Students can find that CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10 Science with Solutions and CBSE Class 10 Science Question Paper 2019 (Series: JMS/1) effectively boost their confidence.
CBSE Class 10 Science Board Question Paper 2019 (Series: JMS/1) with Solutions
Time allowed: 3 hours
Maximum marks: 80
Recycle:
- The question paper comprises five sections – A, B, C, D and E. You are to attempt all the sections.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Internal choice is given in sections B, C, D and E.
- Question numbers 1 and 2 in Section A are one mark questions. They are to be answered in one word or in one sentence.
- Question numbers 3 to 5 in Section B are two marks questions. These are to be answered in 30 words each.
- Question numbers 6 to 15 in Section C are three marks questions. These are to be answered in about 50 words each.
- Question numbers 16 to 21 in Section D are five marks questions. These are to be answered in 70 words each.
- Question numbers 22 to 27 in Section E are based on practical skills. Each question is a two marks question. These are to be answered in brief.
SET – I Code No. 31/1/1
Section – A
Question 1.
What is the function of a galvanometer in a circuit?
Answer:
Galvanometer detects the presence of electric current in a circuit.
![]()
Question 2.
Write one important function of stomata pores in the leaves of the plants.
Answer:
Exchange of gases takes place through the stomata pores of the leaves.
Section – B
Question 3.
Why is respiration considered as an Exothermic reaction? Explain.
OR
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write one equation each for these reactions.
Answer:
During respiration, glucose is decomposed into carbon dioxide gas and water vapours using oxygen gas from air in the living cells of our body and heat energy is released during this process. So respiration is a type of exothermic reaction.
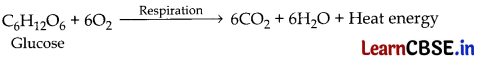
OR
In a decomposition reaction, one substance breaks up into two or more chemical substances, while in a combination reaction two or more substances combine to form one single substance. So these two reactions are called opposites of each other.
Examples of decomposition reaction:
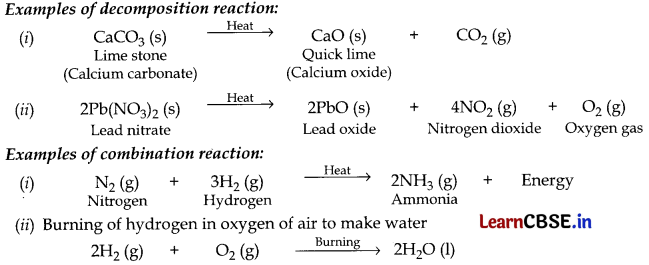
Question 4.
Write two different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide energy in human body. Write the products formed in each case.
Answer:
(i) Aerobic respiration in presence of oxygen in Mitochondria.
(ii) Anaerobic respiration in lack of oxygen in muscle cells
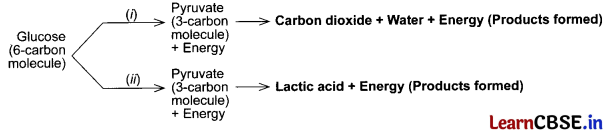
Question 5.
Define the term power of accommodation. Write the modification in the curvature of the eye lens which enables us to see the nearby objects clearly.
Answer:
The ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length, so as to clearly focus rays coming from distant as well as near objects on the retina, is called the power of accommodation of the eye. The ciliary muscles contract which increases the curvature of eye lens and it thickens which enables us to see the nearby objects clearly.
Section – C
Question 6.
2 g of silver chloride is taken in a china dish and the china dish is placed in sunlight for sometime. What will be your observation in this case? Write the chemical reaction involved in the form of a balanced chemical equation. Identify the type of chemical reaction.
OR
Identify the type of reactions taking place in each of the following cases and write the balanced chemical equation for the reactions.
(a) Zinc reacts with silver nitrate to produce zinc nitrate and silver.
(b) Potassium iodide reacts with lead nitrate to produce potassium nitrate and lead iodide.
Answer:
Observation. The white colour of silver chloride turns grey in sunlight. This is due to the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine by light.

This is a double displacement reaction in which exchange of ions between the reactants happens.
Question 7.
Identify the acid and the base from which sodium chloride is obtained. Which type of salt is it? When is it called rock salt? How is rock salt formed?
Answer:
Acid – Hydrochloric acid (HC1)
Base – Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH)
Sodium chloride is a neutral salt as pH of its aqueous solution is 7.
