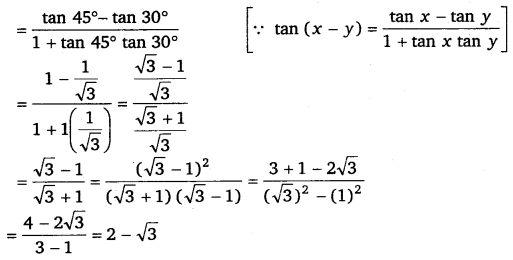
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 6:
\(\cos \left(\frac{\pi}{4}-x\right) \cos \left(\frac{\pi}{4}-y\right)-\sin \left(\frac{\pi}{4}-x\right) \sin \left(\frac{\pi}{4}-y\right)\) = sin (x + y)
Ans:
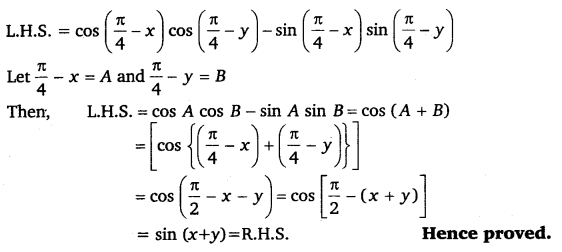
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 7:
Prove that: \(\frac{\tan \left(\frac{\pi}{4}+x\right)}{\tan \left(\frac{\pi}{4}-x\right)}=\left(\frac{1+\tan x}{1-\tan x}\right)^{2}\)
Ans:
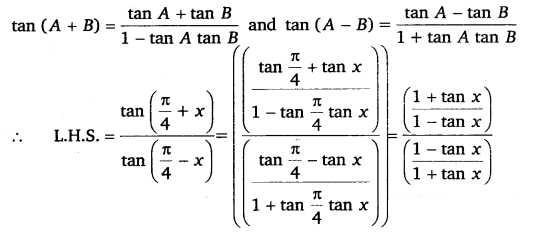
= \(\left(\frac{1+\tan x}{1-\tan x}\right)^{2}\)
= R.H.S
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 8:
Prove that: \(\frac{\cos (\pi+x) \cos (-x)}{\sin (\pi-x) \cos \left(\frac{\pi}{2}+x\right)}\) = cot
2
x
Ans:
L.H.S = \(\frac{\cos (\pi+x) \cos (-x)}{\sin (\pi-x) \cos \left(\frac{\pi}{2}+x\right)}\)
= \(\frac{[-\cos x][\cos x]}{(\sin x)(-\sin x)}=\frac{-\cos ^{2} x}{-\sin ^{2} x}\)
= cot 2 x
= R.H.S
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 9:
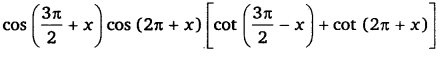 = 1
= 1
Ans:
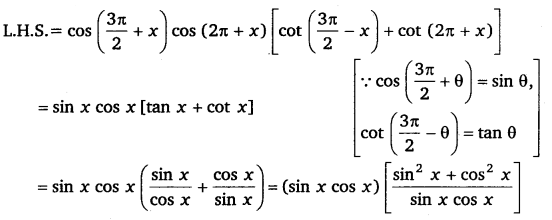
= 1 = R.H.S
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 10:
Prove that: sin (n + 1) x sin (n + 2) x + cos (n + 1) x cos (n + 2) x = cos x
Ans:
L.H. S. = sin (n + 1 )x sin (n + 2) x + cos (n +1) x cos (n + 2) x
[By the formula, cos (A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B]
= cos [(n + 2) x + (n + 1) x]
= cos (4x + 2x – 4x – x)
= cos x = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 11:
Prove that: \(\cos \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)-\cos \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)=-\sqrt{2} \sin x\)
Ans:
It is known that
cos A – cos B = \(-2 \sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cdot \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S.= \(=\cos \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)-\cos \left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)\)
= \(– 2 \sin \left\{\frac{\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)+\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)}{2}\right\} \cdot \sin \left\{\frac{\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}+x\right)-\left(\frac{3 \pi}{4}-x\right)}{2}\right\}\)
= – 2 sin (\(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)) sin x
= – 2 sin (- \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)) sin x
= – √2 sin x = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 12:
Prove that: sin
2
6x – sin
2
4x = sin 2x sin 10 x
Ans:
It is known that
sin A + sin B = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
sin A – sin B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
L.H.S.= sin
2
6x – sin
2
4x
= (sin 6x + sin 4x) (sin 6x – sin 4x)
= (2 sin 5x cos x) (2 cos 5x sin x)
= (2 sin 5x cos 5x) (2 sin x cos x)
= sin 10x sin 2x = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 13:
Prove that: cos
2
2x cos
2
6x = sin 4x sin 8x
Ans:
It is known that
cos A + cos B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos A – cos = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S = cos
2
2x – cos
2
6x
= (cos 2x + cos 6x) (cos 2x – 6x)
= \(\left[2 \cos \left(\frac{2 x+6 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{2 x-6 x}{2}\right)\right]\left[-2 \sin \left(\frac{2 x+6 x}{2}\right) \sin \frac{(2 x-6 x)}{2}\right]\)
∴ L.H.S.= cos
2
2x – cos
2
6x
= (cos 2x + cos 6x) (cos 2x – 6x)
