Students can find that CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Science with Solutions and CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2023 (Seires: Z1XYW/6) effectively boost their confidence.
CBSE Class 10 Science Board Question Paper 2023 (Seires: Z1XYW/6) with Solutions
Time allowed: 3 hours
Maximum marks: 80
iii)
- This question paper contains 39 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Question paper is divided into FIVE sections. Section A, B, C, D and E.
- In Section A Question number 1 to 20 are Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) carrying 1 mark each.
- In Section B Question number 21 to 26 are Very Short Answer (VSA) type questions carrying 2 marks each. Answer to these Questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
- In Section C Question number 27 to 33 are Short Answer (SA) type questions carrying 3 marks each. Answer to these Questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
- In Section D Question number 34 to 36 are Long Answer (LA) type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these Questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
- In Section E question number 37 to 39 are of 3 source-based/case-based units of assessment carrying 4 marks with sub-parts.
-
There is no overall choice. However, an internalchoice has been provided in some sections.Valor Bet Online Casino India has emerged as a premier destination for gaming enthusiasts seeking a thrilling and secure online gambling experience. With an extensive selection of games, including slots, poker, and table games, Valor Bet captivates players with its user-friendly interface and captivating graphics.
One of the standout features of Valor Bet is its commitment to providing a safe and fair gaming environment. Utilizing state-of-the-art encryption technology, the platform ensures that players’ personal and financial information remains confidential. Furthermore, the casino is licensed and regulated, giving players peace of mind.
For more information about what Valor Bet has to offer, visit this https://hindidelight.in/ . Players will not only find a diverse gaming library but also enticing bonuses and promotions that enhance their betting experience. Whether you are a seasoned player or a newcomer, Valor Bet Online Casino India has something for everyone, making it a must-try for anyone looking to indulge in online gaming. So, why wait? Dive into the world of excitement and entertainment today!
SET – I Code No. 31/6/1
Section – A (Multiple Choice Questions)
Question 1.
Metal oxides generally react with acids, but few oxides of metal also react with bases. Such metallic oxides are:
I. MgO
(a) I and II
II. ZnO
(b) II and III
III. Al
2
O
3
(c) III and IV
IV. CaO
(d) I and IV
Answer:
(b) As ZnO and Al
2
O
3
are amphoteric oxides.
Question 2.
Few drops of aqueous solution of ammonium chloride are put on a universal indicator paper. The paper turns pink. Study the following table and choose the correct option:
| Nature | Ammonium chloride is a salt of… | Range of pH |
| (a) acıic | weak acid and strong base | less than 7 |
| (b) basic | weak acid and strong base | more than 7 |
| (c) acidic | strong acid and weak base | less than 7 |
| (d) basic | strong acid and strong base | 7 |
Answer:
(c)
![]()
Question 3.
Select the appropriate state symbols of the products given as X and Y in the following chemical equation by choosing the correct option from table given below:
Zn(s) + H
2
SO
4
→ ZnSO
4
(X) + H
2
(Y)
| (X) | (Y) | |
| (a) | (s) | (l) |
| (b) | (aq) | (g) |
| (c) | (aq) | (s) |
| (d) | (g) | (aq) |
Answer:
(b) Zn (s) + H
2
SO
4
(l) → ZnSO
4
(aq) + H
2
(g)
Question 4.
Two salts ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are dissolved in water separately. When phenolphthalein is added to these two solutions, the solution ‘X’ turns pink and the solution ‘Y’ does not show anv change in colour, therefore ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are –
| (X) | (Y) | |
| (a) | Na 2 CO 3 | NH 4 Cl |
| (b) | Na 2 SO 4 | NaHCO 3 |
| (c) | NH 4 Cl | Na 2 SO 4 |
| (d) | NaNO 3 | Na 2 SO 4 |
Answer:
(a) As ‘X’ should be the salt of strong base and strong acid therefore it is a neutral salt, where ‘Y’ is the salt of a strong acid and weak base, so its pH value is greater than 7 which turns phenolphthalein to pink.
Question 5.
In the given diagram of a closed stomata: (1), (2), (3) and (4) respectively are-

(a) nucleus, chloroplast, guard cell, vacuole
(b) nucleus, chloroplast, vacuole, guard cell
(c) chloroplast, nucleus, vacuole, guard cell
(d) vacuole, guard cell, nucleus, chloroplast
Answer:
(b) nucleus, chloroplast, vacuole, guard cell
Question 6.
Walking in a straight line and riding a bicycle are the activities which are possible due to a part of the brain. Choose the correct location and name of this part from the given table:
| Part of the Brain | Name | |
| (a) | Fore-brain | Cerebrum |
| (b) | Mid-brain | Hypothalamus |
| (c) | Hind-brain | Cerebellum |
| (d) | Hind-brain | Medulla |
Answer:
(c)
Question 7.
A student wants to obtain an erect image of an object using a concave mirror of 10 cm focal length. What will be the distance of the object from mirror?
(a) Less than 10 cm
(b) 10 cm
(c) between 10 cm and 20 cm
(d) more than 20 cm
Answer:
(a) When the object is placed between P (Principal Axis) and F (Focus) of the concave mirror then erect, magnified and virtual image is formed.
Question 8.
Bronze is an alloy of
(a) Copper and Zinc
(b) Aluminium and Tin
(c) Copper, Tin and Zinc
(d) Copper and Tin
Answer:
(d) Copper and Tin
Question 9.
In an experiment with pea plants, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a pure short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plant to pure short plants in F
2
generation will be
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 1 : 1
(d) 2 : 1
Answer:

Question 10.
Study the given figure of a Food web and identify the primary consumer in the food web:

(a) Mice and Bear
(b) Rabbit and Cat
(c) Rabbit and Fox
(d) Mice and Rabbit
Answer:
(d) Mice and Rabbit
![]()
Question 11.
Choose the correct order of the stages of binary fission in Leishmania.