Deposits of salt are large crystals that are often brown due to impurities. This is called rock salt. Beds of rock salt were formed when seas of bygone ages dried up.
Question 8.
Write characteristics of image formed by a plane mirror.
Answer:
The characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors:
- The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual and erect. It cannot be received on a screen.
- The image formed by a plane mirror is of the same size as the object.
- The image formed by a plane mirror is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of the mirror.
- The image formed in a plane mirror is laterally inverted.
Question 9.
Write three types of blood vessels. Give one important feature of each.
Answer:
Three types of blood vessels are:
- Arteries – Arteries carry the oxygenated blood away from the heart to the various. organs of the body.
- Veins – Veins carry deoxygenated blood from different organs of the body back to the heart.
- Capillaries – Capillaries are the smallest vessels where exchange of material between the blood and surrounding cells takes place.
Question 10.
Trace the sequence of events which occur when a bright light is focused on your eyes.
Answer:
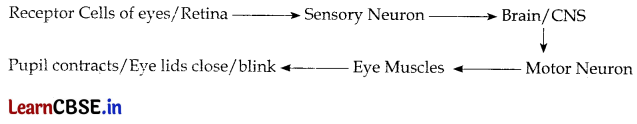
Question 11.
What are plant hormones? Name the plant hormones responsible for the following:
(i) Growth of stem
(ii) Promotion of cell division
(iii) Inhibition of growth
(iv) Elongation of cells
Answer:
The chemical compounds or organic molecules produced in the plant cells that regulate various physiological functions like growth, development and responses to the environment are called plant hormones.
- Growth of.stem – Gibberellins
- Promotion of cell division – Cvtokinins
- Inhibition of growth – Abscisic acid
- Elongation of cells – Auxins
![]()
Question 12.
Name the plant Mendel used for his experiment. What type of progeny was obtained by Mendel in F
1
and F
2
generations when he crossed the tall and short plants? Write the ratio he obtained in F
2
generation plants.
OR
Explain how equal genetic contribution of male and female parents is ensured in the progeny.
Answer:
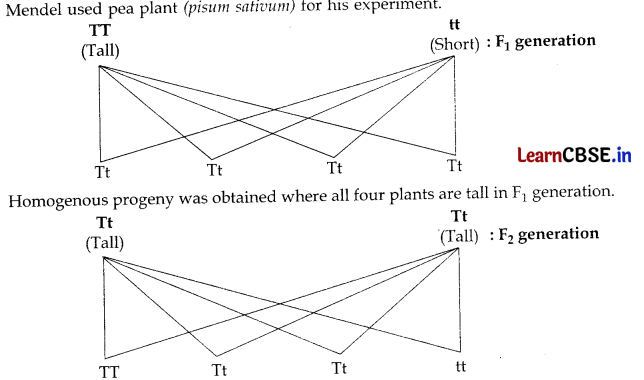
OR
Both the parents contribute equal DNA material to progeny. Every sexually reproducing organism bears two sets of all genes, one inherited from each parent. Each germ cell must have only one gene set. Thus the male gamete and female gamete carry one gene for each characteristic from the gene pairs of parents. But when a male gamete fuses with a female gamete during fertilisation, they make a new cell called zygote with a full set of genes. Thus zygote grows and develops to form a new organism having equal characteristics from both the parents which it has inherited through genes.
Question 13.
What is a rainbow? Draw a labelled diagram to show the formation of a rainbow.
Answer:
The splitting sunlight into its coloured components is a rainbow. It is a natural optical phenomenon caused by the dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets in the earth’s atmosphere.
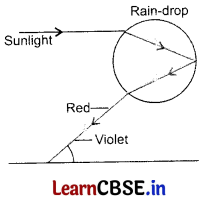
Question 14.
How can we help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Suggest any three methods.
OR
Define an ecosystem. Draw a block diagram to show the flow of energy in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Problems of waste disposal can be reduced by our combined effort. We can reduce it in the following ways:
you
collect
(iii) By re-using some of the wastes before throwing them finally in the garbage heaps. For example, some of the plastic containers can be reused for storing food articles in the kitchen.
OR
All the interacting organisms in an area together with the non-living constituents of the environment form an ecosystem. Ecosystem consists of biotic and abiotic components.
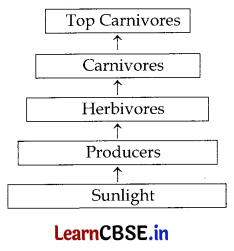
Question 15.