= [2 cos 4x cos (-2x)] [- 2 sin 4x sin (- 2x)]
= [2 cos 4x cos 2x] [- 2 sin 4x (- sin 2x)]
= (2 sin 4x cos 4x) (2 sin 2x cos 2x)
= sin 8x sin 4x
= R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 14:
Prove that: sin 2x + 2 sin 4x + sin 6x = 4 cos
2
x sin 4x
Ans:
L.H.S.= sin 2x + 2 sin 4x + sin 6x
= [sin 2x + sin 6x] + 2 sin 4x
= \(\left[2 \sin \left(\frac{2 x+6 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{2 x-6 x}{2}\right)\right]\) + 2 sin 4x
[∵ sin A + sin B = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
= 2 sin 4x cos (- 2x) + 2 sin 4x
= 2 sin 4x cos 2x + 2 sin 4x
= 2 sin 4x (cos 2x + 1)
= 2 sin 4x (2 cos
2
x – 1 + 1)
= 2 sin 4x (2 cos
2
x)
= 4 cos
2
x sin 4x
= R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 15:
cot 4x (sin 5x + sin 3x) = cot x (sin 5x – sin 3x)
Ans:
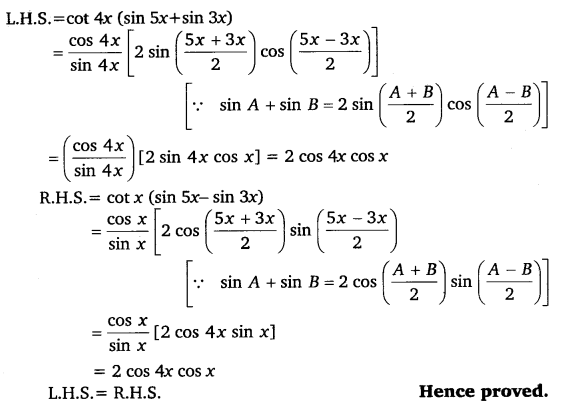
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 16:
Prove that: \(\frac{\cos 9 x-\cos 5 x}{\sin 17 x-\sin 3 x}=-\frac{\sin 2 x}{\cos 10 x}\)
Ans:
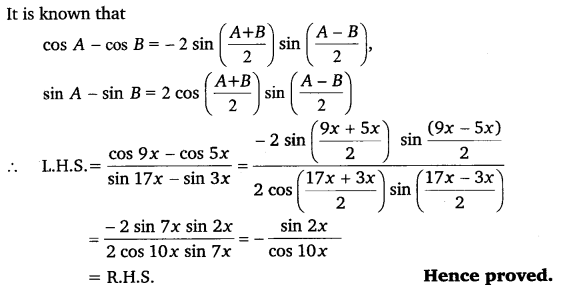
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 17:
Prove that: \(\frac{\sin 5 x+\sin 3 x}{\cos 5 x+\cos 3 x}\) = tan 4x
Ans:
It is known that
sin A + sin = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos A + cos = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S = \(\frac{\sin 5 x+\sin 3 x}{\cos 5 x+\cos 3 x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \sin \left(\frac{5 x+3 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{5 x-3 x}{2}\right)}{2 \cos \left(\frac{5 x+3 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{5 x-3 x}{2}\right)}\)
= \(\frac{2 \sin 4 x \cos x}{2 \cos 4 x \cos x}=\frac{\sin 4 x}{\cos 4 x}\)
= tan 4x = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 18:
Prove that: \(\frac{\sin x-\sin y}{\cos x+\cos y}=\tan \frac{x-y}{2}\).
Ans:
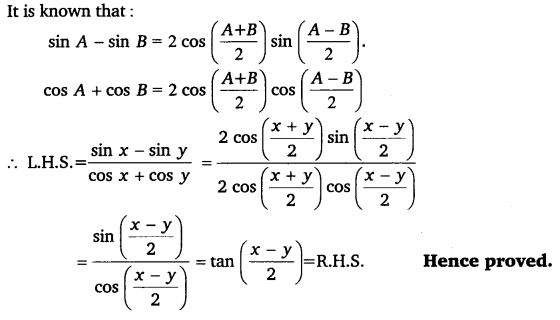
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 19:
Prove that: \(\frac{\sin x+\sin 3 x}{\cos x+\cos 3 x}\) = tan 2x
Ans:
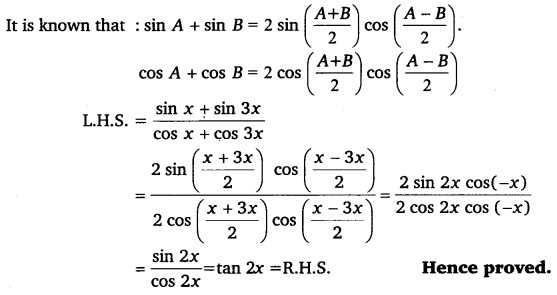
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 20:
Prove that: \(\frac{\sin x-\sin 3 x}{\sin ^{2} x-\cos ^{2} x}\) = 2 sin x
Ans:
It is known that
sin A – sin B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
cos 2 A – sin 2 A = cos 2A
∴ L.H.S. = \(=\frac{\sin x-\sin 3 x}{\sin ^{2} x-\cos ^{2} x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \cos \left(\frac{x+3 x}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{x-3 x}{2}\right)}{-\cos 2 x}\)
= \(\frac{2 \cos 2 x \sin (-x)}{-\cos 2 x}\)
= – 2 × (- sin x) = 2 sin x
= R.H.S
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 21:
Prove that: \(\frac{\cos 4 x+\cos 3 x+\cos 2 x}{\sin 4 x+\sin 3 x+\sin 2 x}\) = cot 3x
Ans:
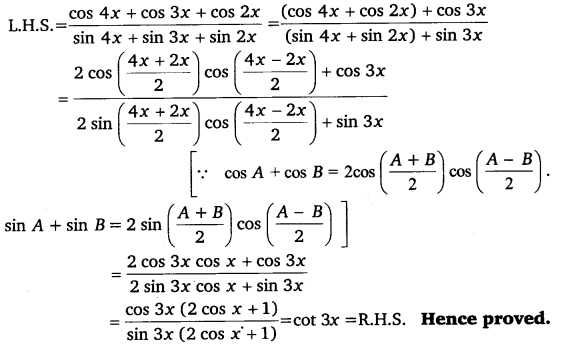
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 22:
Prove that : cot x cot 2x – cot 2x cot 3x – cot 3x cot x = 1
Ans:
L.H.S.= cot x cot 2x – cot 2x cot 3x – cot 3x cot x
= cot x cot 2x – cot 3x (cot 2x + cot x)
= cot x cot 2x – cot (2x + x) (cot 2x + cot x)
= cot x cot 2x – \(\left[\frac{\cot 2 x \cot x-1}{\cot x+\cot 2 x}\right]\) (cot 2x + cot x)
[∵ cot (A + B) = \(\frac{\cot A \cot B-1}{\cot A+\cot B}\)]
= cot x cot 2x – (cot 2x cot x – 1)
= 1 = R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 23:
Prove that: tan 4x = \(\frac{4 \tan x\left(1-\tan ^{2} x\right)}{1-6 \tan ^{2} x+\tan ^{4} x}\).
