We have given these Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 2 Acids Bases and Salts to solve different types of questions in the exam. Previous Year Questions & Important Questions of Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Science Chapter 2 will help the students to score good marks in the board examination.
Important Questions of Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Science Chapter 2
Question 1.
With the help of an example explain what happens when a base reacts with a non- metallic oxide. What do you infer about the nature of non-metal oxide? (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
Oxides of non-metals react with bases to form salt and water. For example, the reaction between carbon dioxide and calcium hydroxide. Calcium hydroxide, which is a base, reacts with carbon dioxide to produce salt and water.

Hence, oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature.
Question 2.
What is observed when carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water
(i) for a short duration?
(ii) for a long duration? Also write the chemical equations for the reactions involved. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
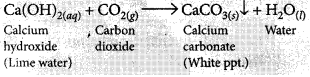
(i) When CO
2
is passed through lime water for short interval of time, it turns milky due to the formation of insoluble calcium carbonate.
(ii) If CO
2
is passed for long duration through lime water, the white precipitate formed dissolves due to the formation of soluble calcium hydrogen carbonate and the solution becomes clear.
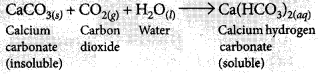
Question 3.
2 mL of sodium hydroxide solution is added to a few pieces of granulated zinc metal taken in a test tube. When the content are warmed, a gas evolves which is bubbled through a soap solution before testing. Write the equation of the chemical reaction involved and the test to detect the gas. Name the gas which will be evolved when the same metal reacts with dilute solution of a strong acid.
Answer:
It is observed that active metals like zinc react with strong bases like NaOH, KOH etc. to liberate hydrogen gas and corresponding salt.
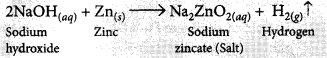
The evolution of gas is confirmed by the bubble formation in soap solution.
Test to detect H
2
gas: When burning matchstick is kept on the mouth of this test tube, pop sound is heard which confirms the presence of H
2
gas. When Zn metal reacts with dilute solution of strong acid, H
2
gas is evolved.
![]()
Question 4.
Write the names of the product formed when zinc reacts with NaOH. Also write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction involved. Write a test to confirm the presence of the gas evolved during this reaction. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 3.
Question 5.
To. a solution of sodium hydroxide in a test tube, two drops of phenolphthalein are added.
(i) State the colour change observed.
(ii) If dil HCl is added dropwise to the solution, what will be the colour change?
(iii) On adding few drops of NaOH solution to the above mixture the colour of the solution reappears. Why? (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(i) On adding phenolphthalein to NaOH solution, the colour becomes pink.
(ii) On adding dilute HCl solution dropwise to the same test tube, the pink colour disappears and the solution again becomes colourless.
(iii) On again adding NaOH to the above mixture, pink colour reappears because the medium becomes basic again.
Question 6.
A cloth’strip dipped in onion juice is used for testing a liquid ‘X. The liquid ‘X changes its
odour. Which type of an indicator is onion juice? The liquid ‘X turns blue litmus red. List the observations the liquid ‘X will show on reacting with the following :
(a) Zinc granules
(b) Solid sodium carbonate
Write the chemical equations for the reactions involved.
Answer:
Onion juice is an olfactory indicator. Olfactory indicators give one type of odour in acidic medium and a different odour in basic medium. As the liquid ‘X’ turns blue litmus red, hence it is an acidic solution.
(a) Acids react with active metals such as zinc, magnesium etc. and evolve hydrogen gas, for example,
Zn
(s)
dil.H
2
SO
4(aq)
→ ZnSO
4
H
2(g)
(b) Acids react with metal carbonates to give carbon dioxide with brisk effervescence.
For example, Na
2
CO
3
+ H
2
SO
4
→ Na
2
SO
4
+ CO
2
+ H
2
O
Question 7.
(a) Write the chemical name and formula of marble.
(b) It has been found that marbles of Taj are getting corroded due to development of industrial areas around it. Explain this fact giving a chemical equation.
(c) (i) What happens when CO
2
is passed through lime water?
(ii) What happens when CO
2
is passed in excess through lime? (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(a) The chemical formula of marble (lime stone) is CaCO
3
. Its chemical name is calcium carbonate.
(b) Taj Mahal, one of the seven wonders of the world situated at Agra, is continuously losing its luster day by day due to rapid industrialisation which causes acid rain.