What is water harvesting? List two main advantages associated with water harvesting at the community level. Write two causes for the failure of sustained availability of groundwater.
Answer:
Water harvesting is the concept of capture, collection and storage of every drop of water that has fallen on the land in small pits, lakes, watershed systems, small earthern dams, constructed dykes, sand and limestone reservoirs, rooftop water collecting systems, etc.
Advantages associated with water harvesting:
- It increases the production and income of the watershed community.
- It also mitigates droughts and floods and increases the life of downstream dams and reservoirs.
plastic,
- Loss of vegetation cover.
- Diversion for high demanding water crops.
- Pollution from industrial effluents and urban wastes.
Section – D
Question 16.
(a) List in tabular form three chemical properties on the basis of which we can differentiate between a metal and a non-metal.
(b) Give reasons for the following:
(i) Most metals conduct electricity well.
(ii) The reaction of iron
(iii) oxide [Fe203] with heated aluminium is used to join cracked machine parts.
Answer:
| Metals | Non-metals |
| (i) Metals lose electrons to form positive ions; are electropositive nature. | (i) Non-metals gain electrons to form in negative ions; are electronegative in nature. |
| (ii) React with dilute acids to liberate hydrogen gas. | (ii) Do not react with dilute acids. |
(iii) Metals react with oxygen to form basic oxides
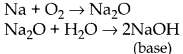
Metals react with chlorine to form ionic chlorides 2Na + Cl 2 → NaCl A few reactive metals react with hydrogen to form ionic metal hydrides. 2Na + H 2 → 2NaH |
(iii) Non-metals react with oxygen to form acidic oxides
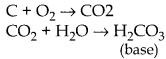
Non-metals react with chlorine to form covalent chlorides H 2 + Cl 2 → 2HCl Non-metals react with hydrogen to form covalent hydrides. H 2 + S → H 2 S |
(b) (i) Most metals allow the current to pass from one end to the other due to the movement of valence electrons present in it.
(ii) This displacement reaction is highly exothermic. The amount of heat evolved is so large that the metals are produced in the molten state and is thus used to join cracked machine parts and it is known as thermit reaction.
![]()
Question 17.
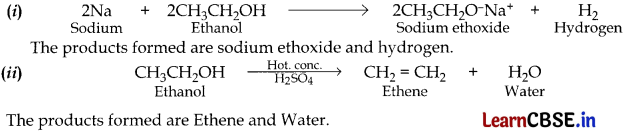
Write the chemical formula and name of the compound which is the active ingredient of all alcoholic drinks. List its two uses. Write chemical equation and name of the product formed when this compound reacts with
(i) sodium metal
(ii) hot concentrated sulphuric acid
OR
What is methane? Draw its electron dot structure. Name the type of bonds formed in this compound. Why are such compounds:
(i) poor conductors of electricity? and
(ii) have low melting and boiling points? What happens when this compound bums in oxygen.
Answer:
Chemical formula: C
2
H
5
OH
Name of compound: Ethanol; It is the active ingredient of all alcoholic drinks.
Uses of ethanol:
- It is used in medicines such as tincture iodine, cough syrups and many tonics.
-
Ethanol is a very good solvent and is also soluble in water in all proportions. So it is used in many chemical industries.
OR
Methane is a compound formed between carbon and hydrogen and its chemical formula is CH
4
. Methane is widely used as a fuel and is a major compound of biogas and CNG.
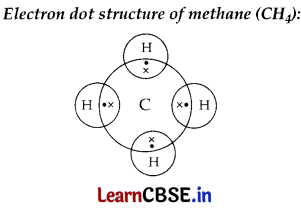
Covalent bonds are formed in this compound.
(i) Since the electrons are shared between atoms and no charged particles are formed, such covalent compounds are generally poor conductors of electricity.
(ii) Covalently bonded molecules have weak intermolecular forces. This gives rise to the low melting and boiling points of these compounds.
When methane burns in oxygen, a large amount of heat and light is released with carbon dioxide and water.
CH
2
+ 2O
2
→ CO
2
+ 2H
2
O + heat and light
Question 18.
Define pollination. Explain the different types of pollination. List two agents of pollination. How does suitable pollination lead to fertilization?
OR
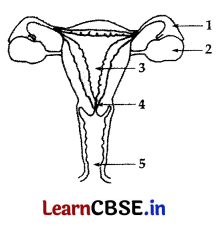
(a) Identify the given diagram. Name the parts 1 to 5.
(b) What is contraception? List three advantages of adopting contraceptive measures.