Ans:
It is known that:
tan 2A = \(\frac{2 \tan A}{1-\tan ^{2} A}\)
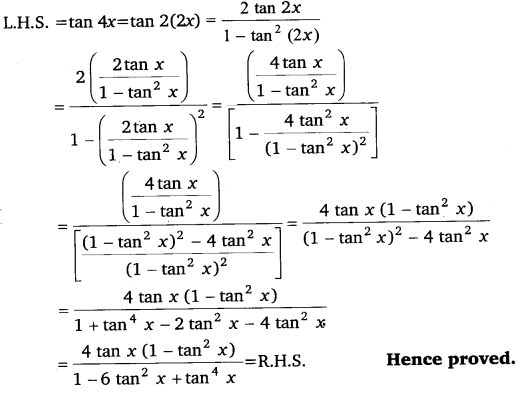
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 24:
Prove that: cos 4x = 18 sin
2
x cos
2
x
Ans:
L.H.S. = cos 4x = cos 2(2x)
= 1 – 2 sin
2
2x [∵ cos 2A = 1 – 2 sin
2
A]
= 1 – 2(2 sin x cos x)
2
[∵ sin 2A = 2 sin A cos A]
= 1 – 8 sin
2
x cos
2
x
= R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Ex 3.3 Class 11 Maths Question 25:
Prove that: cos 6x = 32 cos
6
x – 48 cos
4
x + 18 cos
2
x – 1
Ans:
We know that: cos 3x = 4 cos
3
x – 3cos x
On replacing x by 2x, we get
cos 3(2x) = 4 cos
3
(2x) – 3 cos 2x
⇒ cos 6x = 4 (2cos
2
x – 1)
3
– 3 (2cos
2
x – 1)
[∵ cos 2x = 2cos
2
x – 1]
= 4 [8 cos
6
x – 12 cos
4
x + 6 cos
2
x – 1] – 6 cos
2
x + 3
[∵ (a – b)
3
= a
3
– 3a
2
b + 3ab
2
– b
3
]
= 32 cos
6
x – 48 cos
4
x + 24 cos
2
x – 4 – 6 cos
2
x + 3
⇒ cos 6x = 32 cos
6
x – 48 cos
4
x + 18 cos
2
x – 1
Hence proved.
Class 11 Maths NCERT Solutions Chapter 3 Exercise 3.4
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 1:
Find the principal and general solutions of the equation, tan x = √3
Ans:
tan x = √3
It is known that:
tan \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = √3 and
tan (\(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\)) = tan ( π + \(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
= tan \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = √3
Therefore, the principal solutions are x = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) and \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\).
Now, tan x = tan \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
⇒ x = nπ + \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is x = nπ + \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 2:
Find the principal and general solutions of the equation: sec x = 2
Ans:
sec x = 2
It is known that:
sec \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = 2 and
sec \(\frac{5 \pi}{3}\) = sec (2π – \(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
= sec \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) = 2
Therefore, the principal solutions are x = \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) and \(\frac{5 \pi}{3}\).
Now, sec x = sec \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
cos x = cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) [∵ sec x = \(\frac{1}{\cos x}\)]
⇒ x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n e Z
Therefore, the general solution is x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 3:
Find the principal and general solutions of the equation cot cot x = – √3.