The sulphuric acid present in the acid rain causes the marble (CaCO
3
) to be washed off as calcium sulphate (CaSO
4
), leading to the deterioration of such a splendid piece of architecture.
CaCO
3(s)
+ H
2
SO
4(aq)
→ CaSO
4(aq)
+ H
2
O
l
+ CO
2(g)
(c) Refer to answer 2.
Question 8.
On diluting an acid, it is advised to add acid to water and not water to acid. Explain why it is so advised? (Board Term I, 2014)
Draw a labelled diagram to show the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas in laboratory.
(ii) Test the gas evolved first with dry and then with wet litmus paper. In which of the two cases, does the litmus paper show change in colour?
(iii) State the reason of exhibiting acidic character by dry HCl gas/HCl solution.
Answer:
Diluting a concentrated acid with water is a highly exothermic process. So, when water is added to concentrated acid, large amounts of heat is liberated which changes some water to steam explosively which can splash the acid and even the glass apparatus may break due to excessive heating.
Question 9.
(i) Draw a labelled diagram to show the preparation of hydrogen chloride gas in laboratory.
(ii) Test the gas evolved first with dry and then with wet litmus paper. In which of the two cases, does the litmus paper show change in colour?
(iii) State the reason of exhibiting acidic character by dry HCl gas/HCl solution. (2020)
Answer:
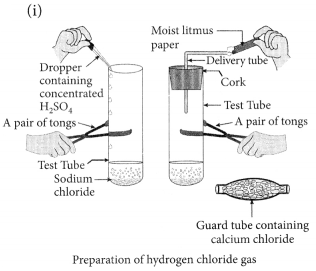
(ii) There is no change in the colour of ‘dry’ blue litmus paper but ‘moist’ blue litmus paper turns red if brought near the mouth of the test tube.
This shows that HCl gas does not show acidic behaviour in absence of water but it shows acidic behaviour in presence of water.
(iii) When HC1 gas dissolves in water, forms hydrochloric acid solution i.e., HCl
(aq)
which then produces H
+
(aq)
or H
3
O
+
(aq)
ions.
HCl + H
2
O → H
3
O
+
+ Cl
–
Due to the presence of H
+
or H
3
O
+
it shows acidic behaviour.
Question 10.
Complete and balance the following chemical equations :
(i) NaOH
(aq)
+ Zn
(s)
→
(ii) CaCO
3(s)
+ H
2
O
(l)
+ CO
2(g)
→
(iii) HCl
(aq)
+ H
2
O
(l)
→
Answer:
(i) 2NaOH
(aq)
+ Zn
(s)
→ Na
2
ZnO
2(aq)
+ H
2(g)
(ii) CaCO
3(s)
+ CO
2(g)
+ H
2
O
l
→ Ca(HCO
3
)
2(aq)
(iii) HCl
(aq)
+ H
2
O
l
> H
3
O+ Cl
–
(aq)
Question 11.
How the following substances will dissociate to produce ions in their solutions?
(i) Hydrochloric acid
(ii) Nitric acid
(iii) Sulphuric acid
(iv) Sodium hydroxide
(v) Potassium hydroxide
(vi) Magnesium hydroxide (Board Term 1, 2017)
Answer:
Dissociation of various substances to produce ions in their solutions are :
(i) Hydrochloric acid (HCl):
HCl
(aq)
⇌ H
+
(aq)
+ Cl
–
(aq)
(ii) Nitric acid (HNO
3
HNO
3
(aq)
⇌ + H
+
aq
+ NO
–
3
(aq)
(iii) Sulphuric acid (H
2
SO
4
):
H
2
SO
4
(aq)
⇌ 2H
+
(aq)
+ SO
2-
4(aq)
(iv) Sodium hydroxide (NaOH):
NaOH
(aq)
⇌ Na
+
(aq)
+ OH
–
(aq)
(v) Potassium hydroxide (KOH) :
KOH
(aq)
⇌ K
+
(aq)
+ OH
–
(aq)
(vi) Magnesium hydroxide [Mg(OH)
2
] :
Mg(OH)
2(aq)
⇌ Mg
2+
+
(aq)
+ 2OH
–
(aq)
Question 12.
Sugandha prepares HCl gas in her school laboratory using certain chemicals. She puts both dry and wet blue litmus papers in contact with the gas.