Answer:
The transfer of pollen grains from anthers (male sexual parts) of a flower to the stigma part of the pistil (female sexual part) is known as pollination. Pollination is done by insects, birds, wind and water.
Pollination can occur in two ways:
(i) Self pollination. When the pollen grains from the anther of a flower are transferred tc? the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant, it is called self pollination.
paper,
When a pollen grain falls on the stigma of the carpel, it grows a pollen tube downwards through the style towards the female gamete in the ovary. A male gamete moves down the tube. When the pollen tube enters the ovule, its tip bursts open and male gamete comes out of the pollen tube and combines with the nucleus of the female gamete and forms zygote. This process is known as fertilization.
OR
(a) The given diagram is the Human Female Reproductive System.
The parts are:
- Oviduct or Fallopian tube ovary
- Ovary
- Uterus
- Cervix
-
Vagina
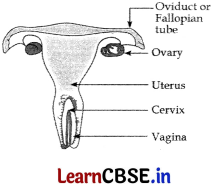
(b) The methods used to prevent pregnancy as a consequence of sexual intercourse is called contraception.
Advantages of adopting contraceptive measures are:
- It helps in controlling the size of the family which can improve the standard of living.
- The general health of the female can be improved as reproduction demands high pressure on the body and mind of the female.
- It helps in preventing sexually transmitted diseases.
- These methods check the population growth of a country by controlling child birth rate.
- Frequent and unwanted pregnancies can be avoided by using contraception.
Question 19.
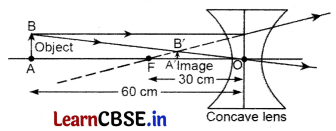
An object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use lens formula to find the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) formed by the lens in this case.
(iii) Draw ray diagram to justify your answer of part (ii).
Answer:
u = -60 cm,
f = -30 cm
(i) Lens formula, \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
\(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -30}\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ -60 }\) = \(\frac { 2+1 }{ -60 }\) = \(\frac { 3 }{ -60 }\)
v = \(\frac { -60 }{ 3 }\) = -20 cm
The image is at a distance of 20 cm from the lens.
glass
- virtual,
- erect,
- in front of the lens between ‘O’ and ‘F’,
- on the same side of the object, and
- diminished
(iii)
Question 20.
(a) With the help of a suitable circuit diagram prove that the reciprocal of the equivalent resistance of a group of resistances joined in parallel is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
(b) In an electric circuit two resistors of 12 Ω each are joined in parallel to a 6V battery. Find the current drawn from the battery.
OR
An electric lamp of resistance 20 Ω and a conductor of resistance 4 Ω are connected to a 6 V battery as shown in the circuit.
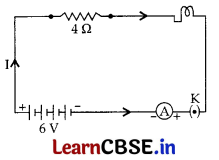
Calculate:
(a) the total resistance of the circuit,
(b) the current through the circuit,
(c) the potential difference across the (i) electric lamp and (ii) conductor, and
(d) power of the lamp.
Answer:
(a) Connect 3 resistors R
1
, R
2
and R
3
in parallel between the point XY with a battery, a plug key and an ammeter in series as shown in the figure.
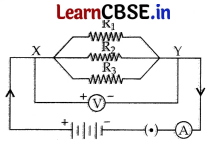
• Connect the voltmeter in parallel with these resistors between the terminals X and Y.
• Plug the key and note the current I in the ammeter and potential difference V across the resistors.
• Take out the plug from the key. Remove the ammeter and voltmeter from the circuit. Insert the ammeter in series with the resistor R
1
. Let the ammeter reading be I
1
.
Similarly measure the currents through R
2
and R
3
. Let these be I
2
and I
3
respectively. It is observed that the total current I is equal to the sum of the separate currents through each branch of the combination.