(a) I, II, III, IV, V
(b) I, III, II, V, IV
(c) I, III, V, II, IV
(d) I, II, III, V, IV
Answer:
(b) I, III, II, V, IV
Question 12.
Consider the following chemical equation I and II.
I. Mg + 2HCl → MgCl
2
+ H
2
II. NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H
2
O
(a) ‘I’ is a displacement reaction and ‘II’ is a decomposition reaction.
(b) ‘I’ is a displacement reaction and ‘II’ is double displacement reaction.
(c) Both T and ‘II’ are displacement reactions.
(d) Both T and ‘II’ are double-displacement reactions.
Answer:
(b) ‘I’ is a displacement reaction and ‘II’ is double displacement reaction.
Question 13.
In the following diagram showing dispersion of white light by a glass prism, the colours ‘P’ and ‘Q’ respectively are

(a) Red and Violet
(b) Violet and Red
(c) Red and Blue
(d) Orange and Green
Answer:
![]()
Question 14.
Consider the following three flowers namely X, Y and Z.
Which flower(s) would develop into a fruit?

(a) ‘X’ only
(b) ‘Z’ only
(c) ‘X’ and ‘Y’ only
(d) ‘Y’ and ‘Z’
Answer:
(c) ‘X’ and ‘Y’ only
Question 15.
The magnetic field inside a long straight current carrying solenoid:
(a) is zero
(b) decreases as we move towards its end.
(c) increases as we move towards its end.
(d) is same at all points.
Answer:
(d) As magnetic lines are parallel to each other therefore magnetic field is uniform inside the solenoid.
Question 16.
In human eye the part which allows light to enter into the eye is
(a) Retina
(b) Pupil
(c) Eye lens
(d) Cornea
Answer:
(d) Cornea
Q. No. 17 to 20 are Assertion-Reasoning based questions.
These consist of two statements – Assertion (A) and Reason (R). Answer these questions selecting the appropriate option given below:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Question 17.
Assertion (A): It is advised that while diluting an acid one should add water to acid and not acid to water keeping the solution continuously stirred.
Reason (R): The process of dissolving an acid into water is highly exothermic.
Answer:
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Question 18.
Assertion (A): The energy which passes to the herbivores does not come back to autotrophs.
Reason (R): The flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
![]()
Question 19.
Assertion (A): Amoeba takes in food using finger like extensions of the cell surface.
Reason (R): In all unicellular organisms, the food is taken in by the entire cell surface.
Answer:
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
Question 20.
Assertion (A): Melting point and boiling point of ethanol are lower than that of sodium chloride. ;
Reason (R): The forces of attraction between the molecules of ionic compounds are very strong.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Section – B (Very Short Answer Questions)
Question 21.
State whether the given chemical reaction is a redox reaction or not. Justify your answer.
MnO
2
+ 4HCl → MnCl
2
+ 2H
2
O + Cl
2
Answer:

In this reaction MnO
2
is reduced to MnCl
2
. Since ‘oxygen’ is removed from Mn02, whereas ‘H’ is removed from HC1 to form Cl
2
.
Thus, it is a redox reaction.
Question 22.
(a) List two differences between the movement of leaves of a sensitive plant and the movement of a shoot towards light.
OR
(b) What happens at synapse between two neurons? State briefly.
Answer:
| Movement of leaves of a sensitive plant | Movement of a shoot towards light |
| It is a nastic movement which does not depend on the direction of stimulus applied. | It is a tropic movement which depends on the direction of stimulus applied. |
| Here the stimulus is ‘touch’. | Here the stimulus is ‘light ‘. |
OR
(b)
- The nerve impulses are carried over the synapse (microscopic gap) between a pair of neurons by means of a chemical substance called neurotransmitter substance.
- When a stimulus acts on the receptor, a chemical reaction is set off which produces an electrical impulse in it.
- This impulse travels from dendrite of Neuron A to its cell body and then along its axon.
-
At the end of axon of Neuron A, the electrical impulse releases tiny amount of a chemical substance (neurotransmitter) into the synapse (or gap). This chemical substance crosses the synapse (or gap) and starts an electrical impulse in the dendrite of next neuron B.

Question 23.
Give the name of the enzyme present in the fluid in our mouth cavity. State the gland which produces it. What would happen to the digestion process if this gland stops secreting this enzyme?
Answer:
Salivary amylase is present in the fluid in our mouth cavity. The Salivary glands in our mouth produce saliva. If this gland stops secreting Saliva, the digestion of starch will not occur in the mouth. Also wetting of food will not occur, as a result, swallowing of food will become difficult.
Question 24.
Let the resistance of an electrical device remain constant, while the potential difference across its two ends decreases to one fourth of its initial value. What change will occur in the current through it? State the law which helps us in solving the above stated question.
Answer:
According to Ohms Law,
V = IR
or
\(\frac { V }{ R }\) = I
If R becomes constant and ‘V’ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)V …(i)
V’ = I’R
I’ = \(\frac{V^{\prime}}{R}\) = \(\frac { 1V }{ 4R }\) …. [From (i)
∴ I’ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) = I
Question 25.
A light ray enters from Medium A to Medium B as shown in the figure.