Ans:
cot x = – √3
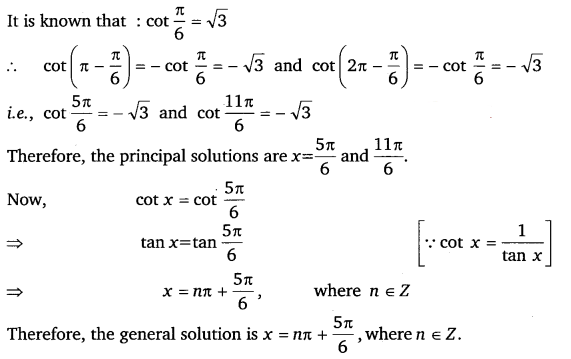
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 4:
Find the principal and general solutions of cosec x = – 2
Ans:
cosec x = – 2
It is known that:
cosec \(\frac{\pi}{6}\) = 2
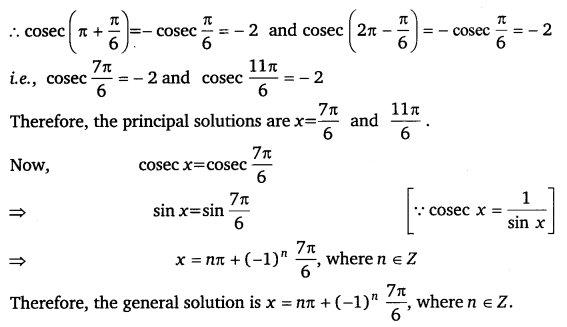
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 5:
Find the general solution of the equation: cos 4x = cos 2x
Ans:
cos 4x = cos 2x
cos 4x – cos 2x = 0
– 2 sin \(\left(\frac{4 x+2 x}{2}\right)\) sin \(\left(\frac{4 x-2 x}{2}\right)\) = 0
[∵ cos A – cos B = 2 \sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \sin \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\(\)]
sin 3x sin x = 0
sin 3x = 0or sin x = 0
3x = nπ or x = nπ, where n ∈ Z
x = \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) or x = nπ, where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 6:
Find the general solution of the equation cos 3x + cosx – cos 2x = 0
Ans:
cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0
2 cos \(\left(\frac{3 x+x}{2}\right)\) cos \(\left(\frac{3 x-x}{2}\right)\) – cos 2x = 0
[∵ cos A + cos B = 2 \(\cos \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
2 cos 2x cos x – cos 2x = 0
cos 2x (2 cos x – 1) = 0
cos 2x = 0 or 2 cos x – 1 = 0
cos 2x = 0 or cos x = \(\frac{1{2}\)
∴ 2x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or cos x = cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{4}\) or x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 7:
Find the general solution of the equation sin 2x + cos x = 0
Ans:
sin 2x + cos x = 0
⇒ 2sin x cos x + cos x = 0
⇒ cos x (2 sin x + 1) = 0
⇒ cos x = 0 or 2 sin x + 1 = 0
Now, cos x = 0
⇒ x = (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) , where n ∈ Z.
or 2 sin x + 1 = 0
⇒ sin x = – \(\frac{1}{2}\)
= – sin \(\frac{\pi}{6}\)
= sin (π + \(\frac{\pi}{6}\))
= sin \(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\)
x = nπ + (- 1)
n
\(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is (2n + 1) \(\frac{\pi}{2}\) or nπ + (- 1)
n
\(\frac{7 \pi}{6}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 8:
Find the general solution of the equation sec
2
2x = 1 – tan 2x.
Ans:
sec
2
2x = 1 – tan 2x
1 + tan
2
2x = 1 – tan 2x
tan
2
x + tan 2x = 0
=> tan 2x (tan 2x + 1) = 0
=> tan 2x = 0 or tan 2x + 1 = 0
Now, tan 2x = 0
=> tan 2x = tan 0
2x = nπ + 0, where n ∈ Z
x = \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\), where n ∈ Z
or tan 2x + 1 = 0
= tan 2x = – 1
= – tan \(\frac{\pi}{4}\)
= tan (π – \(\frac{\pi}{4}\))
= tan \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\)
2x = nπ + \(\frac{3 \pi}{4}\) where n ∈ Z
x = \(\frac{n \pi}{2}+\frac{3 \pi}{8}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is \(\frac{n \pi}{2}\) or \(\frac{n \pi}{2}+\frac{3 \pi}{8}\) where n ∈ Z.
Ex 3.4 Class 11 Maths Question 9:
Find the general solution of the equation sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
Ans:
sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
⇒ (sin x + sin 5x) + sin 3x = 0
\(\left[2 \sin \left(\frac{x+5 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{x-5 x}{2}\right)\right]\) + sin 3x = 0
[∵ sin A + sin B = 2 sin \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)]
2 sin 3x cos (2x) + sin 3x = 0
2 sin 3x cos 2x + sin 3x = 0
sin 3x (2 cos 2x +1) = 0
sin 3x = 0 or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0
Now sin 3x = 0
⇒ 3x = nπ, where n ∈ Z
i.e., x = \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) where n ∈ Z
or 2 cos 2x + 1 = 0
cos 2x = \(-\frac{1}{2}\)
= – cos \(\frac{\pi}{3}\)
= cos (π – \(\frac{\pi}{3}\))
cos 2x = cos \(\frac{2 \pi}{3}\)
⇒ 2x = 2nπ ± \(\frac{2\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
⇒ x = nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z
Therefore, the general solution is \(\frac{n \pi}{3}\) or nπ ± \(\frac{\pi}{3}\), where n ∈ Z.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths Chapter 3 Miscellaneous Exercise
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 1:
Prove that:
\(2 \cos \frac{\pi}{13} \cos \frac{9 \pi}{13}+\cos \frac{3 \pi}{13}+\cos \frac{5 \pi}{13}\) = 0
Ans:
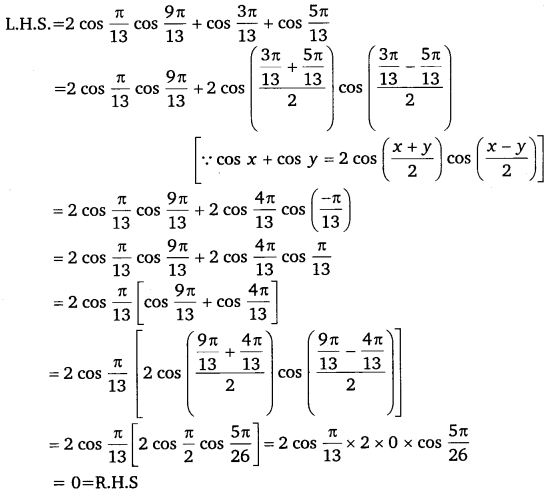
Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 2:
Prove that: (sin 3x + sin x) sin x + (cos 3x – cos x) cos x = 0.