I = I
1
+ I
2
+ I
3
Let R
p
be the equivalent resistance of the parallel combination of resistors. By applying Ohm’s law to the parallel combination of resistors, we have I = \(\frac{V}{R_P}\)
On applying Ohm’s law to each resistor, we get
I
1
= \(\frac{V}{R_1}\);
I
2
= \(\frac{V}{R_2}\);
I
3
= \(\frac{V}{R_3}\)
Hence \(\frac{V}{R_P}\) = \(\frac{V}{R_1}\) + \(\frac{V}{R_2}\) + \(\frac{V}{R_3}\)
OR
\(\frac{1}{R_p}\) = \(\frac{1}{R_1}\) + \(\frac{1}{R_2}\) + \(\frac{1}{R_3}\)
Thus, the reciprocal of the equivalent resistance of a group of resistances joined in parallel is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
(b) \(\frac{1}{R_eq}\) = \(\frac{1}{R_1}\) + \(\frac{1}{R_2}\) = \(\frac{1}{12}\) + \(\frac{1}{12}\) = \(\frac{2}{12}\)
R
eq
= 6 Ω
∴ I = \(\frac{V}{R_eq}\) = \(\frac{6}{6}\) = 1A
OR
R
1
= 20 Ω,
R
2
= 4 Ω,
V = 6V
(a) Total resistance, R = R
1
+ R
2
= 20 + 4 = 24 Ω
(b) Current, I = \(\frac{V}{R}\) = \(\frac{6}{24}\) = \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 0.25A
(c) Potential difference across
(i) Electric lamp, V
1
= IR
1
= 0.25 × 20 = 5 volts
(ii) Conductor, V
2
= IR
2
= 0.25 × 4 = 1 volt
(d) Power of the lamp, P = VI = 6 × 0.25 = 1.5 W …where [ V = V
1
+ V
2
![]()
Question 21.
What is a solenoid? Draw the pattern of magnetic field lines of (i) a current carrying solenoid and (it) a bar magnet. List two distinguishing features between the two fields.
Answer:
A solenoid is a long cylindrical coil with many close turns of insulated copper wire wrapped in the shape of a cylinder.
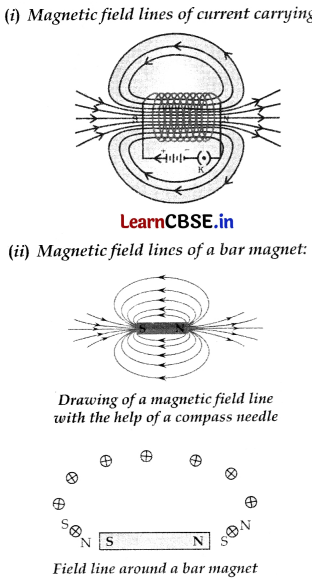
Distinguishing features between the two fields:
(a) The strength of magnetic field due to solenoid can be changed while the magnetic field strength due to bar magnet cannot be changed.
(b) Solenoid produces magnetic field as long as current flows in its coils while bar magnet produces a permanent magnetic field.
Section – E
Question 22.
Blue litmus solution is added to two test tubes A and B containing dilute HCl and NaOH solution respectively. In which test tube a colour change will be observed? State the colour change and give its reason.
OR
What is observed when 2 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid is added to 1 g of sodium carbonate taken in a clean and dry test tube? Write chemical equation for the reaction involved.
Answer:
Colour change will be observed in test tube ‘A’ containing dilute HCl.
Reason: Blue litmus turns red.
HCl is a strong acid. So H
+
ion concentration increases when it is added to a solution which leads to the decrease in pH value. Acids have the tendency to change blue litmus to red.
OR
Hydrochloric acid decomposes sodium carbonate to form sodium chloride and liberates C02 gas which turns lime water milky.
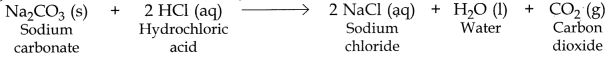
Question 23.
In three test tubes A, B and C, three different liquids namely, distilled water, underground water and distilled water in which a pinch of calcium sulphate is dissolved, respectively are taken. Equal amount of soap solution is added to each test tube and the contents are shaken. In which test tube will the length of the foam (lather) be longest? Justify your answer.
Answer:
In test tube ‘A’ which contains distilled water the length of the foam will be longest. The sample of water that produces a good amount of foam with soap is called soft water whereas the one that produces very less foam with soap is called hard water.
The hardness of the water is due to the presence of sulphates, chlorides and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium ions in water. Ground water and distilled water with a pinch of calcium sulphate are hard waters, soap reacts with the salts present in them and form insoluble precipitates in water.
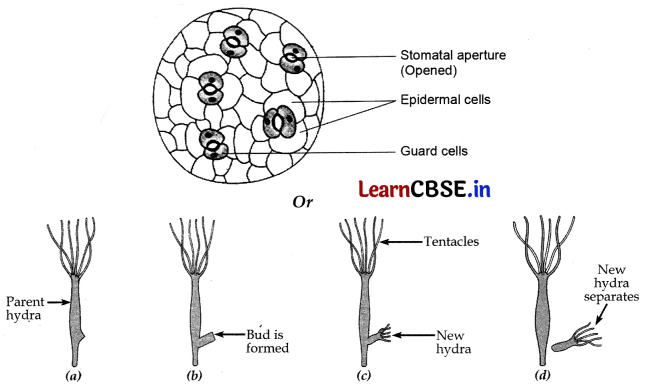
Question 24.