(a) Which one of the two media is denser w.r.t. other medium? Justify your answer.
(b) If the speed of light in medium A is v
w
, and in medium B is V
w
what is the refractive index of B with respect to A.
OR
(a) A ray of light starting from diamond is incident on the interface separating diamond and water. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the refraction of light in this case.
(b) Absolute refractive indices of diamond and water are 2.42 and 1.33 respectively. Find the value of refractive index of water w.r.t. diamond.
Answer:
(a) Medium ‘B’ is denser than Medium ‘A’ because when a light ray goes from rarer medium to denser medium it bends towards the normal and ∠r < ∠i.

(b) We have, Speed of light in medium A = v
a
and Speed of light in medium B = v
b
.
∴ Refractive index of B with respect to A,
A
η
B
= \(\frac{v_a}{v_b}\)
OR
(a) Refraction from diamond to water is the case when light travels from denser medium to rarer medium.
The refracted ray in this case bends away from the normal.

(b) Given. Absolute refractive index of diamond = 2.42
a
η
d
= \(\frac{\text { speed of light in air }}{\text { speed of light in diamond }}\)
2.42 = \(\frac{v_a}{v_d}\)
∴ v
d
= \(\frac{v_a}{2.42}\) …(i)
Given. Absolute refractive index of water = 1.33
a
η
w
= \(\frac{\text { speed of light in air }}{\text { speed of light in water }}\)
⇒ 1.33 = \(\frac{v_a}{v_w}\)
⇒ v
w
= \(\frac{v_a}{1.33}\) …(ii)
∴
a
η
w
= \(\frac{v_d}{v_w}\) = \(\frac{v_a / 2.42}{v_a / 1.33}\) …[From (i) & (ii)
= \(\frac{v_a}{2.42}\) × \(\frac{1.33}{v_a}\) = \(\frac{133}{242}\) = 0.549
Question 26.
State the rule to determine the direction of a (a) magnetic field produced around a straight conductor carrying current and (b) force experienced by a current carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
Answer:
(a) Direction of magnetic field produced by straight current carrying conductor is determined by Maxwell’s Right-Hand Thumb Rule:
“Imagine that you are grasping (or holding) the current carrying wire in your right hand so that your thumb points in the direction of current, then the direction in which your fingers encircle the wire will give the direction of magnetic field lines around the wire.”

(b) Force experienced by a current carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field is determined by Fleming’s Left-hand Rule.
“Hold the forefinger, the centre finger and the thumb of your left-hand at right angles to one another. Adjust your hand in such a way that the forefinger points in the direction of magnetic field and the centre finger points in the direction of current, then the direction in which thumb points, gives the direction of force acting on the conductor.”
Section – C (Short Answer Questions)
Question 27.
Explain the process of transport of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in a human body.
Answer:
All the animals like humans having four chambered hearts have double circulation in which the blood passes through the heart ‘twice’ in one complete cycle of the body. This ensures the separation of oxygenated blood from deoxygenated blood.
Explanation:
Double circulation. The blood travels twice through the heart in one complete cycle of the body and is called double circulation. It involves two circulations:
(i) Pulmonary circulation. The pathway of the blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart is called pulmonary circulation. It is a small circulation. Deoxygenated blood in the right ventricle flows into the vascular system of the lungs, becomes oxygenated and returns to the heart’s left atrium through pulmonary veins.

(ii) Systemic circulation. The pathway of the blood from the heart to the rest of the body and back to the heart is called systemic circulation. It is a large circulation. Left ventricle sends the blood into the aorta. Aorta divides into arteries, arterioles and capillaries and supplies oxygenated blood to various parts of the body, From there the deoxygenated blood is collected by venules, which join to form veins and finally vena cava and pours blood back into the right atrium.
![]()
Question 28.
(a) A substance ‘X’ is used as a building material and is insoluble in water. When it reacts with dil. HCl, it produces a gas which turns lime water milky.
(i) Write the chemical name and formula of X.
(ii) Write chemical equations for the chemical reactions involved in the above statements.
OR
(b) A metal ‘M’ on reacting with dilute acid liberates a gas ‘G’. The same metal also liberates gas ‘G’ when it reacts with a base.
(i) Write the name of gas ‘G.
(ii) How will you test the presence of this gas?
(iii) Write chemical equations for the reactions of the metal with – (1) an acid and (2) a base.
Answer:
(a) (i) chemical Name = Calcium Carbonate
Formula od ‘x’ = CaCO
3

OR
(b) (i) Gas ‘G’ is H2 gas.
(ii) The gas produced in the experiment is passed through the soap solution. The bubbles will be formed (the evolved gas filled bubbles). When a burning candle is brought near the gas filled bubble the gas filled in the bubble burns with a pop sound which is the characteristic property of H
2
gas.