(i) Name the reagents used by Sugandha to prepare HCl gas.
(ii) State the colour changes observed with the dry and wet blue litmus papers.
(iii) Show the formation of ions when HCl gas combines with water. (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(i) Dense white fumes of hydrogen chloride gas are evolved on heating solid sodium chloride with concentrated sulphuric acid.
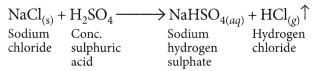
(ii) Refer to answer 9(ii).
(iii) Refer to answer 9(iii).
Question 13.
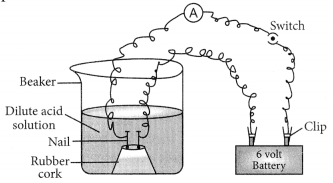
(a) Illustrate an activity to investigate whether all compounds containing hydrogen are acidic.
(b) What happens when hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide are dissolved in water. Explain by giving equation of each. (Board Term 1, 2016)
Answer:
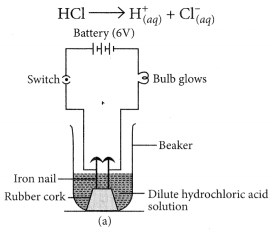
(a) Take two beakers, one containing HCl acid and other containing alcohol which is not an acid but contains hydrogen. Now, fix two iron nails on a rubber cork and insert in a beaker and connect the nail to the two terminal of 6V battery through a switch and a bulb. Pour some dilute HCl solution in beaker and switch on the current. The bulb starts glowing. This shows that acids get dissociated as H
+
and Cl
–
ions and these ions are responsible for conducting electricity.
Let us now take alcohol solution in the beaker and switch on the current. The bulb does not glow in this case. This shows that alcohol does not conduct electricity.
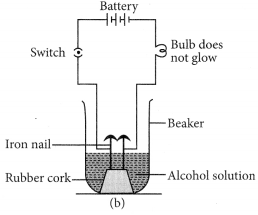
So, all acids have hydrogen but all hydrogen containing compounds are not acid.
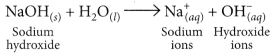
(b) HCl dissociates in aqueous solution to give hydrogen ions (or hydronium ions) and chloride ions.
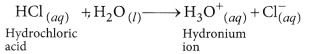
NaOH when dissolved in water produces sodium ions and hydroxide ions in the solution.
Question 14.
An aqueous solution ‘A’ turns phenolphthalein solution pink. On addition of an aqueous solution ‘B’ to ‘A’ the pink colour disappears. The following statement is true for solution ‘A’ and ‘B’:
(a) A is strongly basic and B is a weak base.
(b) A is strongly acidic and B is a weak acid.
(c) A has pH greater than 7 and B has pH less than 7.
(d) A has pH less than 7 and B has pH greater than 7. (2020)
Answer:
(c) As the aqueous solution of A turns phenolphthalein solution pink, hence A is basic in nature. On adding an acidic solution, the pink colour will disappear. Hence, B is an acid.
Question 15.
Out of HCl and CH
3
COOH, which one is a weak acid and why? Explain with the help of an example. (AI 2019)
Answer:
Out of HCl and CH
3
COOH, CH
3
COOH is a weak acid because it dissociates partially in the solution. This can be proved with the help of following example.
If 1 M HCl and 1 M CH
3
COOH are taken in the beaker as shown in the figure, greater deflection is observed in case of HCl which shows that more ions are produced by HCl in solution which produce more current.
Question 16.
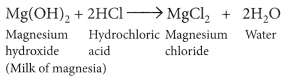
Explain how an antacid works. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
The acidity produced due to excess hydrochloric acid in the stomach which cause indigestion, produce pain and irritation. Milk of magnesia (chemically magnesium hydroxide) is used as an antacid. Since, it is basic in nature, reacts with the excess hydrochloric acid present in the stomach and neutralises it.
Question 17.
(a) Three acidic solutions A, B and C have pH = 0, 3 and 5 respectively.
(i) Which solution has highest concentration of H
+
ions?
(ii) Which solution has the lowest concentration of H
+
ions?
(b) How concentrated sulphuric acid can be diluted? Describe the process. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
(a) (i) The solution having lower pH will have more hydrogen ion concentration. Hence, solution ‘A’ will have highest H
+
ion concentration.
(ii) Solution CC’ i.e., pH = 5 has the lowest concentration of H
+
ions.