A student is observing the temporary mount of a leaf peel under a microscope. Draw labelled diagram of the structure (of stomata) as seen under the microscope.
OR
Draw a labelled diagram in proper sequence to show budding in hydra.
Answer:
Question 25.
In the experimental set up to show that “CO
2
is given out during respiration”, name the substance taken in the small test tube kept in the conical flask. State its function and the consequences of its use.
Answer:
KOH (Potassium hydroxide) solution is taken in the small test tube in the experiment set up to show CO
2
is given out during respiration.
KOH absorbs CO
2
released by germinating seeds, creates a vacuum and causes rise in water level in the delivery tube.
Question 26.
While studying the dependence of potential difference (V) across a resistor on the current (I) passing through it, in order to determine the resistance of the resistor, a student took 5 readings for different values of current and plotted a graph between V and I. He got a straight line graph passing through the origin. What does the straight line signify? Write the method of determining resistance of the resistor using this graph.
OR
What would you suggest to a student if while performing an experiment he finds that the pointer/needle of the ammeter and voltmeter do not coincide with the zero marks on the scales when circuit is open? No extra ammeter/voltmeter is available in the laboratory.
Answer:
The straight line graph of potential difference (V) across a resistor on the current (I) passing through it represents that the potential difference (V) is directly proportional to the current flowing through it.
To determine the resistance from the graph, read the current value in amperes, corresponding to a given voltmeter reading and take the ratio \(\left(\frac{\mathrm{V}}{\mathrm{I}}\right)\).
∴ R = \(\frac { V }{ I }\), where ‘R’ is the resistance, ‘V’ is the potential difference and I is the current.
OR
This is called the zero error of the scale of ammeter or voltmeter. If there is a zero error, then this error is subtracted from the value that is depicted when the circuit is closed, otherwise, the accurate current or potential difference will not be recorded.
![]()
Question 27.
List four precautions which a student should observe while determining the focal length of a given convex lens by obtaining image of a distant object on a screen.
Answer:
The precautions while determining the focal length of a given convex lens by obtaining image of a distant object on a screen are:
- A convex lens should be placed on the lens holder kept on a optical bench at a point ‘A’.
- The position of the screen is adjusted on the other side of the lens in such a way that a clear and sharp image of the object is formed on it.
- The base of the lens and white screen should be in a line with the measuring scale.
- There should not be any obstacle in the path of the convex lens.
SET – II Code No. 31/1/2
Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in Set I.
Section – A
Question 1.
Name and define the SI unit of current.
Answer:
1. Ampere (A) is the SI unit of current.
One ampere is defined as the flow of one coulomb of charge per second, that is 1 Ampere = 1 Coulomb/1 second.
Question 2.
Name two waste products stored in older xylem of trees.
Answer:
Two waste products stored in older xylem of trees. Resin and gum
Section – B
Question 3.
Explain, why do stars twinkle?
OR
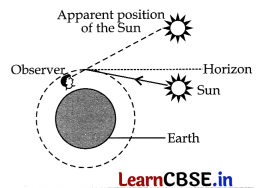
Explain about the phenomenon of two minutes early sun rise than the actual sunrise.
Answer:
The twinkling of a star is due to atmospheric refraction of starlight. The atmospheric refraction occurs in a medium of gradually changing refractive index. Since the atmosphere bends starlight towards the normal, the apparent position of the star is slightly different from its actual position. This apparent position of the star is not stationary, but keeps on changing slightly, as the physical conditions of the earth’s atmosphere are not stationary. Since the stars are very distant, they act as point-sized sources of light.
As the path of rays of light coming from the star goes on varying slightly, the apparent position of the star fluctuates and the amount of starlight entering the eye flickers the star sometimes appears brighter, and at some other time, fainter, which is the twinkling effect.
OR
TheSun can be seen about two minutes before sunrise because when the Sun is slightly below the horizon, the Sun’s light coming from less dense air to more dense air is refracted downwards as it passes through the atmosphere. Thus due to this atmospheric refraction, the Sun appears to be raised above the horizon when actually it is sjightly below the horizon.
Question 4.
How is O
2
and CO
2
transported in human beings?