Ans:
L.H.S. = (sin 3x + sin x) sin x + (cos 3x – cos x) cos x
= sin 3x sin x + sin
2
x + cos 3x cos x – cos
2
x
= cos 3x cos x + sin 3x sin x – (cos
2
x – sin
2
x)
= cos (3x – x) – cos 2x
[∵ cos(A – B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B]
= cos 2x – cos 2x = 0
=R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 3:
Prove that:
(cos x + cos y)
2
+ (sin x – sin y)
2
= 4 cos
2
\(\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\)
Ans:
L.H.S.= (cos x + cos y)
2
+ (sin x – sin y)
2
= cos
2
x + cos
2
y + 2 cos x cos y + sin
2
x + sin
2
y – 2 sin x sin y
= (cos
2
x + sin
2
x) + (cos
2
y + sin
2
y) + 2 (cos x cos y – sin x sin y)
= 1 + 1 + 2 cos (x + y)
[∵ cos (A + B) = (cos A cos B – sin A sin B)]
= 2 + 2 cos (x + y)
= 2 [1 + cos (x + y)]
= 2[1 + \(2 \cos ^{2}\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\) – 1]
[∵ cos 2A = 2 cos
2
A – 1]
= 4 c0s
2
\(\left(\frac{x+y}{2}\right)\)
= R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 4:
Prove that:
(cos x – cos y)
2
+ (sin x – sin y)
2
= 4 sin
2
\(\frac{x-y}{2}\)
Ans:
L.H.S.= (cos x – cos y)
2
+ (sin x – sin y)
2
= cos
2
x + cos
2
y – 2 cos x cos y + sin
2
x + sin
2
y – 2 sin x sin y
= (cos
2
x + sin
2
x) + (cos
2
y + sin
2
y) – 2 [cos x cos y + sin x sin y]
= 1 + 1 – 2 [cos (x – y)]
= 2 [1 – {1 – 2 sin
2
\(\left(\frac{x-y}{2}\right)\)}]
[∵ cos 2A = 1 – 2 sin
2
A]
= 4 sin
2
\(\left(\frac{x-y}{2}\right)\)
= R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 5:
Prove that: sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x + sin 7x = 4 cos x cos 2x sin 4x
Ans:
It is known that sin A + sin B = 2 \(\sin \left(\frac{A+B}{2}\right) \cdot \cos \left(\frac{A-B}{2}\right)\)
∴ L.H.S. = (sin x + sin 3x) + (sin 5x + sin 7x)
= (sin x + sin 5x) + (sin 3x + sin 7x)
= \(2 \sin \left(\frac{x+5 x}{2}\right)\) . \(\cos \left(\frac{x-5 x}{2}\right)+2 \sin \left(\frac{3 x+7 x}{2}\right) \cos \left(\frac{3 x-7 x}{2}\right)\)
= 2 sin 3x cos (- 2x) + 2 sin 5x cos (- 2x)
= 2 sin 3x cos 2x + 2 sin 5x cos 2x
= 2 cos 2x [sin 3x + sin 5x]
= 2 cos 2x [latex]2 \sin \left(\frac{3 x+5 x}{2}\right) \cdot \cos \left(\frac{3 x-5 x}{2}\right)[/latex]
= 2 cos 2x [2 sin 4x . cos (- x)]
= 4 cos 2x sin 4x cos x
= R.H.S.
Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 6:
Prove that: \(\frac{(\sin 7 x+\sin 5 x)+(\sin 9 x+\sin 3 x)}{(\cos 7 x+\cos 5 x)+(\cos 9 x+\cos 3 x)}\) = tan 6x
Ans:
It is known that
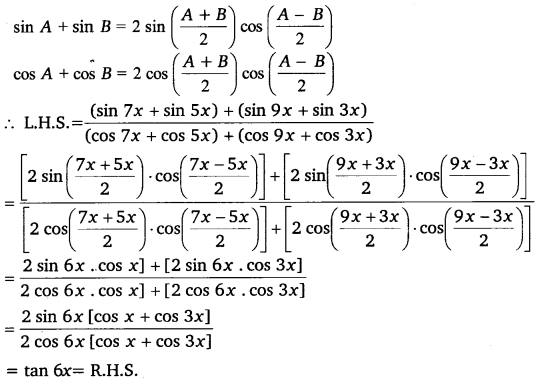
Hence proved.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 7:
Prove that: sin 3x + sin 2x – sin x = 4 sin x cos \(\frac{x}{2}\) cos \(\frac{3 x}{2}\).
Ans:
L.H.S. = sin 3x + sin 2x – sin x
= sin 3x + (sin 2x – sin x)
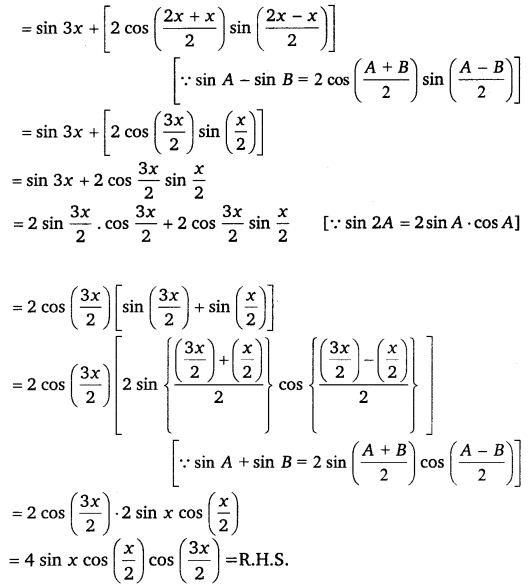
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 8:
Find sin \(\frac{x}{2}\), cos \(\frac{x}{2}\) and tan \(\frac{x}{2}\) for tan x = – \(\frac{4}{3}\), x in quadrant II.