(b) Mixing of an acid with water is called dilution. This process is highly exothermic and therefore, acid is always added to the water not water to acid. The process for diluting concentrated sulphuric acid is :
(i) Take about 10 mL of water in a beaker.
(ii) Add concentrated sulphuric acid dropwise to water and swirl the beaker slowly.
Question 18.
A compound P forms the enamel of teeth. It is the hardest substance of the body. It doesn’t dissolve in water but gets corroded when the pH is lowered below 5.5.
(a) Identify the compound P.
(b) How does it undergo damage due to eating chocolate and sweets? What should we do to prevent tooth decay? (Board Term I, 2014, 2013)
Answer:
(a) The compound P is calcium phosphate, (b) Eating chocolates and sweets produce large amount of acid in the mouth which is not completely neutralised by the saliva produced in the mouth. Excess acid attacks the enamel and tooth decay starts as pH of the mouth falls below 5.5. The best way to prevent tooth decay is to clean the teeth by using toothpastes after eating food. Toothpastes which are generally basic neutralise the excess acid in the mouth.
Question 19.
Baking soda is a mixture of
(a) sodium carbonate and acetic acid
(b) sodium carbonate and tartaric acid
(c) sodium hydrogen carbonate and tartaric acid
(d) sodium hydrogen carbonate and acetic acid.
Answer:
(c) : Baking soda is a mixture of sodium hydrogen carbonate and a mild edible acid like tartaric acid or citric acid.
Question 20.
The chemical formula for plaster of Paris is
(a) CaSO
4
.2H
2
O
(b) CaSO
4
.2H
2
O
(c) CaSO
4
.\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\)H
2
O
(d) 2CaSO
4
.2H
2
O
Answer:
(c, d) : Plaster of Paris is calcium sulphate hemihydrate which can be represented as,
CaSO
4
. \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) H
2
O and 2CaSO
4
.H
2
0.
Question 21.
“Sodium hydrogen carbonate is a basic salt”. Justify this statement. How is it converted into washing soda? (AI2019)
Answer:
Sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO
3
) is basic in nature as on hydrolysis it gives a mixture of strong base (NaOH) and weak acid (H
2
CO
3
). Sodium hydrogen carbonate is converted to washing soda in the following way:
(i) Thermal decomposition of NaHCO
3
:
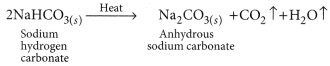
(ii) Recrystallisation of sodium carbonate:
![]()
Question 22.
Write the chemical formula of Bleaching powder. How is bleaching powder prepared? For what purpose is it used in drinking water? (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
The chemical formula of bleaching powder is CaOCl
2
.
It is prepared by the action of chlorine gas on dry slaked lime Ca(OH)
2
.
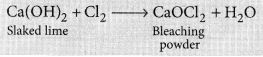
The chlorine used in the above reaction is the by-product produced during the electrolysis of brine. It is used in disinfecting drinking water as chlorine liberated by it, kills the germs.
Question 23.
A student collected common names and formulae of some substances but he forgot to note which formula is for which compound. Help him to match the correct formula. (Board Term I, 2013)
| (i) Caustic soda | NaHCO 3 . |
| (ii) Slaked lime | CaO |
| (iii) Baking soda | NaOH |
| (iv) Lime | Ca(OH) 2 . |
Answer:
(i) Caustic soda → NaOH
(ii) Slaked lime → Ca(OH)
2
(iii) Baking soda → NaHCO
3
(iv) Lime → CaO
Question 24.
List the important products of the Chlor-alkali process. Write one important use of each. (2020)
Answer:
Sodium hydroxide is prepared by electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium chloride (brine). The complete reaction can be represented as:
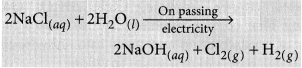
The process of electrolysis of sodium chloride solution is called chlor-alkali process because of the products formed : chlor for chlorine and alkali for sodium hydroxide. The three very useful products obtained by the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution are sodium hydroxide, chlorine and hydrogen.
At anode : Cl
2
gas is liberated At cathode : H
2
gas is liberated.
Uses of sodium hydroxide: In the manufacture of soaps and detergents.
Uses of chlorine : As a germicide and disinfectant for sterilisation of drinking water and for water of swimming pools.
Uses of hydrogen: In the manufacture of ammonia which is used for the preparation of various fertilizers like urea, ammonium sulphate etc.