Answer:
(i) Transport of oxygen. The haemoglobin present in the red blood cells takes the oxygen from alveoli of the lungs. The oxygen is carried by blood to all parts of the body. As the blood passes through the tissues of the body, the oxygen from the blood diffuses into the cells.
(ii) Transport of carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water. It is present in our blood plasma in a dissolved state and is transported from the body tissues to lungs where it diffuses from blood to air in the lungs and then expelled out through nostrils during exhaling.
Question 5.
Write the structure of eye lens and state the role of ciliary muscles in the human eye.
Answer:
The eye lens is a transparent biconvex structure in the eye. The ciliary muscles hold the crystalline lens to provide the finer adjustment of focal length required to focus objects at different distances on the retina by relaxing and contracting themselves.
Section – C
Question 6.
Identify the acid and base which form sodium hydrogen carbonate. Write chemical equation in support of your answer. State whether this compoun is acidic, basic or neutral. Also write its pH value.
Answer:
Sodium hydrogen carbonate is formed by a chemical reaction between a weak acid – carbonic acid and strong base – sodium hydroxide.
NaOH + H
2
CO
3
→ NaHCO
3
+ H
2
O
The compound formed is weak basic in nature and has pH value slightly above 7.
Question 9.
Define the term transpiration. Design an experiment to demonstrate this process.
Answer:
The loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant is known as transpiration. This is achieved by both, heat of the sun and the pressure difference between the roots and soil.
and
- Take two small pots having the same amount of soil.
- One should have a plant in it. Place a stick of the same height as the plant in the other pot.
- Cover the soil in both pots with a plastic sheet so that moisture cannot escape by evaporation.
- Cover both sets with plastic sheets and place in bright sunlight for half an hour.
- We could observe water droplets accumulated inside the plastic sheet of the pot in which the plant is placed.
- This experiment shows that water has been lost through the stomata of the leaves of the plant whereas it cannot be seen in the other pot in which a stick is kept.
Question 10.
What is feedback mechanism of hormonic regulation? Take the example of insulin to explain this phenomenon.
Answer:
The mechanism through which the timing and amount of hormone is released and regulated in our body by the glands is called feedback mechanism of hormonic regulation.
For example, if the sugar level in the blood rises, this is detected by the cells of the pancreas which respond by producing more insulin to oxidize the sugar. As the blood sugar level falls, insulin secretion is reduced automatically.
Section – D
Question 17.
(a) Write chemical equations for the following reactions:
(i) Calcium metal reacts with water.
(ii) Cinnabar is heated in the presence of air.
(iii) Manganese dioxide is heated with aluminium powder.
(b) What are alloys? List two properties of alloys.
Answer:
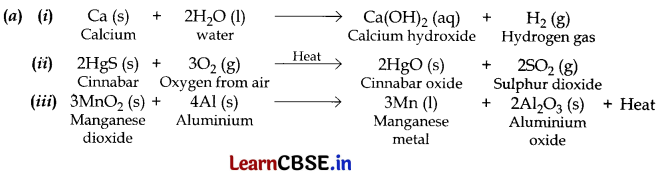
(b) Alloys are homogeneous mixtures of two or more metals or a metal and a non-metal. The properties of an alloy are different from the properties of the constituent metals.
In general-
- alloys are stronger than the metals from which they are made.
- alloys are more resistant to corrosion.
Question 18.
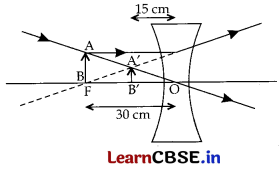
An object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use lens formula to determine the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) in this case,
(iii) Draw a labelled diagram to justify your answer of part (ii).
Answer:
Object distance, u = -30 cm;
Focal length, f = -30 cm
(i) Lens formula, \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
So \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ f }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ u }\)
⇒ \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ -30 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ -30 }\) = \(\frac { 1+1 }{ -30 }\) = \(\frac { 2 }{ -30 }\)
v = -15 cm
The image distance is 15 cm in front of the lens.
metals
- virtual,
- erect,
- diminished,
- in front of the lens between ‘O’ & ‘F’, and
- 15 cm from the lens on the same side as the object.
(iii)
SET – III Code No. 31/1/3
Except for the following questions, all the remaining questions have been asked in Set I \& Set II.
Section – A
Question 1.
Name the acid present in ant sting.
Answer:
Acid present in ant sting. Methanoic acid
Question 2.
Write the function of voltmeter in an electric circuit.