Ans:

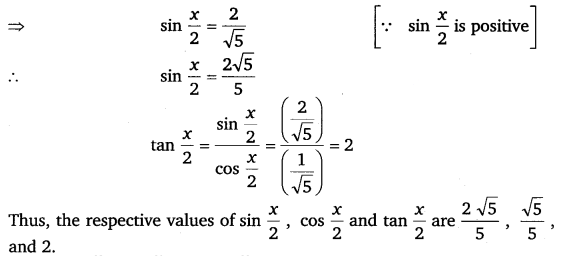
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 9:
Find sin \(\frac{x}{2}\), cos \(\frac{x}{2}\) and tan \(\frac{x}{2}\) for cos x = – \(\frac{1}{3}\), x in quadrant III.
Ans:
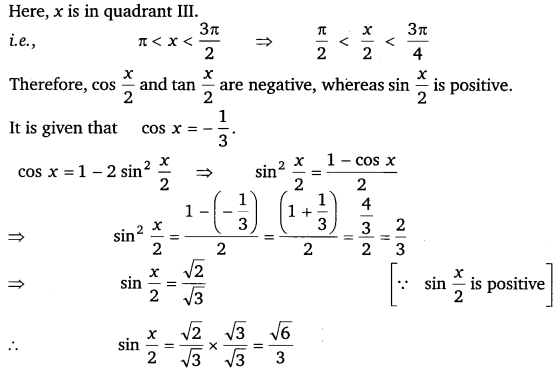
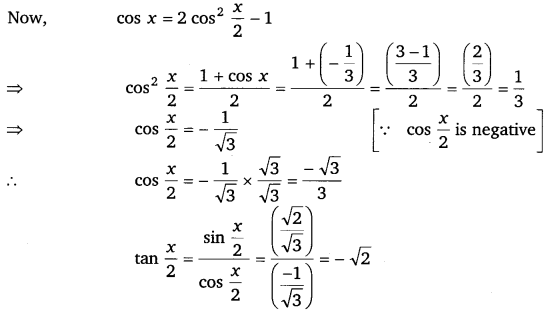
Thus, the respective values of sin \(\frac{x}{2}\), cos \(\frac{x}{2}\) and tan \(\frac{x}{2}\) are \(\frac{\sqrt{6}}{5}\), \(\frac{\sqrt{3}}{3}\) and – √2.
Miscellaneous Exercise Class 11 Maths Question 10:
Find sin \(\frac{x}{2}\), cos \(\frac{x}{2}\) and tan \(\frac{x}{2}\) for sin x = \(\frac{1}{4}\), x in quadrant II.
Ans:
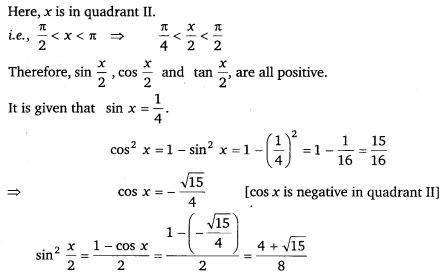
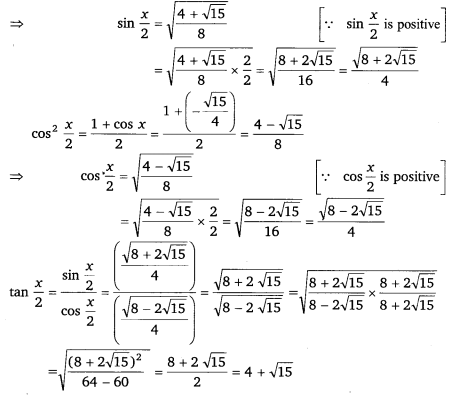
Thus, the respective values of sin \(\frac{x}{2}\), cos \(\frac{x}{2}\) and tan \(\frac{x}{2}\) are \(\sqrt{\frac{8+2 \sqrt{15}}{4}}\), \(\sqrt{\frac{8-2 \sqrt{15}}{4}}\) and 4 + √15.
त्रिकोणमितीय फलन प्रश्नावली 3.1 का हल हिंदी में
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित डिग्री माप के संगत रेडियन माप ज्ञात कीजिए।
(i) 25°
(ii) – 47° 30′
(iii) 240°
(iv) 520°
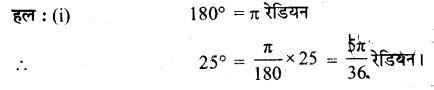

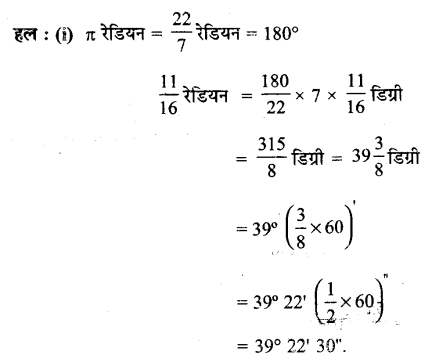
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित रेडियन माप के संगत डिग्री माप ज्ञात कीजिए (π = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\)) का प्रयोग करें:
(i) \(\frac { 11 }{ 16 }\)
(ii) -4
(iii) \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 3 }\)
(iv) \(\frac { 7\pi }{ 6 }\)


प्रश्न 3.
एक-पहिया एक मिनट में 360° परिक्रमण करता है तो एक सेकंड में कितने रेडियन माप का कोण बनाएगा?
हल:
परिक्रमण में पहिया द्वारा बना कोण = 27 रेडियन
360 परिक्रमण में पहिया द्वारा बना कोण = 360 x 2π रेडियन
1 मिनट अर्थात् 60 सेकण्ड में 360 x 2π रेडियन का कोण बनता है।
1 सेकण्ट में चहिया द्वारा बना कोण = \(\frac { 360\times 2\pi }{ 60 }\) = 12π रेडियन।
प्रश्न 4.