Question 25.
How is washing soda prepared from sodium carbonate? Give its chemical equation. State the type of this salt. Name the type of hardness of water which can be removed by it? (2020)
Answer:
Washing soda is prepared by recrystallisation of sodium carbonate:
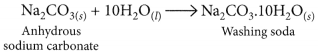
It is used to remove the permanent hardness of water. Hard water is treated with a calculated amount of washing soda when chlorides and sulphates of calcium and magnesium present in hard water get precipitated as insoluble calcium and magnesium carbonates which can be easily filtered off. The water thus becomes soft.
CaCl
2
+ Na
2
CO
3
→ CaCO
3
↓ + 2NaCl
MgSO
4
+ Na
2
CO
3
→ MgCOsub>3↓ + Na
2
SO
4
Question 26.
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Only one half of water molecule is shown in the formula of plaster of Paris.
(ii) Sodium hydrogen carbonate is used as an antacid.
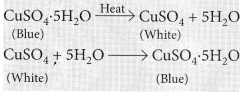
(iii) On strong heating, blue coloured copper sulphate crystals turn white. (2020)
Answer:
(i) Only one half of water molecule is shown in the formula of plaster of Paris (CaSO
4
. \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) H
2
O) as one molecule of water is being shared by two molecules of calcium sulphate (CaSO
4
). So the effective water of crystallisation for one CaSO
4
unit comes to half molecule of water.
(ii) Acidity can be neutralised by a base. Sodium hydrogen carbonate can be used as an antacid solution because it is a weak base and will react
with excess acid produced in the stomach due to hyperacidity and will neutralise it.
(iii) Blue coloured copper sulphate crystals are hydrated copper sulphate, CuSO
4
.5H
2
O. On heating blue copper sulphate crystals looses its water of crystallisation and turns into anhydrous copper sulphate which is white in colour.
![]()
Question 27.
During electrolysis of brine, a gas ‘G’ is liberated at anode. When this gas ‘G’ is passed through slaked lime, a compound ‘C’ is formed, which is used for disinfecting drinking water.
(i) Write formula of ‘G’ and ‘C’.
(ii) State the chemical equations involved.
(iii) What is common name of compound ‘C’ ? Give its chemical name. (2020)
Answer:
(i) During electrolysis of brine, chlorine is obtained at anode. When chlorine is passed through slaked lime, bleaching powder is formed which is used for disinfecting drinking water. Hence, G is Cl
2
and C is CaOCl
2
.
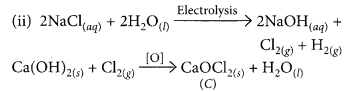
(iii) Common name of C is bleaching powder. Its chemical name is calcium hypochlorite.
Question 28.
Identify the acid and the base from which sodium chloride is obtained. Which type of salt is it? When is it called rock salt? How is rock salt formed? (Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Sodium chloride is obtained by the neutralisation of sodium hydroxide (base) with hydrochloric acid (acid). It is a neutral salt. Common salt found in the form of solid deposits is often brown in colour due to presence of impurities which is called rock salt. Rock salt is formed by evaporation of salty water of inland lakes.
Question 29.
A white powder is added while baking cakes to make it soft and spongy. Name its main ingredients. Explain the function of each ingredient. Write the chemical reaction taking place when the powder is heated during baking. (AI2019)
Answer:
The white powder added while baking cakes to make it soft and spongy is baking powder. Its main ingredients are sodium hydrogen carbonate and a mild edible acid like tartaric acid or citric acid. NaHCO
3
decomposes to give out CO
2
which causes the cake to rise and makes it soft and spongy. The function of tartaric acid or citric acid is to neutralise sodium carbonate formed during heating which can otherwise make the cake bitter. Reaction taking place when the powder is heated:
![]()
Question 30.
The pH of a salt used to make tasty and crispy pakoras is 14. Identify the salt and write a chemical equation for its formation. List its two uses. (2018)
Answer:
Salt used to make tasty and crispy pakoras is sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO
3
), pH = 9. On large scale, sodium bicarbonate is prepared as:
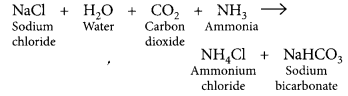
Two uses of sodium bicarbonate are as follows :
(i) It is used as an antacid in medicines.
(ii) It is used as an additive in food and drinks.