Answer:
Function of voltmeter in an electric circuit is to find out the potential difference between two points.
Section – B
Question 3.
What happens to the image distance in the normal human eye when we decrease the distance of an object, say 10 m to 1 m? Justify your answer.
Answer:
There will be no change in the image distance in the normal human eye. This is because the image is always formed on the retina.
Question 4.
List two different functions performed by pancreas in our body.
Answer:
Functions of pancreas:
(i) Secretes enzyme trypsin for the breakdown of proteins.
(ii) Secretes hormone insulin to regulate sugar level in the blood.
Section – C
Question 7.
List three advantages each of:
(i) exploiting resources with short term aims, and
(ii) using a long term perspective in managing our natural resources.
Answer:
(i) Advantages of exploiting resources with short term aims:
(a) They provide immediate advantages to fulfill basic needs of the present generation.
(b) To get huge profit without any accountability.
(c) Will lead to fast industrialisation and modernisation.
(ii) Advantages of using a long term perspective in managing our natural resources:
(a) It will fulfill the needs of not only the present generations but will help to conserve our natural resources for the benefit of the future generations.
(b) It will help to prevent the exploitation of resources to the hilt to obtain short-term aims.
(c) Damage caused to the environment will be reduced.
Question 9.
Nervous and hormonal systems together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings. Justify this statement with the help of an example.
Answer:
Nervous and hormonal systems together perform the functipn of control and coordination in human beings. Nervous system is connected to receptors of all senses. Information obtained from sensory organs is passed rapidly to the Central Nervous System for interpretation. On this basis message is sent to effector organ or organs (muscles, glands, etc.) The action can be voluntary or involuntary.
Nervous system is also connected with the functioning of endocrine or hormonal systems. Endocrine glands pour the secretions into blood which transports them to all parts of the body. Target cells have receptors for picking up the hormones and working as per hormonal stimulus. There is a feedback mechanism which determines the requirement of hormones and the activity of endocrine glands.
![]()
Question 11.
What is photosynthesis? Explain its mechanism.
Answer:
(a) Green plants obtain their food by the process of photosynthesis. This mode of nutrition is called autotrophic nutrition. This type of nutrition involves the intake of simple inorganic materials from the environment and use an external energy source like the sun to synthesise complex high energy organic material. The process by which green plants make their own food (glucose) using inorganic material like carbon-dioxide and water by using sunlight energy is called photosynthesis.
![]()
Question 15.
Explain the following:
(a) Sodium chloride is an ionic compound which does not conduct electricity in solid state whereas it does conduct electricity in molten state as well as in aqueous solution.
(b) Reactivity of aluminium decrease if it is dipped in nitric acid.
(c) Metals like calcium and magnesium are never found in their free state in nature.
Answer:
(a) Sodium chloride does not conduct electricity in solid state whereas it does conduct electricity in molten state as well as in aqueous solution. This is because in solid state movement of ions is not possible due to rigid structure. Movement of ions is what causes electricity.
In molten and aqueous state, ions are free to move and so they conduct electricity.
items
and
Section – D
Question 17.
(a) Draw magnetic field lines produced around a current carrying straight conductor passing through a cardboard. Name, state and apply the rule to mark the direction of these field lines.
(b) How will the strength of the magnetic field change when the point where magnetic field is to be determined is moved away from the straight wire carrying constant current? Justify your answer?
Answer:
(a) To mark the direction of magnetic field lines, we will use the Right hand thumb rule. According to this, if the current carrying straight conductor is held in the right hand in such a way that the thumb points towards the direction of current, then your fingers will wrap around the conductor in the direction of the field lines.
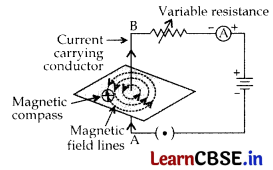
(b) The strength of the magnetic field decreases when the point where magnetic field is to be determined in moved away from a straight wire carrying constant current. This is because the strength of the magnetic field is inversely proportional to the distance from the origin. As the distance increases the strength decreases.
Question 21.
Write the main difference between an acid and a base. With the help of suitable examples explain the term neutralization and the formation of –
(i) acidic,
(ii) basic and
(iii) neutral salts.
Answer:
Acids are sour in taste and change the colour of the blue litmus to red. Their pH is less than 7.
Bases are bitter in taste and change colour of red litmus to blue. Their pH is more than 7. The reaction between an acid and a base to give a salt and water is known as a neutralisation reaction. In general, a neutralisation reaction can be written as