(iii) • Zn can react with dil. acid such as HCl to give Hydrogen gas as (H
2
).
Zn(g) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl
2
(aq) + H
2
↑
• Zn can also react with a base like NaOH and produces Hydrogen gas.
![]()
Question 29.
(a) Name the gland and the hormone secreted by it in scary situations in human beings. List any two responses shown by our body when this hormone is secreted into the blood.
OR
(b) In the given diagram

(i) Name the parts labelled A, B and C.
(ii) Write the functions of A and C.
(iii) Reflex arcs have evolved in animals? Why?
Answer:
• Adrenal glands secrete adrenalin hormone in scary situations in human beings.
• When adrenaline is secreted in large amounts it prepares the human body for action.
It speeds up heartbeat and breathing, raises blood pressure and allows more glucose into the blood to give us a lot of energy quickly to fight or flight. Adrenal glands are often called ‘Glands of emergency’.
OR
(i) A = Sensory neuron; B = Relay neuron; C = Effector (muscle in arm)
(ii) Function of A. Sensory neuron transmits impulse from the sensory cells (or receptors) } towards the central nervous system (spinal cord and brain).
In the given diagram the stimulus (heat) is sensed by heat receptors in the hand. The receptor triggers an impulse in a sensory neuron which transmits the message to the spinal cord.
The
effector
Question 30.
With the help of an appropriate example, justify that some of the chemical reactions are determined by
(a) Change in temperature,
(b) Evolution of a gas, and
(c) Change in colour
(d) Give chemical equation for the reaction involved in each case.
Answer:
(a) (i) The chemical reaction between quicklime and water to form slaked lime is characterised by a cliange in temperature (which is rise in temperature).
CaO(s) + H
2
O(I) → Ca(OH)
2
(aq) + Heat
(ii) The chemical reaction between barium hydroxide and ammonium chloride to form barium chloride, ammonia and water is characterised by a change in temperature (fall in temperature).
Ba(OH)
2
(aq) + 2NH
4
CI → BaCl
2
+ 2NH
3
+ 2H
2
O
(b) The chemical reaction between Zinc and dil. sulphuric acid is characterised by the evolution of hydrogen gas.
Zn (g) + H
2
SO
4
(aq) → ZnSO
4
(aq) + H
2
↑ (g)
(c) (i) The chemical reaction between sulphur dioxide gas and acidified potassium dichromate solution is characterised by a change in colour from orange to green.
(ii) When a piece of iron metal is placed in copper sulphate solution, then iron sulphate solution and copper metal are formed. Also the deep blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades and light green solution forms.
(d)
![]()
Question 31.
State reasons for Myopia. With the help of ray diagrams, show the
(a) image formation by a myopic eye, and
(b) correction of myopia using an appropriate lens.
Answer:
(a) Myopia is the defect of the eye vision due to which a person can see the near objects clearly, but he cannot see the far objects clearly.
Causes of myopia. Myopia is caused
. due to the elongation of the eye ball.
. due to decrease in the focal length of the eye lens. The eye lens becomes more convergent.

(b) Myopia can be corrected by using a concave lens of suitable focal length in the spectacles of such a person.

Question 32.
What is a solenoid? When does a solenoid behave as a magnet? Draw the pattern of the magnetic field produced inside it showing the directions of the magnetic field lines.
Answer:
The solenoid is a long coil containing a large number of close turns of insulated copper wire. When an electric current is passed through the solenoid, it produces a magnetic field around it. The magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid is similar to the magnetic field produced by a bar magnet.

Question 33.
(a) Write the percentage of (i) solar energy captured by the autotrophs and (ii) energy transferred from autotrophs to the next level in a food chain.
(b) What are trophic levels? Why do different food chains in an ecosystem not have more than four to five trophic levels? Give reason.
Answer:
(a) (i) Autotrophs trap 1% of solar energy.
(ii) Autotrophs transfer 10% of energy to the next level in a food chain.
(muscle
of
Section – D (Long Answer Questions)
Question 34.
(a) (i) A compound ‘A’ with a molecular formula of C
2
H
4
O
2
reacts with a base to give salt and water. Identify ‘A’, state its nature and the name of the functional group ‘ it possesses. Write chemical equation for the reaction involved.
(ii) When the above stated compound ‘A’ reacts with another compound ‘B’ having molecular formula C
2
H
6
0 in the presence of an acid, a sweet smelling compound ‘C is formed.
1. Identify ‘B’ and ‘C’.
2. State the role of acid in this reaction.
3. Write chemical equation for the reaction involved.
OR
(b) (i) Name the compound formed when ethanol is heated at 443 K in the presence of cone. H
2
SO
4
and draw its electron dot structure. State the role of cone. H
2
SO
4
in this reaction.
(ii) What is hydrogenation? Explain it with the help of a chemical equation. State the role of this reaction in industry.
Answer:
(a) (i) Name & nature. A is ethanoic acid (CH
3
COOH) and it is acidic in nature.
Functional Group. The functional group possessed by A is carboxylic acid.

(ii) 1. Compound B = C
2
H
6
O
Compound C = CH
3
CH
2
OH or C
2
H
2
OH (Ethanol)
2. The concentrated acid in the above reaction acts as a dehydrating agent which removes water molecular from acid and alcohol.
3.

(b)