Note : In the question paper, the given pH is 14 which should be 9.
Question 31.
Write one point of difference between each of the following:
(i) A hydrated salt and an anhydrous salt.
(ii) Washing soda and soda ash.
(iii) Baking soda and baking powder. (Board Term 1,2017)
Answer:
(i)
| Hydrated salt | Anhydrous salt |
| A salt with one or more chemically combined water molecule is called hydrated salt, e.g., washing soda, Na 2 CO 3 .10H 2 .O | A salt in which all water molecules are removed, is called anhydrous salt, e.g., soda ash, Na 2 .CO 3 . |
(ii)
| Washing soda | Soda ash |
| The hydrated salt of sodium carbonate containing 10 molecules of water of crystallisation, is known as washing soda i.e., Na 2 CO 3 .10H 2 .O. | The anhydrous sodium carbonate (Na 2 CO 3 .) which does not contain water of crystallisation, is known as soda ash. |
(iii)
| Baking soda | Baking powder |
| Baking soda is sodiumhydrogen carbonate with the formula, NaHCO 3 . | Baking powder is a mixture of NaHCO 3 . and tartaric acid or citric acid. |
Question 32.
Complete the following table:
| Sample Solution | Red litmus solution | Blue litmus solution | Phenolp-hthalein solution |
| Acetic acid | |||
| Sodium hydroxide | |||
| Baking soda |
Answer:
| Sample solution | Red litmus solution | Blue | Phenolp- |
| Acetic acid (CH 3 .COOH) | No effect | litmus | hthalein |
| Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) | Blue | solution | solution |
| Baking Soda (NaHCO 3 .) | Blue | Red | Colourless |
Question 33.
A white coloured powder is used by doctors for supporting fractured bones.
(a) Write chemical name and formula of the powder.
(b) When this white powder is mixed with water a hard solid mass is obtained. Write balanced chemical equation for this change. (Board Term I, 2016)
Answer:
(a) Chemical name of the powder is calcium sulphate hemihydrate. Chemical formula of the powder is CaSO
4
. \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) ApH
2
O.
(b) When water is added to plaster of Paris, it sets into a hard mass in about half an hour. The setting of plaster of Paris is due to its hydration to form crystals of gypsum which set to form a hard, solid mass.
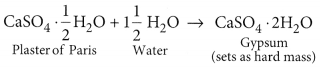
Question 34.
(a) Define an acid-base indicator. Mention one synthetic acid-base indicator.
(b) If someone in the family is suffering from a problem of acidity after overeating, which of the following substances would you suggest as a remedy?
Lemon juice, vinegar or baking soda solution. Mention the property on the basis of which you will choose the remedy. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
(a) Acid – base indicators : The indicators which show different colours in acidic and basic medium are called acid-base indicators. Phenolphthalein is a synthetic indicator.
(b) Acidity can be neutralised by a base. Hence, we should choose baking soda solution because it is a weak base and will react with excess acid produced in the stomach due to hyperacidity and will neutralise it.
Question 35.
Define water of crystallisation. Give the chemical formula for two compounds as examples. How can it be proved that the water of crystallisation makes a difference in the state and colour of the compounds? (2020)
Answer:
Water of crystallisation : It is the fixed number of water molecules present in one formula unit of a salt, e.g., Gypsum (CaSO
4
.2H
2
O) has two molecules of water of crystallisation.
In hydrated copper sulphate (CuSO
4
.5H
2
O), there are five molecules of water of crystallisation.
Activity:
– Take few crystals of copper sulphate in a dry boiling tube. These are blue in colour.
– Heat the boiling tube by holding it with a test tube holder on the flame of the burner.
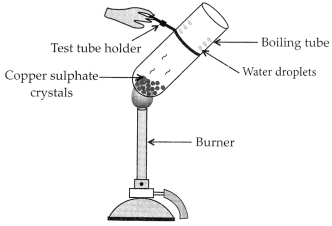
Observations : You will observe that the colour of copper sulphate crystals after heating becomes white. You may also notice water droplets on the mouth side of the boiling tube which are obtained from water of crystallisation.After adding 2-3 drops of water on the white sample of copper sulphate (obtained after heating) you will observe that the blue colour of copper sulphate crystals is restored.
Question 36.
(a) A student dropped a few pieces of marble in dilute hydrochloric acid contained in a test tube. The evolved gas was passed through lime water. What change would be observed in lime water? Write balanced chemical equations for both the changes observed.