एक वृत्त जिसकी त्रिज्या 100 सेमी है, 22 सेमी लंबाई की चाप वृत्त के केन्द्र पर कितने डिग्री माप का कोण बनाएगी ? (π = \(\frac { 22 }{ 7 }\) का प्रयोग कीजिए)

प्रश्न 5.
एक वृत्त जिसका व्यास 40 सेमी. है, की एक जीवा 20 सेमी. लंबाई की है तो इसके संगत छोटे चाप की लंबाई ज्ञात कीजिए।
हल:
व्यास = 40 सेमी
त्रिज्या = 20 सेमी
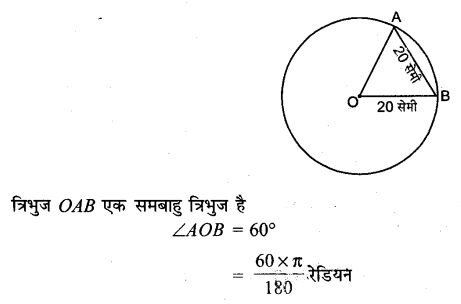

प्रश्न 6.
यदि दो वृत्तों के समान लंबाई वाले चाप अपने केन्द्रों पर क्रमशः 60° तथा 75° के कोण बनाते हों, तो उन्क लिन्याओं को अनुपात ज्ञात कीजिए।
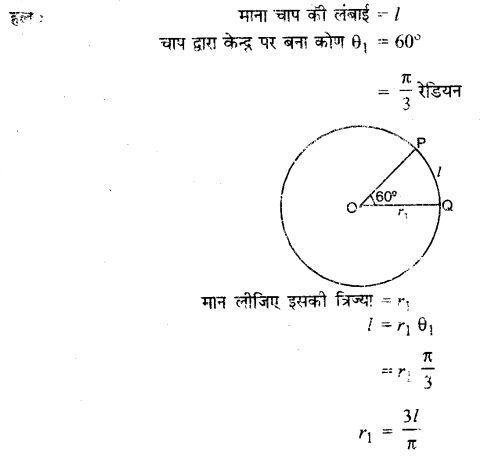


प्रश्न 7.
75 सेमी लम्बाई वाले एक दोलायमान दोलक का एक सिरे से दूसरे सिरे तक दोन करने से जो कोण बनता है, उसका माप रेडियन में ज्ञात कीजिए, जबकि उसके नोक द्वारा बनाए गए चाय की लम्बाई निम्नलिखित हैं:
(i) 10 सेमी
(ii) 15 सेमी
(iii) 21 सेमी

Exercise 3.1
Q.1: Calculate the radian measurement of the given degree measurement:
(i). 25 ∘
(ii). 240 ∘
(iii). − 47 ∘ 30 ‘
(iv). 520 ∘
Q.2: Calculate the degree measurement of the given degree measurement: [Use π = \(\\ \frac { 22 }{ 7 } \)]
(i) \(\\ \frac { 11 }{ 16 } \)
(ii) -4
(iii) \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 3 } \)
(iv) \(\frac { 7\pi }{ 6 } \)
Q.3: In a minute, wheel makes 360 revolutions. Through how many radians does it turn in 1 second?
Q.4: Calculate the degree measurement of the angle subtended at the centre of a circle of radius 100 m by an arc of length 22 m.
Q.5: In a circle of diameter 40 m, the length of the chord 20 m. Find the length of minor arc of chord.
Q.6: In two circles, arcs which has same length subtended at an angle of 60 ∘ and 75 ∘ at the center. Calculate the ratio of their radii.
Q.7: Calculate the angle in radian through which a pendulum swings if the length is 75 cm and the tip describes an arc of length
(i) 10 cm
(ii) 15 cm
(iii) 21 cm
Exercise 3.2
Q.1: Calculate the values of five trigonometric func. if cos y = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) and y lies in 3 rd quadrant.
(i) sec y
(ii) sin y
(iii) cosec y
(iv) tan y
(v) cot y
Q.2: Calculate the other five trigonometric function if we are given the values for sin y = \(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 5 } \), where y lies in second quadrant.
Q.3: Find the values of other five trigonometric functions if c o t y =\(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 4 } \) , where y lies in the third quadrant.
Q.4: Find the values of other five trigonometric if s e c y =\(\\ \frac { 13 }{ 5 } \) , where y lies in the fourth quadrant.
Q.5: Find the values of other five trigonometric function if tan y = \(– \frac { 5 }{ 12 } \) and y lies in second quadrant.
Q.6: Calculate the value of trigonometric function sin 765°.
Q.7: Calculate the value of trigonometric function cosec [-1410°]
Q.8: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function tan \(\frac { 19\pi }{ 3 } \) .
Q.9: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function sin \(-\frac { 11\pi }{ 3 } \) .