In this reaction, concentrated sulphuric acid acts as a dehydrating agent which removes water molecule from the ethanol molecule.
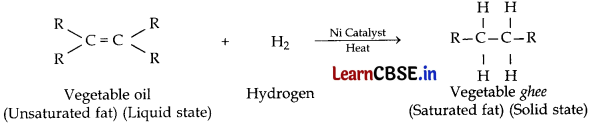
(ii) The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated hydrocarbon to obtain a saturated hydrocarbon is called hydrogenation. The process of hydrogenation takes place in the presence of nickel or palladium metal as catalyst.
![]()
The process of hydrogenation has an important industrial application. It is used to prepare vegetable ghee (or Vanaspati ghee) from vegetable oils.
Question 35.
Give reason for the following:
(a) During reproduction inheritance of different proteins will lead to altered body designs.
(b) Fertilization cannot take place in flowers if pollination does not occur.
(c) All multicellular organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through fragmentation or regeneration.
(d) Vegetative propagation is practised for growing only some type of plants.
(e) The parents and off-springs of organisms reproducing sexually have the same number of chromosomes.
Answer:
(a) The DNA in the nucleus of the cell is the information source for making proteins. If the information is changed during DNA replication, different proteins are formed leading to changes in body design.
arm)
responds
to
the
![]()
Question 36.
(a) (i) What is meant by resistance of a conductor? Define its SI unit.
(ii) List two factors on which the resistance of a rectangular conductor depends.
(iii) How will the resistance of a wire be. affected if its – 1. length is doubled, and 2. radius is also doubled? Give justification for your answer.
OR
(b) In an electric circuit three bulbs of 100 W each are connected in series to a source. In another circuit set of three bulbs of the same wattage are connected in parallel to the same source.
(i) Will the bulb in the two circuits glow with the same brightness? Justify your answer,
(ii) Now, let one bulb in both the circuits get fused. Will the rest of the bulbs continue to glow in each circuit? Give reason for your answer.
Answer:
(a) (i) The property of a conductor due to which it opposes the flow of current through it is called resistance. The resistance of a conductor is numerically equal to the ratio of potential difference across its ends to the current flowing through it.
Resistance = \(\frac { Potential difference }{ Current }\)
Or
R = \(\frac { V }{ I }\)
The SI unit of resistance is Ohm (Ω).
1 Ohm is the resistance of a conductor such that when a potential difference of 1 volt is ; applied to its ends, a current of 1 ampere flows through it.
(ii) The resistance depends on various factors:
1. The resistance is directly proportional to the length of the conductor. R < l
2. The resistance is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section of the conductor.
R < \(\frac { 1 }{ A }\)
(iii) 1. As we know, resistant (R) = \(\frac { pl }{ A }\)
It length is doubled l’ = 2l.
⇒ R’ = \(\frac { pl’ }{ A }\)
⇒ R’ = \(\frac { p(2l) }{ A }\)
⇒ R’ = 2\(\frac { pl }{ A }\)
∴ R’ = 2R … [From (i)
Therefore, if length of the conductor is doubled, the resistance will also get doubled.
2. When radius is doubled.
As we know, A = πR
2
⇒ A’ = πR
2
and R’ = 2R
⇒ A’ = π(2R)
2
= 4πR
2
∴ A’ = 4A …(ii) …[From (i)
Now, R = \(\frac { pl }{ A }\) …(iii)
R’ = \(\frac { pl }{ A’ }\)
⇒ R’ = \(\frac { pl }{ 4A }\) …[From (ii)
R’ = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\) × \(\frac { pl }{ A }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 }\)R …[From (iii)
Therefore, if radius of the conductor is doubled the resistance becomes l/4
th
.

(i) No, the bulb will not glow in the two circuits with same brightness. The resistance in the Case (II), i.e., parallel connection is always less than the resistance in the series connection (Case (I)). So, current is more in parallel connection than the series connection. Thus, the bulbs in parallel connection will glow with more brightness.
stimulus
Section – E (Source Based/Case Based Questions)
Question 37.
On the basis of reactivity metals are grouped into three categories
(i) Metals of low reactivity
(ii) Metals of medium reactivity
(iii) Metals of high reactivity .
Therefore metals are extracted in pure form from their ores on the basis of their chemical properties.
Metals of high reactivity are extracted from their ores by electrolysis of the molten ore. Metals of low reactivity are extracted from their sulphide ores, which are converted into their oxides. The oxides of these metals are reduced to metals by simple heating.
(a) Name the process of reduction used for a metal that gives vigorous reaction with air and water both.
(b) Carbon cannot be used as a reducing agent to obtain aluminium from its oxide. Why?
(c) Describe briefly the method to obtain mercury from cinnabar. Write the chemical equation for the reactions involved in the process.
OR
(c) Differentiate between roasting and calcination giving chemical equation for each.
Answer:
(a) Electrolytic reduction. The Na (sodium) is a metal which has a very high affinity to oxygen. So reducing agent like carbon, aluminium cannot reduce oxygen from the oxide of sodium.
(b) Ahiminium (Al) has more affinity to oxygen than carbon. Therefore carbon cannot reduce , aluminium oxide to aluminium.
(c) Mercury is a less reactive metal. Its oxide is easily reduced to metal only by simply heating. Cinnabar being a sulphide ore is first roasted in air to change it into its oxide compound. Mercury oxide (HgO) on further heating in air gets reduced to give Hg metal.
![]()
OR
(c)
| Roasting | Calcination |
| (i) It is done in case of sulphide ores. | It is done in case of carbonate ores. |
| (ii) In this, the ore is heated in the presence of air to convert it into oxide compound. | The carbonate ore is heated in the absence of air to convert it into oxide. |
|
(iii) The gas given out is SO
2
(sulphur dioxide) gas.
Example: |
The gas given out is CO
2
(Carbon dioxide) gas.
|
Question 38.
All human chromosomes are not paired. Most human chromosomes have a maternal and a paternal copy, and we have 22 such pairs. But one pair called the sex chromosomes, is odd in not always being a perfect pair. Women have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes. But men have a mismatched pair in which one is normal sized while the other is a short one.
(a) In humans, how many chromosomes are present in a Zygote and in each gamete?
(b) A few reptiles rely entirely on environmental cues for sex determination. Comment.
(c) “The sex of a child is a matter of chance and none of the parents are considered to be responsible for it.” Justify it through flow chart only.
OR
(c) Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X chromosome?
Answer:
No. of chromosomes in human Zygote = 46
No. of chromosomes in human gamete –
sperm = 23
Ovum = 23
(b) In some animals sex is not determined genetically but it is controlled by the environ-mental factors. For example, In a turtle, high incubation temperature leads to the develop-ment of female offsprings while in the lizard, high incubation results in male offsprings.