(b) State the chemical property in each case on which the following uses of baking soda are based:
(i) as an antacid
(ii) as a constituent of baking powder. (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
(a) When marble reacts with dilute HCl carbon dioxide gas is liberated.
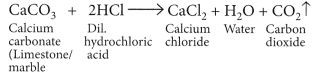
When CO
2
gas is passed through lime water, insoluble calcium carbonate is formed which appears milky.
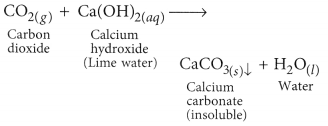
(b) (i) The excess acid formed in the stomach due to various reasons (one being overeating) is neutralised by sodium hydrogen carbonate. Hence, it is used as an ingredient of antacid.
(ii) Baking soda (sodium hydrogen carbonate) is a constituent of baking power. On heating it gives out CO
2
which causes the cake to rise and make it soft and spongy.
Question 37.
(a) What are anhydrous and hydrated salts? Explain with a suitable example of each]
(b) How is plaster of Paris prepared? What reaction takes place when it sets to a hard mass? (Board Term I, 2017)
Answer:
(a) Refer to answer 31(i).
(b) It is prepared from gypsum which is calcium sulphate dihydrate (CaSO
4
.2H
2
O). Gypsum is heated in a kiln to a temperature of 100°C (373 K). At this temperature, it loses three-fourth of its water of crystallisation forming plaster of Paris.

Refer to answer 33(b).
Question 38.
(a) Write the chemical formula of hydrated copper sulphate and anhydrous copper sulphate. Giving an activity illustrate how these two are interconvertible.
(b) Write chemical names and formulae of plaster of Paris and gypsum. (Board Term 1, 2016)
Answer:
(a) The chemical formula of hydrated copper sulphate is CuSO
4
.5H
2
O
(s)
and anhydrous copper sulphate is CuSO
4(s)
.
For activity refer to answer 35.
(b) Plaster of Paris is calcium sulphate hemihydrate; CaSO
4
.\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) H
2
O and Gypsum is calcium sulphate dihydrate;
(CaSO
4
.2H
2
O).
Question 39.
How is sodium hydroxide produced? Write the balanced chemical equation also. Why is this process called as chlor-alkali process? In this process name the products given off at:
(a) anode
(b) cathode
Write one use of each of these products. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
Refer to answer 24.
Question 40.
What is water of crystallization? Write the common name and chemical formula of a commercially important compound which has ten water molecules as water of crystallization. How is this compound obtained? Write the chemical equation also. List any two uses of this compound. (Board Term I, 2015)
Answer:
Water of crystallization : Crystals of some salts contain certain amount of associated water.
The water associated with the crystal (or molecule) of any salt is called water of crystallisation.
The hydrated salt is known as washing soda which is sodium carbonate containing 10 molecules of water of crystallization, i.e., it is sodium carbonate decahydrate. Its molecular formula is Na
2
CO
3
.10H
2
O.
It can be obtained by heating baking soda followed by recrystallisation from its aqueous solution.
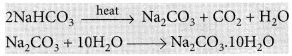
Uses of sodium carbonate:
(i) For the manufacture of glass, soap, papers and chemicals like caustic soda (NaOH), borax, etc.
(ii) For washing purposes (laundry works).
Question 41.
(a) Name and describe giving chemical equation the process used for producing sodium hydroxide. Why is this process so named?
(b) Give one use of each of any two products obtained in this process. (Board Term I, 2014)
Answer:
Refer to answer 24.
Question 42.
(a) You have three solutions – A, B and C having a pH of 6, 2 and 9 respectively. Arrange these solutions in increasing order of hydrogen ion concentration. Which of the three is most acidic? What happens to the hydrogen ion concentration in A as it is diluted?
(b) If someone is suffering from a stomach problem called acidity, why is a solution of baking soda offered as a remedy?
(c) Write chemical name and formula of baking soda. (Board Term I, 2013)
Answer:
(a) The solution having lower pH will have more hydrogen ion concentration. Hence, solution B (i.e., pH = 2) will have more hydrogen ion concentration.
![]()
Solution B is most acidic.
Adding water to solution A, will reduce the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
(b) Refer to answer 26(ii).
(c) Refer to answer 31(iii).