Q.10: Calculate the value of the trigonometric function cot \(-\frac { 15\pi }{ 4 } \)
Exercise 3.3
Q.1: Prove:
sin²\(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + cos² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) – tan² \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)
Q.2: Prove:
2 sin² \(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + c o s e c ² \(\frac { 7\pi }{ 6 } \) 6 cos ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) =\(\\ \frac { 3 }{ 2 } \)
Q.3: Prove:
cot ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 6 } \) + c o s e c \(\frac { 5\pi }{ 6 } \) + 3 tan ² latex s=2]\frac { \pi }{ 6 } [/latex] = 6
Q.4: Prove:
2 sin ² \(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } \) + 2 cos ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) + 2 sec ² \(\frac { \pi }{ 3 } \) = 10
Q.5: Calculate the value of:
(i). sin 75 ∘
(ii). tan 15 ∘
Q.6:Prove:
cos ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – x ) cos ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – y ) – sin ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – x ) sin ( \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \) – y ) = sin ( x + y )
Q.7: Prove:
\(\frac { tan(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } +x) }{ tan(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } -x) } ={ \left( \frac { 1+tanx }{ 1-tanx } \right) }^{ 2 }\)
Q.8: Prove:
\(\frac { cos(\pi +x)cos(-x) }{ sin(\pi -x)cos\left( \frac { \pi }{ 2 } +x \right) } ={ cot }^{ 2 }x\)
Q.9: Prove:
\(cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 2 } +x)cos(2\pi +x)[cot(\frac { 3\pi }{ 2 } -x)+cot(2\pi +x)]=1\)
Q.10: Prove:
sin ( n + 1 ) x sin ( n + 2 ) x + cos ( n + 1 ) x cos ( n + 2 ) x = cos x
Q.11 Prove:
\(cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } +x)-cos(\frac { 3\pi }{ 4 } -x)\)= − √2 sin x
Q.12: Prove:
sin² 6 x – sin ² 4 x = sin2 x sin 10 x
Q.13: Prove:
cos ² 2 x – cos ² 6 x = sin 4 x sin 8 x
Q.14:Prove:
sin 2 x + 2 sin 4 x + sin 6 x = 4 cos ² x sin 4 x
Q.15: Prove:
cot 4 x ( sin 5 x + sin 3 x ) = cot x ( sin 5 x – sin 3 x )
Q.16: Prove:
\(\frac { cos9x-cos5x }{ sin17x-sin3x } =-\frac { sin2x }{ cos10x } \)
Q.17: Prove:
\(\frac { sin5x+sin3x }{ cos5x+cos3x } =tan4x\)
Q.18: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx-siny }{ cosx+cosy } =tan\frac { x-y }{ 2 } \)
Q.19: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx+sin3x }{ cosx+cos3x } =tan2x\)
Q.20: Prove:
\(\frac { sinx-sin3x }{ { sin }^{ 2 }x-{ cos }^{ 2 }x } =2sinx\)
Q.21: Prove:
\(\frac { cos4x+cos3x+cos2x }{ sin4x+sin3x+sin2x } =cot3x\)
Q.22: Prove:
cot x cot 2 x – cot 2 x cot 3 x – cot 3 x cot x = 1
Q.23: Prove:
\(tan4x=\frac { 4tanx(1-{ tan }^{ 2 }x) }{ 1-6{ tan }^{ 2 }x+{ tan }^{ 4 }x } \)
Q.24: Prove:
cos 4 x = 1 – 8 sin² x cos² x
Q.25: Prove:
cos 6 x = 32 cos 6 x – 48 cos 4 x + 18 cos 2 x − 1
Exercise 3.4
Q.1: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: tan x = √3
Q.2: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: sec x = 2
Q.3: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: cot = − √3
Q.4: Find general solutions and the principle solutions of the given equation: cosec x = -2
Q.5: Find the general solution of the given equation: cos 4x = cos 2x
Q.6: Find the general solution of the given equation: cos 3x + cos x – cos 2x = 0
Q.7: Find the general solution of the given equation: sin 2x + cos x = 0
Q.8: Find the general solution of the given equation: sec² 2 x = 1 – tan 2 x
Q.9: Find the general solution of the given equation: sin x + sin 3x + sin 5x = 0
Miscellaneous Exercise
Q.1: Prove that:
\(2cos\frac { \pi }{ 13 } cos\frac { 9\pi }{ 13 } +cos\frac { 3\pi }{ 13 } +cos\frac { 5\pi }{ 13 } =0\)
Q.2: Prove that:
( sin 3 x + sin x ) sin x + ( cos 3 x – cos x ) cos x = 0
Q-3: Prove that:
( cos x + cos y )² + ( sin x – sin y ) ² = 4 cos ²\(\\ \frac { x+y }{ 2 } \)
Q-4: Prove that:
( cos x – cos y ) ² + ( sin x – sin y ) ² = 4 sin ² \(\\ \frac { x-y }{ 2 } \)
Q-5: Prove that:
sin x + sin 3 x + sin 5 x + sin 7 x = 4 cos x cos 2 x cos 4 x
Q-6: Prove that:
\(\frac { (sin7x+sin5x)+(sin9x+sin3x) }{ (cos7x+cos5x)+(cos9x+cos3x) } =tan6x\)
Q-7: Show that: sin 3 y + sin 2 y – sin y = 4 sin y cos\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) cos\(\\ \frac { 3y }{ 2 } \)
Q-8: The value of tan y =\(– \frac { 4 }{ 2 } \) where y in in 2 nd quadrant then find out the values of sin\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan\(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
Q-9: The value of cos y = \(– \frac { 1 }{ 3 } \) where y in in 3 rd quadrant then find out the values of sin \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
Q-10: The value of sin y = \(\\ \frac { 1 }{ 4 } \) where y in in 2 nd quadrant then find out the values of sin \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) , cos \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) a n d tan \(\\ \frac { y }{ 2 } \) .
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Maths All Chapters
- Chapter 1 Sets
- Chapter 2 Relations and Functions
- Chapter 3 Trigonometric Functions
- Chapter 4 Principle of Mathematical Induction
- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations
- Chapter 6 Linear Inequalities
- Chapter 7 Permutation and Combinations
- Chapter 8 Binomial Theorem
- Chapter 9 Sequences and Series
- Chapter 10 Straight Lines
- Chapter 11 Conic Sections
- Chapter 12 Introduction to Three Dimensional Geometry
- Chapter 13 Limits and Derivatives
- Chapter 14 Mathematical Reasoning
- Chapter 15 Statistics
- Chapter 16 Probability