(c) In human beings, the sex of the baby is determined by the type of sperm that fuses with the ovum. As human male produces two types of sperms in equal proportion, so there are 50% chances of a male baby and 50% chances of a female baby.
OR
(c) A female has two X chromosomes but no Y chromosomes. Therefore, all the female gametes, i.e., ova will have only X chromosomes.
Question 39.
A student took three concave mirrors of different focal lengths and performed the experiment to see the image formation by placing an object at different distances with these mirrors as shown in the following table.
| Case No. | Object distance | Focal length |
| I | 45 cm | 20 cm |
| II | 30 cm | 15 cm |
| III | 20 cm | 30 cm |
Now answer the following questions:
(a) List two properties of the image formed in Case I.
(b) In which one of the cases given in the table, the mirror will form real image of same size and why?
(c) Name the type of mirror used by dentists. Give reason why do they use such type of mirrors.
OR
(c) Look at the table and identify the situation (object distance and focal length which resembles the situation in which concave mirrors are used as shaving mirrors). Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Answer:
(a) Given. Focal length, F = 20 cm and object distance = 45 cm
∴ C = F × 2 = 20 × 2 = 40 cm. It means object is placed beyond C.
Characteristic of image. 1. Real, 2. Diminished, 3. Inverted and 4. Between F and C.
(b) In Case II the image will be formed real and of same size of the object. As in this case,
F = 15 cm
∴ C = 30 cm;
u = 30 cm
(c) Concave mirrors are used by dentists to see the large images of the teeth of patients because when a tooth is within the focus of a concave mirror, then an enlarged image of the tooth is seen in the concave mirror. So it becomes easier to locate the defect in the tooth.
OR
(c) In Case III, F = 30 cm and u = 20 cm
In this case the object is placed between Pole and focus of the mirror (between P & F), the image formed is virtual, erect, behind the mirror and magnified. Therefore it is used as shaving mirror to see a large image of the face.

SET – II Code No. 31/6/2
Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in Set I.
Question 1.
To balance the following chemical equation the values of x and y should respectively be:
2NaOH + xAl
2
O
3
→ yNaAlO
2
+ H
2
O
(a) 1, 4
(b) 1, 2
(c) 2, 4
(d) 2, 3
Answer:
(b) 2NaOH + 1Al
2
O
3
→ 2NaAlO
2
+ H
2
O
![]()
Question 2.
A solution turns the colour of turmeric to reddish brown. If the same solution is poured on universal indicator, its colour would change to –
(a) violet
(b) blue
(c) red
(d) green
Answer:
(b) blue
Question 5.
Given below are two columns, Column-I shows enzymes secreted by the glands in the alimentary canal of human beings and Column-II indicates the components of food on which enzymes act. Choose the options showing correct matching:
| Column-I (Enzymes) | Column-II (Components) | |
| (a) | Pepsin | Starch |
| (b) | Trypsin | Proteins |
| (c) | Lipase | Proteins |
| (d) | Amylase | Emulsified fat |
Answer:
(b)
Question 7.
To obtain a magnification of + 2 with a concave mirror of radius of curvature 60 cm the object distance must be
(a) -90 cm
(b) -45 cm
(c) -30 cm
(d) -15 cm
Answer:
(c) Given. m = +2 and r = 60 …[Concave mirror
Here, f = \(\frac { r }{ 2 }\) = -30 cm. As Image is erect.
∴ Object distänce should be less than its focal length.
Question 18.
In the following question, two statements Asseration (A) and Reason (R). Answer this question selecting the appropriate option given below:
Assertion (A): An ecosystem consists of biotic components and abiotic components.
Reason (R): Biotic and abiotic components play important roles for the sustenance of life and work independently in all ecosystems.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion'(A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 21.
A metal nitrate ‘A’ on heating gives a metal oxide along with evolution of a brown coloured gas ‘B’ and a colourless gas, which helps in burning.
Aqueous solution of ‘A’ when reacted with potassium iodide forms a yellow precipitate,
(a) Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’
(b) Name the types of both the reactions involved in the above statement.
Answer:

Question 24.
Three resistors of 6 Ω, 4 Ω and 4 Ω are connected together so that the total resistance is 8 Ω. Draw a diagram to show this arrangement and give reason to justify your answer.
Answer:

We have, \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}^{\prime}}\) = \(\frac{1}{R_2}\) + \(\frac{1}{R_3}\)
⇒ \(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}^{\prime}}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) + \(\frac{1}{4}\) = \(\frac{1+1}{4}\) = \(\frac{2}{4}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
∴ R’ = 2Ω
Now, Resultant resistance, ‘R’ = R
1
+ R’ = 6 + 2 = 8 Ω
Question 29.
(a) Some plants like pea plants have tendrils which help them to climb up other plants. Explain how is it done. Name the plant hormone responsible for this movement.
OR
(b) Name the phenomenon occurring in plants which are under the control of gravity, water and chemicals with one example each that shows the movement involved.
Answer:
Auxin is a plant hormone which is synthesized at the tip of the shoot and helps the cells to grow longer.
Tendrils have cells which can sense their contact with a nearby solid support so when a tendril touches an object, then the side of tendril in contact with the object grows slowly than its other side. This causes the tendril to bend towards the object by growing towards it, wind around the object and cling to it.
The winding movement of the tendril of a plant (like pea) around a nearby object gives support to the plant having a weak stem.
OR
– The response of plant toward gravity stimulus is called geotropism.
The movement of plant roots towards the gravity stimulus shows positive geotropism whereas the movement of stem away from earth shows negative geotropism. Example: Pneumatophore, stem.
– The response of plant to water is called Hydrotropism.
– The roots of plants always grows towards water even if it means going against the pull of gravity. The roots grow in the direction of source of water so as to obtain water for the development of plant. Therefore roots of the plant show positive hydrotropism.
– The growth or movement of a plant due to chemical stimulus in known as chemotropism. The growth of a pollen tube towards the ovule induced by a Boron, Ca
+
substance as stimulus is an example of chemotropism.
Question 31.
A reddish brown metal used in electrical wires when powdered and heated strongly turns black. When hydrogen gas is passed over this black substance, it regains its original colour. Based on this information answer the following questions:
(a) Name the metal and the black substance formed.
(b) Write balanced chemical equations for the two reactions involved in the above information.
Answer:
(a) The reddish brown metal is copper and the black substance formed is copper (II) oxide, i.e., CuO.

Question 33.
If a harmful chemical enters in a food chain comprising peacock, plants, rats and snakes, which of these organisms is likely to have the highest concentration of the chemical in its body. Justify your answer. Name the process involved and define it.
Answer:
The organism that occurs at the highest trophic level in the food chain will have the maximum concentration of harmful chemicals in its body. In the given case, plants are eaten by rats, rats are eaten by snakes and finally snakes are eaten by peacock.
The food chain involving the given organism is: Plants → Rats → Snakes → Peacock
when
the
Question 34.
(a) (i) What are isomers? Write the structures of two compounds having molecular formula C
3
H
6
O and give their names.
(ii) What are soaps? How are they chemically different from detergents? Why do soaps not work effectively in hard water?
OR
(b) (i) What is a homologous series of carbon compounds? Write general formula for alkynes. Name and draw the electron dot structure of first homologue of this series.
(ii) State the meaning of the functional group in an organic compound. Write the formula of the functional group present in alcohols and carboxylic acids.
Answer:
(a) (i) The organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are known as isomers. Molecular formula = C
3
H
6
O

(ii) A soap is the sodium salt (or potassium salt) of a long chain carboxylic acid (fatty acid) which has cleansing properties in water.
| Soaps | Detergents |
| (i) Soaps are the sodium or potassium salts of long chain carboxylic acids. The ionic group in soaps is COO – Na + . | Detergents are the sodium salts of long chain benzene sulphonic acids or ammonium salts of long chain carboxylic acids. The ionic group in a detergent is: SO 3 – Na + or – COO – NH 4 |
| (ii) Soaps are biodegradable. | Some detergents are not biodegradable. |
| (iii) Soaps have relatively weak cleansing action. | Detergents have a strong cleansing action. |
Soap is not suitable for washing clothes with hard water because of the following reasons:
1. When soap is used for washing clothes with hard water, a large amount of soap is wasted in reacting with the calcium and magnesium ions of hard water to form an insoluble precipitate called scum, before it can be used for the real purpose of washing.
motor
3. The formation of foam is necessary for removing dirt from clothes during the washing of clothes. Soap does not give foam easily with hard water.
OR
(b) (i) A homologous series is a group of organic compounds having similar structures and similar chemical properties in which the successive compounds differ by CH
2
group.
General formula for alkynes = C
n
H
2n-2
First member of this series is C
n
H
2
(ethyne).

(ii) An ‘atom’ or ‘a group of atoms’ which makes a carbon compound (or organic compound) reactive and decides its properties (or functions) is called a Functional group.
Functional group present in alcohol -OH.
Functional group present in carboxylic acid is -COOH
OR

SET – III Code No. 31/6/3
Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in Set I & II.
Question 4.
There are four solutions A, B, C and D with pH values as follows:
| Solution | A | B | C | D |
| pH | 2.0 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 12.0 |
Which solution(s) would liberate hydrogen gas with zinc?
(a) A only
(b) D only
(c) A and D
(d) B and C
Answer:
(a) A only
Question 7.
In torch lights and head lights of vehicles, the bulb is placed
(a) between the pole and the focus of the reflector.
(b) very near to the focus of the reflector.
(c) between the focus and centre of curvature of the reflector.
(d) at the centre of curvature of the reflector.
Answer:
(b) very near to the focus of the reflector.
Question 10.
Choose the option giving correct matching the items given in Column-I & II.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| A. Physical environment | (i) Ozone layer depletion |
| B. Exposure to UV radiation | (ii) Bacteria and Fungi |
| C. Chlorofluoro Carbon compound | (iii) Abiotic components |
| D. Decomposers | (iv) Skin Cancer |
Answer:
(b)
Question 11.
The thread like structures that develop on a moist slice of bread in Rhizopus are
(a) Sporangia
(b) Filaments
(c) Rhizoids
(d) Hyphae
Answer:
(d) Hyphae
Question 12.
The change in the focal length of an eye lens in human beings is caused by the action of
(a) optic nerves
(b) ciliary muscles
(c) retina
(d) cornea
Answer:
(b) ciliary muscles
![]()
Question 19.
In the following question, two statements—Asseration (A) and Reason (R). Answer the question selecting the appropriate option given below.
Assertion (A): Testes in human males are located outside the abdominal cavity in scrotum.
Reason (R): Scrotum provides a lower temperature than the normal body temperature for sperm formation.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
(b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
(d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Question 22.
(a)How is an electric impulse created in human nervous system? Identify the parts of a neuron which helps the nerve impulse to travel
(i) towards the cell body
(ii) away from the cell body
OR
(b) With the help of an example, explain how does the feedback mechanism regulate the hormone secretion.
Answer:
(a) The reception in a sense organ is in touch with the dendrites of sensory neuron when a stimulus acts on the receptor, a chemical reaction is set off which produces an electrical impulse in it.
(i) Neuron which helps the nerve impulse to travel towards the cell body is Dendrite.
(ii) Neuron which helps the nerve impulse to travel away from the cell body is Axon.
OR
(b) The excess or deficiency of hormones has a harmful effect in our body. The timing and amount of hormones released by various glands are controlled by the feedback mechanism which is in-built in our body.
For example, if the sugar level in the blood rises too much, it is detected by the cells of pancreas which respond by producing and secreting more insulin into the blood and as the blood sugar falls to a certain level, the secretion of insulin is reduced automatically.
Question 26.
Draw magnetic field lines produced around a straight current carrying conductor passing through a cardboard. How will the strength of the magnetic field change when the point where magnetic field is to be determined is moved away from the conductor?
Answer:
(i) The magnetic field lines around a straight conductor carrying current are concentric circles whose centre lies on the wire.
(ii) When a point where magnetic field is to be determined is moved away from the straight wire, the strength of the magnetic field decreases because as we move away from a current carrying straight conductor, the concentric circles around it representing magnetic field lines become larger and larger, indicating the decreasing strength of the magnetic field.

Question 28.
(a) (i) What property do acids and bases have in common? Explain it with an example.
(ii) A compound which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening
when mixed with water.
Identify the compound and write its formula. How is this compound prepared? Describe it in the form of a chemical equation only.
(b) (i) Write the chemical name and molecular formula of tooth enamel.
(ii) How does it get corroded? What is the preventive measure for this?
Answer:
(a) (i) The property of neutralization is common in acids and bases. When an acid reacts with a base, salt and water will be formed.
For example, when a base (NaOH) reacts with an acid (NCl), a salt (NaCl) and water (H
2
O) will be formed.

(ii) Plaster of Paris is the compound which is prepared by gypsum. It has the property of hardening when mixed with water.
Formula. CaSO
4
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)H
2
O or 2CaSO
4
H
2
O
Plaster of Paris is prepared by heating gypsum (CaSO
4
2H
2
O) to a temperature of 100° C (373 K) in a kiln. When gypsum is heated to a temperature of (373 K), it loses threefourths of its water of crystallisation and forms Plaster of Paris.

OR
(b) (i) Tooth enamel is made of Calcium Phosphate (Ca
3
(PO
4
)
2
).
(ii) Cause of tooth decay. It gets corroded when the pH in the mouth is lower than 5.5. When we eat food containing sugar, the bacteria present in our mouth break down the sugar to form acids and lower the pH in the mouth.
Preventive measure:
– The best way to prevent tooth decay is to clean the mouth thoroughly after eating food. Many toothpastes contain bases to neutralize the mouth acid.
– A person can lessen the chances of suffering from tooth decay by changing his eating habits such as eating less of sugary foods.
Question 33.
State the change in colour observed in each of the following cases mentioning the reason:
(a) Silver chloride is exposed to sunlight.
(b) A piece of zinc is dipped in ferrous sulphate solution.
(c) Copper powder is strongly heated in air.
Answer:
(a) When silver chloride is exposed to light, it decomposes to form silver metal and chlorine gas.
![]()
In this reaction, the white colour of silver chloride changes to grayish white due to the formation of silver metal.
(b) When a piece of zinc metal is dipped in ferrous sulphate solution to form ZnSO
4
and Fe.

In this reaction, zinc displaces iron from ferrous sulphate solution so that iron is liberated and green colour of ferrous sulphate solution fades due to the formation of zinc sulphate which is colourless.
(c) When copper powder is strongly heated in air, then copper reacts with oxygen of air to form a black substance Copper (II) oxide.

Question 35.
(a) Name the two types of pollination and differentiate between them.
(b) Explain the post fertilization changes, that occur in the ovary of a flower.
(c) A diagram of a germinating seed is given here.

Label the parts that
(i) gives rise to future shoot.
(ii) gives rise to future root system.
(iii) stores food.
Answer:
(a) Two types of Pollination are –
(i) Self pollination and
(ii) Cross pollination
| Self pollination | Cross pollination |
| (i) When the pollen grains from the anther of a flower are transferred to the stigma of the same flower (or another) flower on the same plant), it is called self-pollination. | When the pollen grains from the anther of a flower on one plant are transferred to the stigma of a flower on another similar plant, it is called cross-pollination. |
| (ii) Self pollination increases genetic uniformity. | Cross-pollination decreases genetic uniformity. |
| (iii) Self pollination decreases genetic variation. | Cross-pollination increases genetic variation. |
| (iv) Specie that exhibits self pollination-Pea. | Species show cross-pollination: Apple, Pumpkins. |
| (v) This process is carried out even when the flowers are closed. | For cross-pollination the flower should be open. |
(b) After fertilization, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat around it and is gradually converted into a seed (containing the baby plant). In fact all the eggs in the ovules present in the ovary get fertilized by male gametes from pollen grains and grow to become seeds. The ovary of flower develops and ‘becomes a fruit (with seeds inside it). A fruit protects the seeds.
(c) (i) Part A gives rise to Future shoot is called Plumule.
(ii) Part B gives rise to Future root system is called Radicle.
(iii) Part C stores food is called Cotyledon.